自定义RecyclerView.ItemDecoration,实现Item的等间距分割以及分割线效果
转自 https://www.jianshu.com/p/3b860938e503
1.背景
RecyclerView 是谷歌 V7 包下新增的控件,用来替代 ListView 和 GridView 使用的一个控件。在使用的过程中,往往需要使用到 divider 的效果 ( item 之间的分割线 )。而 RecyclerView 并不像 ListView 一样自带有 divider 的属性。而是需要用到 RecyclerView.ItemDecoration 这样一个类,但是 ItemDecoration 是一个抽象类,而且 android 内部并没有给它做一些效果的实现。那么就需要我们自己去继承并实现其中的方法,本文讲述的就是在 GridLayoutManager 和 LinearLayoutManager 下如何去实现 ItemDecoration。至于 RecyclerView.ItemDecoration 的具体分析,大家可以去看看这篇文章 深入理解 RecyclerView 系列之一:ItemDecoration 这里不作过多的阐述。
2.实现基本的 Item 的 divider
2.1 创建 SpacesItemDecoration
创建一个类 SpacesItemDecoration 继承于 RecyclerView.ItemDecoration ,实现其中的 onDraw 和 getItemOffsets 方法,在这里我们的设计是左右距离相等,上下距离相等。
public class SpacesItemDecoration extends RecyclerView.ItemDecoration {
private int leftRight;
private int topBottom;
public SpacesItemDecoration(int leftRight, int topBottom) {
this.leftRight = leftRight;
this.topBottom = topBottom;
}
@Override
public void onDraw(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
super.onDraw(c, parent, state);
}
@Override
public void getItemOffsets(Rect outRect, View view, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
}
}
在这里我们主要实现的方法是 onDraw 和 getItemOffsets, getItemOffsets 主要是确定 divider 的范围,而 onDraw 是对 divider 的具体实现。
2.2 LinearLayoutManager 下 divider 的实现
首先在 getItemOffsets 方法中需要判断当前的 RecyclerView 所采用的哪种 LayoutManager。这里要注意的是 GridLayoutManager 是继承 LinearLayoutManager 的,所以需要先判断是否为 GridLayoutManager。
private SpacesItemDecorationEntrust getEntrust(RecyclerView.LayoutManager manager) {
SpacesItemDecorationEntrust entrust = null;
//要注意这边的GridLayoutManager是继承LinearLayoutManager,所以要先判断GridLayoutManager
if (manager instanceof GridLayoutManager) {
entrust = new GridEntrust(leftRight, topBottom, mColor);
} else {//其他的都当做Linear来进行计算
entrust = new LinearEntrust(leftRight, topBottom, mColor);
}
return entrust;
}
然后我们来看具体的实现,首先判断是 VERTICAL 还是 HORIZONTAL 。对于 VERTICAL,每一个 item 必需的是 top,left 和 right,但是最后一个 item 还需要 bottom。而对于 HORIZONTAL ,每一个 item 必需的是 top,left 和 bottom,但是最后一个 item 还需要 right。
@Override
public void getItemOffsets(Rect outRect, View view, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
LinearLayoutManager layoutManager = (LinearLayoutManager) parent.getLayoutManager();
//竖直方向的
if (layoutManager.getOrientation() == LinearLayoutManager.VERTICAL) {
//最后一项需要 bottom
if (parent.getChildAdapterPosition(view) == layoutManager.getItemCount() - 1) {
outRect.bottom = topBottom;
}
outRect.top = topBottom;
outRect.left = leftRight;
outRect.right = leftRight;
} else {
//最后一项需要right
if (parent.getChildAdapterPosition(view) == layoutManager.getItemCount() - 1) {
outRect.right = leftRight;
}
outRect.top = topBottom;
outRect.left = leftRight;
outRect.bottom = topBottom;
}
}
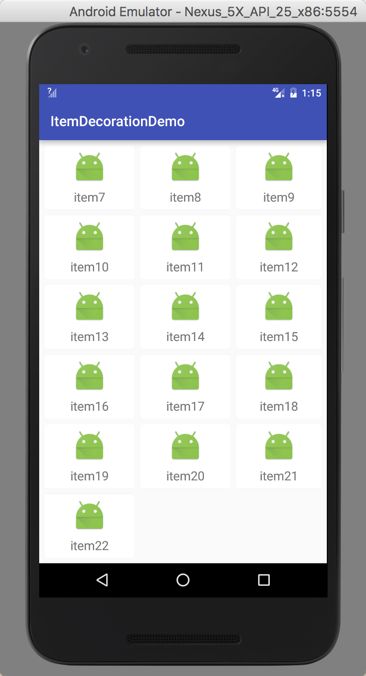
就这样,divider 效果就实现了(当然是没有任何的颜色的)。调用方式只需要。
int leftRight = dip2px(7);
int topBottom = dip2px(7);
rv_content.addItemDecoration(new SpacesItemDecoration(leftRight, topBottom));
VERTICAL
HORIZONTAL.png
2.3 GridLayoutManager 下 divider 的实现
对于 GridLayoutManager 下的实现,相比 LinearLayoutManager 要复杂一些。首先当然是判断 VERTICAL 还是 HORIZONTAL。一般来说有三种情况的,如图所示:
样式.png
由于第二种布局样式考虑的情况比较多,目前没有找到比较好的方法去进行判断,所以在这里只对另外两种布局样式进行考虑
@Override
public void getItemOffsets(Rect outRect, View view, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
GridLayoutManager layoutManager = (GridLayoutManager) parent.getLayoutManager();
final GridLayoutManager.LayoutParams lp = (GridLayoutManager.LayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams();
final int childPosition = parent.getChildAdapterPosition(view);
final int spanCount = layoutManager.getSpanCount();
if (layoutManager.getOrientation() == GridLayoutManager.VERTICAL) {
//判断是否在第一排
if (layoutManager.getSpanSizeLookup().getSpanGroupIndex(childPosition, spanCount) == 0) {//第一排的需要上面
outRect.top = topBottom;
}
outRect.bottom = topBottom;
//这里忽略和合并项的问题,只考虑占满和单一的问题
if (lp.getSpanSize() == spanCount) {//占满
outRect.left = leftRight;
outRect.right = leftRight;
} else {
outRect.left = (int) (((float) (spanCount - lp.getSpanIndex())) / spanCount * leftRight);
outRect.right = (int) (((float) leftRight * (spanCount + 1) / spanCount) - outRect.left);
}
} else {
if (layoutManager.getSpanSizeLookup().getSpanGroupIndex(childPosition, spanCount) == 0) {//第一排的需要left
outRect.left = leftRight;
}
outRect.right = leftRight;
//这里忽略和合并项的问题,只考虑占满和单一的问题
if (lp.getSpanSize() == spanCount) {//占满
outRect.top = topBottom;
outRect.bottom = topBottom;
} else {
outRect.top = (int) (((float) (spanCount - lp.getSpanIndex())) / spanCount * topBottom);
outRect.bottom = (int) (((float) topBottom * (spanCount + 1) / spanCount) - outRect.top);
}
}
}
在这里,对于 VERTICAL 下,每个 item 需要的是 bottom,然后第一排需要 top,同时在这里使用了 GridLayoutManager 的一个方法 layoutManager.getSpanSizeLookup().getSpanGroupIndex(childPosition, spanCount) 该方法可以用于判断 item 在布局中所处于的行数。因为这里的 outRect 的值会一起统计到每个 item 的宽高之中。为了保证每个 item 的大小一致,所以这里的每个 item 的 left 和 right 的和必须保持一致,具体的计算方法如下:
计算方式.png
这样,GridLayoutManager 的效果就实现了,调用方法跟LinearLayoutManager 下是一样的。效果如下
VERTICAL
HORIZONTAL
3.实现 Item 的带颜色分割线的效果
3.1 LinearManager 下的实现
上述基本实现了 item 分割的效果,但是它没有办法设置颜色。要实现颜色,首先我们得传入一个颜色色值。
//color的传入方式是resouce.getcolor
protected Drawable mDivider;
public SpacesItemDecorationEntrust(int leftRight, int topBottom, int mColor) {
this.leftRight = leftRight;
this.topBottom = topBottom;
if (mColor != 0) {
mDivider = new ColorDrawable(mColor);
}
}
有了颜色,那么我们就需要去重写 onDraw 方法了,我们需要去确定绘制的区域。先贴上代码
@Override
public void onDraw(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
LinearLayoutManager layoutManager = (LinearLayoutManager) parent.getLayoutManager();
//没有子view或者没有没有颜色直接return
if (mDivider == null || layoutManager.getChildCount() == 0) {
return;
}
int left;
int right;
int top;
int bottom;
final int childCount = parent.getChildCount();
if (layoutManager.getOrientation() == GridLayoutManager.VERTICAL) {
for (int i = 0; i < childCount - 1; i++) {
final View child = parent.getChildAt(i);
final RecyclerView.LayoutParams params = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//将有颜色的分割线处于中间位置
float center = (layoutManager.getTopDecorationHeight(child) - topBottom) / 2;
//计算下边的
left = layoutManager.getLeftDecorationWidth(child);
right = parent.getWidth() - layoutManager.getLeftDecorationWidth(child);
top = (int) (child.getBottom() + params.bottomMargin + center);
bottom = top + topBottom;
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);
mDivider.draw(c);
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < childCount - 1; i++) {
final View child = parent.getChildAt(i);
final RecyclerView.LayoutParams params = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//将有颜色的分割线处于中间位置
float center = (layoutManager.getLeftDecorationWidth(child) - leftRight) / 2;
//计算右边的
left = (int) (child.getRight() + params.rightMargin + center);
right = left + leftRight;
top = layoutManager.getTopDecorationHeight(child);
bottom = parent.getHeight() - layoutManager.getTopDecorationHeight(child);
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);
mDivider.draw(c);
}
}
}
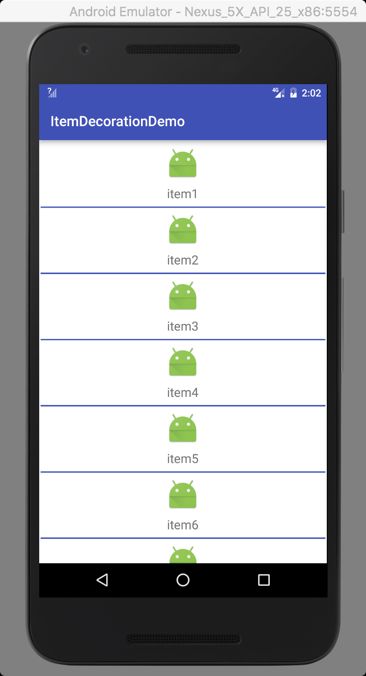
RecyclerView 的机制是去绘制要显示在屏幕中的 View,而没有显示出来的是不会去绘制。所以这边需要使用的是 layoutManager.getChildCount() 而不是 layoutManager.getItemCount()。对于 LinearManager 下来说,需要绘制分割线的区域是两个 item 之间,这里分为 VERTICAL 和 HORIZONTAL。我们拿 VERTICAL 来进行分析,首先获取 item 以及它的 LayoutParams,在这里计算 float center = (layoutManager.getTopDecorationHeight(child) - topBottom) / 2; 因为一个 RecyclerView 可以添加多个 ItemDecoration,而且方法的调用顺序是先实现所有 ItemDecoration 的 getItemOffsets 方法,然后再去实现 onDraw 方法。目前没有找到办法去解决每个 ItemDecoration 的具体区域。所以退而求其次的将分割线绘制在所有 ItemDecoration 的中间区域(基本能满足一般的需求,当然可以自己修改位置满足自己的需求)。然后我们要去确定绘制的区域,left 就是所有 ItemDecoration 的宽度,right 就是 parent 的宽度减去所有 ItemDecoration 的宽度。top 是 child 的底部位置然后还要加上center(center的目的是绘制在中间区域),bottom 就是 top 加上需要绘制的高度。同理在 HORIZONTAL 模式下可以类似的实现。使用一个 ItemDecoration 的效果
int leftRight = dip2px(2);
int topBottom = dip2px(2);
rv_content.addItemDecoration(new SpacesItemDecoration(leftRight, topBottom,getResources().getColor(R.color.colorPrimary)));
VERTICAL
HORIZONTAL
当然你也可以使用多个 ItemDecoration
int leftRight = dip2px(10);
int topBottom = dip2px(10);
rv_content.addItemDecoration(new SpacesItemDecoration(leftRight, topBottom));
rv_content.addItemDecoration(new SpacesItemDecoration(dip2px(2), dip2px(2), getResources().getColor(R.color.colorPrimary)));
VERTICAL
HORIZONTAL
3.2 GridManager 下的实现
GridManager 下的实现的步骤类似与 LinearManager,不同的是确定绘制分割线的区域。它的分割线的区域是相邻的 item 之间都需要有分割线。废话不多说,先上代码。
@Override
public void onDraw(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
final GridLayoutManager layoutManager = (GridLayoutManager) parent.getLayoutManager();
final GridLayoutManager.SpanSizeLookup lookup = layoutManager.getSpanSizeLookup();
if (mDivider == null || layoutManager.getChildCount() == 0) {
return;
}
//判断总的数量是否可以整除
int spanCount = layoutManager.getSpanCount();
int left, right, top, bottom;
final int childCount = parent.getChildCount();
if (layoutManager.getOrientation() == GridLayoutManager.VERTICAL) {
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
final View child = parent.getChildAt(i);
//将带有颜色的分割线处于中间位置
final float centerLeft = ((float) (layoutManager.getLeftDecorationWidth(child) + layoutManager.getRightDecorationWidth(child))
* spanCount / (spanCount + 1) + 1 - leftRight) / 2;
final float centerTop = (layoutManager.getBottomDecorationHeight(child) + 1 - topBottom) / 2;
//得到它在总数里面的位置
final int position = parent.getChildAdapterPosition(child);
//获取它所占有的比重
final int spanSize = lookup.getSpanSize(position);
//获取每排的位置
final int spanIndex = lookup.getSpanIndex(position, layoutManager.getSpanCount());
//判断是否为第一排
boolean isFirst = layoutManager.getSpanSizeLookup().getSpanGroupIndex(position, spanCount) == 0;
//画上边的,第一排不需要上边的,只需要在最左边的那项的时候画一次就好
if (!isFirst && spanIndex == 0) {
left = layoutManager.getLeftDecorationWidth(child);
right = parent.getWidth() - layoutManager.getLeftDecorationWidth(child);
top = (int) (child.getTop() - centerTop) - topBottom;
bottom = top + topBottom;
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);
mDivider.draw(c);
}
//最右边的一排不需要右边的
boolean isRight = spanIndex + spanSize == spanCount;
if (!isRight) {
//计算右边的
left = (int) (child.getRight() + centerLeft);
right = left + leftRight;
top = child.getTop();
if (!isFirst) {
top -= centerTop;
}
bottom = (int) (child.getBottom() + centerTop);
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);
mDivider.draw(c);
}
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
final View child = parent.getChildAt(i);
//将带有颜色的分割线处于中间位置
final float centerLeft = (layoutManager.getRightDecorationWidth(child) + 1 - leftRight) / 2;
final float centerTop = ((float) (layoutManager.getTopDecorationHeight(child) + layoutManager.getBottomDecorationHeight(child))
* spanCount / (spanCount + 1) - topBottom) / 2;
//得到它在总数里面的位置
final int position = parent.getChildAdapterPosition(child);
//获取它所占有的比重
final int spanSize = lookup.getSpanSize(position);
//获取每排的位置
final int spanIndex = lookup.getSpanIndex(position, layoutManager.getSpanCount());
//判断是否为第一列
boolean isFirst = layoutManager.getSpanSizeLookup().getSpanGroupIndex(position, spanCount) == 0;
//画左边的,第一排不需要左边的,只需要在最上边的那项的时候画一次就好
if (!isFirst && spanIndex == 0) {
left = (int) (child.getLeft() - centerLeft) - leftRight;
right = left + leftRight;
top = layoutManager.getRightDecorationWidth(child);
bottom = parent.getHeight() - layoutManager.getTopDecorationHeight(child);
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);
mDivider.draw(c);
}
//最下的一排不需要下边的
boolean isRight = spanIndex + spanSize == spanCount;
if (!isRight) {
//计算右边的
left = child.getLeft();
if (!isFirst) {
left -= centerLeft;
}
right = (int) (child.getRight() + centerTop);
top = (int) (child.getBottom() + centerLeft);
bottom = top + leftRight;
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);
mDivider.draw(c);
}
}
}
}
我们就 VERTICAL 的情况下来进行分析,首先横向的分割线,只需要在最左侧的 item 绘制出来的时候进行分割线的绘制就行了。当然最后一排是不需要的。
if (!isFirst && spanIndex == 0) {
left = layoutManager.getLeftDecorationWidth(child);
right = parent.getWidth() - layoutManager.getLeftDecorationWidth(child);
top = (int) (child.getTop() - centerTop) - topBottom;
bottom = top + topBottom;
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);
mDivider.draw(c);
}
水平的分割线的计算方式类似与 LinearLayoutManager 下的计算方式。这里不过多阐述。而竖直方向的会有一些区别。由于 GridLayoutManager 下,item 的数量不一定能够刚好整除每排的数量。所以这边的绘制区域是根据每个 item 来进行确定的。能被整除的或者当数量不足的时候最后一项不需要竖直的分割线。同时要注意补齐 centerTop(分割线绘制在中间区域的位置)。
//最右边的一排不需要右边的
boolean isRight = spanIndex + spanSize == spanCount;
if (!isRight) {
//计算右边的
left = (int) (child.getRight() + centerLeft);
right = left + leftRight;
top = child.getTop();
if (!isFirst) {
top -= centerTop;
}
bottom = (int) (child.getBottom() + centerTop);
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);
mDivider.draw(c);
}
HORIZONTAL 下的情况可以进行类似的分析,代码的调用方式跟LinearLayoutManager 下是一样的。
VERTICAL
HORIZONTAL
4 最后
至此,RecyclerView 的 divide r效果已经基本实现了。当然,你可以在这基础上进行修改,尤其是 GridLayoutManager 情况下比较复杂,可以根据实际的布局进行对应的修改,满足自己的一些需求。欢迎大家一起相互交流。代码已经上传 https://github.com/hzl123456/SpacesItemDecoration
(ps:在实际的使用过程中,当对 RecyclerView 的 item 进行增加和删除的操作是,会使 ItemDecoration 的分割区域计算错误。原因是在添加和删除操作的时候,只会计算更新的部分区域的 OutRect,导致出现问题,这个时候我们只需要在添加和删除操作之后调用 RecyclerView 的 invalidateItemDecorations() 方法就可以解决问题了)