service的绑定原理
看完service的启动流程,继续撸一下service的绑定流程
1.service的绑定流程
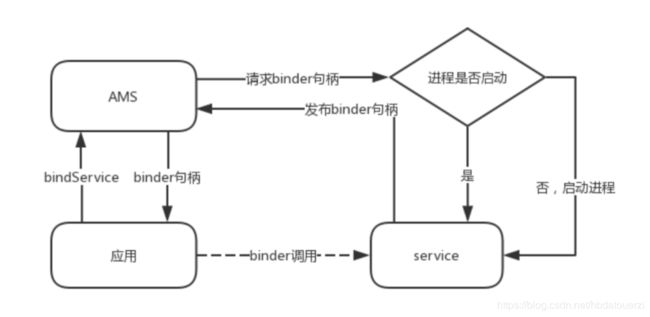
首先我们看下如下图所示的service的绑定原理,应用向AMS发起bindService,然后AMS检查自己是否有对应service的binder句柄,如果有,则直接返回,如果没有则会向service请求对应的binder句柄。
然后若service所在的进程没有启动,则先启动进程,进程启动完了之后,service会将句柄发布到AMS,然后AMS再返回给应用,这样应用就可以直接向service发起binder调用了。
我们再来看下bindService的具体的代码流程,
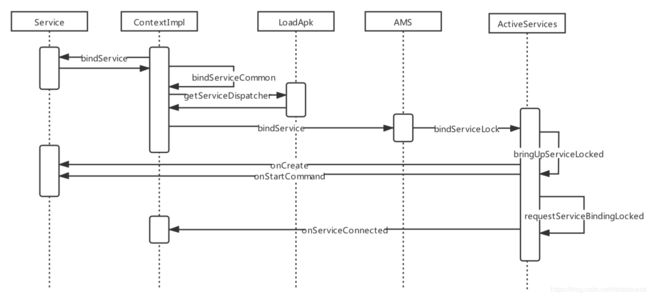
这里我们需要重点关注的有以下几个方法
首先我们看下应用端的流程
应用端绑定流程
如下所示为bindServiceCommon方法,我们可以看到传入的参数为ServiceConnection,而最终ServiceConnection被转化成为IServiceConnection传递给了AMS,这是因为ServiceConnection不是binder对象,不能够在进程之间传递,需要将其转化成为binder对象之后才可以。
//ContextImpl
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags, Handler
handler, UserHandle user) {
......
IServiceConnection sd;
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(), handler, flags);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Not supported in system context");
}
ActivityManager.getService().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
.......
}
接下来我们看下getServiceDispatcher是如何实现的,
如下所示,在注释1处,从mServices当中取出map,key为context,再从取出的map当中取出
ServiceDispatcher,如注释2所示。若取出的ServiceDispatcher为空,则new一个新的对象put进去,最后再返回ServiceDispatcher里面的IServiceConnection对象。
//LoadApk
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Handler handler, int flags) {
synchronized (mServices) {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = null;
//1.mServices是一个map,key为context
ArrayMap map = mServices.get(context);
if (map != null) {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Returning existing dispatcher " + sd + " for conn " + c);
//2.从map里面取出ServiceDispatcher
sd = map.get(c);
}
if (sd == null) {
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Creating new dispatcher " + sd + " for conn " + c);
if (map == null) {
map = new ArrayMap<>();
mServices.put(context, map);
}
map.put(c, sd);
} else {
sd.validate(context, handler);
}
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
}
接着我们再来看下ServiceDispatcher的构造函数,
注释1处,new了一个InnerConnection对象,这个就是要跨进程传递给AMS的binder对象,注释2处就是我们传入的ServiceConnection对象
当服务连接上之后,InnerConnection对象的connected方法会被调用,然后我们传入的ServiceConnection也会被调用
ServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection conn,
Context context, Handler activityThread, int flags) {
//1.binder对象
mIServiceConnection = new InnerConnection(this);
//2.我们传入的ServiceConnection对象
mConnection = conn;
mContext = context;
mActivityThread = activityThread;
mLocation = new ServiceConnectionLeaked(null);
mLocation.fillInStackTrace();
mFlags = flags;
}
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead)
throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
//3.服务connected
sd.connected(name, service, dead);
}
}
}
需要注意的点
如下图所示为应用端的调用图,应用端和AMS最终是通过IServiceConnection进行交互,然后再调用ServiceConnection。
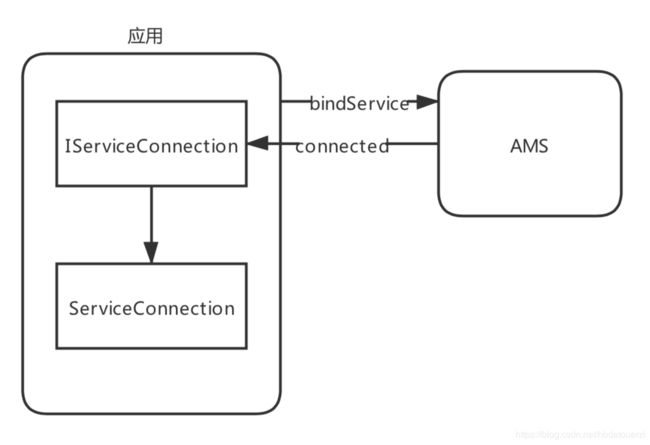
从以下代码中可以看出,context和ServiceConnection可以唯一确定一个ServiceDispatcher,进而确定IServiceConnection,因此同一个activity使用不同的ServiceConnection,和不同的activity使用同一个ServiceConnection,对于AMS来说都是不一样的绑定。
ArrayMap map = mServices.get(context);
服务端的绑定流程
当AMS收到bindService请求之后会执行ActiveServices的bindServiceLocked的方法,然后执行bringUpServiceLocked–>realStartServiceLocked–>requestServiceBindingsLocked。
首先我们来看下realStartServiceLocked
在注释1处,通知应用端创建service对象,并执行onCreate周期函数。
在注释2处,当service创建成功之后,请求service发布其binder句柄
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
......
try {
......
mAm.notifyPackageUse(r.serviceInfo.packageName,
PackageManager.NOTIFY_PACKAGE_USE_SERVICE);
app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
//1.通知应用端,创建service对象,执行onCreate
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
r.postNotification();
created = true;
} catch (DeadObjectException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Application dead when creating service " + r);
mAm.appDiedLocked(app);
throw e;
} finally {
if (!created) {
// Keep the executeNesting count accurate.
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
// Cleanup.
if (newService) {
app.services.remove(r);
r.app = null;
}
// Retry.
if (!inDestroying) {
scheduleServiceRestartLocked(r, false);
}
}
}
if (r.whitelistManager) {
app.whitelistManager = true;
}
//2.请求service发布其binder句柄
requestServiceBindingsLocked(r, execInFg);
......
}
我们再来看下requestServiceBindingLocked,是如何请求发布句柄的。
在注释1处,如果service没有启动,则直接返回
在注释2处,向service请求binder对象,会执行应用端的scheduleBindService方法。
在注释4处,应用端远程调用AMS,向AMS发布binder对象。
//ActiveServices
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i,
boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//1.若service没有启动,则直接返回false
if (r.app == null || r.app.thread == null) {
return false;
}
if ((!i.requested || rebind) && i.apps.size() > 0) {
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "bind");
r.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
//2.向service请求对象
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.repProcState);
if (!rebind) {
i.requested = true;
}
i.hasBound = true;
i.doRebind = false;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Crashed while binding " + r, e);
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
//ActivityThread
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent,
boolean rebind, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
BindServiceData s = new BindServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.intent = intent;
s.rebind = rebind;
sendMessage(H.BIND_SERVICE, s);
}
//ActivityThread
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
//3.执行onbind
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
//4.向AMS发布binder对象
ActivityManager.getService().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
ensureJitEnabled();
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(s, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to bind to service " + s
+ " with " + data.intent + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
}