python-Day7
学习要有定位,明确目标地去学习。希望自己能坚持下去,并有所收获---leaves(ps月初有事耽误计划了,进度落后计划蛮多了,算了。不多想,复习,学会才是硬道理,坚持fighting!)
python06 -- python的pickle模块以及mysql数据库初始用
一、python的pickle模块
1.1 pickle模块的作用
pickle是为了序列化/反序列化数据的,可以把数据持久化存储。eg:你有些数据想下次运行程序的时候直接使用,或者想把数据传给网络上的其他程序,就可以使用pickle打包,那边的python程序用pickle反序列化就可以了。
1.2 pickle模块的所有函数
In [32]: import pickle
In [33]: dir(pickle)
Out[33]:
'classmap',
'compatible_formats',
'decode_long',
'dispatch_table',
'dump',
'dumps',
'encode_long',
'format_version',
'load',
'loads',
'marshal',
'mloads',
're',
'struct',
'sys',
'whichmodule']1.3 pickle的常用方法
1.pickle.dump("数据",文件名) 把字典转为二进制
2.pickle.load("文件名") 把二进制转为字典
##pickle代码小练习
In [32]: import pickle
In [37]: users = {'AA': 'we231', 'Xman': '123', 'tt': '123', 'woniu': '21'}
In [39]: fo = open("test.txt",'wb')
In [42]: fo = open("test.txt",'wb')
In [43]: pickle.dump(users,fo) #数据---> 文件
In [44]: fo.close()
##查看test.txt文件内容
[root@test ketang]# cat test.txt
(dp0
S'AA'
p1
S'we231'
p2
sS'Xman'
p3
S'123'
p4
sS'tt'
p5
g4
sS'woniu'
p6
S'21'
p7
s.[root@test ketang]#
In [9]: fi = open('test.txt','rb+')
In [10]: print pickle.load(fi)
{'AA': 'we231', 'Xman': '123', 'tt': '123', 'woniu': '21'}1.4 通过pickle实现用户的增删改查
#/usr/local/python
#coding:utf-8
'''
##使用pickle实现对users.txt文件中用户密码的增、删、改、查功能(具体见github06/pickle代码)
'''
from pickle import dump ,load
#定义全局变量filename,用于测试
filename = 'users.txt'
##注意事先要将users写入到users.txt文件中(此处在1.3中ipython的环境中操作过了)
users = {'AA': 'AA123', 'Xman': '123', 'tt': '123', 'woniu': '21', 'KK': 'k123'}
#获取所有用户名密码,从filename文件中读取
def getUsers():
with open(filename,'rb') as readf:
res = load(readf)
return res
#添加用户
def addUser(name,password):
tmp = getUsers()
if (not name) or (not password):
errmsg = "Wrong name or password"
return errmsg
if (name in tmp):
errmsg = "name is exists"
return errmsg
tmp[name] = password
msg = "%s:%s ---->adding" %(name,password)
with open(filename,'wb') as updatef:
dump(tmp,updatef)
return msg
##更改用户
def updateUser(name,password):
tmp = getUsers()
if name not in tmp:
errmsg = 'The update username is not exist'
return errmsg
msg = "Update %s:%s ---->%s" %(tmp[name],password,name)
tmp[name] = password
with open(filename,'wb') as updatef:
dump(tmp,updatef)
return msg
#删除用户
def deleteUser(name):
tmp = getUsers()
if name not in tmp:
errmsg = 'The delete username is not exist'
return errmsg
msg = "Delete %s ---->%s" %('users.txt',name)
tmp.pop(name)
with open(filename,'wb') as updatef:
dump(tmp,updatef)
return msg
##查找用户名对应的密码
def findUser(name):
tmp = getUsers()
if name not in tmp :
errmsg = "The username is not exists"
return errmsg
return tmp[name]
##主程序入口
if __name__ == "__main__":
print getUsers()
print findUser('')
print findUser('AA')
print "add user %s" % ('*' * 40)
print addUser('pc','pc123')
print addUser('TT','')
print addUser('','pc123')
print addUser('AA','pc123')
print "update user %s" % ('*' * 40)
print updateUser('AA1','123')
print updateUser('AA','AA123')
print "delete user %s" % ('*' * 40)
print deleteUser('AA1')
print deleteUser('pc')二、MySQL存储数据
2.1 安装mysql以及mysql扩展
yum install -y mysql mysql-server
##安装完成后设置开机启动以及数据库密码
[root@test mysqlData]# chkconfig --level 1234 mysqld on #设置开机启动
[root@test mysqlData]# chkconfig --list mysqld
mysqld 0:off 1:on 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
[root@test mysqlData]#
# /etc/init.d/mysqld start 启动数据库
#
[root@test mysqlData]#
[root@test mysqlData]# netstat -ntpl ##查看数据库运行状态
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:2208 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3014/hpiod
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:199 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3032/snmpd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3416/mysqld
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2667/portmap
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3102/httpd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3052/sshd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3068/cupsd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3472/sendmail: acce
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:766 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2704/rpc.statd
[root@test mysqlData]#
##设置数据库密码
##mysqladmin -u 用户名 -p"密码" password 新密码 ===>回车后输入旧密码
刚安装数据库的话第一次设置密码命令
## mysqladmin -uroot password "123456"
##mysql扩展安装
1.yum install python-pip
2. pip install MySQL-python
##安装完成后的检查(在ipython中import MySQLdb as mysql 无报错信息则成功)
In [1]: import MySQLdb as mysql
In [2]:2.2 数据库的简单操作
##创建库
mysql> create database reboot; #创建库
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> show databases; #列出所有库
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| reboot |
| reboot10 |
| test |
+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> use reboot; #切换库,使用reboot库
Database changed
#创建表
mysql> create table users(
-> id int AUTO_INCREMENT primary key
-> ,name varchar(20) not null comment '用户名'
-> ,name_cn varchar(50) not null comment '中文名'
-> ,password varchar(50) not null comment '用户密码'
-> ,email varchar(50) comment '电子邮件'
-> ,mobile varchar(11) not null comment '手机号码'
-> ,role varchar(10) not null comment '1:sa;2:php;3:ios;4:test'
-> ,status tinyint
-> ,create_time datetime comment '创建时间'
-> ,last_time datetime comment '最后登录时间'
-> ,unique key name (name) ) engine=innodb comment '用户表';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec)
mysql> desc users; #查看表信息,表中字段定义及类型
+-------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(20) | NO | UNI | NULL | |
| name_cn | varchar(50) | NO | | NULL | |
| password | varchar(50) | NO | | NULL | |
| email | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
| mobile | varchar(11) | NO | | NULL | |
| role | varchar(10) | NO | | NULL | |
| status | tinyint(4) | YES | | NULL | |
| create_time | datetime | YES | | NULL | |
| last_time | datetime | YES | | NULL | |
+-------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show tables; #查看库中有哪些表
+------------------+
| Tables_in_reboot |
+------------------+
| users |
+------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
##mysql数据库中插入数据
mysql> insert into users (name,name_cn,password,email,mobile,role,status,create_time) values ('ss','ss','ss123 ','[email protected]','ssss','user','0','2016-11-30 15:37:48');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec)
mysql>
mysql> select * from users; #查找表中所有数据
+----+------+---------+----------+-------------------+--------+------+--------+---------------------+-----------+
| id | name | name_cn | password | email | mobile | role | status | create_time | last_time |
+----+------+---------+----------+-------------------+--------+------+--------+---------------------+-----------+
| 1 | ss | ss | ss123 | [email protected] | ssss | user | 0 | 2016-11-30 15:37:48 | NULL |
+----+------+---------+----------+-------------------+--------+------+--------+---------------------+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)2.3 python交互环境下对mysql的操作
##导入数据库
In [8]: import MySQLdb as mysql
##连接数据库
In [9]: data = mysql.connect(user='root',passwd='123456',db='reboot',charset='utf8')
##建立游标,添加这行后数据库就初始化完成
In [10]: cur = data.cursor()
In [11]: data.autocommit(True) ##设置自动提交,比较重要
##在ipython端添加数据
#在ipython段查询所有数据
In [13]: cur.execute('select * from users')
Out[13]: 1L
In [14]: import datetime #导入datetime
In [15]: ##datetime模块可以实现在数据库中create_time生成时间
In [16]: sql = "insert into users(name,name_cn,password,email,mobile,role,status,create_time) values ('cc'
...: ,'cc','cC23 ','[email protected]','CCC','user','0','%s') " %(datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y
...: -%m-%d %H:%M:%S"))
In [17]: print sql
insert into users(name,name_cn,password,email,mobile,role,status,create_time) values ('cc','cc','cC23 ','[email protected]','CCC','user','0','2016-11-30 16:04:33')
In [18]: cur.execute(sql)
Out[18]: 1L
#再次查询所有数据发现新增加了一条数据
In [19]: cur.execute("select * from users;")
Out[19]: 2L
##在mysql段查询所有数据确认新增数据
mysql> select * from users;
+----+------+---------+----------+-------------------+--------+------+--------+---------------------+-----------+
| id | name | name_cn | password | email | mobile | role | status | create_time | last_time |
+----+------+---------+----------+-------------------+--------+------+--------+---------------------+-----------+
| 1 | ss | ss | ss123 | [email protected] | ssss | user | 0 | 2016-11-30 15:37:48 | NULL |
| 2 | cc | cc | cC23 | [email protected] | CCC | user | 0 | 2016-11-30 16:04:33 | NULL |
+----+------+---------+----------+-------------------+--------+------+--------+---------------------+-----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
##ipython交互下查找数据
###查询所有数据
In [20]: select_sql = "select name,name_cn,password,email,mobile,role,status,create_time from users"
In [21]: cur.execute(select_sql)
Out[21]: 2L
In [22]: res = cur.fetchall() ##查找所有数据使用cur.fetchall(),单条数据则使用cur.fetchone()
In [23]: print res
((u'ss', u'ss', u'ss123 ', u'[email protected]', u'ssss', u'user', 0, datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 30, 15, 37, 48)), (u'cc', u'cc', u'cC23 ', u'[email protected]', u'CCC', u'user', 0, datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 30, 16, 4, 33)))
###查询单条数据
In [24]: select_sql = "select name,name_cn,password,email,mobile,role,status,create_time from users where
...: name = 'ss'"
In [25]: cur.execute(select_sql)
Out[25]: 1L
In [26]: res = cur.fetchone()
In [27]: print res
(u'ss', u'ss', u'ss123 ', u'[email protected]', u'ssss', u'user', 0, datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 30, 15, 37, 48))
In [28]:
###ipython交互模式下查询所有数据以及将数据重组成我们想要的形式
In [36]: select_sql = "select name,name_cn,password,email,mobile,role,status,create_time from users "
In [37]: cur.execute(select_sql)
Out[37]: 4L
In [38]: res = cur.fetchall()
In [39]: print res
((u'ss', u'ss', u'ss123 ', u'[email protected]', u'ssss', u'user', 0, datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 30, 15, 37, 48)), (u'cc', u'cc', u'cC23 ', u'[email protected]', u'CCC', u'user', 0, datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 30, 16, 4, 33)), (u'admin', u'admin', u'admin ', u'[email protected]', u'admin', u'admin', 0, datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 30, 16, 25, 17)), (u'TT', u'TT', u'tt123 ', u'[email protected]', u'123223', u'sa', 0, datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 30, 16, 26, 17)))
##思考:如何将上述res更改成为我们想要的字典形式
In [40]: fields = ['name','name_cn','password','email','mobile','role','status','create_time']
原生实现方式:
In [7]: select_sql = "select %s from users" %','.join(fields)
In [8]: print select_sql
select name,name_cn,password,email,mobile,role,status,create_time from users
In [9]: cur.execute(select_sql)
Out[9]: 4L
In [10]: res = cur.fetchall()
In [11]: res
Out[11]:
((u'ss',
u'ss',
u'ss123 ',
u'[email protected]',
u'ssss',
u'user',
0,
datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 30, 15, 37, 48)),
(u'cc',
u'cc',
u'cC23 ',
u'[email protected]',
u'CCC',
u'user',
0,
datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 30, 16, 4, 33)),
(u'admin',
u'admin',
u'admin ',
u'[email protected]',
u'admin',
u'admin',
0,
datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 30, 16, 25, 17)),
(u'TT',
u'TT',
u'tt123 ',
u'[email protected]',
u'123223',
u'sa',
0,
datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 30, 16, 26, 17)))
In [12]: users = []
In [13]: for row in res :
...: user = {}
...: for k ,v in enumerate(fields):
...: user[v] = row[k]
...: users.append(user)
...:
In [14]: users
Out[14]:
[{'create_time': datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 30, 15, 37, 48),
'email': u'[email protected]',
'mobile': u'ssss',
'name': u'ss',
'name_cn': u'ss',
'password': u'ss123 ',
'role': u'user',
'status': 0},
{'create_time': datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 30, 16, 4, 33),
'email': u'[email protected]',
'mobile': u'CCC',
'name': u'cc',
'name_cn': u'cc',
'password': u'cC23 ',
'role': u'user',
'status': 0},
{'create_time': datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 30, 16, 25, 17),
'email': u'[email protected]',
'mobile': u'admin',
'name': u'admin',
'name_cn': u'admin',
'password': u'admin ',
'role': u'admin',
'status': 0},
{'create_time': datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 30, 16, 26, 17),
'email': u'[email protected]',
'mobile': u'123223',
'name': u'TT',
'name_cn': u'TT',
'password': u'tt123 ',
'role': u'sa',
'status': 0}]
In [15]:
###高阶的进阶方式代码(字典生成式 + 列表生成式 一行搞定)
In [45]: users = [dict((v,row[k]) for k ,v in enumerate(fields)) for row in res ]
###关闭游标和数据库
In [15]: cur.close()
In [16]: data.close()2.4 自己感悟的数据库操作
2.4.1 高阶用法记录 【字典生成式 + 列表生成式 简化代码】
如下面代码可用 users = [ dict((v,row[k]) for k ,v in enumerate(fields)) for row in res ]
In [12]: users = []
In [13]: for row in res :
...: user = {}
...: for k ,v in enumerate(fields):
...: user[v] = row[k]
...: users.append(user)
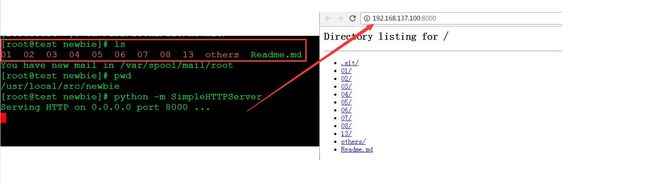
...:2.4.2 python搭建一个临时的下载服务器;
python -m SimpleHTTPServer(默认会解析当前目录下的html文件)
三、总结
python数据库操作流程
1.导入mysql扩展模块, import MySQLdb as mysql
2.链接数据库 db = mysql.connect(各种参数)
3.建立游标, cur = db.cursor() ,自此数据库初始化完成,可以干活了
4.编写mysql的语句(增删改查) sql = "*****"
5.执行sql语句 cur.execute(sql) db.commit() ===>数据提交
6.查询 分为两种 (在mysql中查询 select * from users)
1.查询单条记录, cur.fetchone()
2.查询多条记录 cur.fetchall()
7.注意此时,在mysql中查看数据还是未更新的,需要关闭游标
db.commit() ===>数据提交
将内存中的数据存储到数据库的表上。
mysql设置为默认自动提交 show variables like 'autocommit%';
或者添加db.autocommit(True) 设置交互端自动提交数据
8.关闭游标和数据库
cur.close()
conn.close()