linux基础操作3-串口收发
导:学习过单片机的用户,对串口不会太陌生,在单片机串口编程中,需要用户直接对寄存器以及中断进行控制。
而在 linux 串口编程中,无论是从 linux 官方直接下载的原生态内核,还是任何厂家提供的linux 内核,都会将串口驱动写好,所以对于所有的驱动工程师来说,是完全不需要自己动手写串口驱动的。
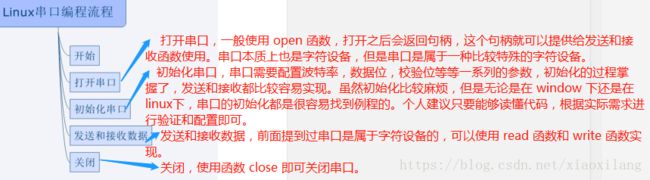
串口的编程:
1.初始化:配置波特率,数据位,校验位
首先定义一个初始化函数
int set_opt(int fd,int nSpeed, int nBits, char nEvent, int nStop)。
int set_opt(int fd,int nSpeed, int nBits, char nEvent, int nStop)
{
struct termios newtio,oldtio;
if ( tcgetattr( fd,&oldtio) != 0) {
perror("SetupSerial 1");
return -1;
}
bzero( &newtio, sizeof( newtio ) );
newtio.c_cflag |= CLOCAL | CREAD;
newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
switch( nBits )
{
case 7:
newtio.c_cflag |= CS7;
break;
case 8:
newtio.c_cflag |= CS8;
break;
}
switch( nEvent )
{
case 'O':
newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB;
newtio.c_cflag |= PARODD;
newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP);
break;
case 'E':
newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP);
newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB;
newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARODD;
break;
case 'N':
newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
break;
}
switch( nSpeed )
{
case 2400:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B2400);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B2400);
break;
case 4800:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B4800);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B4800);
break;
case 9600:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B9600);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B9600);
break;
case 115200:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B115200);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B115200);
break;
case 460800:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B460800);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B460800);
break;
default:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B9600);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B9600);
break;
}
if( nStop == 1 )
newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
else if ( nStop == 2 )
newtio.c_cflag |= CSTOPB;
newtio.c_cc[VTIME] = 0;
newtio.c_cc[VMIN] = 0;
tcflush(fd,TCIFLUSH);
if((tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&newtio))!=0)
{
perror("com set error");
return -1;
}
printf("串口设置完成!\n\r");
return 0;
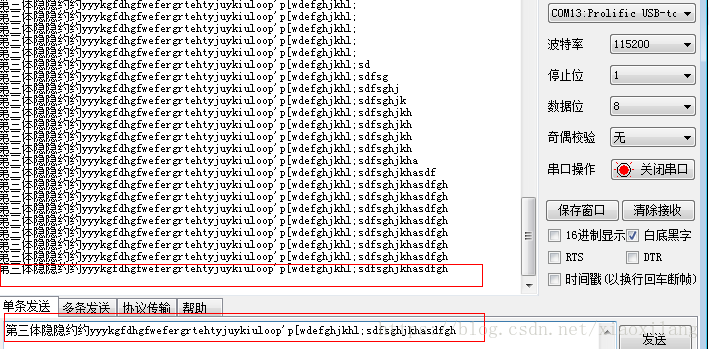
}2.串口收发测试
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int set_opt(int ,int , int , char , int );
void main()
{
int fd,nByte;
char *uart3 = "/dev/ttySAC3";
char *uart_out="请输入:\n";
char buff[512];
memset(buff,0,sizeof(buff));
if((fd=open(uart3,O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY))<0)
{
printf("打开失败\n");
}else
{
set_opt(fd,115200,8,'N',1);
write(fd,uart_out,strlen(uart_out));
while(1)
{
while((nByte=read(fd,buff,512))>0)
{
buff[nByte+1]='\0';
write(fd,buff,strlen(buff));
memset(buff,0,strlen(buff));
nByte=0;
}
}
}
}