使用Fisher线性分类器实现人脸判别的二分类问题和多分类问题(Matlab)
基本思想
若把样本的多维特征空间的点投影到一条直线上,就能把特征空间压缩成一维。那么关键就是找到这条直线的方向,找得好,分得好,找不好,就混在一起。因此fisher方法目标就是找到这个最好的直线方向以及如何实现向最好方向投影的变换。这个投影变换恰是我们所寻求的解向量 ,这是fisher算法的基本问题。
样本训练集以及待测样本的特征数目为n。为了找到最佳投影方向,需要计算出各类均值、样本类内离散度矩阵 和总类间离散度矩阵、样本类间离散度矩阵,根据Fisher准则,找到最佳投影准则,将训练集内所有样本进行投影,投影到一维Y空间,由于Y空间是一维的,则需要求出Y空间的划分边界点,找到边界点后,就可以对待测样本进行一维Y空间的投影,判断它的投影点与分界点的关系,将其归类。
主要用到的函数(二分类问题时):
function W = FisherLDA(w1,w2)
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%w1为第一类样本
%w2为第二类样本
%W为权值向量
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%第一步:计算样本均值向量
M1 = mean(w1);
M2 = mean(w2);
M = mean([w1;w2]);
%第二步:计算类内离散度矩阵Sw
p = size(w1,1);
q = size(w2,1);
S1 = 0;
for i = 1:p
S1 = S1 + (w1(i,:)-M1)'*(w1(i,:)-M1);
end
S2 = 0;
for i = 1:q
S2 = S2 + (w2(i,:)-M2)'*(w2(i,:)-M2);
end
Sw = (p*S1+q*S2)/(p+q);
%第三步:计算类间离散度矩阵Sb
S1 = M - M1;
S2 = M - M2;
Sb = (p*S1'*S1 + q*S2'*S2)/(p+q);
%第四步:求最大特征值和特征向量
A = repmat(0.1,[1,size(Sw,1)]);
B = diag(A);
[V,L]=eig(inv(Sw + B)*Sb);
[a,b]=max(max(L));
W = V(:,b);%最大特征值所对应的特征向量
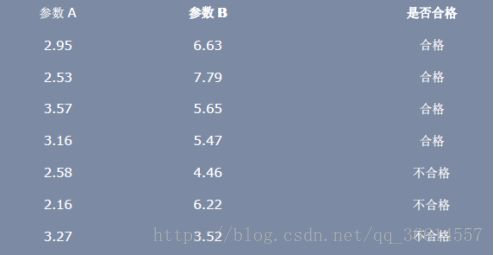
一:
根据上图,我们可以把样本分为两类,一类是合格的产品,一类是不合格的产品。通过LDA算法对训练样本的投影获得判别函数,然后判断测试样本的类别,即输入一个样本的参数,判断该产品是否合格。
实验代码:
w1=[2.95 6.63;2.53 7.79;3.57 5.65;3.16 5.47];
w2=[2.58 4.46;2.16 6.22;3.27 3.52];
W=FisherLDA(w1,w2);
for i=1:length(w1)
y(i)=W'*w1(i,:)';
end
for j=1:length(w2)
y(i+j)=W'*w2(j,:)';
end
thre=mean(y(i:i+1));
x(1)=input('参数A');
x(2)=input('参数B');
dy=W'*x';
if (dy<=thre)
display('合格');
else
display('不合格');
end
运行结果:输入[3 5]:
参数A3
参数B5
合格
二:基于ORL人脸库,实验样本主要来自于两个人,每人45张图片,共有90个样本,其中的80个样本作为训练样本,10个作为测试样本。通过LDA实现两类问题的线性判别。
运行代码:
%读入训练集1
fpath = 'F:\Artificial Intelligence\实验设计\Fisher\TrainingData\1';
flist = dir(sprintf('%s/*.bmp', fpath));
w1 = double(zeros(40,1024));
for imidx = 1:min(length(flist), 200)
%fprintf('[%d]', imidx); %显示进程
fname = sprintf('%s/%s', fpath, flist(imidx).name);
im = imread(fname);
im=reshape(im,[1,1024]);
w1(imidx,:)=im(1:1024);
end
%读入训练集2
fpath = 'F:\Artificial Intelligence\实验设计\Fisher\TrainingData\2';
flist = dir(sprintf('%s/*.bmp', fpath));
w2 = double(zeros(40,1024));
for imidx = 1:min(length(flist), 200)
%fprintf('[%d]', imidx); %显示进程
fname = sprintf('%s/%s', fpath, flist(imidx).name);
im = imread(fname);
im=reshape(im,[1,1024]);
w2(imidx,:)=im(1:1024);
end
W=FisherLDA(w1,w2);
for i=1:40
y(i)=W'*w1(i,:)';
end
for j=1:40
y(i+j)=W'*w2(j,:)';
end
thre=mean(y(i:i+1));
%读入测试集
fpath = 'F:\Artificial Intelligence\实验设计\Fisher\TestingData';
flist = dir(sprintf('%s/*.bmp', fpath));
for imidx = 1:min(length(flist), 200)
%fprintf('[%d]', imidx); %显示进程
fname = sprintf('%s/%s', fpath, flist(imidx).name);
im = imread(fname);
im=reshape(im,[1,1024]);
im=double(im);
test_y=W'*im';
disp(fname);
if test_y>=thre
disp('the figure is of 2');
else
disp('the figure is of 1');
end
end
运行结果:
F:\Artificial Intelligence\实验设计\Fisher\TestingData/1.bmp
the figure is of 1
F:\Artificial Intelligence\实验设计\Fisher\TestingData/10.bmp
the figure is of 2
F:\Artificial Intelligence\实验设计\Fisher\TestingData/2.bmp
the figure is of 1
F:\Artificial Intelligence\实验设计\Fisher\TestingData/3.bmp
the figure is of 1
F:\Artificial Intelligence\实验设计\Fisher\TestingData/4.bmp
the figure is of 1
F:\Artificial Intelligence\实验设计\Fisher\TestingData/5.bmp
the figure is of 1
F:\Artificial Intelligence\实验设计\Fisher\TestingData/6.bmp
the figure is of 2
F:\Artificial Intelligence\实验设计\Fisher\TestingData/7.bmp
the figure is of 2
F:\Artificial Intelligence\实验设计\Fisher\TestingData/8.bmp
the figure is of 2
F:\Artificial Intelligence\实验设计\Fisher\TestingData/9.bmp
the figure is of 2
三:
基于ORL人脸库,基于Fisher线性分类器实现多类人脸的识别问题。将FisherLDA函数改写为多分类函数FisherLDA2(本次使用四分类)
FisherLDA2:
function W = FisherLDA2(w1,w2,w3,w4)
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%w1为第一类样本
%w2为第二类样本
%W为权值向量
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%第一步:计算样本均值向量
M1 = mean(w1);
M2 = mean(w2);
M3=mean(w3);
M4=mean(w4);
M = mean([w1;w2;w3;w4]);
%第二步:计算类内离散度矩阵Sw
p = size(w1,1);
q = size(w2,1);
r=size(w3,1);
s=size(w4,1);
S1 = 0;
for i = 1:p
S1 = S1 + (w1(i,:)-M1)'*(w1(i,:)-M1);
end
S2 = 0;
for i = 1:q
S2 = S2 + (w2(i,:)-M2)'*(w2(i,:)-M2);
end
S3 = 0;
for i = 1:r
S3 = S3 + (w3(i,:)-M3)'*(w3(i,:)-M3);
end
S4 = 0;
for i = 1:s
S4 = S4 + (w4(i,:)-M4)'*(w4(i,:)-M4);
end
Sw = (p*S1+q*S2+r*S3+s*S4)/(p+q+r+s);
%第三步:计算类间离散度矩阵Sb
S1 = M - M1;
S2 = M - M2;
S3=M-M3;
S4=M-M4;
Sb = (p*S1'*S1 + q*S2'*S2+r*S3'*S3+s*S4'*S4)/(p+q+r+s);
%第四步:求最大特征值和特征向量
A = repmat(0.1,[1,size(Sw,1)]);
B = diag(A);
[V,L]=eig(inv(Sw + B)*Sb);
[a,b]=max(max(L));
W = V(:,b);%最大特征值所对应的特征向量
运行代码:
clc
clear
fpath = 'F:\Artificial Intelligence\code\2018.5.8\att_faces.tar\orl_faces\s1';
flist = dir(sprintf('%s/*.pgm', fpath));
w1 = double(zeros(10,644));
for imidx = 1:min(length(flist), 200)
%fprintf('[%d]', imidx); %显示进程
fname = sprintf('%s/%s', fpath, flist(imidx).name);
im = imread(fname);
im=double(imresize(im,[28,23]));
im=reshape(im,[1,644]);
w1(imidx,:)=im;
end
fpath = 'F:\Artificial Intelligence\code\2018.5.8\att_faces.tar\orl_faces\s2';
flist = dir(sprintf('%s/*.pgm', fpath));
w2 = double(zeros(10,644));
for imidx = 1:min(length(flist), 200)
%fprintf('[%d]', imidx); %显示进程
fname = sprintf('%s/%s', fpath, flist(imidx).name);
im = imread(fname);
im=double(imresize(im,[28,23]));
im=reshape(im,[1,644]);
w2(imidx,:)=im;
end
fpath = 'F:\Artificial Intelligence\code\2018.5.8\att_faces.tar\orl_faces\s3';
flist = dir(sprintf('%s/*.pgm', fpath));
w3 = double(zeros(10,644));
for imidx = 1:min(length(flist), 200)
%fprintf('[%d]', imidx); %显示进程
fname = sprintf('%s/%s', fpath, flist(imidx).name);
im = imread(fname);
im=double(imresize(im,[28,23]));
im=reshape(im,[1,644]);
w3(imidx,:)=im;
end
fpath = 'F:\Artificial Intelligence\code\2018.5.8\att_faces.tar\orl_faces\s4';
flist = dir(sprintf('%s/*.pgm', fpath));
w4 = double(zeros(10,644));
for imidx = 1:min(length(flist), 200)
%fprintf('[%d]', imidx); %显示进程
fname = sprintf('%s/%s', fpath, flist(imidx).name);
im = imread(fname);
im=double(imresize(im,[28,23]));
im=reshape(im,[1,644]);
w4(imidx,:)=im;
end
W=FisherLDA2(w1,w2,w3,w4);
for i=1:10
y(i)=W'*w1(i,:)';
y(10+i)=W'*w2(i,:)';
y(20+i)=W'*w3(i,:)';
y(30+i)=W'*w4(i,:)';
end
m(1)=mean(y(1:10));
m(2)=mean(y(11:20));
m(3)=mean(y(21:30));
m(4)=mean(y(31:40));
thre=20;
fpath = 'F:\Artificial Intelligence\code\2018.5.8\att_faces.tar\orl_faces\Testing';
flist = dir(sprintf('%s/*.pgm', fpath));
for imidx = 1:min(length(flist), 200)
%fprintf('[%d]', imidx); %显示进程
fname = sprintf('%s/%s', fpath, flist(imidx).name);
im = imread(fname);
im=double(imresize(im,[28,23]));
im=reshape(im,[1,644]);
test_y=W'*im';
min_index=0;
min_dis=20;
for i=1:4
if(abs(test_y-m(i)))
运行结果:
F:\Artificial Intelligence\code\2018.5.8\att_faces.tar\orl_faces\Testing/1.pgm
this figure is of
2
F:\Artificial Intelligence\code\2018.5.8\att_faces.tar\orl_faces\Testing/10.pgm
this figure is of
3
F:\Artificial Intelligence\code\2018.5.8\att_faces.tar\orl_faces\Testing/2.pgm
this figure is of
3
F:\Artificial Intelligence\code\2018.5.8\att_faces.tar\orl_faces\Testing/3.pgm
this figure is of
4
F:\Artificial Intelligence\code\2018.5.8\att_faces.tar\orl_faces\Testing/4.pgm
this figure is of
1
F:\Artificial Intelligence\code\2018.5.8\att_faces.tar\orl_faces\Testing/5.pgm
not in this 4 classes
F:\Artificial Intelligence\code\2018.5.8\att_faces.tar\orl_faces\Testing/6.pgm
this figure is of
1
F:\Artificial Intelligence\code\2018.5.8\att_faces.tar\orl_faces\Testing/7.pgm
this figure is of
2
F:\Artificial Intelligence\code\2018.5.8\att_faces.tar\orl_faces\Testing/8.pgm
not in this 4 classes
F:\Artificial Intelligence\code\2018.5.8\att_faces.tar\orl_faces\Testing/9.pgm
this figure is of
4
ORL人脸识别数据库下载链接: http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/Research/DTG/attarchive/pub/data/att_faces.tar.Z