4个提高深度学习模型性能的技巧
点击上方“AI遇见机器学习”,选择“星标”公众号
原创干货,第一时间送达
![]()
深度学习是一个广阔的领域,但我们大多数人在构建模型时都面临一些共同的难题
在这里,我们将讨论提高深度学习模型性能的4个难题和技巧
这是一篇以代码实践为重点的文章,所以请准备好你的Python IDE并改进你的深度学习模型!
介绍
过去两年的大部分时间,我几乎都在深度学习领域工作。这是一个相当好的经历,这中间我参与了图像和视频数据相关的多个项目。
在那之前,我处于边缘地带,我回避了对象检测和人脸识别等深度学习概念。直到2017年底才开始深入研究。在这段时间里,我遇到了各种各样的难题。我想谈谈四个最常见的问题,大多数深度学习实践者和爱好者在他们的旅程中都会遇到。
如果你之前参与过深度学习项目,你就能很快理解这些障碍。好消息是克服它们并不像你想的那么难!
在本文中,我们将采用一种非常实际的方法。首先,我们将建立我上面提到的四个常见难题。然后,我们将直接深入Python代码,学习与这些难题作斗争和克服这些难题的关键技巧和技巧。这里有很多东西需要打开,让我们开始吧!
目录
深度学习模型的共同难题
车辆分类案例研究概述
了解每个难题以及如何克服难题以提高深度学习模型的性能
案例研究:改善我们的车辆分类模型的性能
深度学习模型的共同难题
深度学习模型通常在大多数数据上的表现都非常好。在图像数据方面,深度学习模型,尤其是卷积神经网络(CNN),几乎胜过所有其他模型。
我通常的方法是在遇到图像相关项目(例如图像分类项目)时使用CNN模型。
这种方法效果很好,但是在某些情况下,CNN或其他深度学习模型无法执行。我遇到过几次。我的数据很好,模型的体系结构也正确定义,损失函数和优化器也正确设置,但是我的模型没有达到我的预期。
这是我们大多数人在使用深度学习模型时面临的常见难题。
如上所述,我将解决四个此类难题:
缺乏可用于训练的数据
过拟合
欠拟合
训练时间长
在深入探讨和理解这些难题之前,让我们快速看一下我们将在本文中解决的案例研究。
车辆分类案例研究概述
本文是我一直在写的PyTorch面向初学者系列的一部分。你可以在此处查看前三篇文章(我们将从那里引用一些内容):
PyTorch入门指南
在PyTorch中使用卷积神经网络建立图像分类模型
使用PyTorc进行迁移学习
我们将继续阅读上一篇文章中看到的案例研究。这里的目的是将车辆图像分类为紧急或非紧急。
首先,让我们快速构建一个CNN模型,并将其用作基准。我们还将尝试改善此模型的性能。这些步骤非常简单,在之前的文章中我们已经看过几次。
因此,我不会在这里深入每一步。相反,我们将重点放在代码上,你始终可以在我上面链接的先前文章中更详细地进行检查。
你可以从此处获取数据集:https://drive.google.com/file/d/1EbVifjP0FQkyB1axb7KQ26yPtWmneApJ/view
这是为我们的车辆分类项目构建CNN模型的完整代码。
导入库
# 导入库
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from tqdm import tqdm
# 用于读取和显示图像
from skimage.io import imread
from skimage.transform import resize
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
# 用于创建验证集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 用于评估模型
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# PyTorch库和模块
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
from torch.nn import Linear, ReLU, CrossEntropyLoss, Sequential, Conv2d, MaxPool2d, Module, Softmax, BatchNorm2d, Dropout
from torch.optim import Adam, SGD
# 预训练模型
from torchvision import models
加载数据集
# 加载数据集
train = pd.read_csv( emergency_train.csv )
# 加载训练图片
train_img = []
for img_name in tqdm(train[ image_names ]):
# 定义图像路径
image_path = ../Hack Session/images/ + img_name
# 读取图片
img = imread(image_path)
# 标准化像素值
img = img/255
img = resize(img, output_shape=(224,224,3), mode= constant , anti_aliasing=True)
# 转换为浮点数
img = img.astype( float32 )
# 添加图片到列表
train_img.append(img)
# 转换为numpy数组
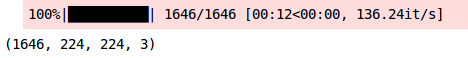
train_x = np.array(train_img)
train_x.shape
创建训练和验证集
# 定义目标
train_y = train[ emergency_or_not ].values
# 创建验证集
train_x, val_x, train_y, val_y = train_test_split(train_x, train_y, test_size = 0.1, random_state = 13, stratify=train_y)
(train_x.shape, train_y.shape), (val_x.shape, val_y.shape)
将图像转换为torch格式
# 转换训练图片到torch格式
train_x = train_x.reshape(1481, 3, 224, 224)
train_x = torch.from_numpy(train_x)
# 转换目标到torch格式
train_y = train_y.astype(int)
train_y = torch.from_numpy(train_y)
# 转换验证图像到torch格式
val_x = val_x.reshape(165, 3, 224, 224)
val_x = torch.from_numpy(val_x)
# 转换目标到torch格式
val_y = val_y.astype(int)
val_y = torch.from_numpy(val_y)
定义模型架构
torch.manual_seed(0)
class Net(Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.cnn_layers = Sequential(
# 定义2D卷积层
Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ReLU(inplace=True),
MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
# 另一个2D卷积层
Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ReLU(inplace=True),
MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
)
self.linear_layers = Sequential(
Linear(32 * 56 * 56, 2)
)
# 前项传播
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cnn_layers(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.linear_layers(x)
return x
定义模型参数
# 定义模型
model = Net()
# 定义优化器
optimizer = Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
# 定义损失函数
criterion = CrossEntropyLoss()
# 检查GPU是否可用
if torch.cuda.is_available():
model = model.cuda()
criterion = criterion.cuda()
print(model)

训练模型
torch.manual_seed(0)
# 模型batch大小
batch_size = 128
# epoch数
n_epochs = 25
for epoch in range(1, n_epochs+1):
# 保持记录训练与验证集损失
train_loss = 0.0
permutation = torch.randperm(train_x.size()[0])
training_loss = []
for i in tqdm(range(0,train_x.size()[0], batch_size)):
indices = permutation[i:i+batch_size]
batch_x, batch_y = train_x[indices], train_y[indices]
if torch.cuda.is_available():
batch_x, batch_y = batch_x.cuda(), batch_y.cuda()
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(batch_x)
loss = criterion(outputs,batch_y)
training_loss.append(loss.item())
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
training_loss = np.average(training_loss)
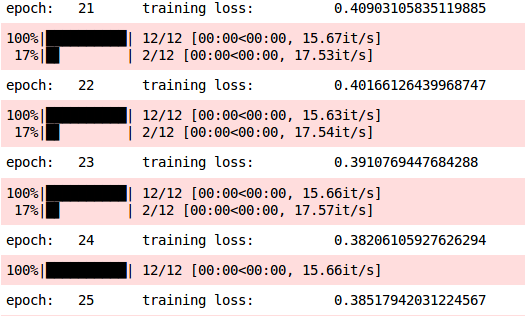
print( epoch: , epoch, training loss: , training_loss)
训练集上预测
# 训练集预测
prediction = []
target = []
permutation = torch.randperm(train_x.size()[0])
for i in tqdm(range(0,train_x.size()[0], batch_size)):
indices = permutation[i:i+batch_size]
batch_x, batch_y = train_x[indices], train_y[indices]
if torch.cuda.is_available():
batch_x, batch_y = batch_x.cuda(), batch_y.cuda()
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(batch_x.cuda())
softmax = torch.exp(output).cpu()
prob = list(softmax.numpy())
predictions = np.argmax(prob, axis=1)
prediction.append(predictions)
target.append(batch_y)
# 训练集精度
accuracy = []
for i in range(len(prediction)):
accuracy.append(accuracy_score(target[i],prediction[i]))
print( training accuracy: , np.average(accuracy))

验证集上预测
# 验证集预测
prediction_val = []
target_val = []
permutation = torch.randperm(val_x.size()[0])
for i in tqdm(range(0,val_x.size()[0], batch_size)):
indices = permutation[i:i+batch_size]
batch_x, batch_y = val_x[indices], val_y[indices]
if torch.cuda.is_available():
batch_x, batch_y = batch_x.cuda(), batch_y.cuda()
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(batch_x.cuda())
softmax = torch.exp(output).cpu()
prob = list(softmax.numpy())
predictions = np.argmax(prob, axis=1)
prediction_val.append(predictions)
target_val.append(batch_y)
# 验证集精度
accuracy_val = []
for i in range(len(prediction_val)):
accuracy_val.append(accuracy_score(target_val[i],prediction_val[i]))
print( validation accuracy: , np.average(accuracy_val))

这是我们的CNN模型。训练精度在88%左右,验证精度接近70%。
我们将努力改进这个模型的性能。但在此之前,让我们先花点时间了解一下难题,这些难题可能是造成这种低性能的原因。
深度学习的难题
深度学习的难题1:缺乏可用的数据来训练我们的模型
深度学习模型通常需要大量的训练数据。一般来说,数据越多,模型的性能就越好。缺乏数据的问题是,我们的深度学习模型可能无法从数据中学习模式或功能,因此它可能无法在未看到的数据上提供良好的性能。
如果你看一下汽车分类的案例研究,我们只有大约1650张图片,因此这个模型在验证集上表现不佳。在使用计算机视觉和深度学习模型时,数据较少的难题是很常见的。
你可以想象,手工收集数据是一项繁琐而耗时的任务。因此,我们可以利用数据增强技术来代替花费数天时间来收集数据。
数据增强是在不实际收集新数据的情况下,生成新数据或增加数据以训练模型的过程。
图像数据有多种数据增强技术,常用的增强技术有旋转、剪切、翻转等。
这是一个非常好的主题,因此我决定写一篇完整的文章。我的计划是在下一篇文章中讨论这些技术及其在PyTorch中的实现。
深度学习难题#2:模型过拟合
我相信你听说过过拟合。这是数据科学家刚接触机器学习时最常见的难题(和错误)之一。但这个问题实际上超越了该领域,它也适用于深度学习。
当一个模型在训练集上执行得非常好,但是在验证集(或不可见的数据)上性能下降时,就会被认为是过拟合。
例如,假设我们有一个训练集和一个验证集。我们使用训练数据来训练模型,并检查它在训练集和验证集上的性能(评估指标是准确性)。训练的准确率是95%而验证集的准确率是62%。听起来熟悉吗?
由于验证精度远低于训练精度,因此可以推断模型存在过拟合问题。下面的例子会让你更好地理解什么是过拟合:
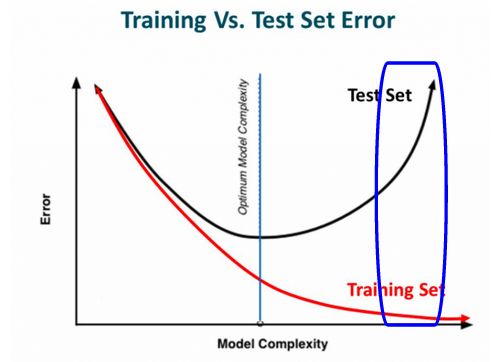
上图中蓝色标记的部分是过拟合模型,因为训练误差非常小并且测试误差非常高。过拟合的原因是该模型甚至从训练数据中学习了不必要的信息,因此它在训练集上的表现非常好。
但是,当引入新数据时,它将无法执行。我们可以向模型的架构中引入Dropout,以解决过拟合的问题。
使用Dropout,我们随机关闭神经网络的某些神经元。假设我们在最初有20个神经元的图层上添加了概率为0.5的Dropout层,因此,这20个神经元中的10个将被抑制,我们最终得到了一个不太复杂的体系结构。
因此,该模型将不会学习过于复杂的模式,可以避免过拟合。现在让我们在架构中添加一个Dropout层,并检查其性能。
模型架构
torch.manual_seed(0)
class Net(Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.cnn_layers = Sequential(
# 定义2D卷积层
Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ReLU(inplace=True),
MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
# Dropout层
Dropout(),
#另一个2D卷积层
Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ReLU(inplace=True),
MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
# Dropout层
Dropout(),
)
self.linear_layers = Sequential(
Linear(32 * 56 * 56, 2)
)
# 前向传播
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cnn_layers(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.linear_layers(x)
return x
在这里,我在每个卷积块中添加了一个Dropout层。默认值为0.5,这意味着一半神经元将被随机关闭。这是一个超参数,你可以选择0到1之间的任何值。
接下来,我们将定义模型的参数,例如损失函数,优化器和学习率。
模型参数
# 定义模型
model = Net()
# 定义优化器
optimizer = Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
# 定义损失函数
criterion = CrossEntropyLoss()
# 检查GPU是否可用
if torch.cuda.is_available():
model = model.cuda()
criterion = criterion.cuda()
print(model)

在这里,你可以看到Dropout中的默认值为0.5。最后,让我们在添加Dropout层之后训练模型:
训练模型
torch.manual_seed(0)
# 模型batch大小
batch_size = 128
# epoch数
n_epochs = 25
for epoch in range(1, n_epochs+1):
# 保持记录训练与验证集损失
train_loss = 0.0
permutation = torch.randperm(train_x.size()[0])
training_loss = []
for i in tqdm(range(0,train_x.size()[0], batch_size)):
indices = permutation[i:i+batch_size]
batch_x, batch_y = train_x[indices], train_y[indices]
if torch.cuda.is_available():
batch_x, batch_y = batch_x.cuda(), batch_y.cuda()
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(batch_x)
loss = criterion(outputs,batch_y)
training_loss.append(loss.item())
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
training_loss = np.average(training_loss)
print( epoch: , epoch, training loss: , training_loss)
现在,让我们使用此训练模型检查训练和验证的准确性。
检查模型性能
#
prediction = []
target = []
permutation = torch.randperm(train_x.size()[0])
for i in tqdm(range(0,train_x.size()[0], batch_size)):
indices = permutation[i:i+batch_size]
batch_x, batch_y = train_x[indices], train_y[indices]
if torch.cuda.is_available():
batch_x, batch_y = batch_x.cuda(), batch_y.cuda()
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(batch_x.cuda())
softmax = torch.exp(output).cpu()
prob = list(softmax.numpy())
predictions = np.argmax(prob, axis=1)
prediction.append(predictions)
target.append(batch_y)
# 训练集精度
accuracy = []
for i in range(len(prediction)):
accuracy.append(accuracy_score(target[i],prediction[i]))
print( training accuracy: , np.average(accuracy))

同样,让我们检查验证集准确性:
# 验证集预测
prediction_val = []
target_val = []
permutation = torch.randperm(val_x.size()[0])
for i in tqdm(range(0,val_x.size()[0], batch_size)):
indices = permutation[i:i+batch_size]
batch_x, batch_y = val_x[indices], val_y[indices]
if torch.cuda.is_available():
batch_x, batch_y = batch_x.cuda(), batch_y.cuda()
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(batch_x.cuda())
softmax = torch.exp(output).cpu()
prob = list(softmax.numpy())
predictions = np.argmax(prob, axis=1)
prediction_val.append(predictions)
target_val.append(batch_y)
# 验证集精度
accuracy_val = []
for i in range(len(prediction_val)):
accuracy_val.append(accuracy_score(target_val[i],prediction_val[i]))
print( validation accuracy: , np.average(accuracy_val))

让我们将其与以前的结果进行比较:
| 训练集准确性 | 验证集准确性 | |
|---|---|---|
| 没有Dropout | 87.80 | 69.72 |
| 有Dropout | 73.56 | 70.29 |
上表表示没有Dropout和有Dropout的准确性。如果你观察没有遗漏的模型的训练和验证准确性,它们是不同步的。训练精度过高,验证精度较低。因此,这可能是一个过拟合的例子。
当我们引入Dropout时,训练和验证集的准确性是同步的。因此,如果你的模型过拟合,你可以尝试添加Dropout层,以减少模型的复杂性。
要添加的Dropout数量是一个超参数,你可以使用该值进行操作。现在让我们看看另一个难题。
深度学习难题3:模型欠拟合
深度学习模型也可能欠拟合,听起来似乎不太可能。
欠拟合是指模型无法从训练数据本身中学习模式,因此训练集上的性能较低。
这可能是由于多种原因造成的,例如没有足够的数据来训练,架构太简单,模型的训练次数较少等。
为了克服欠拟合的问题,你可以尝试以下解决方案:
增加训练数据
制作一个复杂的模型
增加训练的epoch
对于我们的问题,欠拟合不是问题,因此,我们将继续研究提高深度学习模型性能的下一种方法。
深度学习难题4:训练时间过长
有些情况下,你可能会发现你的神经网络需要花很多时间来收敛。这背后的主要原因是输入到神经网络层的分布发生了变化。
在训练过程中,神经网络各层的权值发生变化,激活也随之变化。现在,这些激活是下一层的输入,因此每一次连续的迭代都会改变分布。
由于这种分布的变化,每一层都必须适应不断变化的输入—这就是为什么训练时间增加的原因。
为了克服这一问题,我们可以应用批处理标准化(batch normalization),其中我们正常化的激活隐藏层,并试图作出相同的分布。
现在让我们向架构中添加batchnorm层,并检查它在车辆分类问题上的表现:
torch.manual_seed(0)
class Net(Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.cnn_layers = Sequential(
# 定义2D卷积层
Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ReLU(inplace=True),
# BN层
BatchNorm2d(16),
MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
#另一个2D卷积层
Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ReLU(inplace=True),
# BN层
BatchNorm2d(32),
MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
)
self.linear_layers = Sequential(
Linear(32 * 56 * 56, 2)
)
# 前向传播
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cnn_layers(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.linear_layers(x)
return x
定义模型参数
# 定义模型
model = Net()
# 定义优化器
optimizer = Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.00005)
# 定义损失函数
criterion = CrossEntropyLoss()
# 检查GPU是否可用
if torch.cuda.is_available():
model = model.cuda()
criterion = criterion.cuda()
print(model)

让我们训练模型
torch.manual_seed(0)
# 模型batch大小
batch_size = 128
# epoch数
n_epochs = 5
for epoch in range(1, n_epochs+1):
# 保持记录训练与验证集损失
train_loss = 0.0
permutation = torch.randperm(train_x.size()[0])
training_loss = []
for i in tqdm(range(0,train_x.size()[0], batch_size)):
indices = permutation[i:i+batch_size]
batch_x, batch_y = train_x[indices], train_y[indices]
if torch.cuda.is_available():
batch_x, batch_y = batch_x.cuda(), batch_y.cuda()
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(batch_x)
loss = criterion(outputs,batch_y)
training_loss.append(loss.item())
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
training_loss = np.average(training_loss)
print( epoch: , epoch, training loss: , training_loss)
显然,该模型能够很快学习。在第5个epoch时,我们的训练损失为0.3386,而当我们不使用批量标准化时要25个epoch之后,我们的训练损失才为0.3851。
因此,引入批标准化无疑减少了训练时间。让我们检查训练和验证集的性能:
prediction = []
target = []
permutation = torch.randperm(train_x.size()[0])
for i in tqdm(range(0,train_x.size()[0], batch_size)):
indices = permutation[i:i+batch_size]
batch_x, batch_y = train_x[indices], train_y[indices]
if torch.cuda.is_available():
batch_x, batch_y = batch_x.cuda(), batch_y.cuda()
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(batch_x.cuda())
softmax = torch.exp(output).cpu()
prob = list(softmax.numpy())
predictions = np.argmax(prob, axis=1)
prediction.append(predictions)
target.append(batch_y)
# 训练集精度
accuracy = []
for i in range(len(prediction)):
accuracy.append(accuracy_score(target[i],prediction[i]))
print( training accuracy: , np.average(accuracy))
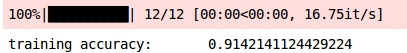
# 验证集预测
prediction_val = []
target_val = []
permutation = torch.randperm(val_x.size()[0])
for i in tqdm(range(0,val_x.size()[0], batch_size)):
indices = permutation[i:i+batch_size]
batch_x, batch_y = val_x[indices], val_y[indices]
if torch.cuda.is_available():
batch_x, batch_y = batch_x.cuda(), batch_y.cuda()
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(batch_x.cuda())
softmax = torch.exp(output).cpu()
prob = list(softmax.numpy())
predictions = np.argmax(prob, axis=1)
prediction_val.append(predictions)
target_val.append(batch_y)
# 验证集精度
accuracy_val = []
for i in range(len(prediction_val)):
accuracy_val.append(accuracy_score(target_val[i],prediction_val[i]))
print( validation accuracy: , np.average(accuracy_val))
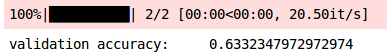
添加批量标准化可以减少训练时间,但是这里存在一个问题。你能弄清楚它是什么吗?该模型现在过拟合,因为我们在训练上的准确性为91%,在验证集上的准确性为63%。记住,我们没有在最新模型中添加Dropout层。
这些是我们可以用来改善深度学习模型性能的一些技巧。现在,让我们结合到目前为止所学的所有技术。
案例研究:提高车辆分类模型的性能
我们已经看到Dropout和批标准化如何帮助减少过拟合并加快训练过程。现在是时候将所有这些技术结合在一起并建立模型了。
torch.manual_seed(0)
class Net(Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.cnn_layers = Sequential(
# 定义2D卷积层
Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ReLU(inplace=True),
# BN层
BatchNorm2d(16),
MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
# 添加dropout
Dropout(),
#另一个2D卷积层
Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ReLU(inplace=True),
# BN层
BatchNorm2d(32),
MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
# 添加dropout
Dropout(),
)
self.linear_layers = Sequential(
Linear(32 * 56 * 56, 2)
)
# 前向传播
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cnn_layers(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.linear_layers(x)
return x
现在,我们将定义模型的参数:
# 定义模型
model = Net()
# 定义优化器
optimizer = Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.00025)
# 定义损失函数
criterion = CrossEntropyLoss()
# 检查GPU是否可用
if torch.cuda.is_available():
model = model.cuda()
criterion = criterion.cuda()
print(model)

最后,让我们训练模型:
torch.manual_seed(0)
# 模型batch大小
batch_size = 128
# epoch数
n_epochs = 10
for epoch in range(1, n_epochs+1):
# 保持记录训练与验证集损失
train_loss = 0.0
permutation = torch.randperm(train_x.size()[0])
training_loss = []
for i in tqdm(range(0,train_x.size()[0], batch_size)):
indices = permutation[i:i+batch_size]
batch_x, batch_y = train_x[indices], train_y[indices]
if torch.cuda.is_available():
batch_x, batch_y = batch_x.cuda(), batch_y.cuda()
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(batch_x)
loss = criterion(outputs,batch_y)
training_loss.append(loss.item())
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
training_loss = np.average(training_loss)
print( epoch: , epoch, training loss: , training_loss)
接下来,让我们检查模型的性能:
prediction = []
target = []
permutation = torch.randperm(train_x.size()[0])
for i in tqdm(range(0,train_x.size()[0], batch_size)):
indices = permutation[i:i+batch_size]
batch_x, batch_y = train_x[indices], train_y[indices]
if torch.cuda.is_available():
batch_x, batch_y = batch_x.cuda(), batch_y.cuda()
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(batch_x.cuda())
softmax = torch.exp(output).cpu()
prob = list(softmax.numpy())
predictions = np.argmax(prob, axis=1)
prediction.append(predictions)
target.append(batch_y)
# 训练集精度
accuracy = []
for i in range(len(prediction)):
accuracy.append(accuracy_score(target[i],prediction[i]))
print( training accuracy: , np.average(accuracy))

# 验证集预测
prediction_val = []
target_val = []
permutation = torch.randperm(val_x.size()[0])
for i in tqdm(range(0,val_x.size()[0], batch_size)):
indices = permutation[i:i+batch_size]
batch_x, batch_y = val_x[indices], val_y[indices]
if torch.cuda.is_available():
batch_x, batch_y = batch_x.cuda(), batch_y.cuda()
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(batch_x.cuda())
softmax = torch.exp(output).cpu()
prob = list(softmax.numpy())
predictions = np.argmax(prob, axis=1)
prediction_val.append(predictions)
target_val.append(batch_y)
# 验证集精度
accuracy_val = []
for i in range(len(prediction_val)):
accuracy_val.append(accuracy_score(target_val[i],prediction_val[i]))
print( validation accuracy: , np.average(accuracy_val))

验证准确性明显提高到73%。太棒了!
结尾
在这篇文章中,我们研究了在使用深度学习模型(如CNNs)时可能面临的不同难题。我们还学习了所有这些难题的解决方案,最后,我们使用这些解决方案建立了一个模型。
在我们将这些技术添加到模型之后,模型在验证集上的准确性得到了提高。总有改进的空间,以下是一些你可以尝试的方法:
调整Dropout率
增加或减少卷积层的数量
增加或减少Dense层的数量
调整隐藏层中的神经元数量,等等。
推荐阅读
干货|学术论文怎么写
资源|NLP书籍及课程推荐(附资料下载)
干货|全面理解N-Gram语言模型
资源|《Machine Learning for OpenCV》书籍推荐
![]()
欢迎关注我们,看通俗干货!
![]()