超级详细的css的position属性
超级详细的css的position属性
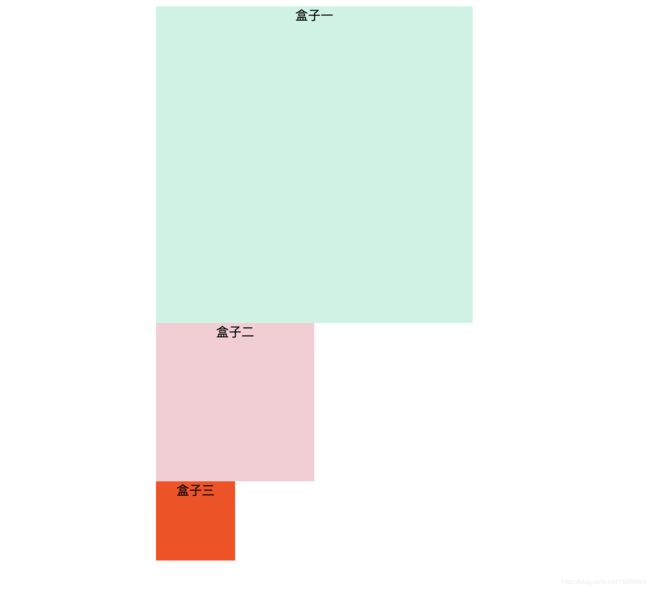
position: static
CSS定位中的默认值。当元素不设定任何position属性时,默认用static,表示没有定位,元素出现在正常的流中
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>position:static</title>
</head>
<style>
body{
margin-left: 200px;
text-align: center;
}
.first {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: #c6f3e4;
}
.second{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #f7ccd3;
position: static;
left: 50px;
top: 100px;
}
.third{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orangered;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="first">盒子一</div>
<div class="second">盒子二</div>
<div class="third">盒子三</div>
</body>
</html>
position:relative
相对定位 相对于正常流中的本身正常位置来进行定位,属于标准流
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>position:relative</title>
</head>
<style>
body{
margin-left: 200px;
text-align: center;
}
.first {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: #c6f3e4;
}
.second{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #f7ccd3;
position: relative;
left: 50px;
top: 100px;
opacity: 0.2;
}
.third{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orangered;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="first">盒子一</div>
<div class="second">盒子二</div>
<div class="third">盒子三</div>
</body>
</html>
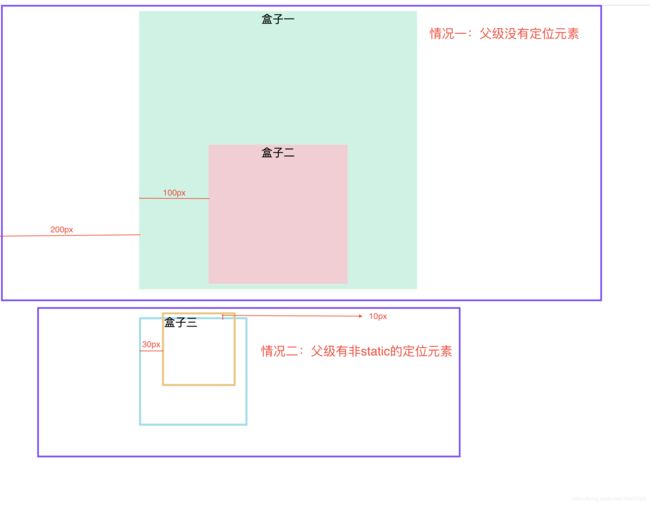
position:absolute
生成绝对定位的元素,其相对于 static 定位以外的第一个父元素进行定位,会脱离正常流,如果元素的父级没有设置定位属性,则依据 body 元素左上角作为参考进行定位
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>position:absolute</title>
</head>
<style>
body{
margin-left: 200px;
}
.first {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: #c6f3e4;
text-align: center;
}
.second{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #f7ccd3;
text-align: center;
position: absolute;
left: 300px;
top: 200px;
}
.third-father{
margin-top: 40px;
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
border: 3px solid #95dfec;
position: relative;
}
.third{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 3px solid #f0c87d;
position: absolute;
left: 30px;
top: -10px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="first">盒子一</div>
<div class="second">盒子二</div>
<div class="third-father">
<div class="third">盒子三</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
position:fixed
fixed相对于浏览器窗口定位,滚动浏览器窗口并不会使其移动,会脱离正常流
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>position:fixed</title>
</head>
<style>
body{
margin-left: 200px;
text-align: center;
}
.second{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #f7ccd3;
}
.third{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orangered;
border-radius: 50%;
position: fixed;
bottom: 50px;
left: 50px;
}
.test-fixed {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: plum;
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="second"></div>
<div class="third"></div>
<div class="test-fixed"></div>
<div class="test-fixed"></div>
<div class="test-fixed"></div>
<div class="test-fixed"></div>
<div class="test-fixed"></div>
<div class="test-fixed"></div>
<div class="test-fixed"></div>
<div class="test-fixed"></div>
</body>
</html>
只是设置了定位:
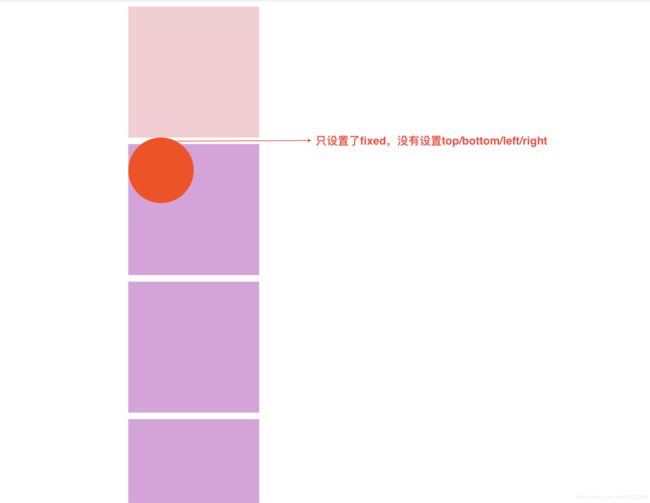
设置了定位和left/bottom:
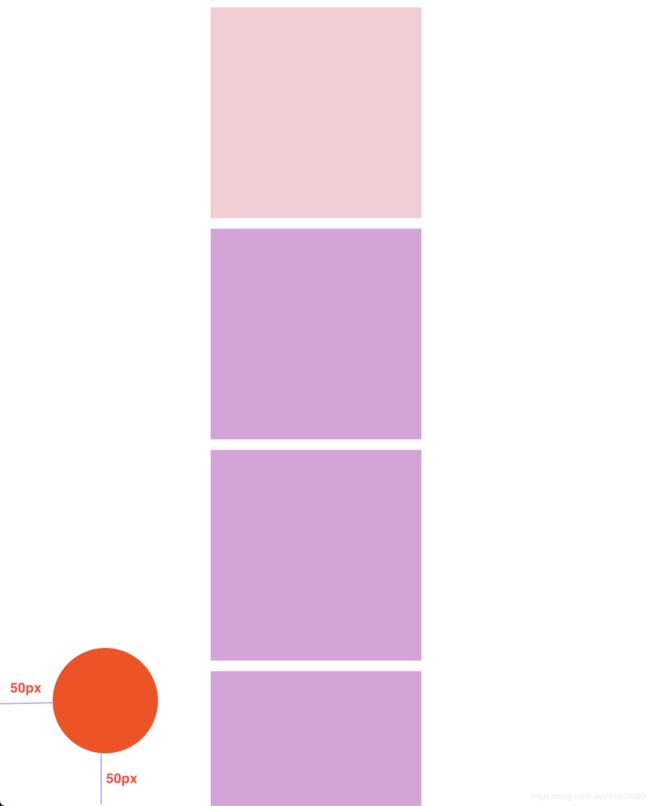
设置好后滚动页面:

position:sticky
可以实现吸顶效果
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>position:sticky</title>
</head>
<style>
body{
margin: 0px 0px 0px 200px;
text-align: center;
}
.second{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #f7ccd3;
}
.third{
width: 200px;
height: 50px;
background-color: orangered;
position: sticky;
top: 50px;
}
.test-fixed {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: plum;
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
<body>
<!-- <div class="first">盒子一</div> -->
<div class="second"></div>
<div class="third"></div>
<div class="test-fixed"></div>
<div class="test-fixed"></div>
<div class="test-fixed"></div>
<div class="test-fixed"></div>
<div class="test-fixed"></div>
<div class="test-fixed"></div>
<div class="test-fixed"></div>
<div class="test-fixed"></div>
</body>
</html>
刚刚设置好定位:
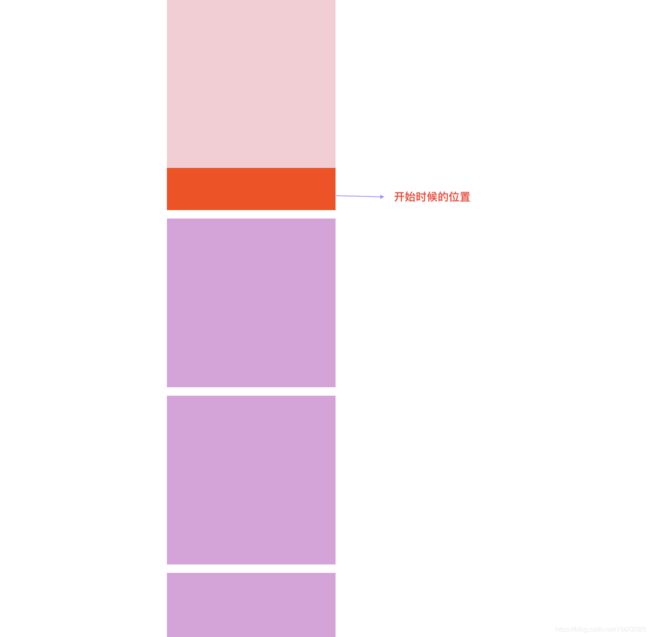
滚动页面,当定位的元素离顶部为50px时候,位置固定,变成于fixed定位相同的效果:
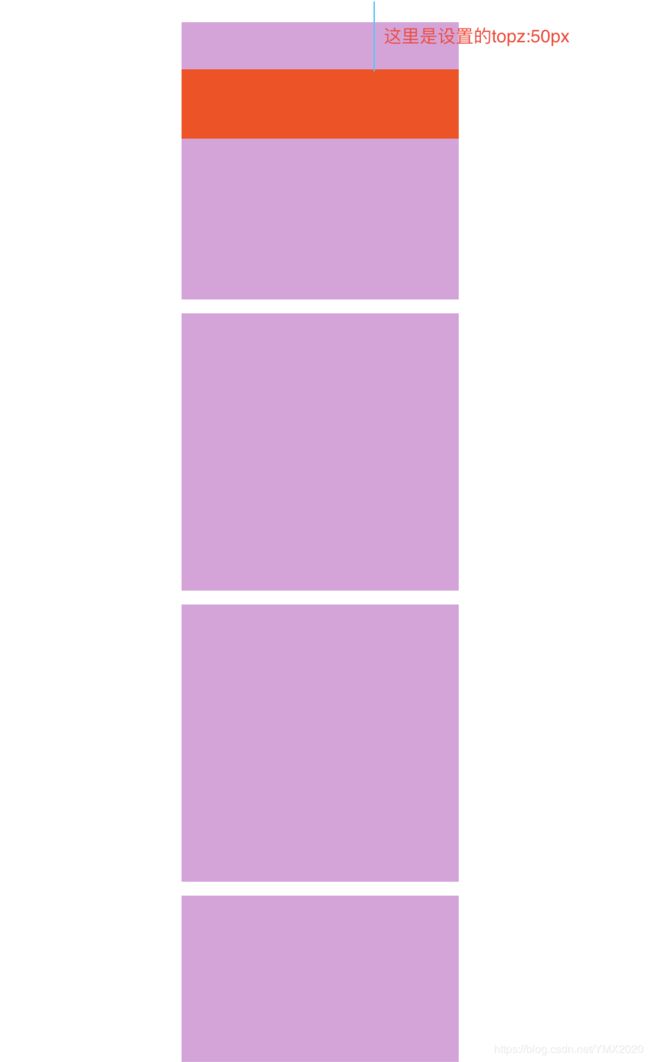
position:sticky各个浏览器支持情况不同,常用的浏览器大致如下:

最后敲黑板划重点来啦:
| 是否标准流 | 相对谁定位 | |
|---|---|---|
| position:static | 是 | 默认值,没有定位 |
| position:relative | 是 | 相对于正常流中的自身正常位置 |
| position:absolute | 否 | 非static 定位以外的第一个父元素进行定位,没有父级定位元素就相对body定位 |
| position:fixed | 否 | 相对浏览器定位 |
| position:sticky | 忽略 | 相对浏览器定位 |