(四十九)Android O Wifi中的状态模式-WifiStateMachine的状态初始化
前言:WifiController和WifiStateMachine中都用到了状态模式,据《Head First设计模式》所讲状态模式就是封装基于状态的行为,并将行为委托到当前状态。
PS:如果条件允许的话,可以先学习下《Head First设计模式》的第十章状态模式,讲的很好。
或者参考https://blog.csdn.net/shuangde800/article/details/10132825(这篇文章和《Head First设计模式》讲的例子是一样的,配图也一样,但没有书全)
1.状态模式
状态模式允许对象在内部状态改变时改变它的行为,对象看起来好像修改了它的类。这个模式将状态封装成为独立的类,并将动作委托到代表当前状态的对象,我们知道行为会随着内部状态而改变。从客户的视角来看,如果说你使用的对象能够完全改变它的行为,那么你会觉得,这个对象实际上是从别的类实例化而来的。然而,实际上,你知道我们实在使用组合通过简单引用不同的状态对象来造成类改变的假象。
状态模式使用分三步:
- 首先,我们定义一个state接口,在这个接口内,糖果机的每个动作都有一个对应的方法。
- 然后为机器中的每个状态实现状态类。这些类将负责在对应的状态下进行机器的行为。
- 最后,我们要摆脱旧的条件代码,取而代之的方式是,将动作委托到状态类。
2.WifiStateMachine中的状态模式
WifiController和WifiStateMachine中都用到了状态模式,它们都继承自同一个类,StateMachine,状态模式的初始化和状态变换逻辑是一样的,就挑WifiStateMachine学习一下状态模式。
状态模式代码相关代码是存放在WifiStateMachine的构造方法里的,主要如下
// CHECKSTYLE:OFF IndentationCheck
addState(mDefaultState);
addState(mInitialState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSupplicantStartingState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSupplicantStartedState, mDefaultState);
addState(mScanModeState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mConnectModeState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mL2ConnectedState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mObtainingIpState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mConnectedState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mRoamingState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mDisconnectingState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mDisconnectedState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mWpsRunningState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mWaitForP2pDisableState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mSupplicantStoppingState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSoftApState, mDefaultState);
// CHECKSTYLE:ON IndentationCheck
setInitialState(mInitialState);
setLogRecSize(NUM_LOG_RECS_NORMAL);
setLogOnlyTransitions(false);
//start the state machine
start();
2.1 状态模式的添加
// CHECKSTYLE:OFF IndentationCheck
addState(mDefaultState);
addState(mInitialState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSupplicantStartingState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSupplicantStartedState, mDefaultState);
addState(mScanModeState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mConnectModeState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mL2ConnectedState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mObtainingIpState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mConnectedState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mRoamingState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mDisconnectingState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mDisconnectedState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mWpsRunningState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mWaitForP2pDisableState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mSupplicantStoppingState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSoftApState, mDefaultState);
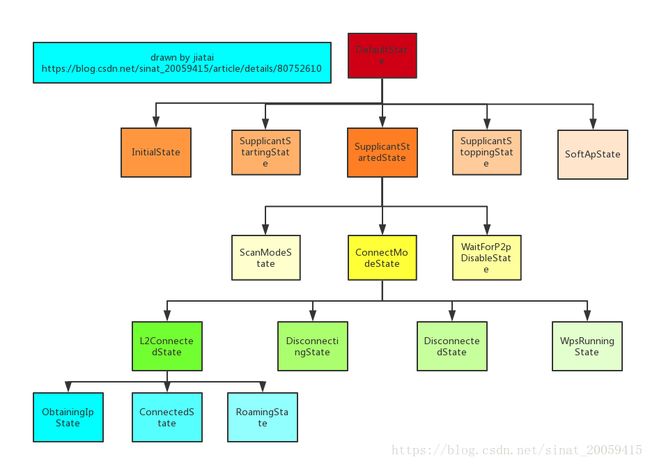
// CHECKSTYLE:ON IndentationCheck或许注意到了addState会有不同的缩进,这其实是StateMachine的状态模式多了个父类的缘故,普通的状态模式就几个状态类,状态类直接只有转换的关系,在地位上是均等的。但是StateMachine中状态类是有父类的,是有层级关系的,用数据结构表示的话就和树一样,父类往下衍生。画成树状图如下所示:
StateMachine.java
/**
* Add a new state to the state machine
* @param state the state to add
* @param parent the parent of state
*/
public final void addState(State state, State parent) {
mSmHandler.addState(state, parent);
}SmHandler是StateMachine的内部类。
/**
* Add a new state to the state machine. Bottom up addition
* of states is allowed but the same state may only exist
* in one hierarchy.
*
* @param state the state to add
* @param parent the parent of state
* @return stateInfo for this state
*/
private final StateInfo addState(State state, State parent) {
if (mDbg) {
mSm.log("addStateInternal: E state=" + state.getName() + ",parent="
+ ((parent == null) ? "" : parent.getName()));
}
StateInfo parentStateInfo = null;
if (parent != null) {
parentStateInfo = mStateInfo.get(parent);
if (parentStateInfo == null) {
// Recursively add our parent as it's not been added yet.
parentStateInfo = addState(parent, null);
}
}
StateInfo stateInfo = mStateInfo.get(state);
if (stateInfo == null) {
stateInfo = new StateInfo();
mStateInfo.put(state, stateInfo);
}
// Validate that we aren't adding the same state in two different hierarchies.
if ((stateInfo.parentStateInfo != null)
&& (stateInfo.parentStateInfo != parentStateInfo)) {
throw new RuntimeException("state already added");
}
stateInfo.state = state;
stateInfo.parentStateInfo = parentStateInfo;
stateInfo.active = false;
if (mDbg) mSm.log("addStateInternal: X stateInfo: " + stateInfo);
return stateInfo;
}看下StateInfo这个类,也是StateMachine的内部类
/**
* Information about a state.
* Used to maintain the hierarchy.
*/
private class StateInfo {
/** The state */
State state;
/** The parent of this state, null if there is no parent */
StateInfo parentStateInfo;
/** True when the state has been entered and on the stack */
boolean active;
/**
* Convert StateInfo to string
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return "state=" + state.getName() + ",active=" + active + ",parent="
+ ((parentStateInfo == null) ? "null" : parentStateInfo.state.getName());
}
}这个类就是记录了当前state的state及其父类state,类似于单链表。再结合上面的代码可以看到
/** The map of all of the states in the state machine */
private HashMap mStateInfo = new HashMap(); 这个hashmap将所有的stateinfo存放起来,其中记录了每个state的stateinfo信息,也就是state/parentStateInfo/active,最终汇聚成了一个树状结构。
再贴一下之前的树状图:
2.2 初始状态的设置
setInitialState(mInitialState);继而调用到SmHandler
/**
* Set the initial state. This must be invoked before
* and messages are sent to the state machine.
*
* @param initialState is the state which will receive the first message.
*/
public final void setInitialState(State initialState) {
mSmHandler.setInitialState(initialState);
} /** @see StateMachine#setInitialState(State) */
private final void setInitialState(State initialState) {
if (mDbg) mSm.log("setInitialState: initialState=" + initialState.getName());
mInitialState = initialState;
}这就是初始化了一个mInitialState这个成员变量,供以后状态变迁的时候知道第一个状态是什么。
2.3 状态机的启动
//start the state machine
start();调用到StateMachine的start方法:
/**
* Start the state machine.
*/
public void start() {
// mSmHandler can be null if the state machine has quit.
SmHandler smh = mSmHandler;
if (smh == null) return;
/** Send the complete construction message */
smh.completeConstruction();
} /**
* Complete the construction of the state machine.
*/
private final void completeConstruction() {
if (mDbg) mSm.log("completeConstruction: E");
/**
* Determine the maximum depth of the state hierarchy
* so we can allocate the state stacks.
*/
int maxDepth = 0;
for (StateInfo si : mStateInfo.values()) {
int depth = 0;
for (StateInfo i = si; i != null; depth++) {
i = i.parentStateInfo;
}
if (maxDepth < depth) {
maxDepth = depth;
}
}
if (mDbg) mSm.log("completeConstruction: maxDepth=" + maxDepth);
mStateStack = new StateInfo[maxDepth];
mTempStateStack = new StateInfo[maxDepth];
setupInitialStateStack();
/** Sending SM_INIT_CMD message to invoke enter methods asynchronously */
sendMessageAtFrontOfQueue(obtainMessage(SM_INIT_CMD, mSmHandlerObj));
if (mDbg) mSm.log("completeConstruction: X");
}遍历树的最大深度,从上面的树状图我们可以立刻得到maxDepth是5。然后初始化两个StateInfo的集合,mStateStack和mTempStateStack。
private final void setupInitialStateStack() {
if (mDbg) {
mSm.log("setupInitialStateStack: E mInitialState=" + mInitialState.getName());
}
StateInfo curStateInfo = mStateInfo.get(mInitialState);
for (mTempStateStackCount = 0; curStateInfo != null; mTempStateStackCount++) {
mTempStateStack[mTempStateStackCount] = curStateInfo;
curStateInfo = curStateInfo.parentStateInfo;
}
// Empty the StateStack
mStateStackTopIndex = -1;
moveTempStateStackToStateStack();
}setupInitialStateStack将初始状态及其父类的StateInfo存放在mTempStateStack这个栈里面。
从树状图可以知道存放了两个成员:mInitialState和mDefaultState
/**
* Move the contents of the temporary stack to the state stack
* reversing the order of the items on the temporary stack as
* they are moved.
*
* @return index into mStateStack where entering needs to start
*/
private final int moveTempStateStackToStateStack() {
int startingIndex = mStateStackTopIndex + 1;
int i = mTempStateStackCount - 1;
int j = startingIndex;
while (i >= 0) {
if (mDbg) mSm.log("moveTempStackToStateStack: i=" + i + ",j=" + j);
mStateStack[j] = mTempStateStack[i];
j += 1;
i -= 1;
}
mStateStackTopIndex = j - 1;
if (mDbg) {
mSm.log("moveTempStackToStateStack: X mStateStackTop=" + mStateStackTopIndex
+ ",startingIndex=" + startingIndex + ",Top="
+ mStateStack[mStateStackTopIndex].state.getName());
}
return startingIndex;
}这里将mTempStateStackTopIndex倒叙插入到mStateStack这个集合中去。结合之前的集合就是将mDefaultState和mInitialState依次插入。mStateStackTopIndex这个值初始化是-1,后面依次增加,移完了之后再把多加的1减掉。
// Empty the StateStack
mStateStackTopIndex = -1;再看下这个是干嘛的:
/** Sending SM_INIT_CMD message to invoke enter methods asynchronously */
sendMessageAtFrontOfQueue(obtainMessage(SM_INIT_CMD, mSmHandlerObj));发送一个SM_INIT_CMD的消息,那负责处理的呢?
/**
* Handle messages sent to the state machine by calling
* the current state's processMessage. It also handles
* the enter/exit calls and placing any deferred messages
* back onto the queue when transitioning to a new state.
*/
@Override
public final void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (!mHasQuit) {
if (mSm != null && msg.what != SM_INIT_CMD && msg.what != SM_QUIT_CMD) {
mSm.onPreHandleMessage(msg);
}
if (mDbg) mSm.log("handleMessage: E msg.what=" + msg.what);
/** Save the current message */
mMsg = msg;
/** State that processed the message */
State msgProcessedState = null;
if (mIsConstructionCompleted || (mMsg.what == SM_QUIT_CMD)) {
/** Normal path */
msgProcessedState = processMsg(msg);
} else if (!mIsConstructionCompleted && (mMsg.what == SM_INIT_CMD)
&& (mMsg.obj == mSmHandlerObj)) {
/** Initial one time path. */
mIsConstructionCompleted = true;
invokeEnterMethods(0);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("StateMachine.handleMessage: "
+ "The start method not called, received msg: " + msg);
}
performTransitions(msgProcessedState, msg);
// We need to check if mSm == null here as we could be quitting.
if (mDbg && mSm != null) mSm.log("handleMessage: X");
if (mSm != null && msg.what != SM_INIT_CMD && msg.what != SM_QUIT_CMD) {
mSm.onPostHandleMessage(msg);
}
}
}由于misConstructionCompleted没有初始化,默认是false,就走到下面的流程中去。
} else if (!mIsConstructionCompleted && (mMsg.what == SM_INIT_CMD)
&& (mMsg.obj == mSmHandlerObj)) {
/** Initial one time path. */
mIsConstructionCompleted = true;
invokeEnterMethods(0);
} /**
* Invoke the enter method starting at the entering index to top of state stack
*/
private final void invokeEnterMethods(int stateStackEnteringIndex) {
for (int i = stateStackEnteringIndex; i <= mStateStackTopIndex; i++) {
if (stateStackEnteringIndex == mStateStackTopIndex) {
// Last enter state for transition
mTransitionInProgress = false;
}
if (mDbg) mSm.log("invokeEnterMethods: " + mStateStack[i].state.getName());
mStateStack[i].state.enter();
mStateStack[i].active = true;
}
mTransitionInProgress = false; // ensure flag set to false if no methods called
}这里可以发现StateMachine的状态模式里的enter方法是先调用父类的,再调用子类的。
我们看下这两个状态的enter方法是做什么的吧:
DefaultState的enter是空的,那看下InitialState
class InitialState extends State {
private void cleanup() {
// Tearing down the client interfaces below is going to stop our supplicant.
mWifiMonitor.stopAllMonitoring();
mDeathRecipient.unlinkToDeath();
mWifiNative.tearDown();
}
@Override
public void enter() {
mWifiStateTracker.updateState(WifiStateTracker.INVALID);
cleanup();
}看起来大概意思就是初始化了嘛,就所有都停掉,重新开始。
/**
* Stop Monitoring for wpa_supplicant events.
*
* TODO: Add unit tests for these once we remove the legacy code.
*/
public synchronized void stopAllMonitoring() {
mConnected = false;
setMonitoringNone();
} private void setMonitoringNone() {
for (String iface : mMonitoringMap.keySet()) {
setMonitoring(iface, false);
}
} /**
* Enable/Disable monitoring for the provided iface.
*
* @param iface Name of the iface.
* @param enabled true to enable, false to disable.
*/
@VisibleForTesting
public void setMonitoring(String iface, boolean enabled) {
mMonitoringMap.put(iface, enabled);
}至于WiFiNative
/**
* Teardown all mode configurations in wifi native.
*
* 1. Stops the Wifi HAL.
* 2. Tears down all the interfaces from Wificond.
*/
public void tearDown() {
stopHalIfNecessary();
if (!mWificondControl.tearDownInterfaces()) {
// TODO(b/34859006): Handle failures.
Log.e(mTAG, "Failed to teardown interfaces from Wificond");
}
} /**
* Teardown all interfaces configured in wificond.
* @return Returns true on success.
*/
public boolean tearDownInterfaces() {
Log.d(TAG, "tearing down interfaces in wificond");
// Explicitly refresh the wificodn handler because |tearDownInterfaces()|
// could be used to cleanup before we setup any interfaces.
mWificond = mWifiInjector.makeWificond();
if (mWificond == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to get reference to wificond");
return false;
}
try {
if (mWificondScanner != null) {
mWificondScanner.unsubscribeScanEvents();
mWificondScanner.unsubscribePnoScanEvents();
}
mWificond.tearDownInterfaces();
// Refresh handlers
mClientInterface = null;
mWificondScanner = null;
mPnoScanEventHandler = null;
mScanEventHandler = null;
mApInterface = null;
return true;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to tear down interfaces due to remote exception");
}
return false;
} private IWifiScannerImpl mWificondScanner;
mWificondScanner = mClientInterface.getWifiScannerImpl();那IWifiScannerImpl是啥呢?只看到有个WifiScannerImpl的类,但对不上,全局搜了也没有对应实现,有可能在驱动那边了=-=先放着吧,待续。
3 总结
WifiStateMachine的状态模式初始化说到底就是组建一个树状结构,然后设置一个初始状态,继而调用初始状态的父类state和其的enter方法完成初始化流程。