python异常定义与原理
异常在程序中的作用
- Error Handling:能够在异常处理语句中捕获并响应错误信息
- Event Notification:即当我们应用程序在传入数据并进行数据处理过程中,针对不合法的事件我们是采取抛出异常而不是返回一个表示不合法的数据结果
- Special-case handling:在异常处理器处理程序个别极端情况,可以通过assert来检查条件是否如我们的预期值一样
- Termination actions:即保证程序中的资源能够在异常发生之后正常关闭
- Unusual control flows:不正常的控制流,使用raise抛出异常信息
异常处理机制
默认异常处理器,即由python自动搜索匹配对应的异常信息
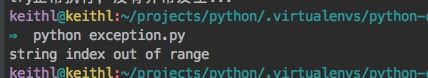
# python命令行,默认是3.6,以下没有特殊说明全部是基于这个版本
>>> str="keithl"
>>> str[10]
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "" , line 1, in <module>
IndexError: string index out of range
捕获异常信息
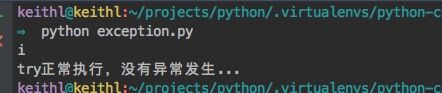
# exception.py
def catch_index():
str="keithl"
try:
print(str[10])
# print(str[2])
except IndexError as e:
print(e)
else:
print("try正常执行,没有异常发生...")
if __name__ == '__main__':
catch_index()
抛出异常,使用raise
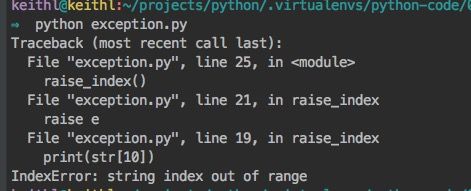
# exception.py
def raise_index():
str = "keithl"
try:
print(str[10])
except IndexError as e:
raise e
if __name__ == '__main__':
raise_index()
自定义异常
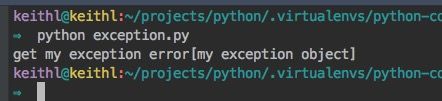
# exception.py
class MyException(Exception):
def __str__(self):
return "my exception object"
def define_exception():
try:
raise MyException
except MyException as e:
print("get my exception error[%s]" % str(e))
if __name__ == '__main__':
define_exception()
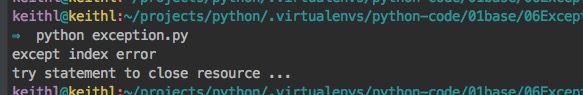
使用finally终止try语句
# exception.py
def raise_index_finally():
str = "keithl"
try:
print(str[10])
except IndexError:
print("except index error")
finally:
print("try statement to close resource ...")
if __name__ == '__main__':
raise_index_finally()
异常语句
try/except/else语句
- 语句块的定义
try:
print("程序业务逻辑.")
except name1:
print("捕获异常name1..")
except (name2, name3):
print("捕获异常name2 或 name3..")
except name4 as var:
print("捕获异常name4,并传递其引用变量到语句块中..")
except: # 5
print("捕获所有异常(上述的name1,name2,name3,name4除外..)")
else:
print("没有异常,try语句正常执行..")
-
try/except/else工作原理
- 当在try语句块中发生异常时,异常类型将会匹配except对应的name,然后根据对应的name分配对应的异常类对象,执行statement中的语句
- 当在try语句块中发生异常但没有在except中匹配到对应的name,python将会查询其他的异常直至进程最高级别的异常并退出程序,打印出默认的异常信息
- 如果try语句正常执行,那么最后也将会执行else语句
-
捕获任意或所有异常
- 使用
except:,即后面没有携带任何异常类,将会捕获先前没有定义的异常类 - 使用
except (e1,e2,..),即只要业务代码中抛出的异常是在定义的一系列异常列表中(e1,e2,…),那么就会在except语句中被捕获处理
- 使用
-
except:与except Exception:except:是捕获所有的异常,但存在不足,一是捕获和业务代码无关的系统错误,二是会拦截其他程序的异常处理except Exception::py3.x建议使用这个Exception类,同时可以避免上述问题,Exception会忽略与系统操作相关的异常,如系统退出py时报出的异常
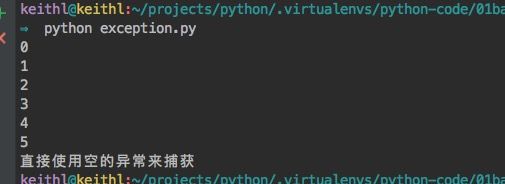
# exception.py
# `except:`执行遇到系统退出的时候会捕获异常
def test_exception():
try:
for i in range(10):
print(i)
if i == 5:
sys.exit(-1)
except:
print("直接使用空的异常来捕获")
if __name__ == '__main__':
test_exception()
>>> python exception.py
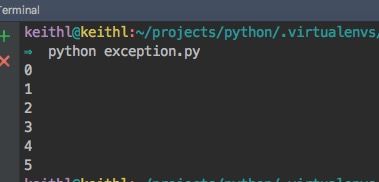
# `except Exception:`在系统退出的时候没有捕获异常
def test_exception():
try:
for i in range(10):
print(i)
if i == 5:
sys.exit(-1)
except Exception:
print("直接使用空的异常来捕获")
if __name__ == '__main__':
test_exception()
>>> python exception.py
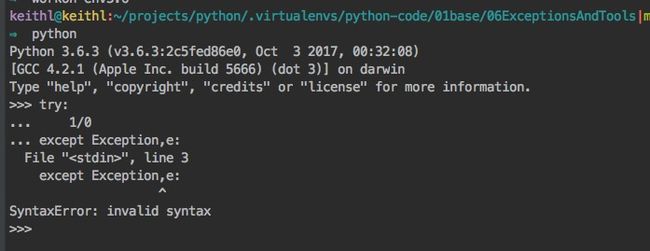
- py2.x与py3.x的异常语句作用域
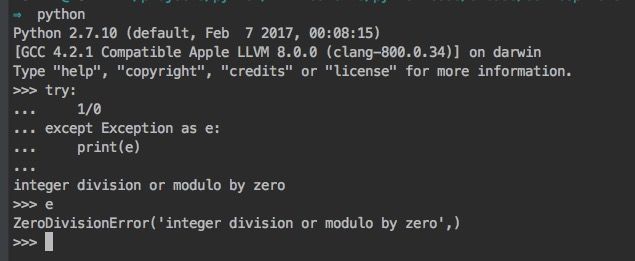
- py2.x可以支持
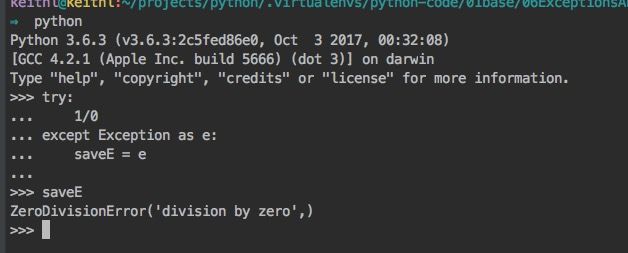
except Exception as e以及except Exception,e,py3.x仅支持except Exception as e - py2.x的异常语句Exception对应的实例变量e是全局变量,在try语句块外还可以直接访问
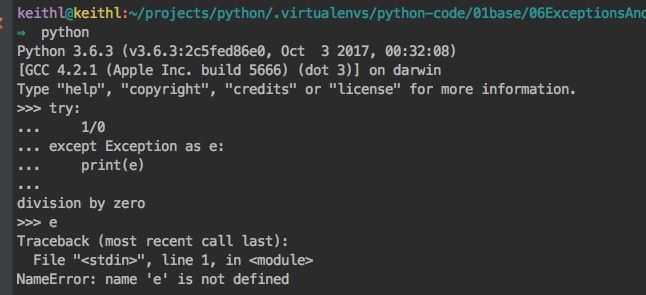
- py3.x的异常语句Exception对应的实例变量e是局部变量,在try语句块外不能访问,但是可以保存在一个全局的变量中
- py2.x可以支持
try/finally语句
- 语句块定义
try:
print("执行业务代码语句块...")
finally:
print("关闭处理业务的资源...")
-
try/finally工作原理
- 当try语句块中的业务逻辑是正常执行的时候,在程序退出返回的时候将会执行finally语句块
- 当try语句块中的业务逻辑出现异常的时候,仍然会执行finally语句块并将异常信息一并向顶层程序抛出
-
示例
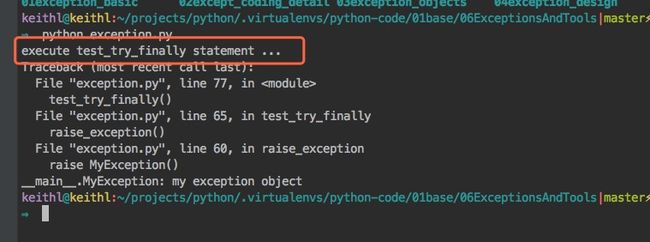
# exception.py
def raise_exception():
raise MyException()
def test_try_finally():
try:
raise_exception()
finally:
print("execute test_try_finally statement ...")
if __name__ == '__main__':
test_try_finally()
>>> python exception.py
try/except/finally语句
- 这个在上面的基础上添加一个异常处理块,其一般模板为
try:
print("处理核心业务逻辑")
except Exception as e1:
print("捕获异常信息e1")
except Exception as e2:
print("捕获异常信息e2")
else:
print("try的业务语句没有异常,正常执行完毕后将执行else语句")
finally:
print("关闭消耗CPU的资源")
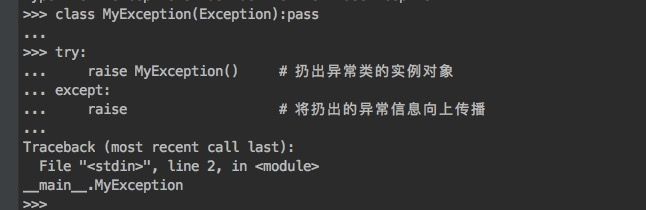
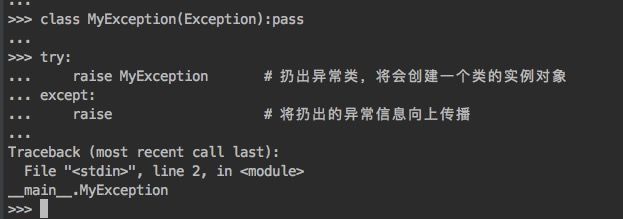
raise语句
-
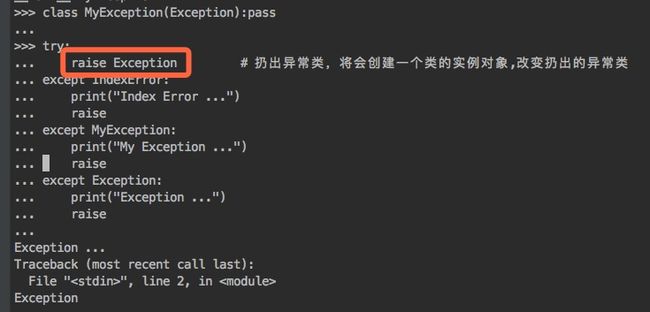
raise:将一个异常类class信息抛出并往顶层程序传播
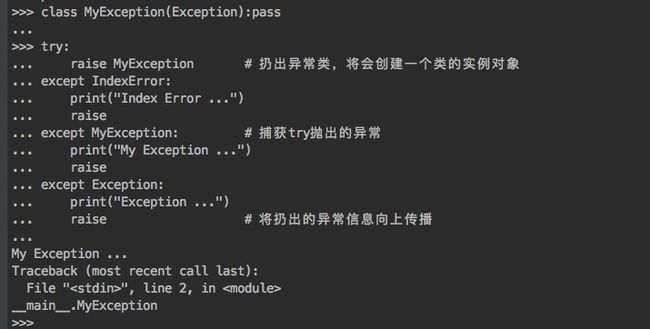
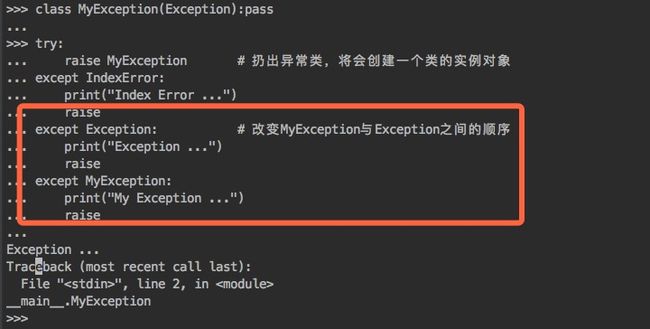
- 在一个try语句中发生的异常信息类会在except语句中按照顺序进行匹配
- 抛出的异常类是except定义的异常类的子类或本类,其他在except定义的异常类将不捕获异常
- 抛出的异常类如果是except定义的异常类的父类,也不会捕获到该父类的异常
- 仅py3.x支持的from语句
raise newException from otherException
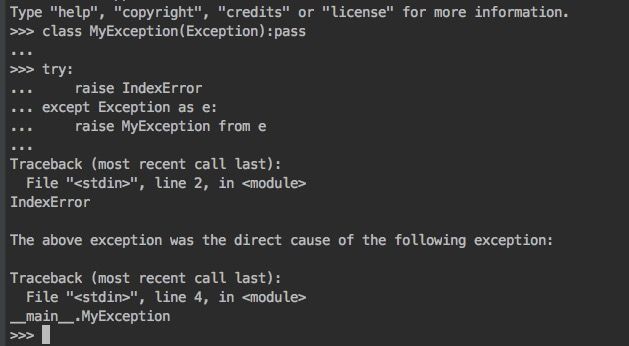
class MyException(Exception):pass
try:
raise IndexError
except Exception as e:
raise MyException from e
assert语句
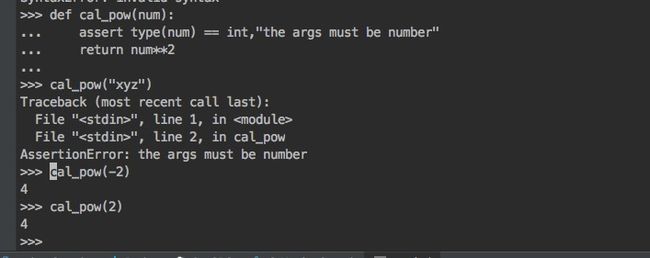
- 语法:
assert test,data # data是可选的 - 工作原理如下:
if __debug__:
if not test:
raise AssertionError(data)
with/as上下文管理器
- 基本语法
with expression [as variable]
with-block
# 表达式expression返回的是一个实现上下文管理器协议的对象
- 场景一:IO操作自动打开和关闭资源
# 打开文件filepath并且自动读取
with open("filepath") as file_object:
for line in file_object:
print(line)
- 场景二:应用在线程锁中,自动获取和释放锁
# 在一个线程中对语句块进行锁操作
lock = threading.Lock() # 导入threading模块
with lock: # 在业务代码执行之前自动获取锁,在执行完成之后自动释放锁,除非有异常抛出
# 执行相关的业务代码
pass
- 场景三:在decimal模块中使用上下文管理来设置decimal操作业务数据的格式,退出后格式自动清除失效
import decimal
with decimal.localcontext() as ctx:
ctx.prec = 2 # 保留小数点后两位
x = decimal.Decimal('5.00') / decimal.Decimal('3.00')
- with表达式语句的工作原理
- 上下文管理器对象必须有实现内置操作符
__enter__和__exit__方法 - 在with语句中返回一个对象管理器并分配一个变量的时候将会回调
__enter__方法 - 执行嵌套的语句块,也就是上面的相关业务代码
- 当有异常信息抛出的时候,就会回调
__exit__的方法,同时携带type,value,traceback三个参数(通过sys.exc_info获取到) - 正常执行完成之后,也会回调
__exit__的方法
- 上下文管理器对象必须有实现内置操作符
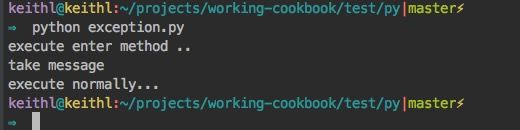
# exception.py
class WithContextObject:
def message(self,args):
print(args)
def __enter__(self):
print("execute enter method ..")
return self
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
if exc_type is None:
print("execute normally...")
else:
print("raise exception ...")
return False
def test_with():
with WithContextObject() as context:
context.message("take message")
if __name__ == '__main__':
test_with()
>>> python exception.py
- 使用多个with上下文管理器
# 基本语法
with open(file_path1) as reader,with open(file_path2) as writer:
for line in reader:
writer.write(line)
# 等价于
with open(file_path1) as reader:
with open(file_path2) as writer:
for line in reader:
writer.write(line)
如有收获,欢迎关注个人公众号: