SpringCloud-简单的入门
Spring-Cloud入门程序
单体应用
什么是单体应用?
项目所有的资源都在一个应用中,打包成一个war包,使用一个tomcat去运行,运行在一个进程中
单体应用的优缺点:
缺点:
1.一个模块挂了,整个项目都受影响
2.单个tomcat更能处理的并发有限,可以做集群,但是不方便局部(某一个模块)扩展
3.维护/开发/升级比较麻烦
4.代码臃肿,编译,打包都比较慢
5.技术选型单一
6.数据库选型单一
优点:
适用于小型项目
而正是鉴于这些缺点,我们做一些比较大的项目时,那么单体就非常的不适合。
所以我们有了微服务架构!
微服务架构
微服务架构的概念:
微服务就是把一个大的系统,拆分成多个小的服务,每个微服务只专注一个业务 每个服务有各自的进程, 微服务之间使用网络通信协议进行数据交互(通常是基于HTTP的RESTful API)。
一张图了解:
下图中,一个单体项目将所有的业务功能放在了一个架构中.造成了代码臃肿也不好看
而 微服务架构模式则是将一个大型项目拆分了多个小的应有!

微服务架构的特点:
● 数据库选型多样化
● 技术选型多样化
● 每个微服务专注一个业务
● 每个业务有自己的进程
● 微服务之间通过网络协议进行通信
● 方便做局部拓展
● 开发/维护/升级更方便
但是相应的微服务架构也是有一些缺点的:
比如:开发成本比较高、部署项目也比较麻烦、技术要求也比较高
微服务架构只是一种思想,更多的需要一种具体的落地方案来实现这种思想
那么我们就可以使用SpringCloud来作为一种比较优秀的方案来实现微服务架构
SpringCloud的入门
SpringCloud是什么?
首先 SpringCloud作为一种具体实现微服务架构的一种落地方案。其次它是基于SpringBoot的服务治理工具包,用于微服务架构中管理和协调服务的
能与SpringCloud相抗衡的还有一个Duddo
- SpringCloud 是全家桶,一系列的解决方案
- Dubbo :RPC框架,解决远程服务调用问题
- Dubbo :基于tcp通信,性能好
- SpringCloud:基于http通信的性能稍差
SpringCloud的核心组件
- 注册中心Eureka : 管理微服务的通信地址(端口、IP地址)
- 配置中心Config : 管理微服务的配置文件
- 网关:zuul :微服务的访问入口
- 负载均衡:Ribbon/Feign :微服务之间的请求以及负载均衡
- 断路器:hystirx : 解决微服务故障问题
那首先让我们从注册中心Eureka入门
注册中心Eureka
概念以及原理详解:
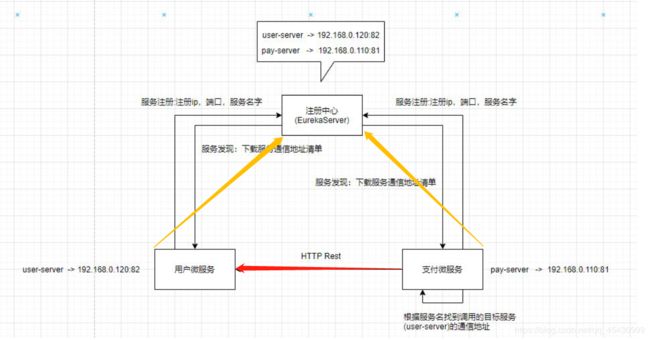
用来管理微服务的通信地址,所有的微服务启动的时候都要向注册中心提交自己的通信地址,注册中心形成一个服务地址清单,所有的微服务也会从注册中心获取服务地址清单,当某个服务要对另外一个服务发起调用,该服务会从地址清单中知道目标服务的通信地址,使用Http发起调研
注意:
注册中心可以实现服务的自动上下线 ,每个微服务都会使用心跳机制(间隔n秒先注册中心发请求,证明还没挂),向注册中心续约(租房交房租)
当某个微服务挂了,就不会再发送心跳请求,那么注册中心就会把该服务标记为下线,从地址清单移除下线的服务地址,那么其他的微服务也会同步地址清单
注册中心Eureka入门程序
1、搭建项目结构
springcloud-parent(父级项目:放所需的jar包)
注册中心EurekaServer(服务端):
- springcloud-eureka-server-3000(—端口:3000)
支付服务EurekaClient[消费者者(客户端):
- springcloud-consumer-pay-server-2000(—端口:2000)
用户服务EurekaClient[提供者(客户端):
- springcloud-producer-user-server-1000(—端口:1000)

父工程管理jar包(pom.xml): - 继承SpringBoot
- 管理公共的内容
- 管理SpringCloud
<!--1.SpringBoot的父工程-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<groupId>cn.itsource</groupId>
<artifactId>springcloud-parent</artifactId>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<modules>
<module>springcloud-producer-user-server-1000</module>
<module>springcloud-consumer-pay-server-2000</module>
<module>springcloud-eureka-server-3000</module>
</modules>
<!-- 3. 抽取公共的内容-->
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<!--所有子模块一定要用到的公共的jar包-->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!--2.管理SpringCloud的jar包-->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Finchley.SR1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
2、EurekaServer(服务端)的搭建
- 导入依赖 : spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server
<parent>
<artifactId>springcloud-parent</artifactId>
<groupId>cn.itsource</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>springcloud-eureka-server-3000</artifactId>
<name>springcloud-eureka-server-3000</name>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- 编写主配置列,打标签 @EnableEurekaServer
/**
* 注册中心配置类
* @EnableEurekaServer : 开启注册中心
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class EurekaServerApplication3000 {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication3000.class, args);
}
}
- application-standalone.yml文件配置EurekaServer
server:
port: 3000
eureka: #Eureka的配置
instance:
hostname: localhost #主机
client: #对Eureka客户端配置
registerWithEureka: false #注册中心自己 , 不准向注册中心自己注册
fetchRegistry: false #注册中心不需要 获取服务的通信地址清单
serviceUrl: #注册中心 服务的注册地址
#defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
defaultZone: http://localhost:3000/eureka/
3、用户服务注册到EurekaServer
- 导入依赖: springcloud-producer-user-server-1000—> spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client ;
<parent>
<artifactId>springcloud-parent</artifactId>
<groupId>cn.itsource</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>springcloud-producer-user-server-1000</artifactId>
<name>springcloud-producer-user-server-1000</name>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 集成Web的jar包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- 主配置类: 可以打上下面的标签,也可以不打
@EnableDiscoveryClient :开启服务发现 (开启注册中心的客户端功能)
@EnableEurekaClient : 开启Eureka client客户端(只是针对Eureka有用)
/**
* 用户微服务
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
public class UserEurekaServerApplication1000 {
public static void main( String[] args )
{
SpringApplication.run(UserEurekaServerApplication1000.class, args);
}
}
- 配置文件进行配置
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:3000/eureka/,http://localhost:3001/eureka/ #注册中心服务端的注册地址
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true #使用ip进行注册
instance-id: user-server:1000 #服务注册到注册中心的id
server:
port: 1000
#应有的名称
spring:
application:
name: user-server
4、支付服务注册到EurekaServer
和用户服务注册到EurekaServer是一样的,只需要修改端口即可
注册中心Eureka 模拟集群
下面来模拟一下 Eureka的集群
我们做注册中心的集群其实就是两个EurekaServer相互注册 , 使用SpirngBoot多配置文件的方式
1、修改hosts文件,增加两个本地主机名:pree1,pree2
hosts文件:C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
127.0.0.1:pree1
127.0.0.1:pree2
2、 EurekaServer集群配置
在Eureka的客户端的配置文件中进行集群配置:
#使用SpringBoot多环境配置的方式来配置 2个 注册中心(模拟集群)
#主配置
spring:
profiles:
active: pree2 #你激活谁,启动的时候就是用的谁的配置
---
#第一个EurekaServer的配置
spring:
profiles: pree1
application:
name: eureka-server
eureka:
instance:
hostname: pree1
prefer-ip-address: true
instance-id: eureka-server:3000
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://pree2:3001/eureka/
server:
port: 3000
---
#第二个EurekaServer的配置
spring:
profiles: pree2
application:
name: eureka-server
eureka:
instance:
hostname: pree2
prefer-ip-address: true
instance-id: eureka-server:3001
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://pree1:3000/eureka/
server:
port: 3001
注意事项:
1、在客户端Eureka的主配置类启动一个EurekaServer之后,要在配置文件修改另外一个EurekaServer的主机名: (启动的时候一定要修改 spring.profiles.active ,不然要端口冲突)
 2、 打开IDEA多实例启动功能:
2、 打开IDEA多实例启动功能:
只有打开下面这个才能够运行多个EurekaServer