Java单元测试常用工具类小结
单元测试
单元测试是系统中非常基础的功能,以功能的最小粒度进行功能测试,保证系统功能的正确行。
Assert
所属类库: JUnit library
类名: Assert
功能描述: 用以判断结果是否符合预期
常用方法:
- assertTrue(String message, boolean condition)
- assertThat(String reason, T actual, Matcher matcher)
- assertEquals(String message, Object expected, Object acutal)
由于Assert其中提供了大量的判断方法,这里就不再一一赘述,在需要之时进行查阅即可。
这里以assertThat为例做一个简要的分析:
其源代码定义如下:
public static void assertThat(T actual, Matcher matcher) {
assertThat("", actual, matcher);
}
其中参数如下:
- T: 只是判断的数据类型, 与第三个参数matcher中的T类型相同
- Matcher: 是hamcrest类库中的Matcher接口,用来实现基本的判断比较,稍后将针对Matcher进行简要的介绍分析
- reason。自定义的描述下信息,在判断为失败的情况下展示。
使用示例如下:
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import static org.hamcrest.number.OrderingComparison.greaterThan;
public class AssertDemo {
/**
* 检查数字值需要大于10
*/
@Test
public void testAssert() {
Long count = 12l;
Assert.assertThat("Count is lower than 10", count, greaterThan(10l));
}
}
这里的单元测试简单用于测试count的值是否大于10,类型为Long。
Hamcrest介绍
官方站点: http://hamcrest.org/JavaHamcrest/distributables
在Spring Boot中的单元测试中,其依赖关系如下:
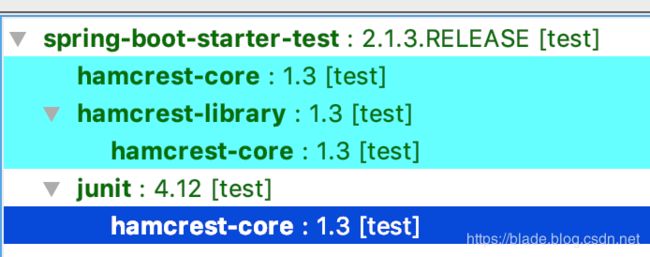
从其中可以看出,hamcrest存在两个类库,其中junit依赖的是hamcrest-core,包括在实际的单元测试中,同样会碰到在类库类库中出现相同的方法。两者的区别是什么呢?
Hamcrest类库进行了拆分,hamcrest-core包括最基本的matchers和抽象类以及创建这些matcher的工厂方法;主要用于构建其它的Matchers。类库路径: org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers。
hamcrest-library: 主要按照功能进行分组的Matcher,他们是可选的,扩展的Mather功能。
org.hamcrest.Matchers包含了core和library中两者的功能。
如何来使用呢?
简单起见,就直接将它们引入进来即可:
import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.*;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.*;
所有的这些Matcher是可以彼此嵌套使用的。
Hamcrest用法
定义实体类:
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
static class Apple {
private Long id;
private String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return id + "-" + name;
}
}
Core
- anything - always matches, true
- describedAs 定制失败描述信息的装饰器
- is 等同于equalTo()
测试代码:
@Test
public void testCore() {
List strs = Lists.newArrayList();
strs.add("abef");
strs.add("what it is");
//无论如何都是成功的
Assert.assertThat(strs, Matchers.anything());
List tstrs = Lists.newArrayList();
tstrs.add("abef");
// 装饰模式,定制化错误提示信息
Assert.assertThat(strs, Matchers.describedAs("Custom Failure Information:%0", Matchers.hasItem("1abef"), "Array Item"));
}
注意这里的decorateAs方法,其中使用的%0的位置占位符。
Logical
- allOf - matches if all matchers match, short circuits (like Java &&)
- anyOf - matches if any matchers match, short circuits (like Java ||)
- not - matches if the wrapped matcher doesn’t match and vice versa
- either(Matcher).or(Matcher)
- both(Matcher).and(Matcher)
使用代码示例:
@Test
public void testLogic() {
Apple apl = new Apple();
Apple apl2 = apl;
// allOf:如果所有匹配器都匹配才匹配
Assert.assertThat("What it is?", Matchers.allOf(Matchers.endsWith("?"), Matchers.startsWith("What")));
// anyOf:如果任何匹配器匹配就匹配
Assert.assertThat("What it is?", Matchers.anyOf(Matchers.endsWith("?"), Matchers.notNullValue()));
// not:如果包装的匹配器不匹配器时匹配,反之亦然
Assert.assertThat("What it is?", Matchers.not(Matchers.endsWith("is")));
// is:如果包装的匹配器匹配器时匹配,反之亦然
Assert.assertThat(apl, Matchers.is(apl2));
Assert.assertThat("What it is?", Matchers.is(Matchers.endsWith("is?")));
}
Object
- equalTo 测试 object 是否相等的,底层使用Object.equals
- hasToString 测试Object.toString
- instanceOf, isCompatibleType 判断类型
- notNullValue, nullValue 判断对象null
- sameInstance 判断是否为同一个对象
使用示例:
@Test
public void testObject() {
Apple apl = new Apple(12l, "name1");
Apple apl2 = apl;
//判断对象是否相等
Assert.assertThat(apl, Matchers.equalTo(apl2));
// has ToString
//测试toString()
Assert.assertThat(apl, Matchers.hasToString("12-name1"));
//InstanceOf
Assert.assertThat(apl, Matchers.instanceOf(Apple.class));
//NotnullValue
Assert.assertThat(apl, Matchers.notNullValue());
//NullValue
Assert.assertThat(null, Matchers.nullValue());
//same instance
Assert.assertThat(apl, Matchers.sameInstance(apl2));
}
Beans
- hasProperty 判断Bean是否特定属性
代码使用示例:
@Test
public void testBean() {
Apple apl = new Apple();
//check 其是否有属性name
Assert.assertThat(apl, Matchers.hasProperty("name"));
}
Collections
这里的集合是指Matcher集合,不是指数据。
- array Matcher数据匹配
- hasEntry, hasKey, hasValue, 检查Map中是否含有an entry, key or value
- hasItem, hasItems,测试一个Collections是否含有元素
- hasItemInArray 检查数组中是否包含一个元素
- isIn(T t): 检查是否在某个Colleciton之内
- arrayContainingInAnyOrder
- arrayContaining()
- arrayWithSize(int/Matcher): 数组大小
- hasSize(int/Mathcer): Collection大小
使用示例:
@Test
public void testCollection() {
List apples = Lists.newArrayList();
apples.add(new Apple(1l, "zhangsan"));
apples.add(new Apple(2l, "lisi"));
Apple[] aplArray = new Apple[]{new Apple(3l, "zhangsan"), new Apple(4l, "wangwu")};
Apple apl = new Apple(1l, "zhagnsan");
Apple testApl = apples.get(0);
String[] strArray = {"12", "34"};
//注意这里只能是Object Array
Assert.assertThat(apples.toArray(aplArray), Matchers.array(Matchers.notNullValue(), Matchers.hasProperty( "name")));
Assert.assertThat(strArray, Matchers.array(Matchers.equalTo("12"), Matchers.equalTo("34")));
Map dataMap = new HashMap();
dataMap.put("key1", "val1");
dataMap.put("key2", "val2");
Assert.assertThat(dataMap, Matchers.hasEntry("key1", "val1"));
Assert.assertThat(dataMap, Matchers.hasValue("val1"));
Assert.assertThat(dataMap, Matchers.hasKey("key1"));
}
@Test
public void testIterable() {
List apples = Lists.newArrayList();
apples.add(new Apple(1l, "zhangsan"));
apples.add(new Apple(2l, "lisi"));
Apple apl = new Apple(1l, "zhangsan");
Apple apl1 = new Apple(2l, "lisi");
//检查单个元素
Assert.assertThat(apples, Matchers.hasItem(apl));
//检查多个元素
Assert.assertThat(apples, Matchers.hasItems(apl1,apl));
Apple[] aplArray = new Apple[2];
//数组元素
Assert.assertThat(apples.toArray(aplArray), Matchers.hasItemInArray(apl));
//在Colleciton中
Assert.assertThat(apl, Matchers.isIn(apples));
}
Number
- closeTo 测试浮点数是否接近一个数字值
- greaterThan, greaterThanOrEqualTo, lessThan, lessThanOrEqualTo 检查数字的大小
使用示例代码:
@Test
public void testNumber() {
// closeTo:测试浮点值接近给定的值
Assert.assertThat(1.5, Matchers.closeTo(1.0, 0.6));
// greaterThan, greaterThanOrEqualTo, lessThan, lessThanOrEqualTo:测试大于,小于
Assert.assertThat(1.0, Matchers.greaterThan(0.5));
Assert.assertThat(1.5, Matchers.lessThanOrEqualTo(1.5));
}
Text
- equalToIgnoringCase 检查字符串相等,忽略大小写
- equalToIgnoringWhiteSpace 检查字符串相等,忽略空白字符
- containsString, endsWith, startsWith 检查字符串匹配
使用示例:
@Test
public void testText() {
// equalToIgnoringCase:测试字符串相等忽略大小写
Assert.assertThat("Hello world", Matchers.equalToIgnoringCase("hello world"));
// equalToIgnoringWhiteSpace:测试字符串忽略空白
Assert.assertThat(" Hello world", Matchers.equalToIgnoringWhiteSpace("Helloworld"));
// containsString, endsWith, startsWith:测试字符串匹配
Assert.assertThat("Hello world", Matchers.containsString("Hello"));
Assert.assertThat("Hello world", Matchers.startsWith("Hello"));
Assert.assertThat("Hello world", Matchers.endsWith("world"));
}
总结
这里所有的这些方法在语言中都是有其他替代选择,他们只是让你阅读起来更容易而已,更符合人的阅读和理解习惯。