Service的bindService和unbindService的处理流程(分析源码)
AMS处理bindService请求:
ActiveServices#bindServiceLocked
bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, final IServiceConnection connection, int flags,
String callingPackage, final int userId){
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType, callingPackage, Binder.getCallingPid(),
Binder.getCallingUid(), userId, true, callerFg, isBindExternal);//创建一个ServiceRecord
ServiceRecord s = res.record;
AppBindRecord b = s.retrieveAppBindingLocked(service, callerApp);//如果没有则创建一个。从IntentBindRecord到AppBindRecord,类似建文件夹的mkdir -r 命令,如果不存在,就按路径递归创建
ConnectionRecord c = new ConnectionRecord(b, activity,
connection, flags, clientLabel, clientIntent); //创建ConnectionRecord
b.connections.add(c); //将ConnectionRecord加入AppBindRecord
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
if (bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false,
permissionsReviewRequired) != null) {//如果r.app != null && r.app.thread != null成立,则bringUpServiceLocked会返回null,最后就不会触发return 0,代码继续往下走
return 0;
}
}
if (s.app != null && b.intent.received) {
if (s.app != null && b.intent.received) {
// Service is already running, so we can immediately
// publish the connection.
//这种情况publishServiceLocked中不会去调用IServiceConnection#connected,所以要在这里调用
c.conn.connected(s.name, b.intent.binder);
if (b.intent.apps.size() == 1 && b.intent.doRebind) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, true);//如果r.bindings不为null,则会触发scheduleBindService
}
}
else if (!b.intent.requested) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, false);
}
}ActiveServices#retrieveServiceLocked()
retrieveServiceLocked(){
ResolveInfo rInfo = AppGlobals.getPackageManager().resolveService(service,
resolvedType, ActivityManagerService.STOCK_PM_FLAGS
| PackageManager.MATCH_DEBUG_TRIAGED_MISSING,
userId);
ComponentName name = new ComponentName(
sInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, sInfo.name);
r = new ServiceRecord(mAm, ss, name, filter, sInfo, callingFromFg, res);
return new ServiceLookupResult(r, null);
}
ActiveServices#bringUpServiceLocked
ActiveServices#bringUpServiceLocked{
//如果r.app不为null说明调用过了realStartServiceLocked,如果r.app.thread != null,则目标进程已经起来了
if (r.app != null && r.app.thread != null) {
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, false);
return null;
}
final String procName = r.processName;
ProcessRecord app;
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
}
ActiveServices#realStartServiceLocked
realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg){
//调用scheduleCreateService()的地方在ActiveServices#realStartServiceLocked.
app.thread.scheduleCreateService()
r.app = app;//为ServiceRecord设置ProcessRecord,所以如果r.app不为null,则证明来过这个方法,即已经调用了scheduleCreateService。
requestServiceBindingsLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean execInFg);//该方法会看有没有调用bindService,如果有,就调用scheduleBindService
sendServiceArgsLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean execInFg, //该方法会去看有没有调用过startService,如果有,就调用scheduleServiceArgs
boolean oomAdjusted);
}
目标进程接收到绑定请求:
handleBindService(BindServiceData data)
handleBindService(BindServiceData data){
if (!data.rebind) {
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
}
ActiveServices#publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service)
publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "PUBLISHING " + r
+ " " + intent + ": " + service);
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter
= new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {//如果之前这个intent对应的IntentBindRecord曾经对binder赋值了,那么就不会继续下去。
b.binder = service;//对binder赋值
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;//设置received赋值为true
for (int conni=r.connections.size()-1; conni>=0; conni--) {
ArrayList clist = r.connections.valueAt(conni);
for (int i=0; i
AMS接收到unbindService请求:
unbindService的流程
ContextImpl#unbindService->AMS#unbindService->ActiveServices#unbindServiceLocked->removeConnection->bringDownServiceLocked->ATP#scheduleStopService->handleStopService->onUnbind()
->ATP#scheduleUnbindService-handleUnbindService
ActiveServices#unbindServiceLocked(IServiceConnection connection)
unbindServiceLocked(IServiceConnection connection){
//为什么一个IServiceConnection会对应多个ConnectionRecord呢?因为在service所在进程,可以使用ServiceConnection多次绑定
rrayList clist = mServiceConnections.get(binder);
while (clist.size() > 0) {
ConnectionRecord r = clist.get(0);
removeConnectionLocked(r, null, null);
if (clist.size() > 0 && clist.get(0) == r) {
// In case it didn't get removed above, do it now.
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Connection " + r + " not removed for binder " + binder);
clist.remove(0);
}
if (r.binding.service.app != null) {
if (r.binding.service.app.whitelistManager) {
updateWhitelistManagerLocked(r.binding.service.app);
}
// This could have made the service less important.
if ((r.flags&Context.BIND_TREAT_LIKE_ACTIVITY) != 0) {
r.binding.service.app.treatLikeActivity = true;
mAm.updateLruProcessLocked(r.binding.service.app,
r.binding.service.app.hasClientActivities
|| r.binding.service.app.treatLikeActivity, null);
}
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked(r.binding.service.app);
}
}
}
ActiveServices#removeConnectionLocked
void removeConnectionLocked(
ConnectionRecord c, ProcessRecord skipApp, ActivityRecord skipAct) {
if (clist != null) {
clist.remove(c);
if (clist.size() == 0) {
s.connections.remove(binder);
}
}
b.connections.remove(c);
if ((c.flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {//这个IServiceConnection 通过bindService的时候,传的flag必须包含BIND_AUTO_CREATE才会执行这里
boolean hasAutoCreate = s.hasAutoCreateConnections();//ServiceRecord中是否有其他IServiceConnection通过bindService时的flag包含
boolean hasAutoCreate = s.hasAutoCreateConnections();//ServiceRecord中是否有其他IServiceConnection通过bindService时的flag包含的
if (!hasAutoCreate) {
if (s.tracker != null) {
s.tracker.setBound(false, mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked(),
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
}
}
bringDownServiceIfNeededLocked(s, true, hasAutoCreate);//里面会检查是否真的要stopService。
}
}
bringDownServiceIfNeededLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean knowConn,
boolean hasConn)
bringDownServiceIfNeededLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean knowConn,
boolean hasConn) {
//这里会检查startQequested,如果调用了startService,这个会是true,相反调用了stopService,这个会被置为false,和是否有其他ConnectionRecord的flag包含BIND_AUTO_CREATE。
if (isServiceNeeded(r, knowConn, hasConn)) {
return;
}
// Are we in the process of launching?
if (mPendingServices.contains(r)) {
return;
}
bringDownServiceLocked(r);//这里会去stopService
}
isServiceNeeded(ServiceRecord r, boolean knowConn, boolean hasConn)
private final boolean isServiceNeeded(ServiceRecord r, boolean knowConn, boolean hasConn) {
// Are we still explicitly being asked to run?
if (r.startRequested) {//检查是否有调用startService
return true;
}
// Is someone still bound to us keepign us running?
if (!knowConn) {
hasConn = r.hasAutoCreateConnections();//如果该其他Connection的flag包含了BIND_AUTO_CREATE,返回true
}
if (hasConn) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
在Service进程中的数据结构:
在handleCreateService中,会有如下操作:
//创建Service对象
Service service = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
//创Context和初始化Service
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);//这个token是ServiceRecord的Bp端。ServiceRecord和ActivityRecord的区别之一就是ServiceRecord实现了Binder,而ActivityRecord没有。}
caller进程的ServiceConnection没有实现binder,而sd的类型是LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd,包含了一个成员实现了IServiceConnection.Stub的。最终sd的成员传到AMS中,在Service所在进程publicService后,
就会调用conn.connected,如果之前已经调用过publicService了,那么conn.connect将在ActiveServices#bindServiceLocked中调用。
Context#bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags, Handler
handler, UserHandle user)
bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags, Handler
handler, UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(), handler, flags);
int res = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
}ServiceConnection存在于LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher中,即mServices中。以Context为key,ArrayMap
private final ArrayMap> mServices
= new ArrayMap>();
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);ServiceDisptcher的构造方法:
ServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection conn,
Context context, Handler activityThread, int flags) {
mIServiceConnection = new InnerConnection(this);//这个就是实现了IServiceConnection.Stub的那个类。是LoadedApk的内部类
mConnection = conn;
mContext = context;
mActivityThread = activityThread;
mLocation = new ServiceConnectionLeaked(null);
mLocation.fillInStackTrace();
mFlags = flags;
} 调用ActiveServices调用InnerConnection的connect方法时,通过binder会调用到ServiceDispatcher#mConnection:ServiceConnection;
InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub
这是LoadedApk的一个内部类,而AMS中的IServiceConnection的Bn服务端就是这个类型。
在AMS端调用Bp端的connect方法,最终调用Bn端的ServiceConnection#onServiceConnected
ActiveServices#mServiceMap:SparseArray
ServiceMap中有如下成员:
final int mUserId;
final ArrayMap mServicesByName = new ArrayMap<>();
final ArrayMap mServicesByIntent = new ArrayMap<>();
而ActiveService存放跟Connection相关的结构如下,使用IServiceConnection为key。
/**
* All currently bound service connections. Keys are the IBinder of
* the client's IServiceConnection.
*/
final ArrayMap> mServiceConnections = new ArrayMap<>(); 其实在ServiceRecord中已经存储了ConnectionRecord,就是bindings:ArrayMap
ServiceRecord#connections:ArrayMap
这个IBinder是IServiceConnection。所以其实所有ConectionRecord都能通过ServiceRecord直接获取,而不一定要沿着
ServiceRecord -> ServiceRecord#bindings:ArrayMap
-> AppBindRecord#connections:ArraySet
其他的一些要注意的问题:
如果Service被bind时,onBind返回null,则ServiceConnection#onServiceConnected不会被调用。因为在Caller进程的LoadedApk#doConnect中有如下逻辑:
doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {//这个service就是onBind返回的那个
// If there is a new service, it is now connected.
if (service != null) {
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
}
}Service A去bind另一个Service B,然后Service A onDestroy 后,Service B也会感受到,如果没有其他绑定,则Service B会onUnbind和onDestroy
如果bindService时没有加上Service.BIND_CREATE_AUTO,那么如果该Service本来还没启动,则此次bindService不会成功。
Service在destroy后,如果在调用onDestroy中及在之前没有unbindService,那么在onDestroy后,会在caller进程中处理这些泄露的注册信息,同时清理BroadcastReceiver在本地的代表。即在调用Activity或者Service的onDestroy后都会去到这个方法,LoadedApk#removeContextRegistrations():
public void removeContextRegistrations(Context context,
String who, String what) {
final boolean reportRegistrationLeaks = StrictMode.vmRegistrationLeaksEnabled();
synchronized (mReceivers) {
ArrayMap rmap =
mReceivers.remove(context);
if (rmap != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < rmap.size(); i++) {
LoadedApk.ReceiverDispatcher rd = rmap.valueAt(i);
IntentReceiverLeaked leak = new IntentReceiverLeaked(
what + " " + who + " has leaked IntentReceiver "
+ rd.getIntentReceiver() + " that was " +
"originally registered here. Are you missing a " +
"call to unregisterReceiver()?");
leak.setStackTrace(rd.getLocation().getStackTrace());
Slog.e(ActivityThread.TAG, leak.getMessage(), leak);
if (reportRegistrationLeaks) {
StrictMode.onIntentReceiverLeaked(leak);
}
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().unregisterReceiver(
rd.getIIntentReceiver());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
}
mUnregisteredReceivers.remove(context);
}
synchronized (mServices) {
//Slog.i(TAG, "Receiver registrations: " + mReceivers);
ArrayMap smap =
mServices.remove(context);
if (smap != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < smap.size(); i++) {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = smap.valueAt(i);
ServiceConnectionLeaked leak = new ServiceConnectionLeaked(
what + " " + who + " has leaked ServiceConnection "
+ sd.getServiceConnection() + " that was originally bound here");
leak.setStackTrace(sd.getLocation().getStackTrace());
Slog.e(ActivityThread.TAG, leak.getMessage(), leak);
if (reportRegistrationLeaks) {
StrictMode.onServiceConnectionLeaked(leak);
}
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().unbindService(
sd.getIServiceConnection());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
sd.doForget();
}
}
mUnboundServices.remove(context);
//Slog.i(TAG, "Service registrations: " + mServices);
}
}
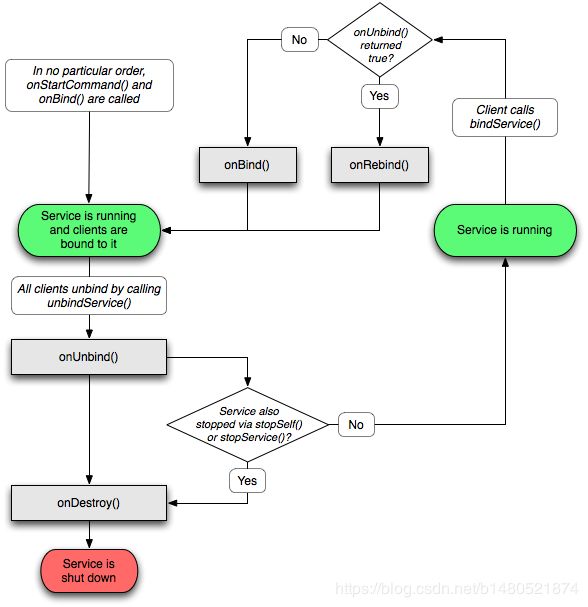
onRebind的回调场景:
client指的不是应用中的哪个组件,而是指整个应用进程,如果一个Service实例因一个进程unbindService而调用了onUnbind,且onUnbind返回true(默认onUnbind返回false),则下一次该进程对该Service实例调用unbindService时,就不调用onbind,而是调用onRebind。注意如果Service实例destroy后,要重新计算了。onRebind没有返回值,所以Service实例创建后第一次被绑定必须调用onBind,这样才能返回IBinder用于发布到AMS中。
Activity A->startService(),bindService,unbindService; 按照这样的步骤ActivityB->bindService就会调用Service#onRebind。其中ActivityA和ActivityB必须为同一应用进程,即同一个Client。
如果Activity A->bindService,unbindService; 按照这样的步骤ActivityB->bindService不会调用Service#onRebind。因为在Activity调用unbindService后,该Service将被destroy,那么就得重新计算了。
https://blog.csdn.net/b1480521874/article/details/85339279