最开始接触ConstraintLayout,完全依赖于拖曳方式实现布局,而在实际操作过程中,完全通过拖曳其实效率反倒是会打折扣,觉得还是有必要结合xml编码来实现布局。总结一些常用的ConstraintLayout的XML属性如下:
1.相对定位
layout_constraint(1)_to(2)Of="(3)"
(1):控件自身对应的位置
(2):相对于约束控件的位置
(3):指定约束的控件:可以为具体的控件id 或者parent
如下:
layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf // 左边左对齐
layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf // 左边右对齐
layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf // 右边左对齐
layout_constraintRight_toRightOf // 右边右对齐
layout_constraintTop_toTopOf // 上边顶部对齐
layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf // 上边底部对齐
layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf // 下边顶部对齐
layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf // 下边底部对齐
layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf // 文本内容基准线对齐
layout_constraintStart_toEndOf // 起始边向尾部对齐
layout_constraintStart_toStartOf // 起始边向起始边对齐
layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf // 尾部向起始边对齐
layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf // 尾部向尾部对齐
2.GONE MARGIN
对应位置的控制可见时通过传统的layout_margin设置,layout_goneMargin当不可见的时候的边距值。如下:
layout_goneMarginStart
layout_goneMarginEnd
layout_goneMarginLeft
layout_goneMarginTop
layout_goneMarginRight
layout_goneMarginBottom
3.倾斜比例
当控件这样设置的时候为居中
layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent
在此基础上可增加倾斜的比例
水平: layout_constraintHorizontal_bias
垂直: layout_constraintVertical_bias
例如:左边占40%,右边占60%
layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.4"
4.最小宽高
当宽或高设置属性为WRAP_CONTENT时可以设置最小宽高
android:minWidth 设置布局的最小宽度
android:minHeight 设置布局的最小高度
5.宽高比:layout_constraintDimensionRatio
设置控件的宽高比例时,控件的宽或者高必须有一个设置为0dp或者MATCH_CONSTRAINT。重点是以水为基准来确定宽高比
第一种情况:
宽或高1个为0dp或MATCH_CONSTRAINT,另一个为具体值或者wrap_content时。
已具体值的宽或高为标准,另一方按照其比例设置大小
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="4:1"
如上高大小确定,宽是高的4倍
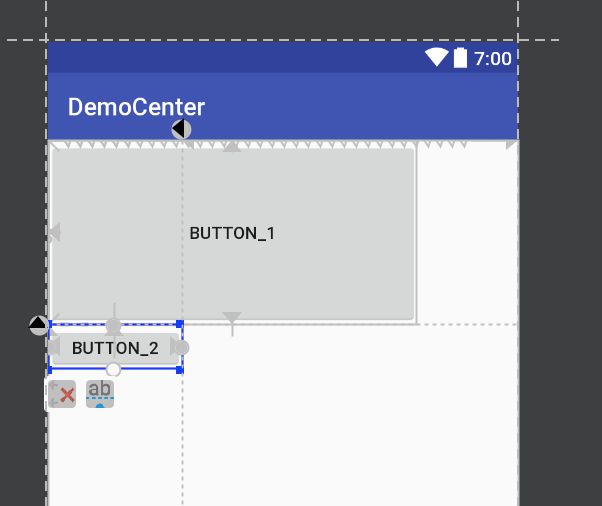
第二种情况:
宽和高都为0dp或MATCH_CONSTRAINT,已确定边为基准,另一边按比例设置大小
上图button_1:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="2:1"
高确定,所以宽是高的2倍
上图button_2:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="3:1"
宽确定,所以高是宽的三分之一
还有另外一种写法不过不推荐:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="H,16:9"这了制定了W,H。
这里的W或H和后面的比例有点难理解。实践了下大概是这个意思:假设比例设置为a:b ,如果前面是H,不论哪一边确定,另外一边的大小都是确定边的b/a倍;如果前面是W,不论哪一边确定,另外一边的大小都是确定边的a/b倍。