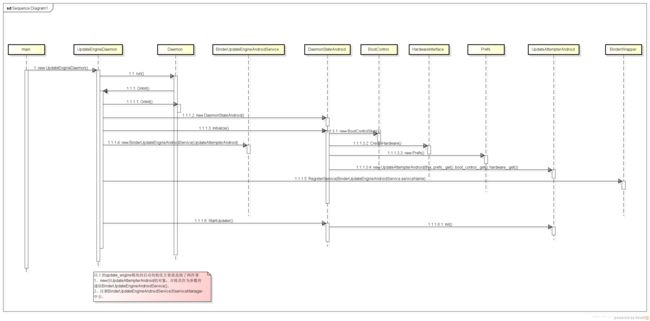
updateEngine的内部启动流程
一、这一块主要分析的就是从update_Engine启动到核心类UpdateAttempterAndroid的这个过程。
代码路径:system/update_engine/
代码分析:
main.cc
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
DEFINE_bool(logtofile, false, "Write logs to a file in log_dir.");
DEFINE_bool(logtostderr, false,
"Write logs to stderr instead of to a file in log_dir.");
DEFINE_bool(foreground, false,
"Don't daemon()ize; run in foreground.");
chromeos_update_engine::Terminator::Init();
brillo::FlagHelper::Init(argc, argv, "Chromium OS Update Engine");
// We have two logging flags "--logtostderr" and "--logtofile"; and the logic
// to choose the logging destination is:
// 1. --logtostderr --logtofile -> logs to both
// 2. --logtostderr -> logs to system debug
// 3. --logtofile or no flags -> logs to file
bool log_to_system = FLAGS_logtostderr;
bool log_to_file = FLAGS_logtofile || !FLAGS_logtostderr;
chromeos_update_engine::SetupLogging(log_to_system, log_to_file);
if (!FLAGS_foreground)
PLOG_IF(FATAL, daemon(0, 0) == 1) << "daemon() failed";
LOG(INFO) << "Chrome OS Update Engine starting";
// xz-embedded requires to initialize its CRC-32 table once on startup.
xz_crc32_init();
// Ensure that all written files have safe permissions.
// This is a mask, so we _block_ all permissions for the group owner and other
// users but allow all permissions for the user owner. We allow execution
// for the owner so we can create directories.
// Done _after_ log file creation.
umask(S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO);
chromeos_update_engine::UpdateEngineDaemon update_engine_daemon; // UpdateEngineDaemon继承自brillo::Daemon ,这里先得到 UpdateEngineDaemon 的对象。UpdateEngineDaemon 的代码在daemon.cc中
int exit_code = update_engine_daemon.Run(); //我们发现UpdateEngineDaemon 并没有Run()这个方法,而是在父类Daemon中有 Run()的实现。
LOG(INFO) << "Chrome OS Update Engine terminating with exit code "
<< exit_code;
return exit_code;
}
/external/libbrillo/brillo/daemons/daemon.cc
int Daemon::Run() {
int exit_code = OnInit(); //又会调到 UpdateEngineDaemon的OnInit()
if (exit_code != EX_OK)
return exit_code;
message_loop_.Run();
OnShutdown(&exit_code_);
// base::RunLoop::QuitClosure() causes the message loop to quit
// immediately, even if pending tasks are still queued.
// Run a secondary loop to make sure all those are processed.
// This becomes important when working with D-Bus since dbus::Bus does
// a bunch of clean-up tasks asynchronously when shutting down.
while (message_loop_.RunOnce(false /* may_block */)) {}
return exit_code_;
}
system/update_engine/deamon.cc
int UpdateEngineDaemon::OnInit() {
// Register the |subprocess_| singleton with this Daemon as the signal
// handler.
subprocess_.Init(this);
int exit_code = Daemon::OnInit(); //调用父类Daemon进行初始化
if (exit_code != EX_OK)
return exit_code;
#if USE_BINDER
android::BinderWrapper::Create();
binder_watcher_.Init();
#endif // USE_BINDER
#if USE_OMAHA //这块不用管,应该是使用OMAHA平台的走下面
// Initialize update engine global state but continue if something fails.
// TODO(deymo): Move the daemon_state_ initialization to a factory method
// avoiding the explicit re-usage of the |bus| instance, shared between
// D-Bus service and D-Bus client calls.
RealSystemState* real_system_state = new RealSystemState();
daemon_state_.reset(real_system_state);
LOG_IF(ERROR, !real_system_state->Initialize())
<< "Failed to initialize system state.";
#else // !USE_OMAHA
DaemonStateAndroid* daemon_state_android = new DaemonStateAndroid(); //得到 DaemonStateAndroid对象,然后传递给指针daemon_state_,daemon_state_的指针类型是DaemonStateInterface,而 DaemonStateAndroid继承自 DaemonStateInterface。
daemon_state_.reset(daemon_state_android);
LOG_IF(ERROR, !daemon_state_android->Initialize()) //DaemonStateAndroid的初始化里主要做了这几件事 1、new boot_control 2、Create hardware 3、new Prefs() 4、new CertificateChecker 5、new UpdateAttempterAndroid,然后将DeamonStateAndroid prefs boot_control hardware的指针传递个 UpdateAttempterAndroid类
<< "Failed to initialize system state.";
#endif // USE_OMAHA
#if USE_BINDER
// Create the Binder Service.
#if USE_OMAHA
binder_service_ = new BinderUpdateEngineBrilloService{real_system_state};
#else // !USE_OMAHA
binder_service_ = new BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService{
daemon_state_android->service_delegate()}; // 将ServiceDelegateAndroidInterface的指针传递给BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService,而 UpdateAttempterAndroid是继承ServiceDelegateAndroidInterface,可以理解就是BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService拿到了UpdateAttempterAndroid的对象。
#endif // USE_OMAHA
auto binder_wrapper = android::BinderWrapper::Get();
if (!binder_wrapper->RegisterService(binder_service_->ServiceName(), // 将BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService 注册到serviceManager中
binder_service_)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to register binder service.";
}
daemon_state_->AddObserver(binder_service_.get()); //将 BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService的对象传递给DaemonStateAndroid
#endif // USE_BINDER
#if USE_DBUS
// Create the DBus service.
dbus_adaptor_.reset(new UpdateEngineAdaptor(real_system_state));
daemon_state_->AddObserver(dbus_adaptor_.get());
dbus_adaptor_->RegisterAsync(base::Bind(&UpdateEngineDaemon::OnDBusRegistered,
base::Unretained(this)));
LOG(INFO) << "Waiting for DBus object to be registered.";
#else // !USE_DBUS
daemon_state_->StartUpdater(); //主要就是调用UpdateAttempterAndroid的init()方法。
#endif // USE_DBUS
return EX_OK;
}
总结:以上的update_engine模块的启动初始化主要就是做了两件事:
1、new出UpdateAttempterAndroid的对象,并将其作为参数传递给BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService()。
2、注册BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService到serviceManager中去。
可见,其实BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService中的applyPayload() suspend()等, 都是调用到了UpdateAttempterAndroid。可见updateEngine的核心其实就是UpdateAttempterAndroid。