【数据结构】堆,大根堆,小根堆,优先队列 详解
目录
- 堆
- 1.堆的数组实现
- 2.小根堆
- 3.大根堆
- 4.优先队列
- 例题
- 1.SP348 EXPEDI - Expedition(有趣的贪心思路,优先队列)
- 2.合并果子
堆
要了解堆之前,请先了解树,因为堆是一颗完全二叉树
如果不知道的话请点击下方链接了解
树,二叉树,完全二叉树详解
要注意的是
-
首先堆是一颗完全二叉树
-
其次堆中存储的值是偏序
Min-heap(小根堆): 父节点的值小于或等于子节点的值
Max-heap(大根堆): 父节点的值大于或等于子节点的值

好吧其实就是实现自动排序
O(logn)时间复杂度内实现插入,删除,O(1)查询
1.堆的数组实现
如果用数组来存储,那么儿子的编号便满足如下的性质
-
左儿子的编号是自己的编号的
x2+1 -
右儿子的编号是自己的编号的
x2+2
int heap[N],sz=0;
void push(int x)
{
int i=sz++;
while(i>0)//往上走
{
//父结点的编号
int p=(i-1)/2;
//如果不需要再交换就break;
if(heap[p]<=x)break;
heap[i]=head[p];
i=p;
}
heap[i]=x;
}
//删除最小值:先把最小值丢掉,先把最后一个节点的值放到根节点处,然后排序交换即可
int pop()
{
//最小值
int ret=heap[0];
int x=heap[--sz];
int i=0;
while(i*2+1<sz)//因为堆是完全二叉树偏左嘛
{
//左右儿子
int a=i*2+1,b=i*2+2;
//选出儿子中最小的
if(b<sz&&heap[b]<heap[a])a=b;
//如果不需要交换就break
if(heap[a]>=x)break;
//交换
heap[i]=heap[a];
i=a;
}
heap[i]=x;
return ret;//返回被丢掉的那个最小值
}
2.小根堆
Min-heap(小根堆): 父节点的值小于或等于子节点的值
#include3.大根堆
Max-heap(大根堆): 父节点的值大于或等于子节点的值
#include4.优先队列
在优先队列中,优先级高的元素先出队列。
标准库默认使用元素类型的<操作符来确定它们之间的优先级关系。
优先队列的第一种用法,也是最常用的用法:
priority_queue<int> q;
通过<操作符可知在整数中元素大的优先级高。
故示例1中输出结果为:9 6 5 3 2
第二种方法:
在示例1中,如果我们要把元素从小到大输出怎么办呢?
这时我们可以传入一个比较函数,使用functional.h函数对象作为比较函数。
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>>q;
其中
第二个参数为容器类型。
第三个参数为比较函数。
故示例2中输出结果为:2 3 5 6 9
第三种方法:
自定义优先级。
struct node
{
friend bool operator< (node n1, node n2)
{
return n1.priority< n2.priority;
}
int priority;
int value;
};
在该结构中,value为值,priority为优先级。
通过自定义operator<操作符来比较元素中的优先级。
在示例3中输出结果为:
优先级值
9 5
8 2
6 1
2 3
1 4
但如果结构定义如下:
struct node
{
friend bool operator> (node n1, node n2)
{
return n1.priority> n2.priority;
}
int priority;
int value;
};
则会编译不过(G++编译器)
因为标准库默认使用元素类型的<操作符来确定它们之间的优先级关系。
而且自定义类型的<操作符与>操作符并无直接联系,故会编译不过。
例题
1.SP348 EXPEDI - Expedition(有趣的贪心思路,优先队列)
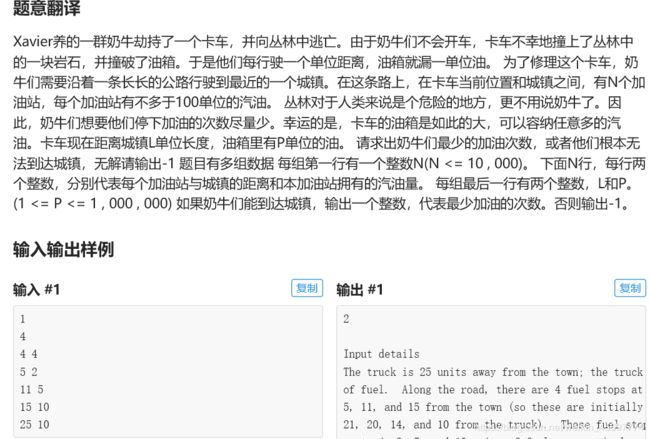
SP348 EXPEDI - Expedition(有趣的贪心,优先队列)
2.合并果子

合并果子
注:如果您通过本文,有(qi)用(guai)的知识增加了,请您点个赞再离开,如果不嫌弃的话,点个关注再走吧,日更博主每天在线答疑 ! 当然,也非常欢迎您能在讨论区指出此文的不足处,作者会及时对文章加以修正 !如果有任何问题,欢迎评论,非常乐意为您解答!( •̀ ω •́ )✧
