【0】README
0.1)为什么有这篇文章?因为 Dijkstra算法的优先队列实现 涉及到了一种新的数据结构,即优先队列(二叉堆)的操作需要更改以适应这种新的数据结构,我们暂且吧它定义为Distance, 而不是单纯的int类型;
0.2)本文源代码均为原创, int类型的优先队列(二叉堆)的操作实现,参见http://blog.csdn.net/PacosonSWJTU/article/details/49498255, (并比较他们的打印结果,很有必要)
【1】因为 Dijkstra算法的优先队列实现, 需要用到二叉堆的相关操作,但是操作的元素类型(ElementType 不是 单纯的int类型), 而是如下:
struct Distance
{
int vertexIndex; //当前顶点下标
int distance; //初始顶点到当前顶点的distance
};【2】看个荔枝
2.1)需要特别说明的是: indexOfVertexInHeap 数组记录的是顶点vertex在 heap中的位置, 如 indexOfVertexInHeap [1] = 4;表明heap的第4个位置记录这 编号为1的vertex;
2.2)优先队列的insert和deleteMin 的执行演示(请将我的手动演示结果同我的代码打印结果做对比,经过对比,你发现它们的效果是一致的,恰好说明了我的代码的可行性):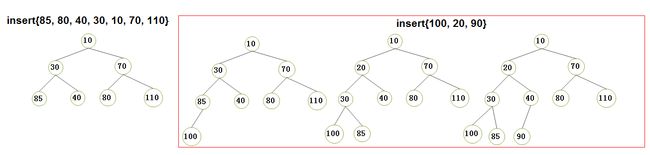
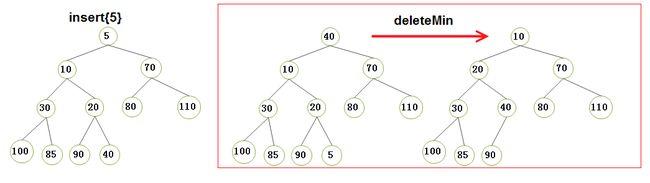
Attention)
- A1)其实本文中的二叉堆优先队列的实现源代码和 int类型的优先队列源代码类似,只不过它们操作的数据类型不一样罢了,当然, 这只需要简单的修改即可;
- A2)打印结果在文末,可以看到,ElementType采用int 和 Distance的打印效果一样,这正证明了我们采用Distance结构体对源码的修改是无误的,相比于单纯的int 类型,只不过Distance又多了一个 顶点下标vertexIndex成员变量而已;
【3】source code + printing results
3.1)download source code:
https://github.com/pacosonTang/dataStructure-algorithmAnalysis/tree/master/chapter9/binaryHeap_dijkstra_prim
3.2)source code at a glance:(for complete code , please click the given link above)
1st file:distance.h
#include
#define Error(str) printf("\n error: %s \n",str)
struct Distance;
typedef struct Distance *Distance;
struct Distance
{
int vertexIndex;
int distance;
};
Distance makeEmptyDistance(); 2nd file:distance.c
#include "distance.h"
#include
// allocate the memory for Distance struct
Distance makeEmptyDistance()
{
Distance element;
element = (Distance)malloc(sizeof(struct Distance));
if(!element)
{
Error("out of space ,from func makeEmptyDistance");
return NULL;
}
return element;
}
3rd file:binaryheap.h
#include
#include
#include "distance.h"
#define ElementType Distance
#define Error(str) printf("\n error: %s \n",str)
struct BinaryHeap;
typedef struct BinaryHeap *BinaryHeap;
void swap(ElementType x, ElementType y);
BinaryHeap initBinaryHeap(int capacity);
void insert(ElementType value, BinaryHeap bh, int*);
ElementType deleteMin(BinaryHeap, int*);
int isFull(BinaryHeap bh);
int isEmpty(BinaryHeap bh);
void percolateUp(int index, BinaryHeap bh);
void percolateDownFromOne(int index, BinaryHeap bh, int*);
void printBinaryHeap(BinaryHeap bh);
void printBinaryHeapFromZero(BinaryHeap bh);
struct BinaryHeap
{
int capacity;
int size;
ElementType *elements;
}; 4th file:binaryheap.c
#include "binaryheap.h"
#include
#define MaxInt (int)pow(2, 16)
//judge whether the BinaryHeap is full or not , also 1 or 0
int isFull(BinaryHeap bh)
{
return bh->size == bh->capacity - 1;
}
//judge whether the BinaryHeap is empty or not , also 1 or 0
int isEmpty(BinaryHeap bh)
{
return bh->size == 0;
}
// get the left child of node under index with startup 1
int leftChildFromOne(int index)
{
return index * 2;
}
void printBinaryHeap(BinaryHeap bh)
{
int i;
ElementType *temp;
if(!bh)
Error("printing execution failure, for binary heap is null, from func printBinaryHeap");
temp = bh->elements;
for(i = 1; i < bh->capacity; i++)
{
printf("\n\t heap[%d] = ", i);
if(i <= bh->size)
printf("vertex[%d] + distance[%d]", bh->elements[i]->vertexIndex+1, bh->elements[i]->distance);
else
printf("NULL");
}
printf("\n");
}
//print the binary heap who starts from index 0
void printBinaryHeapFromZero(BinaryHeap bh)
{
int i;
ElementType *temp;
if(!bh)
Error("printing execution failure, for binary heap is null, from func printBinaryHeap");
temp = bh->elements;
for(i = 0; i < bh->capacity; i++)
{
printf("\n\t index[%d] = ", i);
if(i < bh->size)
printf("%d", bh->elements[i]->distance);
else
printf("NULL");
}
printf("\n");
}
void swap(ElementType x, ElementType y)
{
struct Distance temp;
temp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = temp;
}
ElementType deleteMin(BinaryHeap bh, int* heapIndexRecord)
{
ElementType minimum;
ElementType *data;
if(isEmpty(bh))
{
Error("failed deleting minimum , for the BinaryHeap is empty, from func deleteMin !");
return NULL;
}
data = bh->elements;
minimum = data[1];
swap(data[1], data[bh->size]);
bh->size-- ; // size-- occurs prior to percolateDownFromOne
percolateDownFromOne(1, bh, heapIndexRecord) ;
return minimum;
}
// percolating down the element when its value is greater than children (minimal heap)
//Attention: all of bh->elements starts from index 1
void percolateDownFromOne(int index, BinaryHeap bh, int* heapIndexRecord)
{
ElementType *data;
int size;
struct Distance temp;
int child;
data = bh->elements;
size = bh->size;
for(temp = *data[index]; leftChildFromOne(index) <= size; index = child)
{
child = leftChildFromOne(index);
if(child < size && data[child]->distance > data[child+1]->distance)
child++;
if(temp.distance > data[child]->distance)
{
*data[index] = *data[child];
heapIndexRecord[bh->elements[index]->vertexIndex] = index; //update the heapIndexRecord
}
else
break;
}
*data[index] = temp;
heapIndexRecord[bh->elements[index]->vertexIndex] = index; //update the heapIndexRecord
}
// Attention, the index of the heap starts from 1
// return the index the element inserted into the binary heap
void insert(ElementType value, BinaryHeap bh, int* heapIndexRecord)
{
int i;
if(isFull(bh))
{
Error("failed insertion , for the BinaryHeap is full, from func insert!");
return ;
}
if(!isEmpty(bh))
for(i = ++bh->size; bh->elements[i/2]->distance > value->distance; i /= 2)
{
//copyElement(bh->elements[i/2], bh->elements[i]);
*bh->elements[i] = *bh->elements[i/2];
heapIndexRecord[bh->elements[i]->vertexIndex] = i; //update the heapIndexRecord
}
else
i = ++bh->size;
*bh->elements[i] = *value;
heapIndexRecord[bh->elements[i]->vertexIndex] = i; //update the heapIndexRecord
}
BinaryHeap initBinaryHeap(int capacity)
{
BinaryHeap bh;
ElementType *temp;
int i;
bh = (BinaryHeap)malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryHeap));
if(!bh) {
Error("out of space, from func initBinaryHeap");
return NULL;
}
bh->capacity = capacity;
bh->size = 0;
temp = (ElementType*)malloc(capacity * sizeof(Distance));
if(!temp) {
Error("out of space, from func initBinaryHeap");
return NULL;
}
bh->elements = temp;
for(i=0; i < capacity; i++)
{
temp[i] = (ElementType)malloc(sizeof(struct Distance));
if(!temp[i]) {
Error("out of space, from func initBinaryHeap");
return NULL;
}
}
return bh;
}
// allocate the memory for storing index of vertex in heap and let every element -1
int *makeEmptyArray(int size)
{
int *array;
int i;
array = (int*)malloc(size * sizeof(int));
if(!array)
{
Error("out of space ,from func makeEmptyArray");
return NULL;
}
for(i=0; idistance = data[i];
tempDisStruct->vertexIndex = i;
insert(tempDisStruct, bh, indexOfVertexInHeap);
}
printBinaryHeap(bh);
printIndexOfVertexInHeap(bh->size, indexOfVertexInHeap);
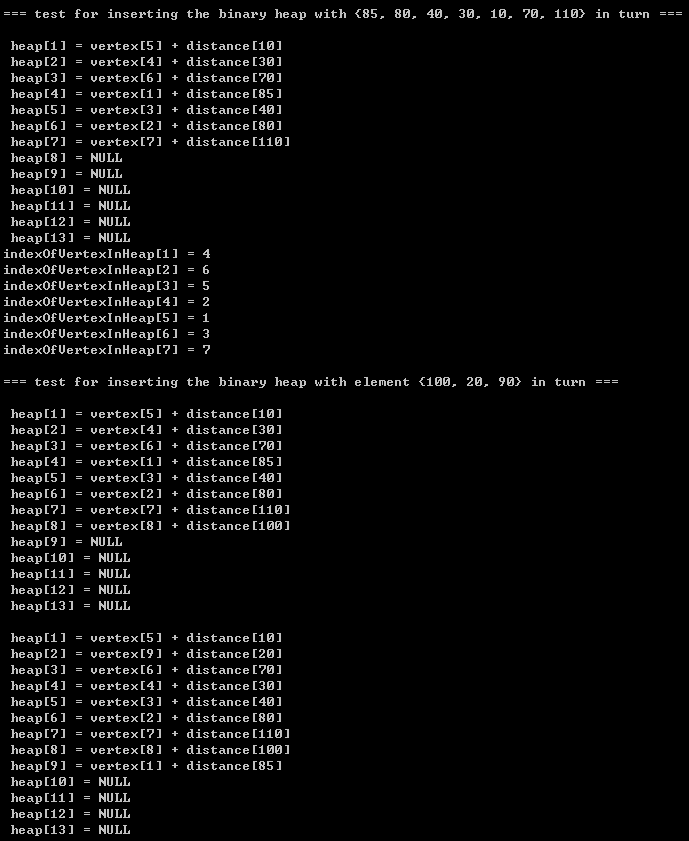
printf("\n\t=== test for inserting the binary heap with element {100, 20, 90} in turn ===\n");
tempDisStruct->distance = 100;
tempDisStruct->vertexIndex = size;
insert(tempDisStruct, bh, indexOfVertexInHeap);
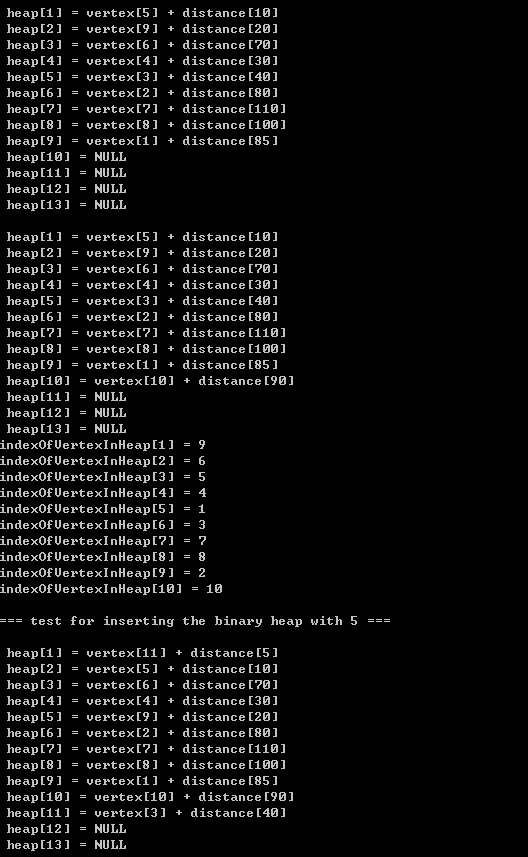
printBinaryHeap(bh);
tempDisStruct->distance = 20;
tempDisStruct->vertexIndex = size+1;
insert(tempDisStruct, bh, indexOfVertexInHeap);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
tempDisStruct->distance = 90;
tempDisStruct->vertexIndex = size+2;
insert(tempDisStruct, bh, indexOfVertexInHeap);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
printIndexOfVertexInHeap(bh->size, indexOfVertexInHeap);
printf("\n\t=== test for inserting the binary heap with 5 ===\n");
tempDisStruct->distance = 5;
tempDisStruct->vertexIndex = size+3;
insert(tempDisStruct, bh, indexOfVertexInHeap);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
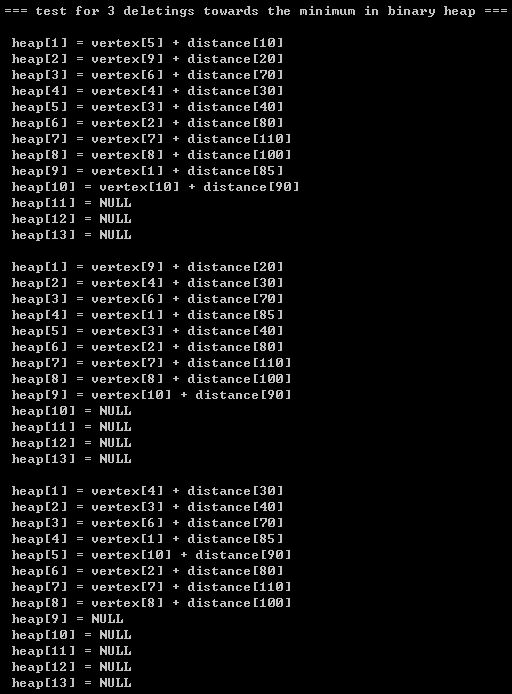
printf("\n\t=== test for 3 deletings towards the minimum in binary heap ===\n");
deleteMin(bh, indexOfVertexInHeap);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
deleteMin(bh, indexOfVertexInHeap);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
deleteMin(bh, indexOfVertexInHeap);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
}