C++11 foreach与std::begin、std::end
C++11 foreach与std::begin、std::end
for遍历元素
C++11增加了一个行特性foreach(Range-based for loops ,基于范围的for循环)。可以对集合、数组、初始化列逐个访问。
for ( range_declaration : range_expression)
loop_statement
//编译时会转换为以下代码
auto && __range = range_expression;
for (auto __begin = std::begin(range),__end = std::end(range);__begin != __end; ++__begin) {
range_declaration = *__begin;
loop_statement
}例子:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
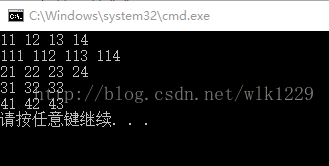
vector a = { 11, 12, 13, 14 };
for (int v: a)//以值的方式访问
{
cout << v << " ";
v = 5;//a中存储的数据不会改变
}
cout << endl;
for (int &v : a)//通过引用的方式访问a,可以改变a中的值
v += 100;
for (int v : a)
{
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
int b[] = { 21, 22, 23, 24 };
for (int v : b)//遍历数组,以值的方式访问
{
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
unordered_map map = {{1,3},{2,3},{3,3}};
for (auto v :map)//遍历Map,以值的方式访问
{
cout << v.second << v.first << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (int v : {41, 42,43})//遍历初始化列表,以值的方式访问
{
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
} 输出结果
std::begin、std::end
为了统一代码并让数组支持迭代器,C++11提供了两个新模版函数std::begin、std::end,这两个模版函数可以作用于容器和数组。
例如:
vector a = { 11, 12, 13, 14 };
for_each(std::begin(a), std::end(a), [](int p) {cout << p << " "; });//使用std::begin、std::end
cout << endl;
int b[] = { 21, 22, 23, 24 };
for_each(std::begin(b), std::end(b), [](int p) {cout << p << " "; });//使用std::begin、std::end
cout << endl; SLT中的定义
//容器时使用
template
auto begin (Container& cont) -> decltype (cont.begin());
template
auto begin (const Container& cont) -> decltype (cont.begin());
//数组时使用
template T* begin (T(&arr)[N]); 自定义支持foreach访问的集合类
为了支持foreach遍历,类内部只需要实现begin和end成员函数,适配以下两个模版
template
auto begin (Container& cont) -> decltype (cont.begin());
template
auto begin (const Container& cont) -> decltype (cont.begin());
实例:
#include
using namespace std;
class MyContainer
{
public:
MyContainer():a{ 1,2,3,4,5 }
{
}
int* begin()//stl::begin模版调用
{
return a;
}
int* end() //stl::end模版可以调用
{
return a + sizeof(a)/sizeof(int);
}
private:
int a[5];
};
int main()
{
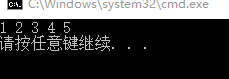
MyContainer a;
for each (int& var in a)
{
cout << var << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
} 输出结果:
扩展:一维数组类型
template
例如:int (&a)[10]
这个语句是定义了一个引用,该引用指向一个长度为10的int类型数组
普通指针无法确定所指向数组的长度,这种类型可以通过sizeof来确定数组的长度。
实例:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
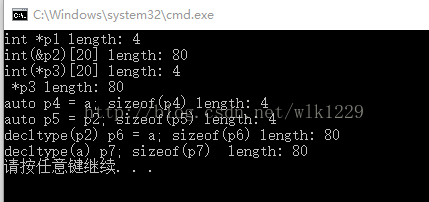
int a[20];
int *p1 = a;
cout << "int *p1 length: " << sizeof(p1) << endl;
int(&p2)[20] = a;
cout<<"int(&p2)[20] length: " << sizeof(p2) << endl;
int(*p3)[20] = &a;
cout << "int(*p3)[20] length: " << sizeof(p3) << endl;
cout << " *p3 length: " << sizeof(*p3) << endl;
int b[3][20];
p3 = b;//szieof(p3) = 4
auto p4 = a; //相当于int *p4;
cout << "auto p4 = a; sizeof(p4) length: " << sizeof(p4) << endl;
auto p5 = p2;//相当于int *p5
cout << "auto p5 = p2; sizeof(p5) length: " << sizeof(p5) << endl;
decltype(p2) p6 = a; // int(&)[20]
cout << "decltype(p2) p6 = a; sizeof(p6) length: " << sizeof(p6) << endl;
decltype(a) p7; //int p7[20]
cout << "decltype(a) p7; sizeof(p7) length: " << sizeof(p7) << endl;
return 0;
}
结果: