13.tensorflow:训练cifar10,搭建cnn网络,保存模型,tensorboard日志,输出loss,accuracy,学习率衰减
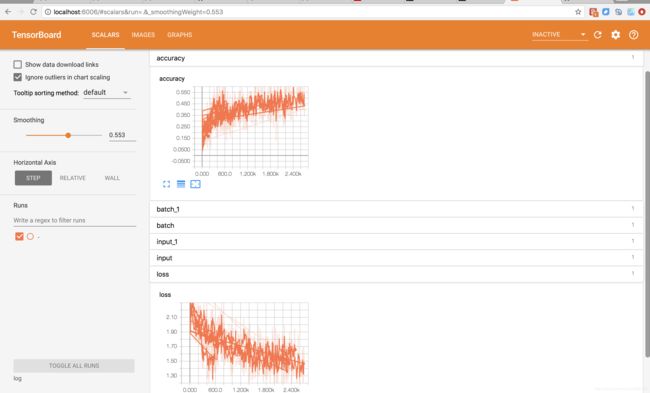
代码中可以保存模型,训练时的log日志,便于观察准确率,损失值等,学习率每隔5000步衰减为原来的0.1倍。
其中cifar10_input.py和cifar10.py来源于https://github.com/tensorflow/models/tree/master/tutorials/image/cifar10其中cifar10.py用于下载cifar10的二进制数据集,注意修改53行中的下载文件路径data_dir,cifar10_input.py用于输入每批次的数据及数据增强。
main.py文件为:其中model为常见的tf.nn.方式搭建;model2为更方便的tf.contrib.layers搭建,二者模型相同;model3增加了多通道卷积,把卷积和为1,3,5的卷积输出结果进行合并;model4增加了batch normal 批量归一化操作。
#coding:utf-8
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.contrib.layers.python.layers import batch_norm
import cifar10_input
import cifar10
cifar10.maybe_download_and_extract()
number_classes = 10
batch_size = 32
steps = 20000
displaystep = 50
init_lr = 0.01
data_dir = '/Users/ming/Downloads/zhangming/pytorch_demo/data/cifar10_data/cifar-10-batches-bin'
images_test, labels_test = cifar10_input.inputs(eval_data = True, data_dir = data_dir, batch_size = batch_size)
images_train, labels_train = cifar10_input.inputs(eval_data = False, data_dir = data_dir, batch_size = batch_size)
# use tf.nn.xx
def model(x):
b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[64]))
w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 3, 64], stddev=0.1))
x = tf.nn.conv2d(x, w, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME") + b
x = tf.nn.relu(x)
x = tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME")
w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[5, 5, 64, 64], stddev=0.1))
b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[64]))
x = tf.nn.conv2d(x, w, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME") + b
x = tf.nn.relu(x)
x = tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME")
w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[5, 5, 64, 128], stddev=0.1))
b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[128]))
x = tf.nn.conv2d(x, w, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME") + b
x = tf.nn.relu(x)
x = tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME")
shp = x.get_shape()
flatten_size = int(shp[1]*shp[2]*shp[3])
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, flatten_size]) # flatten
w = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal([flatten_size, number_classes]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[number_classes]))
x = tf.matmul(x, w) + b
return x
# use tf.contrib.layers.xx
def model2(x):
x = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 64, [5, 5], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu) #输入,输出通道数,核大小,核步长,填充方式,激活
x = tf.contrib.layers.max_pool2d(x, [2, 2], stride=2, padding='SAME') #输入,池化尺寸,池化步长,填充方式
x = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 64, [5, 5], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
x = tf.contrib.layers.max_pool2d(x, [2, 2], stride=2, padding='SAME')
x = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 128, [5, 5], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
x = tf.contrib.layers.max_pool2d(x, [2, 2], stride=2, padding='SAME')
# print(np.shape(x))
shp = x.get_shape()
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, shp[1]*shp[2]*shp[3]]) # flatten
# print(np.shape(x))
x = tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(x, number_classes, activation_fn=None) # output logist
return x
# 在model2基础上增加多通道卷积(卷积核为1,3,5最后再联接一起), 参考google的inception系列
def model3(x):
x = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 64, [5, 5], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
x = tf.contrib.layers.max_pool2d(x, [2, 2], stride=2, padding='SAME')
x1_1 = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 64, [1, 1], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu) # 1X1 核
x3_3 = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 64, [3, 3], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu) # 3x3 核
x5_5 = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 64, [5, 5], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu) # 5x5 核
x = tf.concat([x1_1, x3_3, x5_5], axis=-1) # 连接在一起,得到64*3=192个通道
x = tf.contrib.layers.max_pool2d(x, [2, 2], stride=2, padding='SAME')
x1_1 = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 128, [1, 1], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
x3_3 = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 128, [3, 3], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
x5_5 = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 128, [5, 5], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
x = tf.concat([x1_1, x3_3, x5_5], axis=-1)
x = tf.contrib.layers.max_pool2d(x, [2, 2], stride=2, padding='SAME')
shp = x.get_shape()
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, shp[1]*shp[2]*shp[3]]) # flatten
x = tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(x, number_classes, activation_fn=None) # output logist
return x
# 在model3基础上增加batch normal批量归一化
def model4(x, is_trian = False):
x = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 64, [5, 5], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
x = batch_norm(x, decay=0.9, updates_collections=None, is_training=is_trian) # 训练阶段is_trainging设置为true,训练完毕后使用模型时设置为false
x = tf.contrib.layers.max_pool2d(x, [2, 2], stride=2, padding='SAME')
x1_1 = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 64, [1, 1], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu) # 1X1 核
x1_1 = batch_norm(x1_1, decay=0.9, updates_collections=None, is_training=is_trian)
x3_3 = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 64, [3, 3], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu) # 3x3 核
x3_3 = batch_norm(x3_3, decay=0.9, updates_collections=None, is_training=is_trian)
x5_5 = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 64, [5, 5], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu) # 5x5 核
x5_5 = batch_norm(x5_5, decay=0.9, updates_collections=None, is_training=is_trian)
x = tf.concat([x1_1, x3_3, x5_5], axis=-1) # 连接在一起,得到64*3=192个通道
x = tf.contrib.layers.max_pool2d(x, [2, 2], stride=2, padding='SAME')
x1_1 = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 128, [1, 1], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
x1_1 = batch_norm(x1_1, decay=0.9, updates_collections=None, is_training=is_trian)
x3_3 = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 128, [3, 3], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
x3_3 = batch_norm(x3_3, decay=0.9, updates_collections=None, is_training=is_trian)
x5_5 = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(x, 128, [5, 5], 1, 'SAME', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
x5_5 = batch_norm(x5_5, decay=0.9, updates_collections=None, is_training=is_trian)
x = tf.concat([x1_1, x3_3, x5_5], axis=-1)
x = tf.contrib.layers.max_pool2d(x, [2, 2], stride=2, padding='SAME')
shp = x.get_shape()
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, shp[1]*shp[2]*shp[3]]) # flatten
x = tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(x, number_classes, activation_fn=None) # output logist
return x
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 24, 24, 3]) # cifar data image of shape 24*24*3
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, number_classes]) # 0-9 数字=> 10 classes
iter_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False) # 记录global step 学习率衰减用
# logist = model(x)
# logist = model2(x)
# logist = model3(x)
logist = model4(x, is_trian=True) #训练时is_train=True
pre = tf.nn.softmax(logist)
cost = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y, logits=logist)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(cost)
tf.summary.scalar("loss", cost)
lr = tf.train.exponential_decay(learning_rate=init_lr, global_step=iter_step, decay_steps=5000, decay_rate=0.1)
optim = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=lr).minimize(cost, global_step=iter_step)
correct_pre = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pre, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
acc = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pre, dtype=tf.float32))
tf.summary.scalar("accuracy", acc)
saver = tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=3)
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess)
print "start"
mysummary = tf.summary.merge_all()
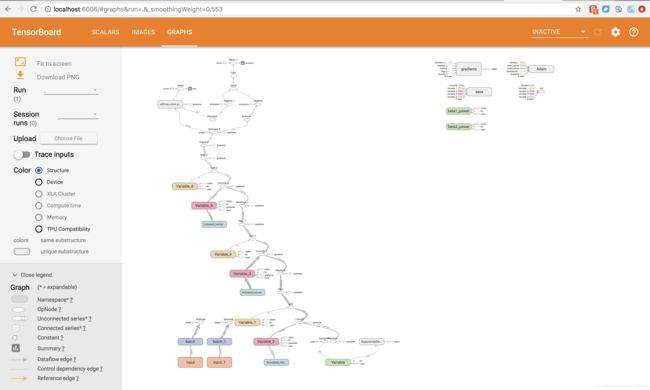
f_summary = tf.summary.FileWriter(logdir="cifar10_model/log", graph=sess.graph) # 保存log日志即可视化网络结构位置
for step in range(steps):
batch_imgs, batch_label = sess.run([images_train, labels_train])
one_hot_label = np.eye(number_classes, dtype=float)[batch_label]
_, loss, learning_rate = sess.run([optim, cost, lr], feed_dict={x:batch_imgs, y:one_hot_label})
tmp_summary = sess.run(mysummary, feed_dict={x:batch_imgs, y:one_hot_label})
f_summary.add_summary(summary=tmp_summary, global_step=step)
if step % displaystep == 0 :
accuracy, predict = sess.run([acc, pre], feed_dict={x:batch_imgs, y:one_hot_label})
print "-"*50
print "truth label:", batch_label
print "pred label:", np.argmax(predict, 1)
print("step:%d, lr:%f, loss:%.4f, accuracy:%.2f" % (step, learning_rate, loss, accuracy))
saver.save(sess, save_path="cifar10_model/model.ckpt", global_step=step) #保存模型位置
print("done...")
image_batch, label_batch = sess.run([images_test, labels_test])
one_hot_label = np.eye(number_classes, dtype=float)[label_batch]
accuracy = sess.run(acc, feed_dict={x:image_batch, y:one_hot_label}) # 在测试集上评估
print("test accuracy:", accuracy)其中,cifar10.py为:
# Copyright 2015 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ==============================================================================
"""Builds the CIFAR-10 network.
Summary of available functions:
# Compute input images and labels for training. If you would like to run
# evaluations, use inputs() instead.
inputs, labels = distorted_inputs()
# Compute inference on the model inputs to make a prediction.
predictions = inference(inputs)
# Compute the total loss of the prediction with respect to the labels.
loss = loss(predictions, labels)
# Create a graph to run one step of training with respect to the loss.
train_op = train(loss, global_step)
"""
# pylint: disable=missing-docstring
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import re
import sys
import tarfile
from six.moves import urllib
import tensorflow as tf
import cifar10_input
FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS
# Basic model parameters.
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer('batch_size', 128,
"""Number of images to process in a batch.""")
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('data_dir', '/Users/ming/Downloads/zhangming/pytorch_demo/data/cifar10_data',
"""Path to the CIFAR-10 data directory.""")
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_boolean('use_fp16', False,
"""Train the model using fp16.""")
# Global constants describing the CIFAR-10 data set.
IMAGE_SIZE = cifar10_input.IMAGE_SIZE
NUM_CLASSES = cifar10_input.NUM_CLASSES
NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN = cifar10_input.NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN
NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_EVAL = cifar10_input.NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_EVAL
# Constants describing the training process.
MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY = 0.9999 # The decay to use for the moving average.
NUM_EPOCHS_PER_DECAY = 350.0 # Epochs after which learning rate decays.
LEARNING_RATE_DECAY_FACTOR = 0.1 # Learning rate decay factor.
INITIAL_LEARNING_RATE = 0.1 # Initial learning rate.
# If a model is trained with multiple GPUs, prefix all Op names with tower_name
# to differentiate the operations. Note that this prefix is removed from the
# names of the summaries when visualizing a model.
TOWER_NAME = 'tower'
DATA_URL = 'https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar-10-binary.tar.gz'
def _activation_summary(x):
"""Helper to create summaries for activations.
Creates a summary that provides a histogram of activations.
Creates a summary that measures the sparsity of activations.
Args:
x: Tensor
Returns:
nothing
"""
# Remove 'tower_[0-9]/' from the name in case this is a multi-GPU training
# session. This helps the clarity of presentation on tensorboard.
tensor_name = re.sub('%s_[0-9]*/' % TOWER_NAME, '', x.op.name)
tf.summary.histogram(tensor_name + '/activations', x)
tf.summary.scalar(tensor_name + '/sparsity',
tf.nn.zero_fraction(x))
def _variable_on_cpu(name, shape, initializer):
"""Helper to create a Variable stored on CPU memory.
Args:
name: name of the variable
shape: list of ints
initializer: initializer for Variable
Returns:
Variable Tensor
"""
with tf.device('/cpu:0'):
dtype = tf.float16 if FLAGS.use_fp16 else tf.float32
var = tf.get_variable(name, shape, initializer=initializer, dtype=dtype)
return var
def _variable_with_weight_decay(name, shape, stddev, wd):
"""Helper to create an initialized Variable with weight decay.
Note that the Variable is initialized with a truncated normal distribution.
A weight decay is added only if one is specified.
Args:
name: name of the variable
shape: list of ints
stddev: standard deviation of a truncated Gaussian
wd: add L2Loss weight decay multiplied by this float. If None, weight
decay is not added for this Variable.
Returns:
Variable Tensor
"""
dtype = tf.float16 if FLAGS.use_fp16 else tf.float32
var = _variable_on_cpu(
name,
shape,
tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=stddev, dtype=dtype))
if wd is not None:
weight_decay = tf.multiply(tf.nn.l2_loss(var), wd, name='weight_loss')
tf.add_to_collection('losses', weight_decay)
return var
def distorted_inputs():
"""Construct distorted input for CIFAR training using the Reader ops.
Returns:
images: Images. 4D tensor of [batch_size, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3] size.
labels: Labels. 1D tensor of [batch_size] size.
Raises:
ValueError: If no data_dir
"""
if not FLAGS.data_dir:
raise ValueError('Please supply a data_dir')
data_dir = os.path.join(FLAGS.data_dir, 'cifar-10-batches-bin')
images, labels = cifar10_input.distorted_inputs(data_dir=data_dir,
batch_size=FLAGS.batch_size)
if FLAGS.use_fp16:
images = tf.cast(images, tf.float16)
labels = tf.cast(labels, tf.float16)
return images, labels
def inputs(eval_data):
"""Construct input for CIFAR evaluation using the Reader ops.
Args:
eval_data: bool, indicating if one should use the train or eval data set.
Returns:
images: Images. 4D tensor of [batch_size, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3] size.
labels: Labels. 1D tensor of [batch_size] size.
Raises:
ValueError: If no data_dir
"""
if not FLAGS.data_dir:
raise ValueError('Please supply a data_dir')
data_dir = os.path.join(FLAGS.data_dir, 'cifar-10-batches-bin')
images, labels = cifar10_input.inputs(eval_data=eval_data,
data_dir=data_dir,
batch_size=FLAGS.batch_size)
if FLAGS.use_fp16:
images = tf.cast(images, tf.float16)
labels = tf.cast(labels, tf.float16)
return images, labels
def inference(images):
"""Build the CIFAR-10 model.
Args:
images: Images returned from distorted_inputs() or inputs().
Returns:
Logits.
"""
# We instantiate all variables using tf.get_variable() instead of
# tf.Variable() in order to share variables across multiple GPU training runs.
# If we only ran this model on a single GPU, we could simplify this function
# by replacing all instances of tf.get_variable() with tf.Variable().
#
# conv1
with tf.variable_scope('conv1') as scope:
kernel = _variable_with_weight_decay('weights',
shape=[5, 5, 3, 64],
stddev=5e-2,
wd=None)
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = _variable_on_cpu('biases', [64], tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=scope.name)
_activation_summary(conv1)
# pool1
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME', name='pool1')
# norm1
norm1 = tf.nn.lrn(pool1, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75,
name='norm1')
# conv2
with tf.variable_scope('conv2') as scope:
kernel = _variable_with_weight_decay('weights',
shape=[5, 5, 64, 64],
stddev=5e-2,
wd=None)
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(norm1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = _variable_on_cpu('biases', [64], tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=scope.name)
_activation_summary(conv2)
# norm2
norm2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75,
name='norm2')
# pool2
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(norm2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME', name='pool2')
# local3
with tf.variable_scope('local3') as scope:
# Move everything into depth so we can perform a single matrix multiply.
reshape = tf.reshape(pool2, [images.get_shape().as_list()[0], -1])
dim = reshape.get_shape()[1].value
weights = _variable_with_weight_decay('weights', shape=[dim, 384],
stddev=0.04, wd=0.004)
biases = _variable_on_cpu('biases', [384], tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
local3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshape, weights) + biases, name=scope.name)
_activation_summary(local3)
# local4
with tf.variable_scope('local4') as scope:
weights = _variable_with_weight_decay('weights', shape=[384, 192],
stddev=0.04, wd=0.004)
biases = _variable_on_cpu('biases', [192], tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
local4 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(local3, weights) + biases, name=scope.name)
_activation_summary(local4)
# linear layer(WX + b),
# We don't apply softmax here because
# tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits accepts the unscaled logits
# and performs the softmax internally for efficiency.
with tf.variable_scope('softmax_linear') as scope:
weights = _variable_with_weight_decay('weights', [192, NUM_CLASSES],
stddev=1/192.0, wd=None)
biases = _variable_on_cpu('biases', [NUM_CLASSES],
tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
softmax_linear = tf.add(tf.matmul(local4, weights), biases, name=scope.name)
_activation_summary(softmax_linear)
return softmax_linear
def loss(logits, labels):
"""Add L2Loss to all the trainable variables.
Add summary for "Loss" and "Loss/avg".
Args:
logits: Logits from inference().
labels: Labels from distorted_inputs or inputs(). 1-D tensor
of shape [batch_size]
Returns:
Loss tensor of type float.
"""
# Calculate the average cross entropy loss across the batch.
labels = tf.cast(labels, tf.int64)
cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels=labels, logits=logits, name='cross_entropy_per_example')
cross_entropy_mean = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='cross_entropy')
tf.add_to_collection('losses', cross_entropy_mean)
# The total loss is defined as the cross entropy loss plus all of the weight
# decay terms (L2 loss).
return tf.add_n(tf.get_collection('losses'), name='total_loss')
def _add_loss_summaries(total_loss):
"""Add summaries for losses in CIFAR-10 model.
Generates moving average for all losses and associated summaries for
visualizing the performance of the network.
Args:
total_loss: Total loss from loss().
Returns:
loss_averages_op: op for generating moving averages of losses.
"""
# Compute the moving average of all individual losses and the total loss.
loss_averages = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(0.9, name='avg')
losses = tf.get_collection('losses')
loss_averages_op = loss_averages.apply(losses + [total_loss])
# Attach a scalar summary to all individual losses and the total loss; do the
# same for the averaged version of the losses.
for l in losses + [total_loss]:
# Name each loss as '(raw)' and name the moving average version of the loss
# as the original loss name.
tf.summary.scalar(l.op.name + ' (raw)', l)
tf.summary.scalar(l.op.name, loss_averages.average(l))
return loss_averages_op
def train(total_loss, global_step):
"""Train CIFAR-10 model.
Create an optimizer and apply to all trainable variables. Add moving
average for all trainable variables.
Args:
total_loss: Total loss from loss().
global_step: Integer Variable counting the number of training steps
processed.
Returns:
train_op: op for training.
"""
# Variables that affect learning rate.
num_batches_per_epoch = NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN / FLAGS.batch_size
decay_steps = int(num_batches_per_epoch * NUM_EPOCHS_PER_DECAY)
# Decay the learning rate exponentially based on the number of steps.
lr = tf.train.exponential_decay(INITIAL_LEARNING_RATE,
global_step,
decay_steps,
LEARNING_RATE_DECAY_FACTOR,
staircase=True)
tf.summary.scalar('learning_rate', lr)
# Generate moving averages of all losses and associated summaries.
loss_averages_op = _add_loss_summaries(total_loss)
# Compute gradients.
with tf.control_dependencies([loss_averages_op]):
opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(lr)
grads = opt.compute_gradients(total_loss)
# Apply gradients.
apply_gradient_op = opt.apply_gradients(grads, global_step=global_step)
# Add histograms for trainable variables.
for var in tf.trainable_variables():
tf.summary.histogram(var.op.name, var)
# Add histograms for gradients.
for grad, var in grads:
if grad is not None:
tf.summary.histogram(var.op.name + '/gradients', grad)
# Track the moving averages of all trainable variables.
variable_averages = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(
MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY, global_step)
with tf.control_dependencies([apply_gradient_op]):
variables_averages_op = variable_averages.apply(tf.trainable_variables())
return variables_averages_op
def maybe_download_and_extract():
"""Download and extract the tarball from Alex's website."""
dest_directory = FLAGS.data_dir
if not os.path.exists(dest_directory):
os.makedirs(dest_directory)
filename = DATA_URL.split('/')[-1]
filepath = os.path.join(dest_directory, filename)
if not os.path.exists(filepath):
def _progress(count, block_size, total_size):
sys.stdout.write('\r>> Downloading %s %.1f%%' % (filename,
float(count * block_size) / float(total_size) * 100.0))
sys.stdout.flush()
filepath, _ = urllib.request.urlretrieve(DATA_URL, filepath, _progress)
print()
statinfo = os.stat(filepath)
print('Successfully downloaded', filename, statinfo.st_size, 'bytes.')
extracted_dir_path = os.path.join(dest_directory, 'cifar-10-batches-bin')
if not os.path.exists(extracted_dir_path):
tarfile.open(filepath, 'r:gz').extractall(dest_directory)
其中,cifar10_input.py为
# Copyright 2015 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ==============================================================================
"""Routine for decoding the CIFAR-10 binary file format."""
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import os
from six.moves import xrange # pylint: disable=redefined-builtin
import tensorflow as tf
# Process images of this size. Note that this differs from the original CIFAR
# image size of 32 x 32. If one alters this number, then the entire model
# architecture will change and any model would need to be retrained.
IMAGE_SIZE = 24
# Global constants describing the CIFAR-10 data set.
NUM_CLASSES = 10
NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN = 50000
NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_EVAL = 10000
def read_cifar10(filename_queue):
"""Reads and parses examples from CIFAR10 data files.
Recommendation: if you want N-way read parallelism, call this function
N times. This will give you N independent Readers reading different
files & positions within those files, which will give better mixing of
examples.
Args:
filename_queue: A queue of strings with the filenames to read from.
Returns:
An object representing a single example, with the following fields:
height: number of rows in the result (32)
width: number of columns in the result (32)
depth: number of color channels in the result (3)
key: a scalar string Tensor describing the filename & record number
for this example.
label: an int32 Tensor with the label in the range 0..9.
uint8image: a [height, width, depth] uint8 Tensor with the image data
"""
class CIFAR10Record(object):
pass
result = CIFAR10Record()
# Dimensions of the images in the CIFAR-10 dataset.
# See http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html for a description of the
# input format.
label_bytes = 1 # 2 for CIFAR-100
result.height = 32
result.width = 32
result.depth = 3
image_bytes = result.height * result.width * result.depth
# Every record consists of a label followed by the image, with a
# fixed number of bytes for each.
record_bytes = label_bytes + image_bytes
# Read a record, getting filenames from the filename_queue. No
# header or footer in the CIFAR-10 format, so we leave header_bytes
# and footer_bytes at their default of 0.
reader = tf.FixedLengthRecordReader(record_bytes=record_bytes)
result.key, value = reader.read(filename_queue)
# Convert from a string to a vector of uint8 that is record_bytes long.
record_bytes = tf.decode_raw(value, tf.uint8)
# The first bytes represent the label, which we convert from uint8->int32.
result.label = tf.cast(
tf.strided_slice(record_bytes, [0], [label_bytes]), tf.int32)
# The remaining bytes after the label represent the image, which we reshape
# from [depth * height * width] to [depth, height, width].
depth_major = tf.reshape(
tf.strided_slice(record_bytes, [label_bytes],
[label_bytes + image_bytes]),
[result.depth, result.height, result.width])
# Convert from [depth, height, width] to [height, width, depth].
result.uint8image = tf.transpose(depth_major, [1, 2, 0])
return result
def _generate_image_and_label_batch(image, label, min_queue_examples,
batch_size, shuffle):
"""Construct a queued batch of images and labels.
Args:
image: 3-D Tensor of [height, width, 3] of type.float32.
label: 1-D Tensor of type.int32
min_queue_examples: int32, minimum number of samples to retain
in the queue that provides of batches of examples.
batch_size: Number of images per batch.
shuffle: boolean indicating whether to use a shuffling queue.
Returns:
images: Images. 4D tensor of [batch_size, height, width, 3] size.
labels: Labels. 1D tensor of [batch_size] size.
"""
# Create a queue that shuffles the examples, and then
# read 'batch_size' images + labels from the example queue.
num_preprocess_threads = 16
if shuffle:
images, label_batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch(
[image, label],
batch_size=batch_size,
num_threads=num_preprocess_threads,
capacity=min_queue_examples + 3 * batch_size,
min_after_dequeue=min_queue_examples)
else:
images, label_batch = tf.train.batch(
[image, label],
batch_size=batch_size,
num_threads=num_preprocess_threads,
capacity=min_queue_examples + 3 * batch_size)
# Display the training images in the visualizer.
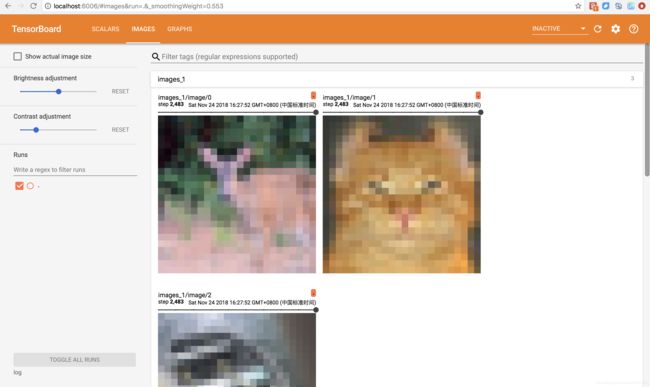
tf.summary.image('images', images)
return images, tf.reshape(label_batch, [batch_size])
def distorted_inputs(data_dir, batch_size):
"""Construct distorted input for CIFAR training using the Reader ops.
Args:
data_dir: Path to the CIFAR-10 data directory.
batch_size: Number of images per batch.
Returns:
images: Images. 4D tensor of [batch_size, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3] size.
labels: Labels. 1D tensor of [batch_size] size.
"""
filenames = [os.path.join(data_dir, 'data_batch_%d.bin' % i)
for i in xrange(1, 6)]
for f in filenames:
if not tf.gfile.Exists(f):
raise ValueError('Failed to find file: ' + f)
# Create a queue that produces the filenames to read.
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filenames)
with tf.name_scope('data_augmentation'):
# Read examples from files in the filename queue.
read_input = read_cifar10(filename_queue)
reshaped_image = tf.cast(read_input.uint8image, tf.float32)
height = IMAGE_SIZE
width = IMAGE_SIZE
# Image processing for training the network. Note the many random
# distortions applied to the image.
# Randomly crop a [height, width] section of the image.
distorted_image = tf.random_crop(reshaped_image, [height, width, 3])
# Randomly flip the image horizontally.
distorted_image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(distorted_image)
# Because these operations are not commutative, consider randomizing
# the order their operation.
# NOTE: since per_image_standardization zeros the mean and makes
# the stddev unit, this likely has no effect see tensorflow#1458.
distorted_image = tf.image.random_brightness(distorted_image,
max_delta=63)
distorted_image = tf.image.random_contrast(distorted_image,
lower=0.2, upper=1.8)
# Subtract off the mean and divide by the variance of the pixels.
float_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(distorted_image)
# Set the shapes of tensors.
float_image.set_shape([height, width, 3])
read_input.label.set_shape([1])
# Ensure that the random shuffling has good mixing properties.
min_fraction_of_examples_in_queue = 0.4
min_queue_examples = int(NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN *
min_fraction_of_examples_in_queue)
print ('Filling queue with %d CIFAR images before starting to train. '
'This will take a few minutes.' % min_queue_examples)
# Generate a batch of images and labels by building up a queue of examples.
return _generate_image_and_label_batch(float_image, read_input.label,
min_queue_examples, batch_size,
shuffle=True)
def inputs(eval_data, data_dir, batch_size):
"""Construct input for CIFAR evaluation using the Reader ops.
Args:
eval_data: bool, indicating if one should use the train or eval data set.
data_dir: Path to the CIFAR-10 data directory.
batch_size: Number of images per batch.
Returns:
images: Images. 4D tensor of [batch_size, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3] size.
labels: Labels. 1D tensor of [batch_size] size.
"""
if not eval_data:
filenames = [os.path.join(data_dir, 'data_batch_%d.bin' % i)
for i in xrange(1, 6)]
num_examples_per_epoch = NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN
else:
filenames = [os.path.join(data_dir, 'test_batch.bin')]
num_examples_per_epoch = NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_EVAL
for f in filenames:
if not tf.gfile.Exists(f):
raise ValueError('Failed to find file: ' + f)
with tf.name_scope('input'):
# Create a queue that produces the filenames to read.
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filenames)
# Read examples from files in the filename queue.
read_input = read_cifar10(filename_queue)
reshaped_image = tf.cast(read_input.uint8image, tf.float32)
height = IMAGE_SIZE
width = IMAGE_SIZE
# Image processing for evaluation.
# Crop the central [height, width] of the image.
resized_image = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(reshaped_image,
height, width)
# Subtract off the mean and divide by the variance of the pixels.
float_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(resized_image)
# Set the shapes of tensors.
float_image.set_shape([height, width, 3])
read_input.label.set_shape([1])
# Ensure that the random shuffling has good mixing properties.
min_fraction_of_examples_in_queue = 0.4
min_queue_examples = int(num_examples_per_epoch *
min_fraction_of_examples_in_queue)
# Generate a batch of images and labels by building up a queue of examples.
return _generate_image_and_label_batch(float_image, read_input.label,
min_queue_examples, batch_size,
shuffle=False)
最终,程序的输出为:
start
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [1 6 8 8 6 4 3 6 0 6 6 0 3 5 6 4 8 3 2 6 0 3 1 4 0 6 6 2 7 6 9 0]
predict label: [6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6]
step:0, lr:0.001000, loss:4.7015, accuracy:0.31
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [3 6 1 4 9 4 9 9 6 4 1 1 6 7 6 3 3 3 0 7 0 0 8 2 0 2 4 1 2 3 8 0]
predict label: [8 8 8 4 8 4 8 2 8 4 8 8 8 2 8 4 4 2 2 4 8 8 8 4 8 1 4 8 8 2 8 8]
step:50, lr:0.000889, loss:2.2750, accuracy:0.19
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [9 6 2 3 1 1 5 9 7 6 3 2 2 8 5 2 8 3 0 0 6 8 4 6 3 1 5 8 4 3 4 8]
predict label: [4 2 1 8 8 4 8 8 4 2 4 4 8 4 2 8 8 2 8 8 4 8 4 4 4 0 4 8 2 4 2 8]
step:100, lr:0.000794, loss:2.1486, accuracy:0.16
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [7 1 3 5 6 5 3 5 2 4 1 3 2 9 8 8 8 5 5 1 1 4 9 1 3 0 7 0 7 0 0 5]
predict label: [1 1 2 4 4 2 2 1 2 4 8 4 0 1 8 1 0 4 8 8 0 8 0 8 1 0 4 8 2 8 0 4]
step:150, lr:0.000708, loss:2.2234, accuracy:0.19
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [2 9 9 7 2 3 8 2 8 5 7 9 1 5 1 1 1 4 1 7 4 4 3 5 8 2 1 1 2 3 4 6]
predict label: [0 1 1 1 0 4 1 4 1 1 2 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 2 4 0 4 1 0 2 1 1 0 1 1 4]
step:200, lr:0.000631, loss:2.0890, accuracy:0.28
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [0 7 3 1 0 3 5 9 8 9 9 8 7 5 2 9 0 5 6 3 6 9 1 4 2 3 5 5 7 2 7 3]
predict label: [1 1 2 1 0 2 9 8 8 0 8 1 2 2 2 8 0 0 4 2 2 8 8 4 4 2 2 2 1 2 2 4]
step:250, lr:0.000562, loss:2.1770, accuracy:0.22
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [5 7 7 9 3 7 6 6 1 3 6 0 2 4 9 9 6 9 1 3 0 8 9 9 2 1 0 6 3 9 1 4]
predict label: [7 4 9 7 4 9 4 4 9 9 9 7 9 4 1 9 9 9 7 7 9 8 9 9 4 9 9 4 7 9 7 9]
step:300, lr:0.000501, loss:2.1736, accuracy:0.22
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [1 3 0 3 7 2 8 9 7 2 1 0 4 7 4 6 2 3 7 8 1 3 6 5 8 2 5 8 2 0 5 6]
predict label: [1 4 0 7 7 0 9 8 7 0 9 9 7 0 7 9 4 9 9 8 1 7 7 4 0 0 3 7 7 8 7 7]
step:350, lr:0.000447, loss:2.1657, accuracy:0.19
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [9 5 0 5 9 5 4 3 2 7 1 4 9 6 6 1 8 8 8 6 2 4 3 4 5 9 7 4 0 0 8 7]
predict label: [1 3 3 3 7 3 3 3 2 1 8 3 7 7 8 1 8 8 8 3 9 3 0 1 0 8 3 3 8 8 8 7]
step:400, lr:0.000398, loss:2.0630, accuracy:0.25
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [5 2 8 2 1 3 7 4 7 0 1 9 5 5 9 8 1 3 8 1 2 1 8 9 7 6 7 9 5 8 0 6]
predict label: [2 7 0 2 1 2 1 2 7 0 1 0 2 7 1 8 1 7 8 0 2 0 8 2 7 2 0 0 7 8 0 1]
step:450, lr:0.000355, loss:1.8217, accuracy:0.41
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [2 5 2 7 7 9 9 5 1 4 0 3 5 8 7 0 9 9 5 7 0 6 9 3 0 8 8 5 5 1 0 7]
predict label: [3 3 3 3 3 1 0 4 1 4 3 3 9 1 7 0 1 7 3 4 0 3 0 3 8 0 0 1 3 1 8 3]
step:500, lr:0.000316, loss:1.9090, accuracy:0.25
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [2 5 1 5 7 6 9 0 3 1 9 7 4 9 4 2 2 0 3 8 3 1 2 8 6 7 9 4 9 4 4 1]
predict label: [4 7 0 1 7 1 1 8 9 1 2 7 1 1 9 2 2 0 4 0 2 1 2 8 2 1 1 2 1 2 2 1]
step:550, lr:0.000282, loss:1.8615, accuracy:0.31
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [8 4 3 5 0 2 7 5 5 9 6 7 1 8 8 4 9 2 3 4 1 8 0 0 1 1 8 3 7 6 4 9]
predict label: [9 2 2 2 1 2 2 3 2 0 2 3 0 1 0 2 2 2 2 2 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 8 7 2 1 9]
step:600, lr:0.000251, loss:1.8923, accuracy:0.25
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [6 0 3 1 0 4 4 0 9 9 8 0 8 3 9 8 7 1 8 1 6 4 9 4 2 4 9 7 6 4 0 7]
predict label: [3 9 3 8 9 4 4 1 0 0 9 0 4 1 9 9 7 1 9 8 7 4 9 4 2 9 0 1 3 8 0 0]
step:650, lr:0.000224, loss:1.8201, accuracy:0.38
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [0 0 8 3 9 7 6 9 4 5 0 8 6 9 5 7 4 3 0 1 8 5 6 5 1 7 6 1 9 9 2 1]
predict label: [0 0 1 0 3 8 3 1 4 3 7 8 3 9 2 7 0 3 2 9 8 7 4 2 0 2 4 1 1 8 3 1]
step:700, lr:0.000200, loss:2.0030, accuracy:0.31
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [0 2 3 5 1 8 3 5 4 0 5 2 5 2 0 2 3 4 4 4 9 1 0 2 6 3 7 0 9 6 0 7]
predict label: [0 7 4 7 9 9 8 7 4 4 7 2 3 2 8 4 4 9 0 4 9 1 8 8 7 9 4 7 9 9 8 7]
step:750, lr:0.000178, loss:2.1102, accuracy:0.28
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [5 3 0 4 5 2 9 3 2 6 6 4 9 0 0 7 0 2 9 7 4 6 6 5 9 4 0 8 7 9 6 0]
predict label: [1 7 0 4 7 4 9 7 2 7 4 2 8 7 0 7 8 7 9 7 4 8 7 7 9 7 0 8 7 8 2 9]
step:800, lr:0.000158, loss:1.8603, accuracy:0.41
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [9 8 6 0 1 0 6 8 4 7 4 8 0 7 3 6 2 9 5 5 6 3 7 3 6 2 6 8 7 0 2 6]
predict label: [9 8 1 0 1 8 3 9 0 7 4 8 0 9 3 4 7 0 7 3 7 9 7 4 4 4 4 0 3 0 0 4]
step:850, lr:0.000141, loss:1.9188, accuracy:0.34
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [3 5 4 7 1 0 1 7 9 7 8 7 7 0 8 3 2 4 8 7 4 9 4 9 6 5 4 1 2 7 7 4]
predict label: [4 3 7 3 1 8 7 3 8 7 8 7 4 8 8 1 1 3 3 7 4 1 3 4 4 3 4 1 3 1 3 4]
step:900, lr:0.000126, loss:1.9119, accuracy:0.31
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [6 9 3 2 5 4 2 5 7 7 1 4 8 4 0 6 0 0 6 2 8 7 3 4 9 6 0 4 4 0 0 9]
predict label: [4 1 3 2 3 9 4 3 3 7 8 4 3 3 8 4 2 1 4 3 8 7 3 1 1 3 0 4 2 0 2 9]
step:950, lr:0.000112, loss:1.7847, accuracy:0.34
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [7 2 5 1 9 1 1 7 9 3 7 9 0 7 7 5 2 1 0 3 2 7 5 0 9 3 1 4 3 7 9 9]
predict label: [7 7 7 1 9 9 1 7 9 7 7 4 9 7 7 8 3 9 8 7 4 4 7 0 9 3 8 7 3 3 9 8]
step:1000, lr:0.000100, loss:1.7640, accuracy:0.44
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [4 5 3 0 3 4 0 2 1 3 2 2 4 7 4 1 3 6 5 0 4 5 7 7 4 1 4 0 5 4 1 6]
predict label: [7 3 2 2 3 2 8 9 1 0 9 4 7 7 2 2 2 4 3 0 4 9 7 7 9 8 1 9 4 0 7 4]
step:1050, lr:0.000089, loss:2.0639, accuracy:0.22
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [3 3 1 0 8 8 5 1 0 9 4 9 9 7 9 8 7 0 5 0 4 5 5 1 1 1 5 1 6 3 7 8]
predict label: [7 7 0 9 9 0 4 0 0 8 4 9 2 6 9 1 3 0 2 0 7 2 3 1 1 1 3 8 7 4 1 9]
step:1100, lr:0.000079, loss:1.8559, accuracy:0.28
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [1 1 9 1 3 2 5 1 4 1 0 6 8 5 9 5 1 8 7 7 4 9 3 4 3 9 4 6 8 9 2 0]
predict label: [2 1 9 9 3 2 4 1 6 1 8 6 8 2 9 3 0 8 4 7 2 9 3 4 3 8 7 4 8 9 8 0]
step:1150, lr:0.000071, loss:1.5269, accuracy:0.56
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [3 4 9 7 0 0 5 2 5 1 7 3 2 2 4 3 7 5 7 4 2 3 1 0 8 1 4 7 2 3 6 2]
predict label: [9 6 9 7 1 0 7 0 2 9 7 4 5 2 6 7 4 5 2 2 5 3 0 8 8 9 0 3 5 3 6 5]
step:1200, lr:0.000063, loss:1.7124, accuracy:0.31
--------------------------------------------------
truth label: [7 6 0 2 0 6 4 1 6 3 1 3 2 2 1 5 5 8 1 4 2 3 2 0 7 7 6 9 6 5 8 2]
predict label: [7 6 1 7 0 6 3 1 6 3 0 1 6 4 9 3 6 8 1 4 5 7 2 0 7 7 6 9 6 6 8 2]
step:1250, lr:0.000056, loss:1.4136, accuracy:0.59
......
训练完成后发现自动创建了cifar10_model文件夹,里面保存的文件为:
cifar10_model文件夹下保存了每隔50步的模型。
log文件夹下保存了显示tensorboard时的信息如准确率,损失,网络可视化结构等信息。
使用tensorboard:
tensorboard --logdir=log
把网址输入浏览器,在浏览器中显示:
准确率和loss:
输入网络的部分图像:
网络结构: