【Linux】GDB调试多线程和多进程以及Core文件
GDB调试器
基本概念
GDB是GNU开源组织发布的一个强大的UNIX下的程序调试工具。或许,各位比较喜欢那种图形界面方式的,像VC、BCB等IDE的调试,但如果你是在UNIX平台下做软件,你会发现GDB这个调试工具有比VC、BCB的图形化调试器更强大的功能。所谓“寸有所长,尺有所短”就是这个道理。
主要功能
1、启动程序,可以按照你的自定义的要求随心所欲的运行程序。2、可让被调试的程序在你所指定的调置的断点处停住。(断点可以是条件表达式)
3、当程序被停住时,可以检查此时你的程序中所发生的事。
4、动态的改变你程序的执行环境。
GDB的基本指令
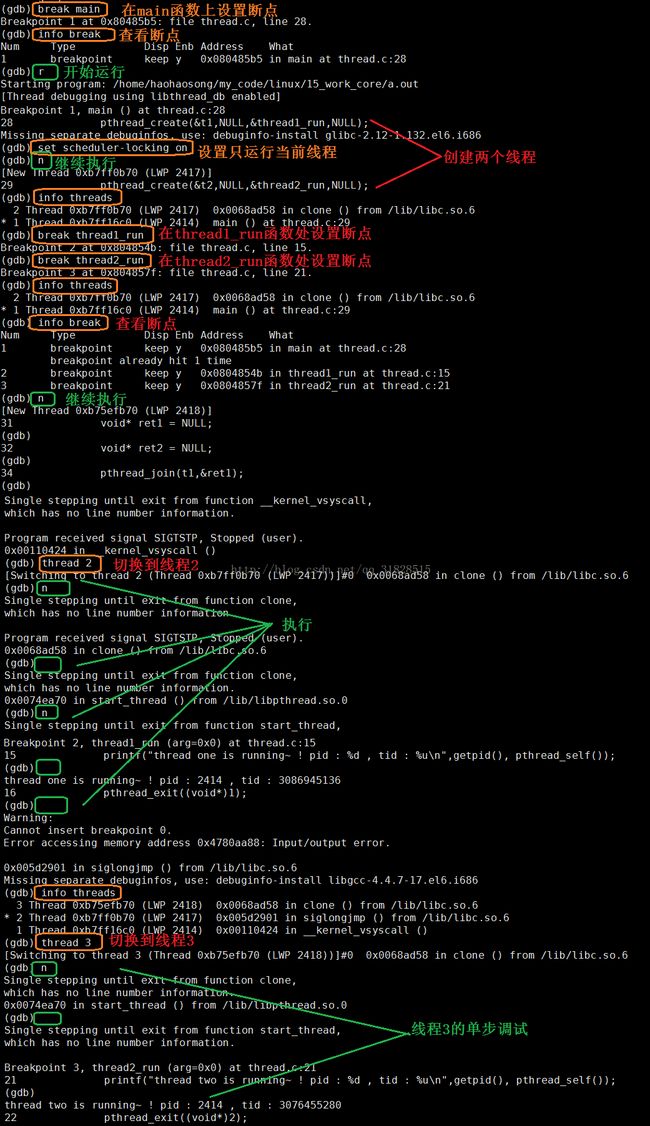
GDB调试多线程
代码示例
#include
#include
#include
#include
void* thread1_run(void* arg)
{
printf("thread one is running~ ! pid : %d , tid : %u\n",getpid(), pthread_self());
pthread_exit((void*)1);
}
void* thread2_run(void* arg)
{
printf("thread two is running~ ! pid : %d , tid : %u\n",getpid(), pthread_self());
pthread_exit((void*)2);
}
int main()
{
pthread_t t1,t2;
pthread_create(&t1,NULL,&thread1_run,NULL);
pthread_create(&t2,NULL,&thread2_run,NULL);
void* ret1 = NULL;
void* ret2 = NULL;
pthread_join(t1,&ret1);
pthread_join(t2,&ret2);
printf("ret1 is :d\n",ret1);
printf("ret2 is :d\n",ret2);
return 0;
} gdb进行调试
GDB调试多进程
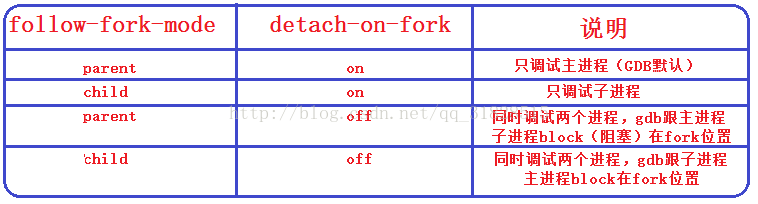
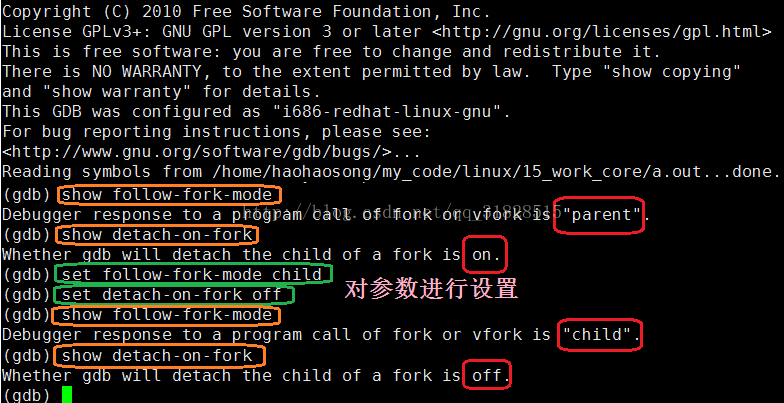
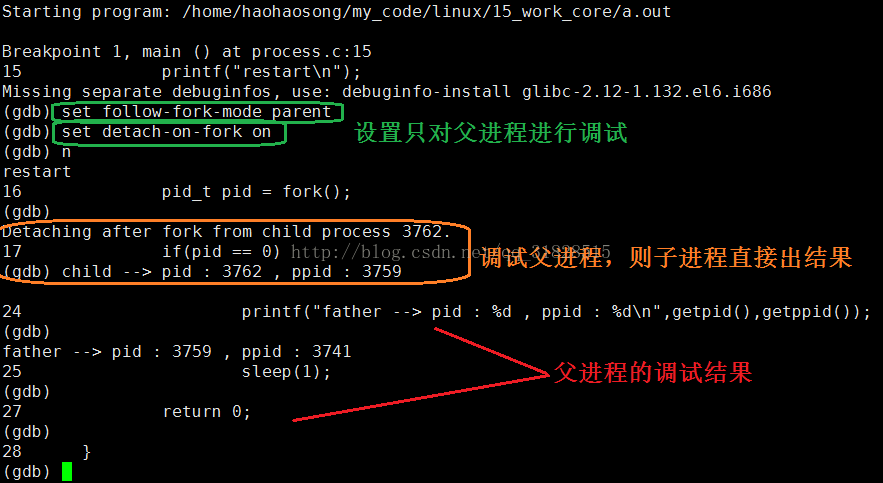
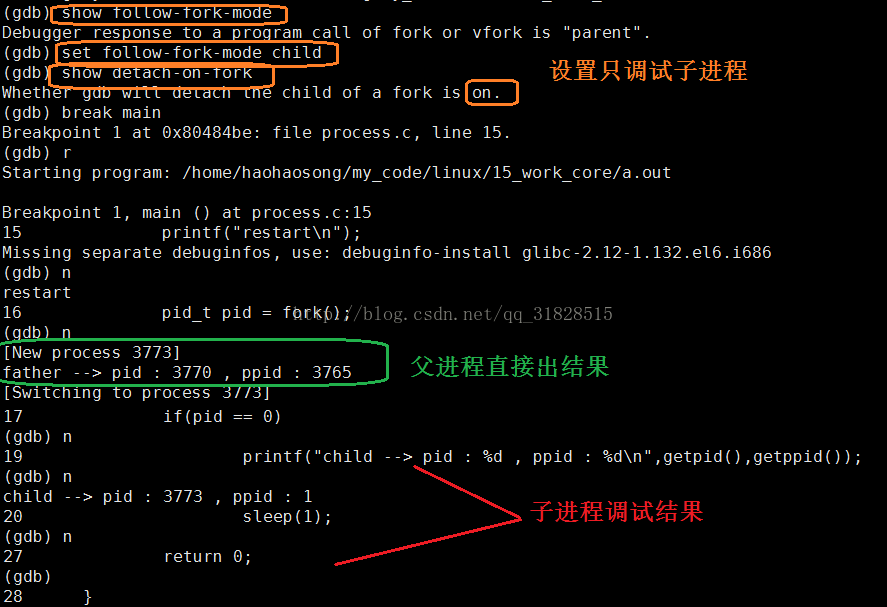
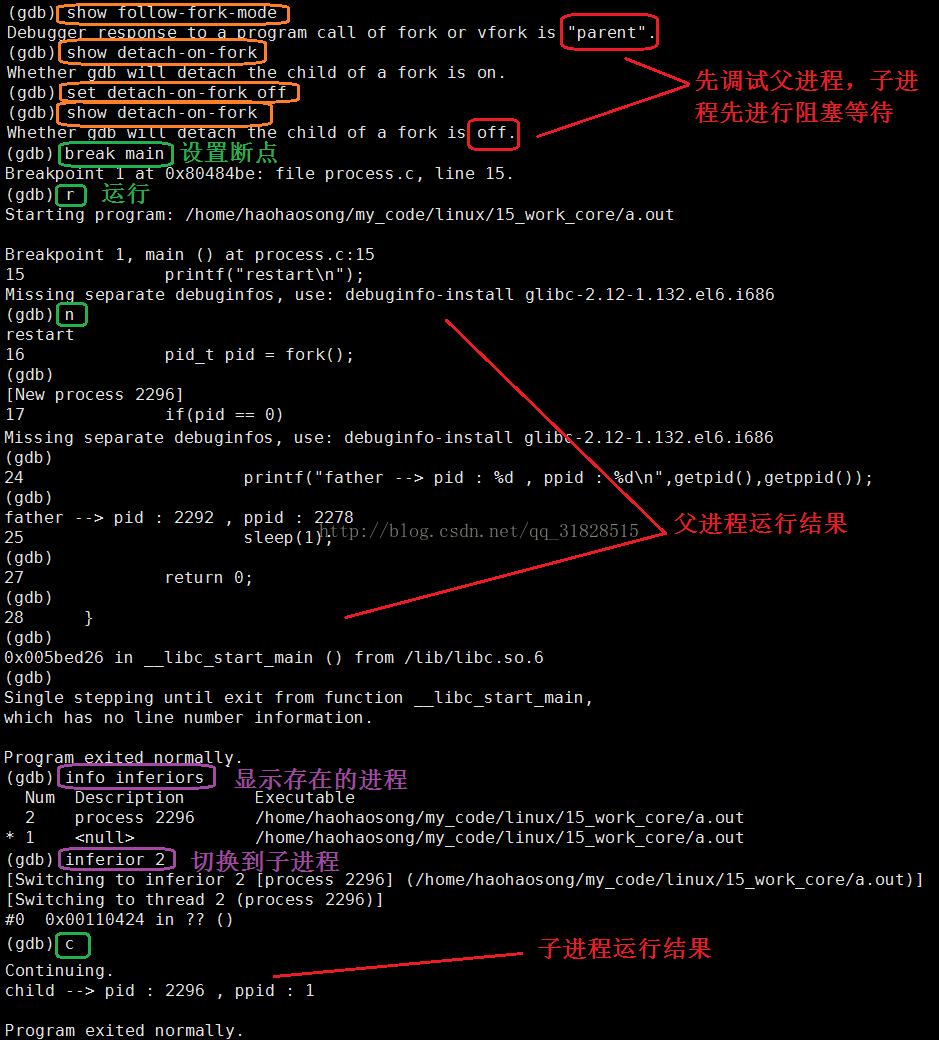
在默认情况下是调试多进程程序时GDB会默认调试主进程,但是GDB支持多进程的分别与同步调试。即GDB支持同时调试多个进程,只需要设置follow-fork-mode(默认为parent)和detach-on-fork(默认为on)即可。我们还可以使用catch fork指令,如果fork异常,会停止程序。
设置方法: set follow-fork-mode[parent|child] set detach-on-fork[on|off]
显示:show follow-fork-mode show detach-on-fork
测试代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
printf("restart\n");
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid == 0)
{
printf("child --> pid : %d , ppid : %d\n",getpid(),getppid());
sleep(1);
}
else
{
printf("father --> pid : %d , ppid : %d\n",getpid(),getppid());
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
} 只调试父进程
只调试子进程
同时进行调试(让父进程运行调试,子进程阻塞等待)
core文件
基本概念
在一个程序崩溃时,它一般会在指定目录下生成一个core文件。core文件仅仅是一个内存映象(同时加上调试信息),主要是用来调试的。
开启或关闭core文件的生成
阻止系统生成core文件 ulimit -c 0
检查生成core文件的选项是否打开 ulimit -a
查看机器参数 uname -a
查看默认参数 ulimit -a
设置core文件大小为1024 ulimit -c 1024
设置core文件大小为无限 ulimit -c unlimit
生成core文件,也可以是指定大小,然后使用gdb ./main core启动,bt查看调用栈即可 ulimit -c unlimited
eg1(可以快速定位出问题的位置)
gdb a.out core.xxx
where
eg2 (在 gdb 中使用)
(gdb) core-file core.xxx
该命令将显示所有的用户定制,其中选项-a代表“all”。
也可以修改系统文件来调整core选项
在/etc/profile通常会有这样一句话来禁止产生core文件,通常这种设置是合理的:
# No core files by default
ulimit -S -c 0 > /dev/null 2>&1
但是在开发过程中有时为了调试问题,还是需要在特定的用户环境下打开core文件产生的设置
在用户的~/.bash_profile里加上ulimit -c unlimited来让特定的用户可以产生core文件
如果ulimit -c 0 则也是禁止产生core文件,而ulimit -c 1024则限制产生的core文件的大小不能超过1024kb