本次设计实验源码位于:http://download.csdn.net/detail/noticeable/9922865
实验目的:通过系统的搭建进一步了解FPGA的SOPC开发流程,并借此了姐pll IP核的应用以及用DE-SOC自带的SDRAM缓存输出数据,并为后面的工程实施提供基础。
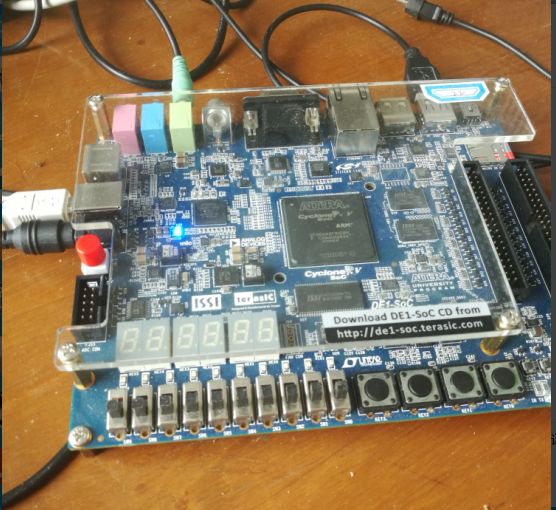
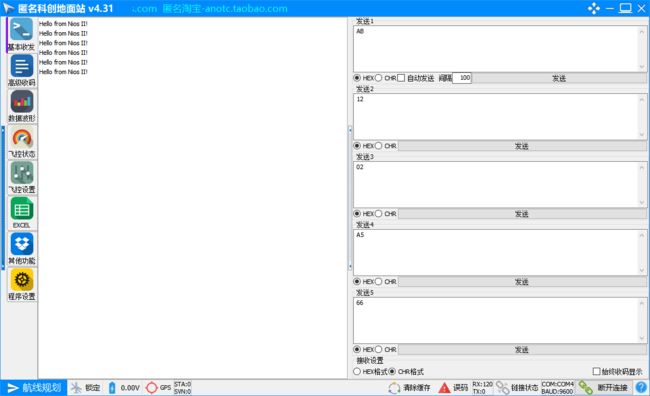
实验现象:uart接口连接串口调试助手显示hellowold
实验步骤:
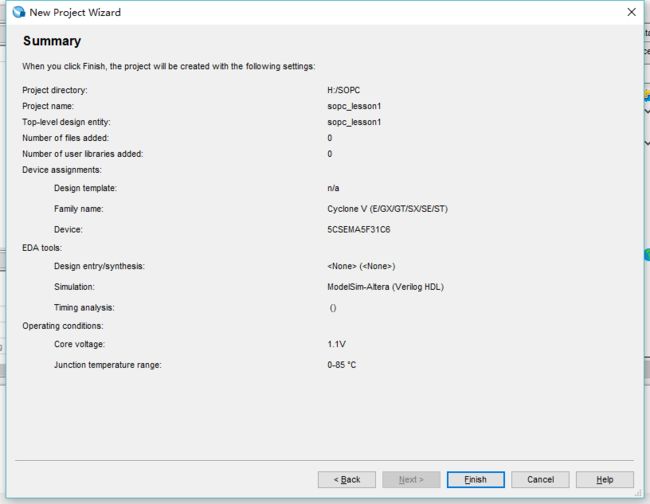
新建sopc_lesson1工程:
并新建一个sopc_lesson1.v文件
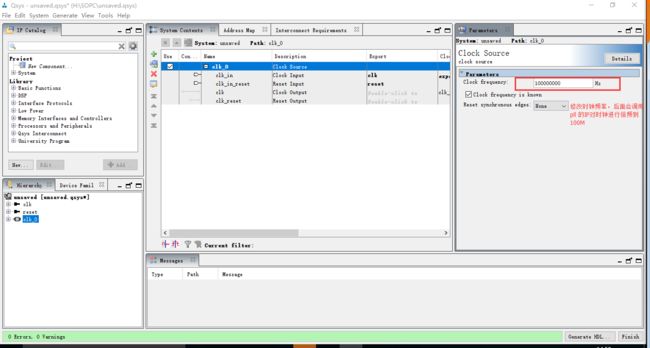
通过![]() 打开qsys工具,修改clk_0的默认时钟
打开qsys工具,修改clk_0的默认时钟
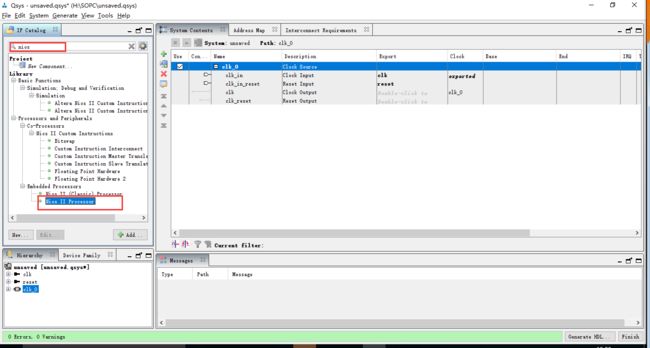
添加NIOS processor内核,且暂时不进行修改,直接finish即可。
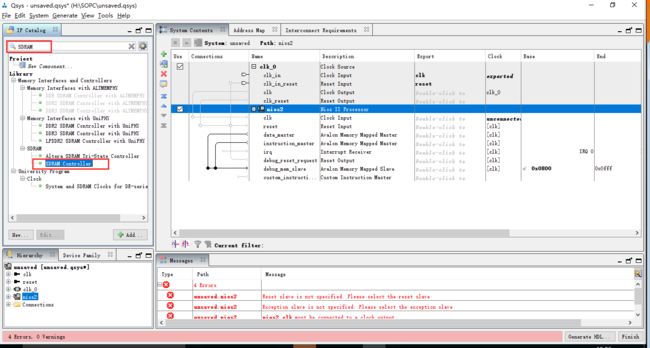
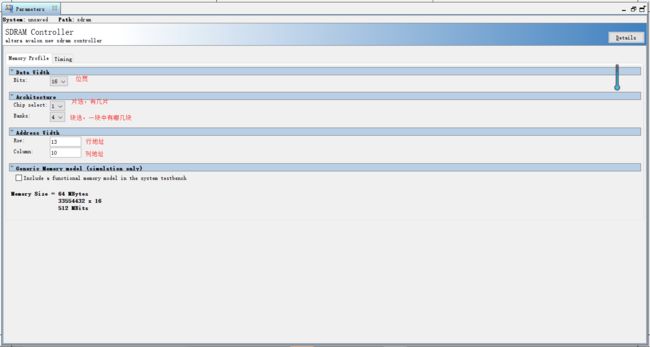
添加存储器,由于DE-SOC开发板FPGA部分板载一块64M的SDRAM,所以这里添加SDRAM
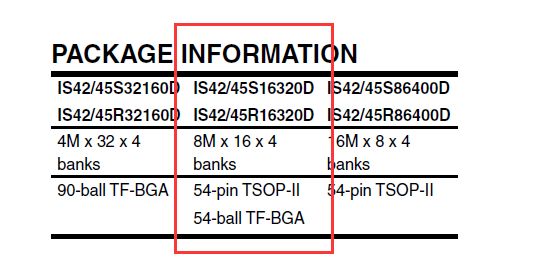
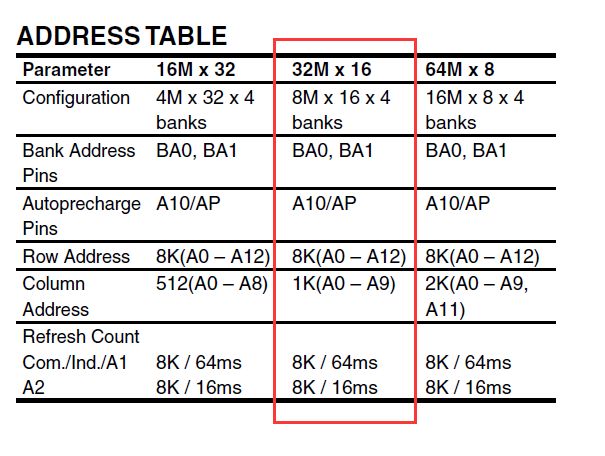
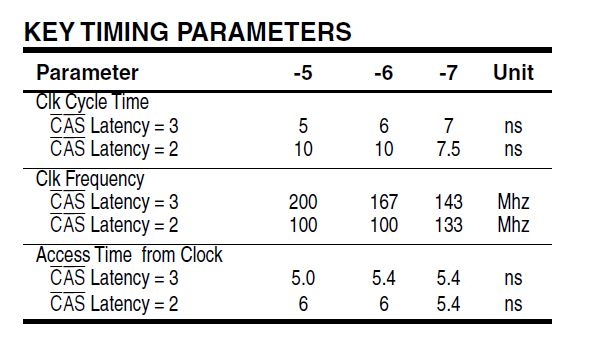
这里的设置是按照开发板上实际的芯片参数设置的,详细操作看芯片手册,芯片手册下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/noticeable/9922132
由芯片手册有
配置结果如下
timing部分的时序约束部分先不改,后面在专门运用SDRAM时再详细说明。
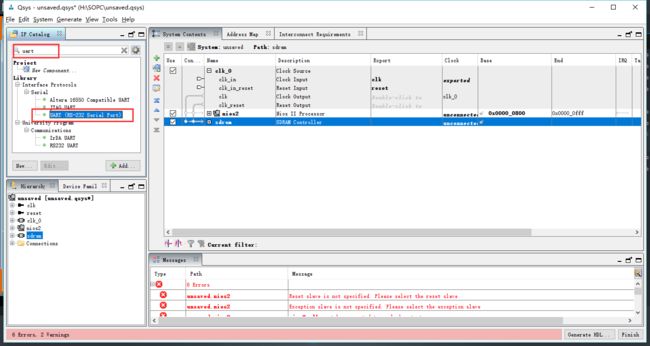
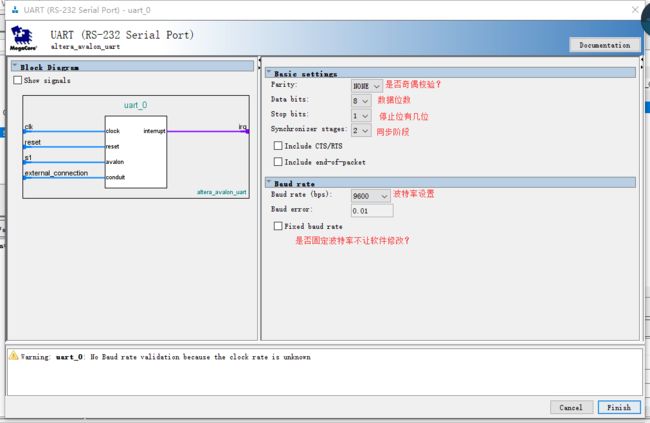
添加uart调试接口
uart设置如下
基本功能设置完成后,之后即为一些与开发板相关的外设的添加:
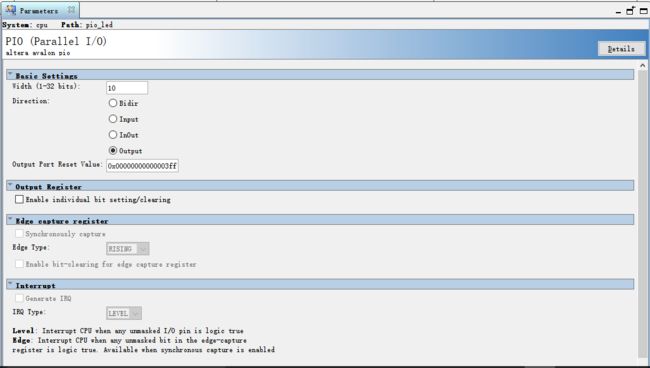
添加pio_led的IO口
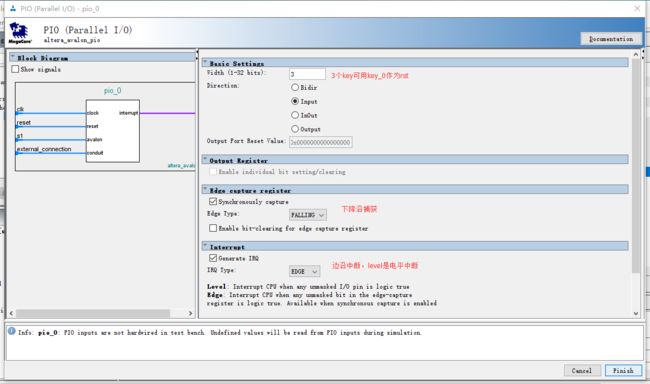
添加pio_key的IO口
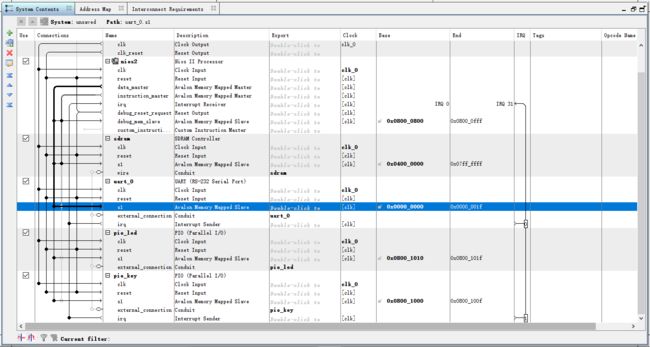
下面即是进行总线的连接
首先即是clk、控制总线和数据总线的连接
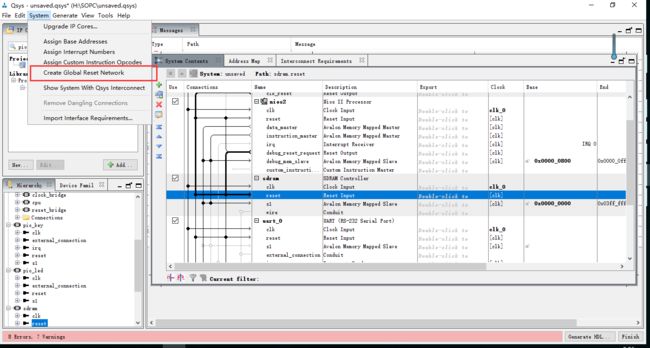
配置rst
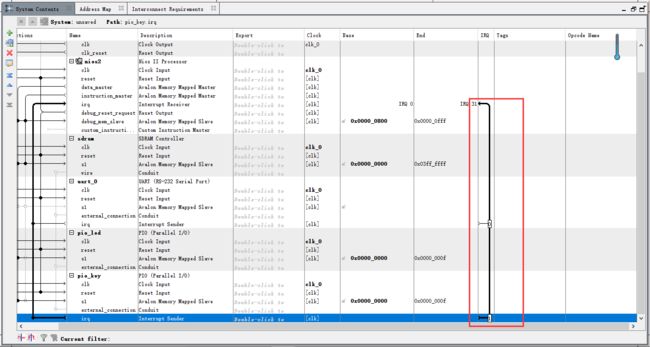
将中断连接到CPU
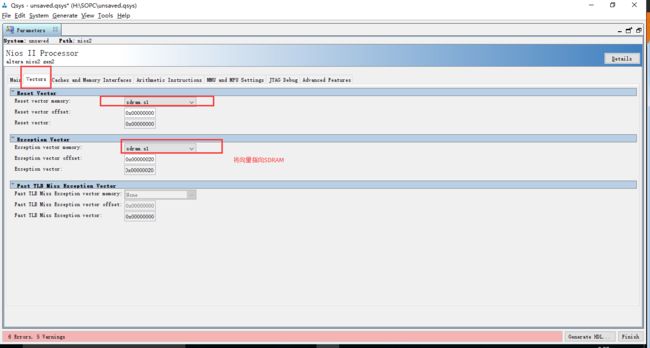
指定中断向量
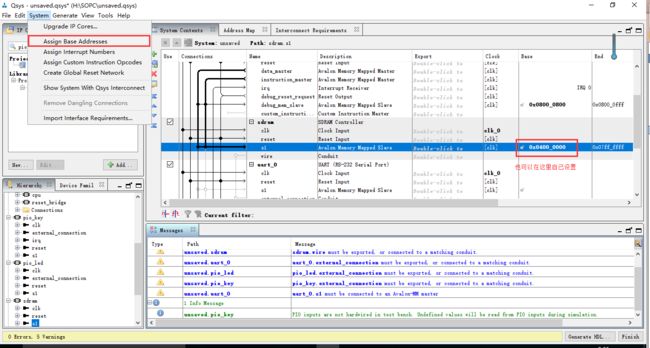
分配基地址
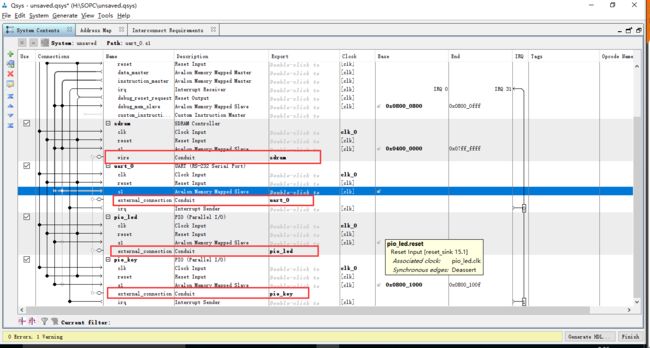
将引脚导出
导出后发现还有一个警告,发现是uart 的s1未连接到 instruction_master上,连接上即可
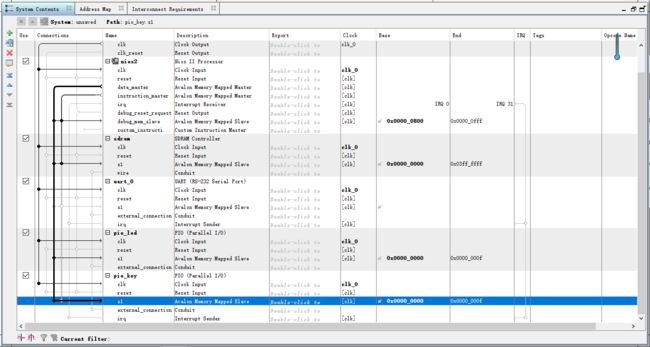
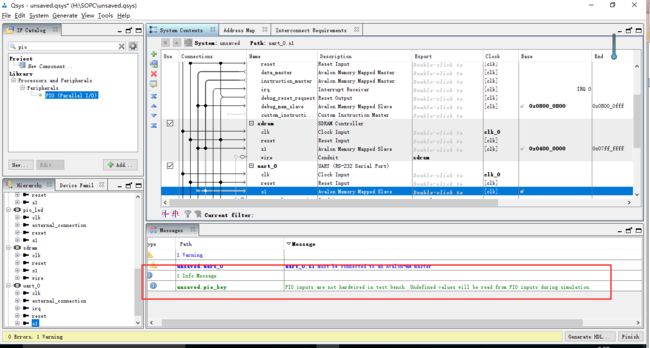
连接完成后的总体连接图
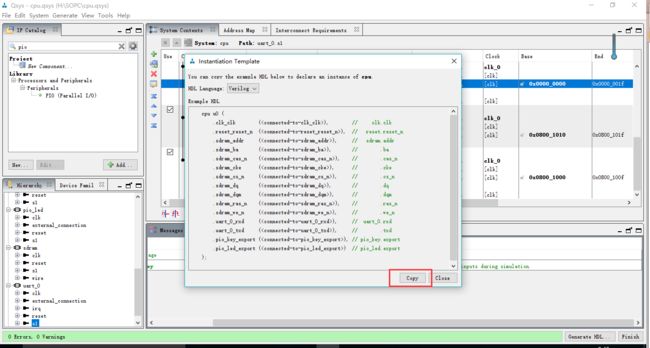
将系统保存,然后点击generate->show instantiation自动生成template
然后将template复制下后,粘贴到之前生成的sopc_lesson.v文件中
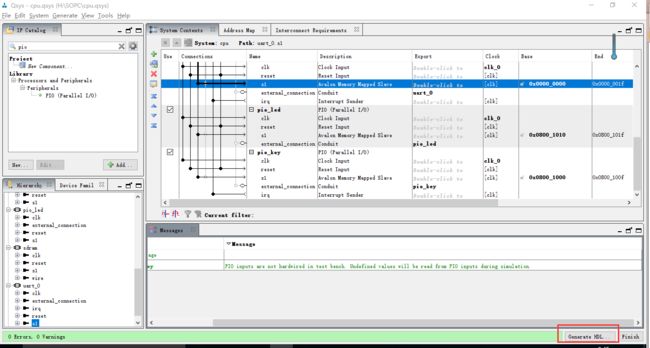
最后点击generate hdl 文件
至此,设计需要的nios II软件核即设计完成了,在quartus II中将cpu.qsys文件添加到文件夹即可。
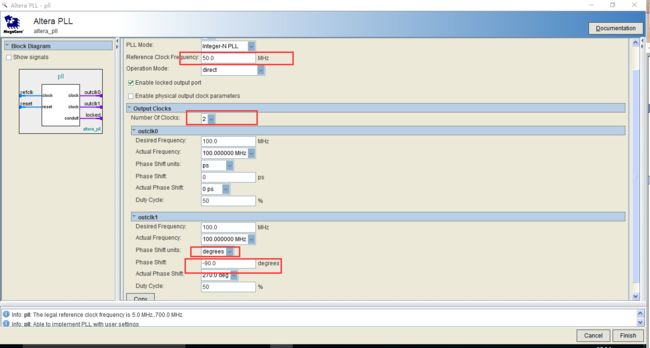
添加锁相环IP核对时钟进行倍频和移相
下面,对sopc_lesson1.v文件进行编写
module sopc_lesson1 ( input wire clk_50m, // clk.clk input wire [2:0] pio_key_export, // pio_key.export output wire [9:0] pio_led_export, // pio_led.export input wire reset_reset_n, // reset.reset_n output wire sdram_clk, //这里自己添加一个SDRAM_CLK output wire [12:0] sdram_addr, // sdram.addr output wire [1:0] sdram_ba, // .ba output wire sdram_cas_n, // .cas_n output wire sdram_cke, // .cke output wire sdram_cs_n, // .cs_n inout wire [15:0] sdram_dq, // .dq output wire [1:0] sdram_dqm, // .dqm output wire sdram_ras_n, // .ras_n output wire sdram_we_n, // .we_n input wire uart_0_rxd, // uart_0.rxd output wire uart_0_txd // .txd ); //这一块可以直接ctrl+o打开H:\SOPC\cpu\synthesis路径下的cpu.v文件复制粘贴 wire nios_clk; wire nios_reset_n; pll pll( .refclk(clk_50m), // refclk.clk .rst(~reset_reset_n), // reset.reset . outclk_0(nios_clk), // outclk0.clk . outclk_1(sdram_clk), // outclk1.clk . locked(nios_reset_n) // locked.export ); cpu u0 ( .clk_clk (nios_clk), // clk.clk .pio_key_export (pio_key_export), // pio_key.export .pio_led_export (pio_led_export), // pio_led.export .reset_reset_n (nios_reset_n), // reset.reset_n .sdram_addr (sdram_addr), // sdram.addr .sdram_ba (sdram_ba), // .ba .sdram_cas_n (sdram_cas_n), // .cas_n .sdram_cke (sdram_cke), // .cke .sdram_cs_n (sdram_cs_n), // .cs_n .sdram_dq (sdram_dq), // .dq .sdram_dqm (sdram_dqm), // .dqm .sdram_ras_n (sdram_ras_n), // .ras_n .sdram_we_n (sdram_we_n), // .we_n .uart_0_rxd (uart_0_rxd), // uart_0.rxd .uart_0_txd (uart_0_txd) // .txd ); endmodule
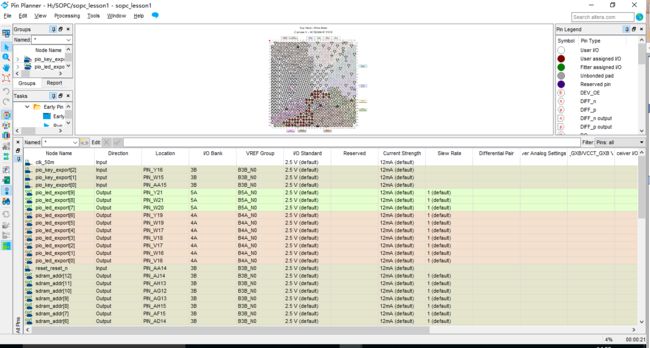
分配引脚:
到这里,整个板载部分逻辑设计及nios相关的设计就完成了,下面即是编写EDS文件然后进行仿真。
编写EDS工程:
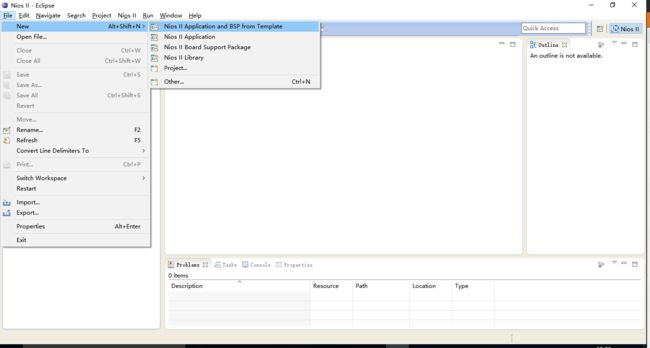
打开tool->NIOS II Software Build Tools for eclipse 并将workspace设定到自己本次工程的目录下
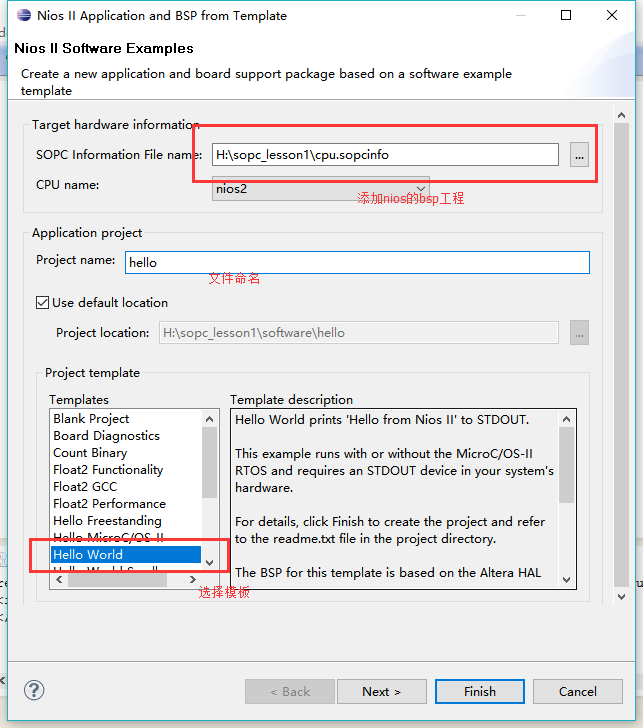
选则创建模板和bsp工程
对nios_bsp进行设置
发现其已经默认设置好了uart_0为输出,默认即可,所以退出。
编译整个工程
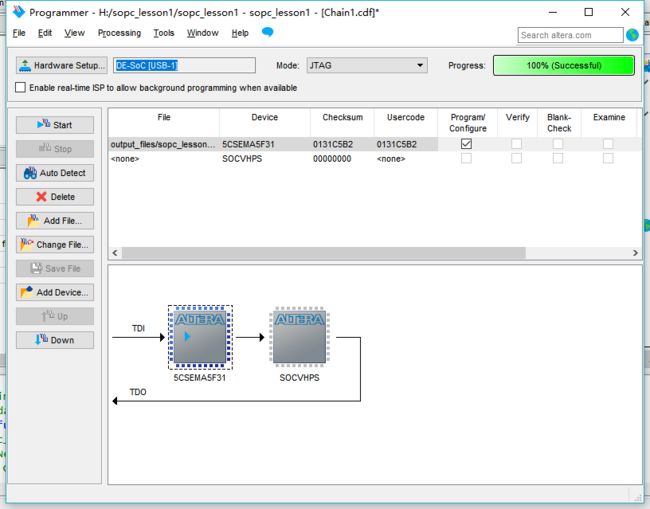
烧写.sof文件
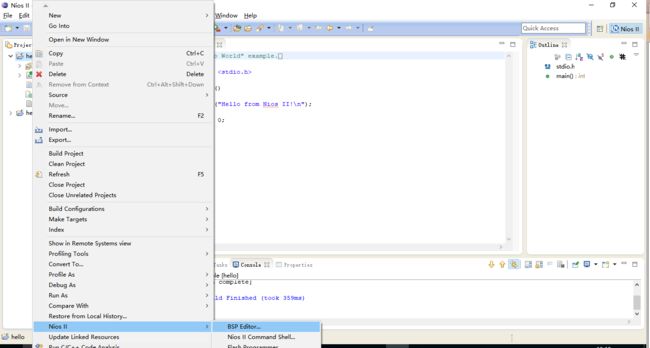
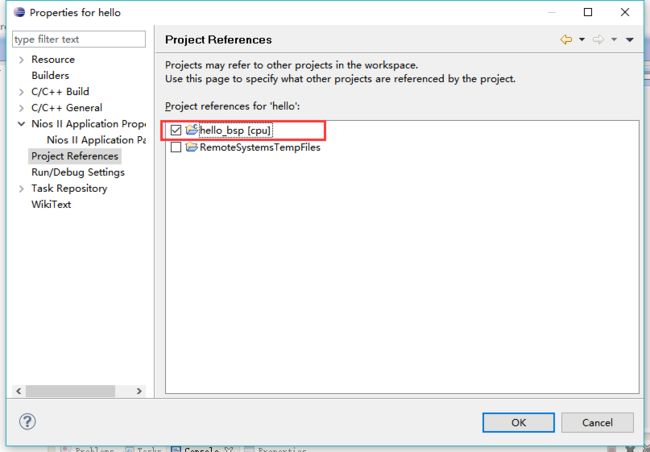
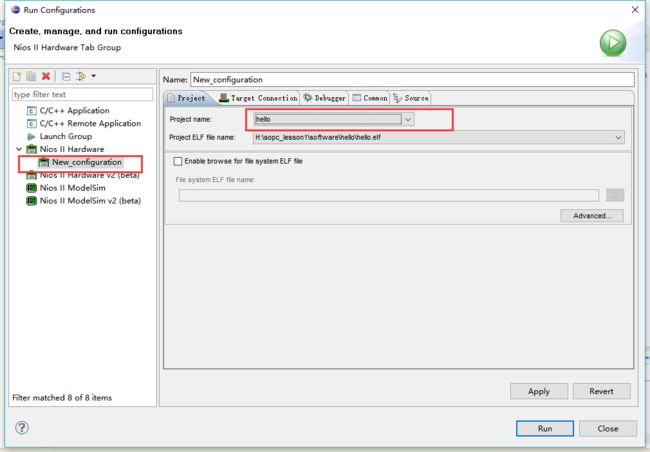
设置关连文件,将hello与bsp关联起来
烧写.elf文件
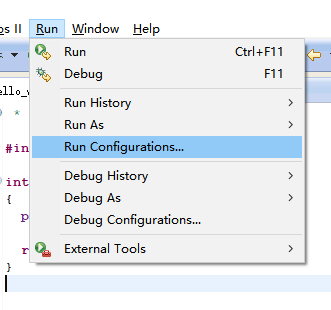
选择project
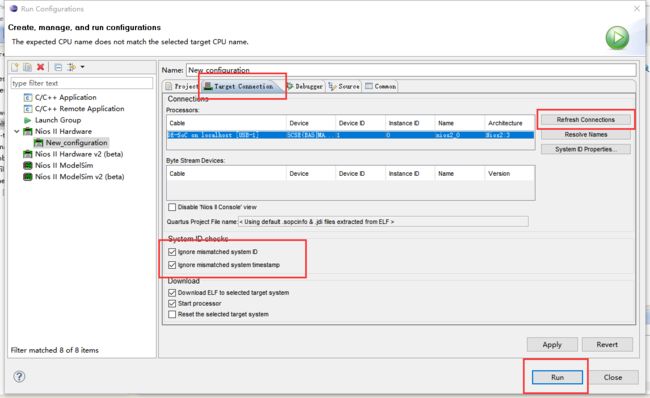
执行下面这步,点击运行
至此程序烧写完成。
实验现象:
将USB-TTL按照GND->GND
TXD->GPIOD0
TXD->GPIOD1
串口调试助手波特率设为9600
.sof文件烧写进开发板时,led灯全亮,按复位键串口调试没有数据接收,
将.elf文件烧写到FPGA后,按下KEY0,串口调试助手接收到信息如图
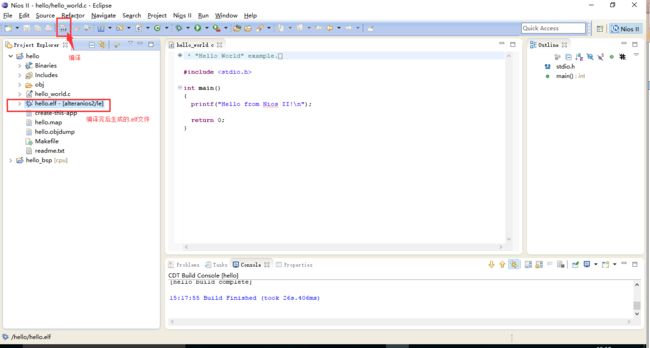
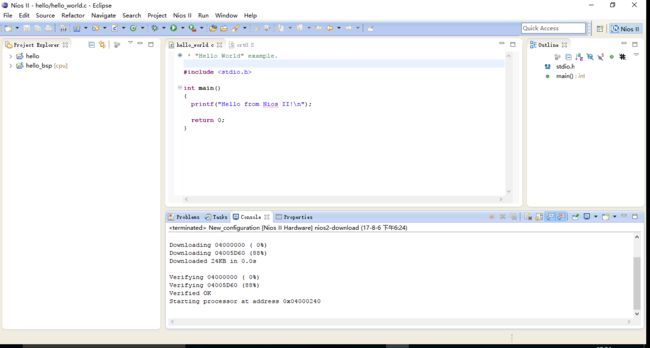
最后对hello_world.c进行如下编程,完成对I/O和基本函数的调用
/* * "Hello World" example. * * This example prints 'Hello from Nios II' to the STDOUT stream. It runs on * the Nios II 'standard', 'full_featured', 'fast', and 'low_cost' example * designs. It runs with or without the MicroC/OS-II RTOS and requires a STDOUT * device in your system's hardware. * The memory footprint of this hosted application is ~69 kbytes by default * using the standard reference design. * * For a reduced footprint version of this template, and an explanation of how * to reduce the memory footprint for a given application, see the * "small_hello_world" template. * */ #include#include //添加包含了系统宏定义的文件 #include //添加包含IO操作函数的.h文件 #include //添加包含usleep的头文件进行精确延时 int main() { printf("Hello from Nios II!\n"); while(1) { IOWR_ALTERA_AVALON_PIO_DATA(PIO_LED_BASE,0);//通过向PIO的基地址写数据,实现对GPIO的控制 //delay(1000000); usleep(1000000);//us级延时 IOWR_ALTERA_AVALON_PIO_DATA(PIO_LED_BASE,0x3ff);//通过向PIO的基地址写数据,实现对GPIO的控制 // delay(1000000); usleep(1000000);//us级延时 } return 0; }
同样的方法再次烧写程序
实验现象:LED以2HZ的频率闪烁