我的架构梦:(十七)Tomcat 源码构建以及源码剖析
Tomcat 源码构建以及源码剖析
- 一、源码构建
- 二、源码剖析
一、源码构建
1、下载源码
这里博主下载的是apache-tomcat-8.5.50-src
http://archive.apache.org/dist/tomcat/tomcat-8/v8.5.50/src/
2、源码导入IDE之前准备工作
-
解压 tar.gz 压缩包,得到目录 apache-tomcat-8.5.50-src
-
进入 apache-tomcat-8.5.50-src 目录,创建一个pom.xml文件,文件内容如下
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion> <groupId>org.apache.tomcatgroupId> <artifactId>apache-tomcat-8.5.50-srcartifactId> <name>Tomcat8.5name> <version>8.5version> <build> <finalName>Tomcat8.5finalName> <sourceDirectory>javasourceDirectory> <resources> <resource> <directory>javadirectory> resource> resources> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.pluginsgroupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-pluginartifactId> <version>3.1version> <configuration> <encoding>UTF-8encoding> <source>1.8source> <target>1.8target> configuration> plugin> plugins> build> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.easymockgroupId> <artifactId>easymockartifactId> <version>3.4version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>antgroupId> <artifactId>antartifactId> <version>1.7.0version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>wsdl4jgroupId> <artifactId>wsdl4jartifactId> <version>1.6.2version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.xmlgroupId> <artifactId>jaxrpcartifactId> <version>1.1version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.eclipse.jdt.core.compilergroupId> <artifactId>ecjartifactId> <version>4.5.1version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.xml.soapgroupId> <artifactId>javax.xml.soap-apiartifactId> <version>1.4.0version> dependency> dependencies> project> -
在 apache-tomcat-8.5.50-src 目录中创建 source 文件夹
-
将 conf、webapps 目录移动到刚刚创建的 source 文件夹中
3、导入源码工程到IDE并进行配置
-
将源码工程导入到 IDEA 中
-
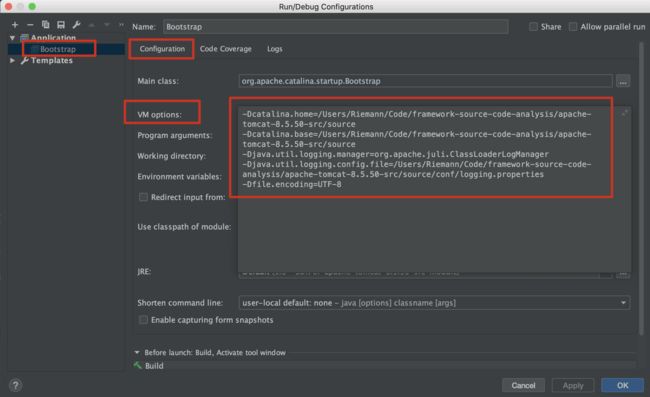
给 tomcat 的源码程序启动类 Bootstrap 配置 VM 参数,因为 tomcat 源码运行也需要加载配置文 件等。
-Dcatalina.home=/Users/Riemann/Code/framework-source-code-analysis/apache-tomcat-8.5.50-src/source -Dcatalina.base=/Users/Riemann/Code/framework-source-code-analysis/apache-tomcat-8.5.50-src/source -Djava.util.logging.manager=org.apache.juli.ClassLoaderLogManager -Djava.util.logging.config.file=/Users/Riemann/Code/framework-source-code-analysis/apache-tomcat-8.5.50-src/source/conf/logging.properties -
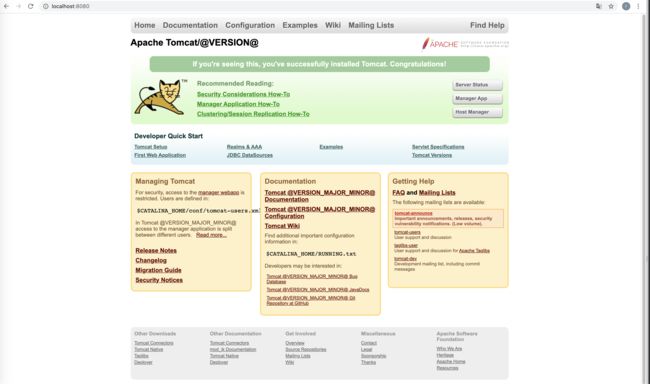
运行 Bootstrap 类的 main 函数,此时就启动了tomcat,启动时候会去加载所配置的 conf 目录下 的server.xml等配置文件,所以访问8080端口即可,但此时我们会遇到如下的一个错误。
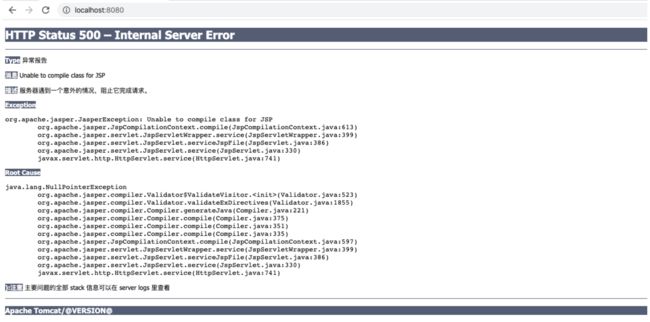
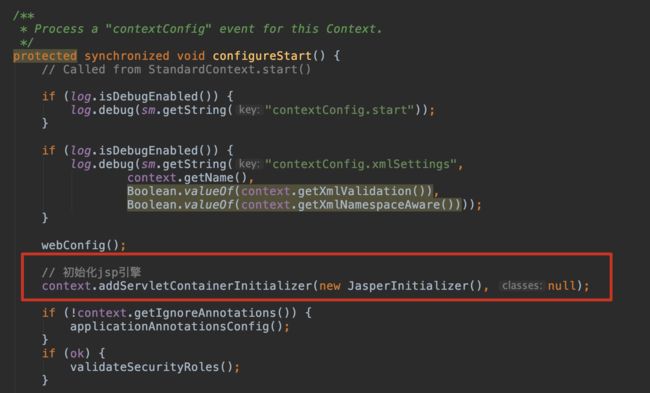
原因是Jsp引擎Jasper没有被初始化,从而无法编译JSP,我们需要在tomcat的源码ContextConfig类中 的configureStart方法中增加一行代码将 Jsp 引擎初始化,如下:
把前面的准备工作都搞好了以后,启动一下:
来到了我们熟悉的页面,这就说明我们的Tomcat源码构建成功!
二、源码剖析
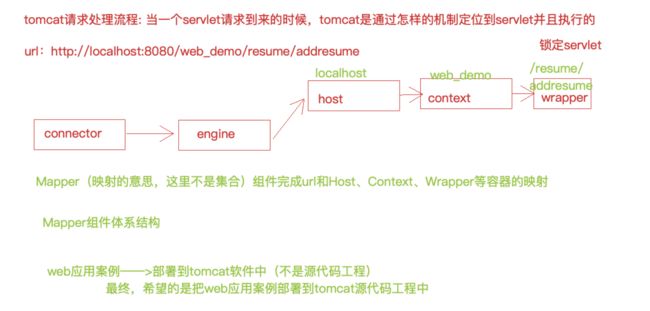
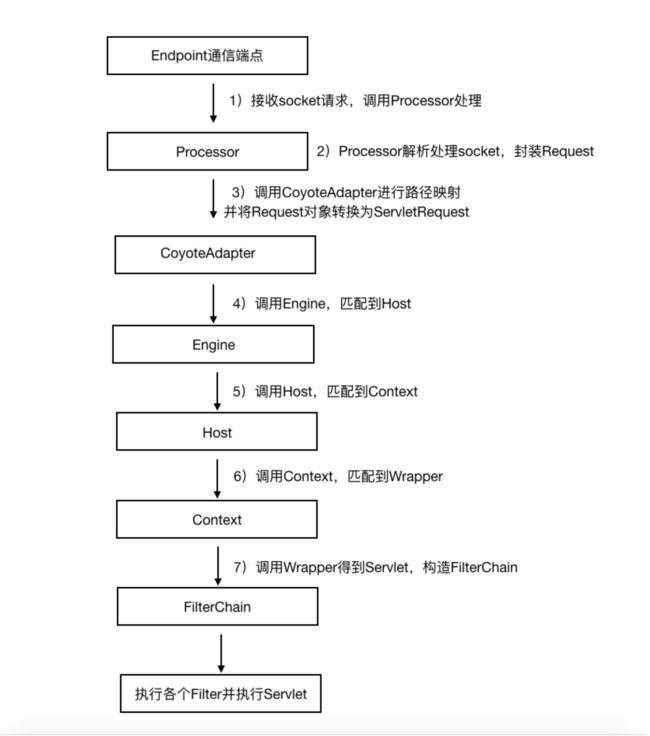
源码追踪部分我们关注两个流程:Tomcat启动流程和Tomcat请求处理流程
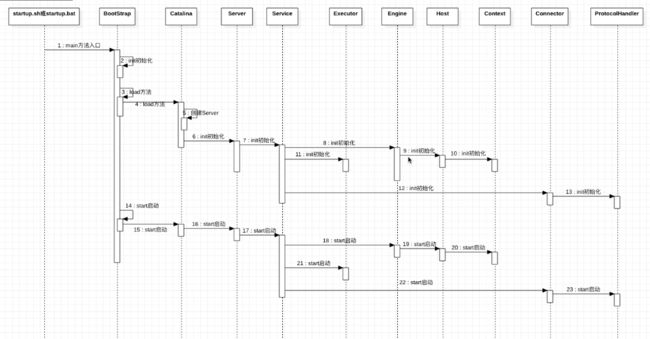
1、Tomcat启动流程
2、Tomcat请求处理流程
2.1 请求处理流程分析
2.2 请求处理流程示意图
3、源码分析
3.1 第一步 main方法入口 Bootstrap#main()
// 时序图中第一步 main方法入口
public static void main(String args[]) {
synchronized (daemonLock) {
if (daemon == null) {
// Don't set daemon until init() has completed
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
try {
// 第二步 init() Bootstrap初始化
bootstrap.init();
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t);
t.printStackTrace();
return;
}
daemon = bootstrap; // daemon表示当前Bootstrap类对象本身
} else {
// When running as a service the call to stop will be on a new
// thread so make sure the correct class loader is used to
// prevent a range of class not found exceptions.
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(daemon.catalinaLoader);
}
}
try {
String command = "start";
if (args.length > 0) {
command = args[args.length - 1];
}
if (command.equals("startd")) {
args[args.length - 1] = "start";
daemon.load(args);
daemon.start();
} else if (command.equals("stopd")) {
args[args.length - 1] = "stop";
daemon.stop();
} else if (command.equals("start")) {
daemon.setAwait(true);
// 第三步 load() Bootstrap加载
daemon.load(args);
// 第十四步 start() Bootstrap启动
daemon.start();
if (null == daemon.getServer()) {
System.exit(1);
}
} else if (command.equals("stop")) {
daemon.stopServer(args);
} else if (command.equals("configtest")) {
daemon.load(args);
if (null == daemon.getServer()) {
System.exit(1);
}
System.exit(0);
} else {
log.warn("Bootstrap: command \"" + command + "\" does not exist.");
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Unwrap the Exception for clearer error reporting
if (t instanceof InvocationTargetException &&
t.getCause() != null) {
t = t.getCause();
}
handleThrowable(t);
t.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
3.2 第二步 init() Bootstrap初始化 Bootstrap#init()
public void init() throws Exception {
// 初始化类加载器
initClassLoaders();
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(catalinaLoader);
SecurityClassLoad.securityClassLoad(catalinaLoader);
// Load our startup class and call its process() method
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Loading startup class");
Class<?> startupClass = catalinaLoader.loadClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");
Object startupInstance = startupClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
// Set the shared extensions class loader
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Setting startup class properties");
String methodName = "setParentClassLoader";
Class<?> paramTypes[] = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = Class.forName("java.lang.ClassLoader");
Object paramValues[] = new Object[1];
paramValues[0] = sharedLoader;
Method method =
startupInstance.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
method.invoke(startupInstance, paramValues);
catalinaDaemon = startupInstance; // catalinaDaemon 是一个 Catalina 的实例
}
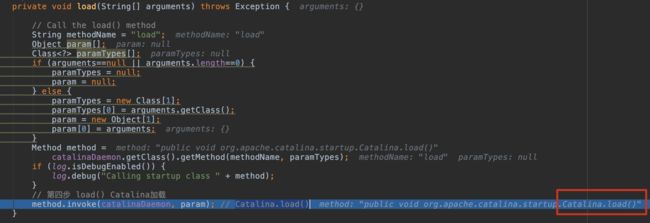
3.3 第三步 load() Bootstrap加载 Bootstrap#load()
private void load(String[] arguments) throws Exception {
// Call the load() method
String methodName = "load";
Object param[];
Class<?> paramTypes[];
if (arguments==null || arguments.length==0) {
paramTypes = null;
param = null;
} else {
paramTypes = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = arguments.getClass();
param = new Object[1];
param[0] = arguments;
}
Method method =
catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Calling startup class " + method);
}
// 第四步 load() Catalina加载
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, param); // Catalina.load()
}
3.4 第四步 load() Catalina加载 反射调用 Catalina#load()
public void load() {
if (loaded) {
return;
}
loaded = true;
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
initDirs();
// Before digester - it may be needed
initNaming();
// Create and execute our Digester
// xml配置文件的解析器,比如解析server.xml
Digester digester = createStartDigester();
InputSource inputSource = null;
InputStream inputStream = null;
File file = null;
try {
try {
file = configFile();
inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
inputSource = new InputSource(file.toURI().toURL().toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("catalina.configFail", file), e);
}
}
if (inputStream == null) {
try {
inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream(getConfigFile());
inputSource = new InputSource
(getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResource(getConfigFile()).toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("catalina.configFail",
getConfigFile()), e);
}
}
}
// This should be included in catalina.jar
// Alternative: don't bother with xml, just create it manually.
if (inputStream == null) {
try {
inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("server-embed.xml");
inputSource = new InputSource
(getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResource("server-embed.xml").toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("catalina.configFail",
"server-embed.xml"), e);
}
}
}
if (inputStream == null || inputSource == null) {
if (file == null) {
log.warn(sm.getString("catalina.configFail",
getConfigFile() + "] or [server-embed.xml]"));
} else {
log.warn(sm.getString("catalina.configFail",
file.getAbsolutePath()));
if (file.exists() && !file.canRead()) {
log.warn("Permissions incorrect, read permission is not allowed on the file.");
}
}
return;
}
try {
inputSource.setByteStream(inputStream);
digester.push(this);
digester.parse(inputSource);
} catch (SAXParseException spe) {
log.warn("Catalina.start using " + getConfigFile() + ": " +
spe.getMessage());
return;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("Catalina.start using " + getConfigFile() + ": " , e);
return;
}
} finally {
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
getServer().setCatalina(this);
getServer().setCatalinaHome(Bootstrap.getCatalinaHomeFile());
getServer().setCatalinaBase(Bootstrap.getCatalinaBaseFile());
// Stream redirection
initStreams();
// Start the new server
try {
// 第五步 getServer() 创建Server
// 第六步 init() Server初始化
getServer().init();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
if (Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE")) {
throw new java.lang.Error(e);
} else {
log.error("Catalina.start", e);
}
}
long t2 = System.nanoTime();
if(log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("Initialization processed in " + ((t2 - t1) / 1000000) + " ms");
}
}
3.5 第五步 getServer() 创建Server Catalina#load()
protected Server server = null;
public Server getServer() {
return server;
}
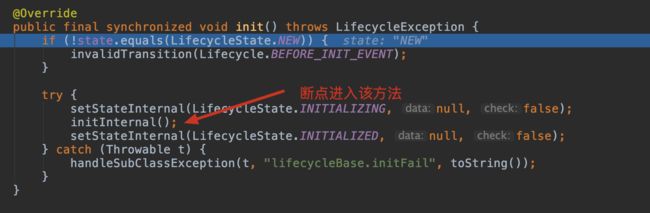
3.6 第六步 init() Server初始化 Catalina#load()
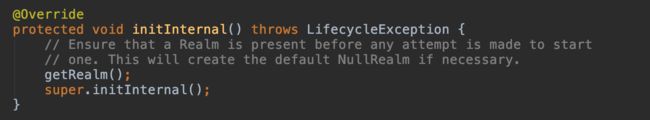
3.6.1 LifecycleBase#init()
3.6.2 StandardServer#initInternal()
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
// Register global String cache
// Note although the cache is global, if there are multiple Servers
// present in the JVM (may happen when embedding) then the same cache
// will be registered under multiple names
onameStringCache = register(new StringCache(), "type=StringCache");
// Register the MBeanFactory
MBeanFactory factory = new MBeanFactory();
factory.setContainer(this);
onameMBeanFactory = register(factory, "type=MBeanFactory");
// Register the naming resources
globalNamingResources.init();
// Populate the extension validator with JARs from common and shared
// class loaders
if (getCatalina() != null) {
ClassLoader cl = getCatalina().getParentClassLoader();
// Walk the class loader hierarchy. Stop at the system class loader.
// This will add the shared (if present) and common class loaders
while (cl != null && cl != ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()) {
if (cl instanceof URLClassLoader) {
URL[] urls = ((URLClassLoader) cl).getURLs();
for (URL url : urls) {
if (url.getProtocol().equals("file")) {
try {
File f = new File (url.toURI());
if (f.isFile() &&
f.getName().endsWith(".jar")) {
ExtensionValidator.addSystemResource(f);
}
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
// Ignore
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
}
cl = cl.getParent();
}
}
// Initialize our defined Services
// 第七步 init() Service初始化
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].init();
}
}
3.7 第七步 init() Service初始化
3.7.1 LifecycleBase#init()
3.7.2 StandardService#initInternal()
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
if (engine != null) {
// 第八步 init() Engine初始化
engine.init();
}
// Initialize any Executors
for (Executor executor : findExecutors()) {
if (executor instanceof JmxEnabled) {
((JmxEnabled) executor).setDomain(getDomain());
}
// 第十一步 init() Executor初始化
executor.init();
}
// Initialize mapper listener
mapperListener.init();
// Initialize our defined Connectors
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
for (Connector connector : connectors) {
try {
// 第十二步 init() Connector初始化
connector.init();
} catch (Exception e) {
String message = sm.getString(
"standardService.connector.initFailed", connector);
log.error(message, e);
if (Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE"))
throw new LifecycleException(message);
}
}
}
}
3.8 第八步 init() Engine初始化
3.8.1 StandardEngine#initInternal()
3.8.2 ContainerBase#initInternal()
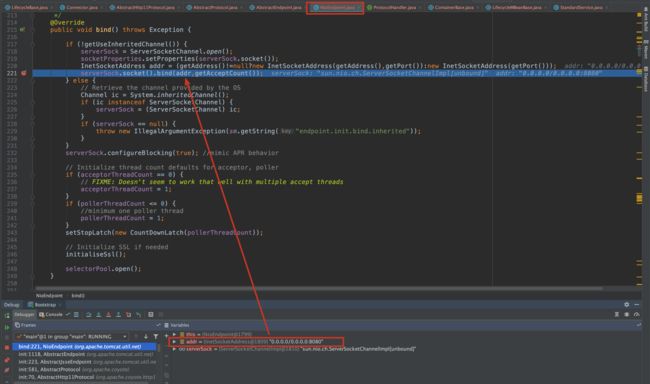
3.9 第十二步 init() Connector初始化 Connector#initInternal()
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
// Initialize adapter
// CoyoteAdapter是连接器转发的一个组件,把request对象转换成ServletRequest对象 (适配器的设计模式)
adapter = new CoyoteAdapter(this);
// ProtocolHandler里有EndPoint和Processor,需要使用adapter。
protocolHandler.setAdapter(adapter);
// Make sure parseBodyMethodsSet has a default
if (null == parseBodyMethodsSet) {
setParseBodyMethods(getParseBodyMethods());
}
if (protocolHandler.isAprRequired() && !AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable()) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerNoApr",
getProtocolHandlerClassName()));
}
if (AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable() && AprLifecycleListener.getUseOpenSSL() &&
protocolHandler instanceof AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol) {
AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol<?> jsseProtocolHandler =
(AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol<?>) protocolHandler;
if (jsseProtocolHandler.isSSLEnabled() &&
jsseProtocolHandler.getSslImplementationName() == null) {
// OpenSSL is compatible with the JSSE configuration, so use it if APR is available
jsseProtocolHandler.setSslImplementationName(OpenSSLImplementation.class.getName());
}
}
try {
// 第十三步 init() ProtocolHandler初始化
protocolHandler.init();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInitializationFailed"), e);
}
}
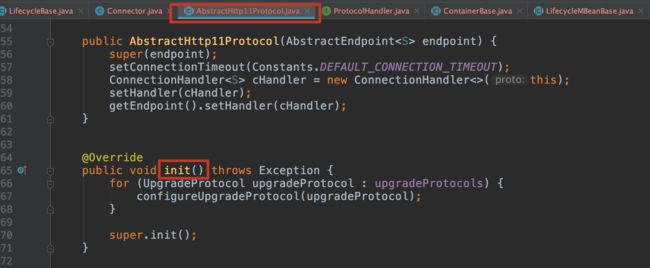
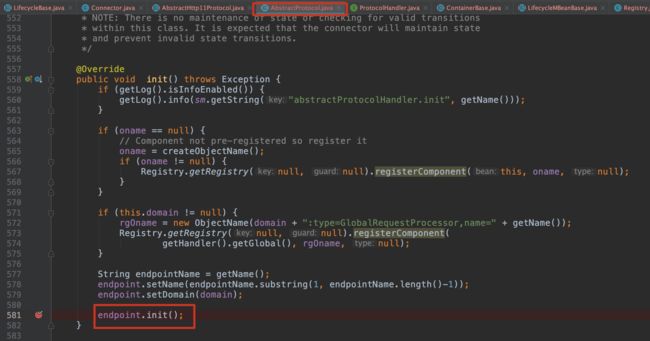
3.10 第十三步 init() ProtocolHandler初始化
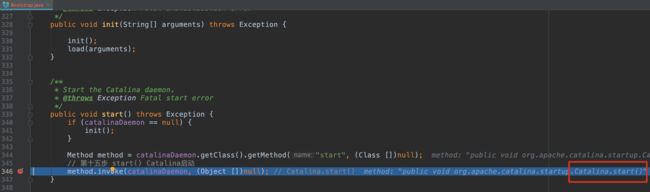
3.11 第十四步 start() Bootstrap启动 Bootstrap#main()
public void start() throws Exception {
if (catalinaDaemon == null) {
init();
}
Method method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("start", (Class [])null);
// 第十五步 start() Catalina启动
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, (Object [])null); // Catalina.start()
}
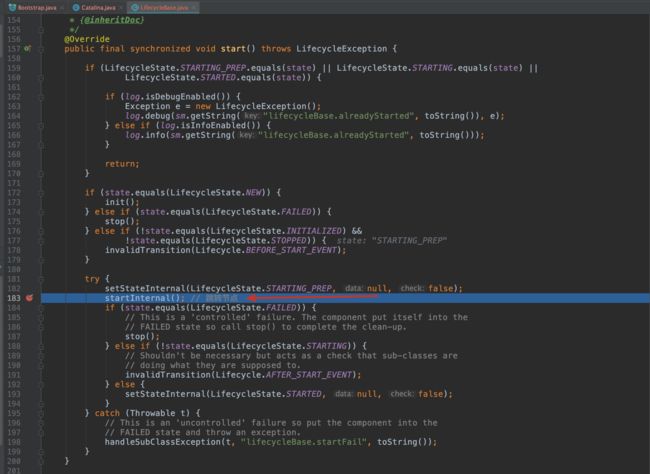
3.12 第十五步 start() Catalina启动 反射机制 Catalina#start()
3.13 第十六步 start() Server启动
public void start() {
if (getServer() == null) {
load();
}
if (getServer() == null) {
log.fatal("Cannot start server. Server instance is not configured.");
return;
}
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
// Start the new server
try {
// 第十六步 start() Server启动
getServer().start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.fatal(sm.getString("catalina.serverStartFail"), e);
try {
getServer().destroy();
} catch (LifecycleException e1) {
log.debug("destroy() failed for failed Server ", e1);
}
return;
}
long t2 = System.nanoTime();
if(log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("Server startup in " + ((t2 - t1) / 1000000) + " ms");
}
// Register shutdown hook
if (useShutdownHook) {
if (shutdownHook == null) {
shutdownHook = new CatalinaShutdownHook();
}
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(shutdownHook);
// If JULI is being used, disable JULI's shutdown hook since
// shutdown hooks run in parallel and log messages may be lost
// if JULI's hook completes before the CatalinaShutdownHook()
LogManager logManager = LogManager.getLogManager();
if (logManager instanceof ClassLoaderLogManager) {
((ClassLoaderLogManager) logManager).setUseShutdownHook(
false);
}
}
if (await) {
await();
stop();
}
}
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
fireLifecycleEvent(CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null);
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
globalNamingResources.start();
// Start our defined Services
// 第十七步 start() Service启动
synchronized (servicesLock) {
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].start();
}
}
}
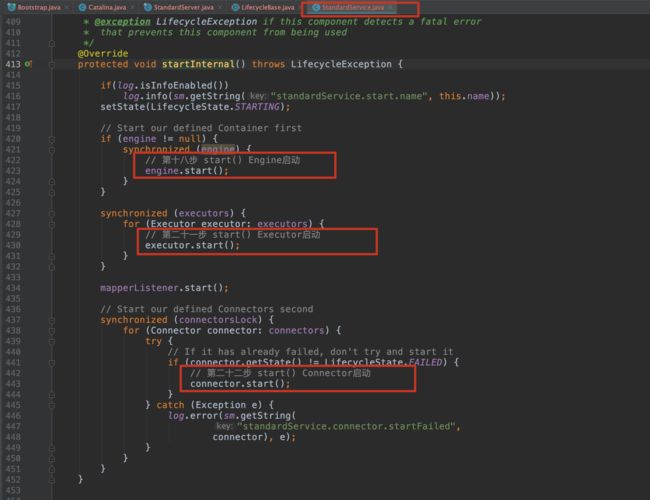
engine和executor的启动我们就不分析了哈,和前面的初始化类似,我们来看下connector的启动方式,继续往下分析。
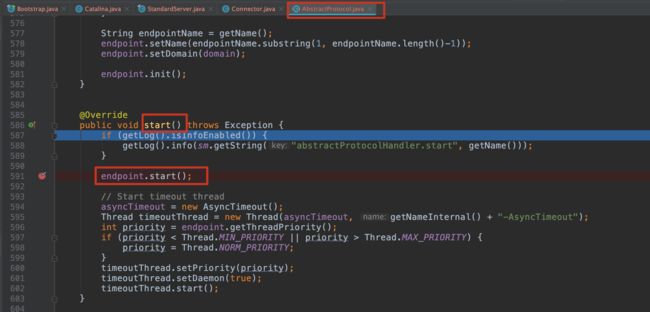
3.15 第二十二步 start() Connector启动
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Validate settings before starting
if (getPort() < 0) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString(
"coyoteConnector.invalidPort", Integer.valueOf(getPort())));
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
try {
// 第二十三步 start() ProtocolHandler启动
protocolHandler.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerStartFailed"), e);
}
}
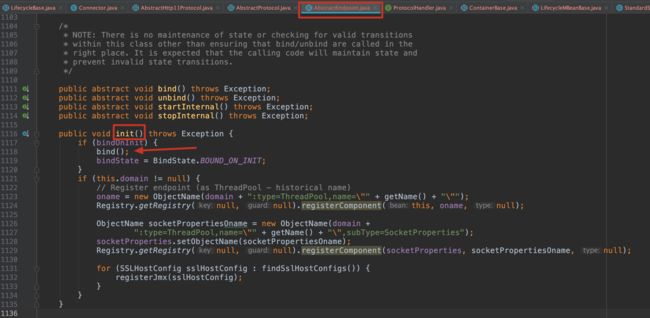
3.16 第二十三步 start() ProtocolHandler启动
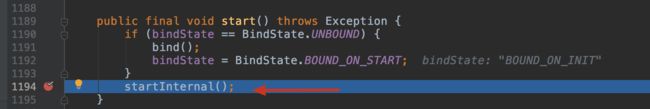
public final void start() throws Exception {
if (bindState == BindState.UNBOUND) {
bind();
bindState = BindState.BOUND_ON_START;
}
startInternal();
}
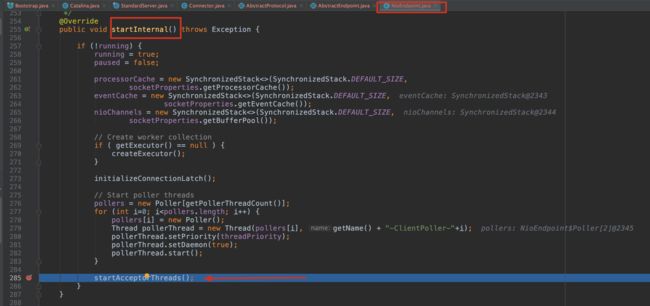
// 初始化只是监听了端口,启动start要启动监听,也就是startAcceptorThreads方法
protected final void startAcceptorThreads() {
int count = getAcceptorThreadCount();
acceptors = new Acceptor[count];
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
acceptors[i] = createAcceptor();
String threadName = getName() + "-Acceptor-" + i;
acceptors[i].setThreadName(threadName);
Thread t = new Thread(acceptors[i], threadName);
t.setPriority(getAcceptorThreadPriority());
t.setDaemon(getDaemon());
t.start();
}
}
@Override
protected AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor createAcceptor() {
return new Acceptor();
}
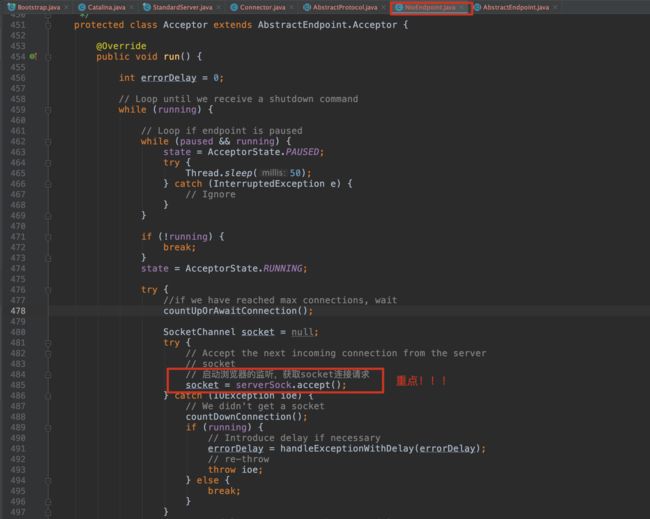
protected class Acceptor extends AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor {
@Override
public void run() {
int errorDelay = 0;
// Loop until we receive a shutdown command
while (running) {
// Loop if endpoint is paused
while (paused && running) {
state = AcceptorState.PAUSED;
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
if (!running) {
break;
}
state = AcceptorState.RUNNING;
try {
//if we have reached max connections, wait
countUpOrAwaitConnection();
SocketChannel socket = null;
try {
// Accept the next incoming connection from the server
// socket
// 启动浏览器的监听,获取socket连接请求
socket = serverSock.accept();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
// We didn't get a socket
countDownConnection();
if (running) {
// Introduce delay if necessary
errorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay);
// re-throw
throw ioe;
} else {
break;
}
}
// Successful accept, reset the error delay
errorDelay = 0;
// Configure the socket
if (running && !paused) {
// setSocketOptions() will hand the socket off to
// an appropriate processor if successful
if (!setSocketOptions(socket)) {
closeSocket(socket);
}
} else {
closeSocket(socket);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), t);
}
}
state = AcceptorState.ENDED;
}
private void closeSocket(SocketChannel socket) {
countDownConnection();
try {
socket.socket().close();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("endpoint.err.close"), ioe);
}
}
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("endpoint.err.close"), ioe);
}
}
}
}
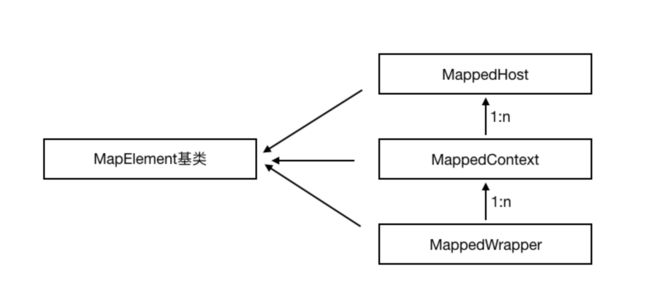
4、Mapper组件体系结构
至此,我们的Tomcat 源码构建以及源码剖析就到此结束了,其实这里源码分析的启动流程机制的源码,有时间的话可以再分析下请求处理机制的源码。