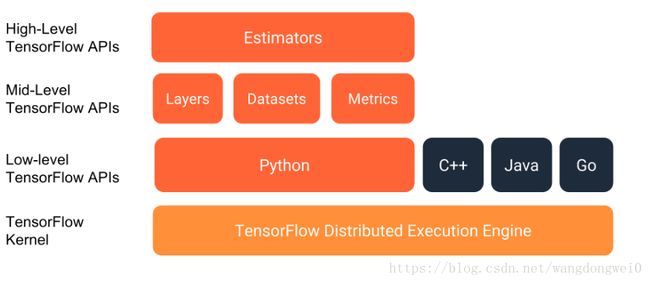
(tensorflow)——tf.estimator自定义估算器使用方法
文章结构
- 1.简介
- 2.自定义Estimator与pre-made Estimator
- 3.使用Pre-made Estimator
- 4.入门 Custom Estimator
- 4.1 Write an Input function
- 4.2 Create feature columns
- 4.3 Write a model function
- 4.3.1 Define the model
- Define the input layer
- Hidden Layers
- Output Layer
- 4.3.2 Implement training, evaluation, and prediction
- Predict
- Calculate the loss
- Evaluate
- Train
- 4.3.1 Define the model
- 5 实战 Custom Estimator
- step 1: 初始化一个tf.estimator.Estimator实例
- step 2: 写model_fn
- step 3: Define the model
- step 4: Implement training, evaluation, and prediction
- step 5: 开始训练
1 简介
在TensorFlow的UG中,他们强烈的建议在写Tensorflow程序时使用estimator的API,使用后发现的确好用!在github上一些开源程序也已经开始使用estimator,比如DeeplabV3+,关于DeeplabV3+的代码注释可以参考我的另一篇博客。
官方原话:
We strongly recommend writing TensorFlow programs with the following APIs:
· Estimators, which represent a complete model. The Estimator API provides methods to train the model, to judge the model’s accuracy, and to generate predictions.
· Datasets for Estimators, which build a data input pipeline. The Dataset API has methods to load and manipulate data, and feed it into your model. The Dataset API meshes well with the Estimators API.
TensorFlow官方文档对Estimator的定义是:High level tools for working with models.
它已经包含了一些内建的机器学习或者深度学习算法模型(Premade Estimators),比如:
BaselineClassifier
BaselineRegressor
BestExporter
BoostedTreesClassifier
BoostedTreesRegressor
DNNClassifier
DNNLinearCombinedClassifier
DNNLinearCombinedRegressor
DNNRegressor
我们可以直接使用上面的模型进行深度学习算法的验证和实现。
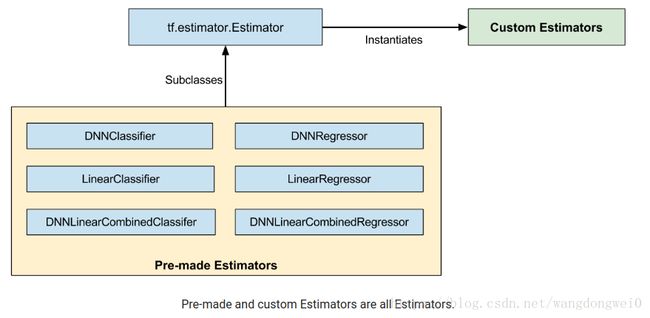
2 自定义Estimator与pre-made Estimator
pre-made Estimator是别人写好的模型(model_fn);自定义estimator需要自己设计模型
首先我们要对pre-made Estimator和custom Estimator的关系有一个清晰的理解:
3 使用Pre-made Estimator
我很少会用到pre-made Estimator,这里就不做介绍了,感兴趣可以参考官方UG
4 入门 Custom Estimator
我的另一篇博客中介绍了DeeplabV3+,源码中就是使用了Custom Estimator,这份源码是一个不错的实例。
此处我们首先另起炉灶,举一个更加简单的例子。之后再谈论DeeplabV3+这个程序。
4.1 Write an Input function
def train_input_fn(features, labels, batch_size):
"""An input function for training"""
# Convert the inputs to a Dataset.
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((dict(features), labels))
# Shuffle, repeat, and batch the examples.
dataset = dataset.shuffle(1000).repeat().batch(batch_size)
# Return the read end of the pipeline.
return dataset.make_one_shot_iterator().get_next()
这个输入函数建立了一个input pipline,每次提取batch大小的(features, labels)
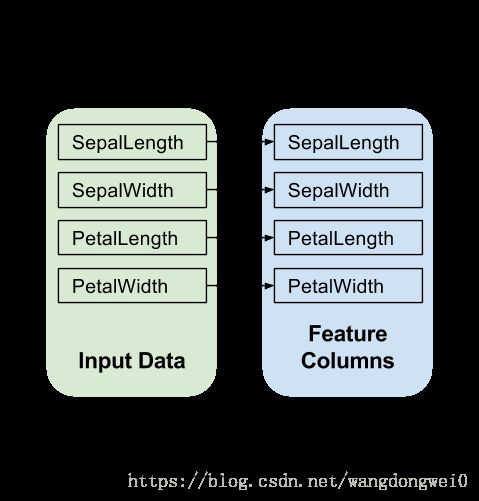
4.2 Create feature columns
我们必须定义模型的feature columns来明确我们的模型应该如何使用各个feature
# Feature columns describe how to use the input.
my_feature_columns = []
for key in train_x.keys():
my_feature_columns.append(tf.feature_column.numeric_column(key=key))
4.3 Write a model function
Custom Estimator应该和DNNClassifier等Pre-made Estimator具有相同的接口:
tf.estimator.Estimator(
model_fn, #模型函数
model_dir=None, #存储目录,训练和验证产生的文件都会存储在这个目录下
config=None, #设置参数对象,主要针对运行环境的一些设置
params=None, #超参数,将传递给model_fn使用
warm_start_from=None #热启动目录路径
)
其中最重要的就是model_fn了,它应该具有以下形式:
my_model(
features, #This is batch_features from input_fn
labels, #This is batch_labels from input_fn
mode, #An instance of tf.estimator.ModeKeys, train、evaluate或predict
params #超参数,对应上面Estimator传来的参数
)
4.3.1 Define the model
上面的4.3只是写了一个函数接口,我们还要进一步详细的定义模型。
4.3.1.1 Define the input layer
model_fn的第一行就应该调用 tf.feature_column.input_layer ,把feature dictionary和feature_columes导入模型中:
# Use `input_layer` to apply the feature columns.
net = tf.feature_column.input_layer(features, params['feature_columns'])
这句话建立了模型input layer并完成了feature columns中定义的转换
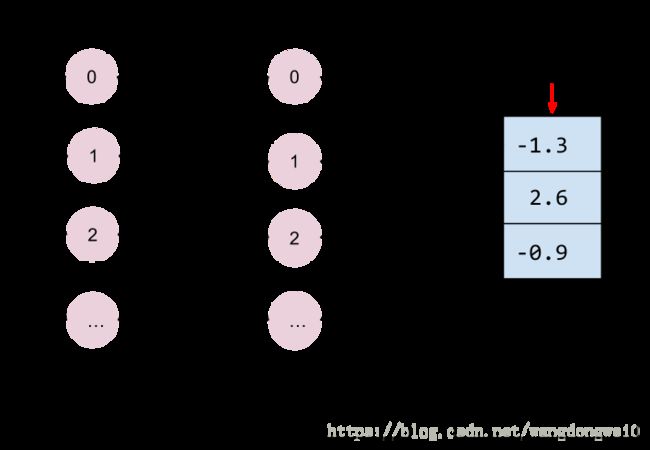
4.3.1.2 Hidden Layers
hidden layers不用多说,建立之后网络呈现如下结构

4.3.1.3 Output Layer
注意,activation=None;
units = params[‘n_classes’],这个实在构造estimator时就已经设定好了
我们把outlayer中的logits传入softmax,就可以输出概率分布。
# Compute logits (1 per class).
logits = tf.layers.dense(net, params['n_classes'], activation=None)
4.3.2 Implement training, evaluation, and prediction
到此为止,模型已经定义好了,我们要着手实现模型的training,evaluation,prediction等功能。
4.3.2.1 Predict
# Compute predictions.
predicted_classes = tf.argmax(logits, 1)
if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT:
predictions = {
'class_ids': predicted_classes[:, tf.newaxis],
'probabilities': tf.nn.softmax(logits),
'logits': logits,
}
return tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(mode, predictions=predictions)
4.3.2.2 Calculate the loss
this is the object that will be optimized !!!
train和evaluate都需要使用它
# Compute loss.
loss = tf.losses.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy(labels=labels, logits=logits)
4.3.2.3 Evaluate
tensorflow提供API去评价一个model的性能,比如tf.metrics
# Compute evaluation metrics.
accuracy = tf.metrics.accuracy(labels=labels,
predictions=predicted_classes,
name='acc_op')
如果我们还需要看其他的评价指标,比如roi等,可以把roi加入metrics字典中去。以下为完整写法。
metrics = {'accuracy': accuracy}
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', accuracy[1])
if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL:
return tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(
mode, loss=loss, eval_metric_ops=metrics)
4.3.2.4 Train
- 首先制定优化器
optimizer = tf.train.AdagradOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1)
- 然后确定train_op
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss, global_step=tf.train.get_global_step())
- 最后返回
return tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(mode, loss=loss, train_op=train_op)
5 实战 Custom Estimator
我们以上一篇博客-《(Deeplab V3+)——tensorflow-deeplab-v3-plus-master源码解读及tf.estimator实践》中的源码为例,介绍如何正确使用tf.estimator.Estimator类。
step 1: 初始化一个tf.estimator.Estimator实例
# Set up a RunConfig to only save checkpoints once per training cycle.
run_config = tf.estimator.RunConfig().replace(save_checkpoints_secs=1e9)
model = tf.estimator.Estimator(
model_fn=deeplab_model.deeplabv3_plus_model_fn,
model_dir=FLAGS.model_dir,
config=run_config,
params={
'output_stride': FLAGS.output_stride,
'batch_size': FLAGS.batch_size,
'base_architecture': FLAGS.base_architecture,
'pre_trained_model': FLAGS.pre_trained_model,
'batch_norm_decay': _BATCH_NORM_DECAY,
'num_classes': _NUM_CLASSES,
'tensorboard_images_max_outputs': FLAGS.tensorboard_images_max_outputs,
'weight_decay': FLAGS.weight_decay,
'learning_rate_policy': FLAGS.learning_rate_policy,
'num_train': _NUM_IMAGES['train'],
'initial_learning_rate': FLAGS.initial_learning_rate,
'max_iter': FLAGS.max_iter,
'end_learning_rate': FLAGS.end_learning_rate,
'power': _POWER,
'momentum': _MOMENTUM,
'freeze_batch_norm': FLAGS.freeze_batch_norm,
'initial_global_step': FLAGS.initial_global_step
})
step 2: 写model_fn
从上面estimator的初始化中:
model_fn=deeplab_model.deeplabv3_plus_model_fn
在deeplab_model.py中定义了该函数,可以看出该函数保持了model_fn应该有的接口
def deeplabv3_plus_model_fn(features, labels, mode, params):
"""Model function for PASCAL VOC."""
# features 是传进来用于训练网络的图像
if isinstance(features, dict):
features = features['feature']
#对图像的各通道进行减去平均值,属于预处理的一部分
images = tf.cast(
tf.map_fn(preprocessing.mean_image_addition, features),
tf.uint8)
step3 Define the model
定义模型同样在model_fn中
#使用generator函数生成网络
network = deeplab_v3_plus_generator(params['num_classes'],
params['output_stride'],
params['base_architecture'],
params['pre_trained_model'],
params['batch_norm_decay'])
#mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN
#在train模式下网络的输出
logits = network(features, mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN)
#根据logits得出各像素点属于的类别
pred_classes = tf.expand_dims(tf.argmax(logits, axis=3, output_type=tf.int32), axis=3)
network使用deeplab_v3_plus_generator函数生成
def deeplab_v3_plus_generator(num_classes,
output_stride,
base_architecture,
pre_trained_model,
batch_norm_decay,
data_format='channels_last'):
"""Generator for DeepLab v3 plus models.
Args:
num_classes: The number of possible classes for image classification.
output_stride: The ResNet unit's stride. Determines the rates for atrous convolution.
the rates are (6, 12, 18) when the stride is 16, and doubled when 8.
base_architecture: The architecture of base Resnet building block.
pre_trained_model: The path to the directory that contains pre-trained models.
batch_norm_decay: The moving average decay when estimating layer activation
statistics in batch normalization.
data_format: The input format ('channels_last', 'channels_first', or None).
If set to None, the format is dependent on whether a GPU is available.
Only 'channels_last' is supported currently.
Returns:
The model function that takes in `inputs` and `is_training` and
returns the output tensor of the DeepLab v3 model.
"""
if data_format is None:
# data_format = (
# 'channels_first' if tf.test.is_built_with_cuda() else 'channels_last')
pass
if batch_norm_decay is None:
batch_norm_decay = _BATCH_NORM_DECAY
if base_architecture not in ['resnet_v2_50', 'resnet_v2_101']:
raise ValueError("'base_architrecture' must be either 'resnet_v2_50' or 'resnet_v2_101'.")
#确定模型的主体网络是resnet50还是resnet101,这里使用的是 from tensorflow.contrib.slim.nets import resnet_v2
#源码查看网址:https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/contrib/slim/python/slim/nets/resnet_v2.py
if base_architecture == 'resnet_v2_50':
base_model = resnet_v2.resnet_v2_50
else:
base_model = resnet_v2.resnet_v2_101
def model(inputs, is_training):
"""Constructs the ResNet model given the inputs."""
if data_format == 'channels_first':
# Convert the inputs from channels_last (NHWC) to channels_first (NCHW).
# This provides a large performance boost on GPU. See
# https://www.tensorflow.org/performance/performance_guide#data_formats
inputs = tf.transpose(inputs, [0, 3, 1, 2])
# tf.logging.info('net shape: {}'.format(inputs.shape))
# encoder
with tf.contrib.slim.arg_scope(resnet_v2.resnet_arg_scope(batch_norm_decay=batch_norm_decay)):
#resnet_v2的返回值是net, end_points
#其中net是 A rank-4 tensor of size [batch, height_out, width_out, channels_out].
#end_points中记录了网络中不同功能的组件,以字典形式
#对于deeplabv3+,这里的logits也就是net,是不需要的,因为我们还需要对这个网络进行变形,得到正确的输出
logits, end_points = base_model(inputs,
num_classes=None,
is_training=is_training,
global_pool=False,
output_stride=output_stride)
if is_training:
#实际上我们不需要base_model的logits节点,所以这部分设置为不恢复
#可以参考博客《使用slim从ckpt里导出指定层的参数》:https://www.jianshu.com/p/160620fb2580
exclude = [base_architecture + '/logits', 'global_step']
variables_to_restore = tf.contrib.slim.get_variables_to_restore(exclude=exclude)
#pre_trained_model是存放预训练模型的路径,参数用来fine-tune
tf.train.init_from_checkpoint(pre_trained_model,
{v.name.split(':')[0]: v for v in variables_to_restore})
inputs_size = tf.shape(inputs)[1:3]
#去除resnet的block4的输出,也就是最后一个卷积层的输出
net = end_points[base_architecture + '/block4']
#使用 空洞空间金字塔池化
encoder_output = atrous_spatial_pyramid_pooling(net, output_stride, batch_norm_decay, is_training)
#设计 decoder解码器
with tf.variable_scope("decoder"):
with tf.contrib.slim.arg_scope(resnet_v2.resnet_arg_scope(batch_norm_decay=batch_norm_decay)):
with arg_scope([layers.batch_norm], is_training=is_training):
with tf.variable_scope("low_level_features"):
low_level_features = end_points[base_architecture + '/block1/unit_3/bottleneck_v2/conv1']
low_level_features = layers_lib.conv2d(low_level_features, 48,
[1, 1], stride=1, scope='conv_1x1')
low_level_features_size = tf.shape(low_level_features)[1:3]
with tf.variable_scope("upsampling_logits"):
net = tf.image.resize_bilinear(encoder_output, low_level_features_size, name='upsample_1')
net = tf.concat([net, low_level_features], axis=3, name='concat')
net = layers_lib.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], stride=1, scope='conv_3x3_1')
net = layers_lib.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], stride=1, scope='conv_3x3_2')
net = layers_lib.conv2d(net, num_classes, [1, 1], activation_fn=None, normalizer_fn=None, scope='conv_1x1')
logits = tf.image.resize_bilinear(net, inputs_size, name='upsample_2')
return logits
return model
最后返回的是logits,至此网络就设计好了。
step4 Implement training, evaluation, and prediction
重新回到model_fn函数中,我们还需要实现training, evaluation, prediction功能
- For mode == ModeKeys.TRAIN: required fields are loss and train_op.
- For mode == ModeKeys.EVAL: required field is loss.
- For mode == ModeKeys.PREDICT: required fields are predictions.
*1、Prediction
#解码预测得到的labels,即pred_classes
#得到RGB图像,每个类别不同颜色
pred_decoded_labels = tf.py_func(preprocessing.decode_labels,
[pred_classes, params['batch_size'], params['num_classes']],
tf.uint8)
# 首先 定义predictions供predict模式使用
predictions = {
'classes': pred_classes,
'probabilities': tf.nn.softmax(logits, name='softmax_tensor'),
'decoded_labels': pred_decoded_labels
}
if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT:
# Delete 'decoded_labels' from predictions because custom functions produce error when used with saved_model
predictions_without_decoded_labels = predictions.copy()
del predictions_without_decoded_labels['decoded_labels']
return tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(
mode=mode,
predictions=predictions,
export_outputs={
'preds': tf.estimator.export.PredictOutput(
predictions_without_decoded_labels)
})
2、training
gt_decoded_labels = tf.py_func(preprocessing.decode_labels,
[labels, params['batch_size'], params['num_classes']], tf.uint8)
labels = tf.squeeze(labels, axis=3) # reduce the channel dimension.
logits_by_num_classes = tf.reshape(logits, [-1, params['num_classes']])
labels_flat = tf.reshape(labels, [-1, ])
valid_indices = tf.to_int32(labels_flat <= params['num_classes'] - 1)
valid_logits = tf.dynamic_partition(logits_by_num_classes, valid_indices, num_partitions=2)[1]
valid_labels = tf.dynamic_partition(labels_flat, valid_indices, num_partitions=2)[1]
preds_flat = tf.reshape(pred_classes, [-1, ])
valid_preds = tf.dynamic_partition(preds_flat, valid_indices, num_partitions=2)[1]
confusion_matrix = tf.confusion_matrix(valid_labels, valid_preds, num_classes=params['num_classes'])
predictions['valid_preds'] = valid_preds
predictions['valid_labels'] = valid_labels
predictions['confusion_matrix'] = confusion_matrix
cross_entropy = tf.losses.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy(
logits=valid_logits, labels=valid_labels)
# Create a tensor named cross_entropy for logging purposes.
tf.identity(cross_entropy, name='cross_entropy')
tf.summary.scalar('cross_entropy', cross_entropy)
if not params['freeze_batch_norm']:
train_var_list = [v for v in tf.trainable_variables()]
else:
train_var_list = [v for v in tf.trainable_variables()
if 'beta' not in v.name and 'gamma' not in v.name]
# Add weight decay to the loss.
with tf.variable_scope("total_loss"):
loss = cross_entropy + params.get('weight_decay', _WEIGHT_DECAY) * tf.add_n(
[tf.nn.l2_loss(v) for v in train_var_list])
# loss = tf.losses.get_total_loss() # obtain the regularization losses as well
if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN:
tf.summary.image('images',
tf.concat(axis=2, values=[images, gt_decoded_labels, pred_decoded_labels]),
max_outputs=params['tensorboard_images_max_outputs']) # Concatenate row-wise.
global_step = tf.train.get_or_create_global_step()
if params['learning_rate_policy'] == 'piecewise':
# Scale the learning rate linearly with the batch size. When the batch size
# is 128, the learning rate should be 0.1.
initial_learning_rate = 0.1 * params['batch_size'] / 128
batches_per_epoch = params['num_train'] / params['batch_size']
# Multiply the learning rate by 0.1 at 100, 150, and 200 epochs.
boundaries = [int(batches_per_epoch * epoch) for epoch in [100, 150, 200]]
values = [initial_learning_rate * decay for decay in [1, 0.1, 0.01, 0.001]]
learning_rate = tf.train.piecewise_constant(
tf.cast(global_step, tf.int32), boundaries, values)
elif params['learning_rate_policy'] == 'poly':
learning_rate = tf.train.polynomial_decay(
params['initial_learning_rate'],
tf.cast(global_step, tf.int32) - params['initial_global_step'],
params['max_iter'], params['end_learning_rate'], power=params['power'])
else:
raise ValueError('Learning rate policy must be "piecewise" or "poly"')
# Create a tensor named learning_rate for logging purposes
tf.identity(learning_rate, name='learning_rate')
tf.summary.scalar('learning_rate', learning_rate)
optimizer = tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(
learning_rate=learning_rate,
momentum=params['momentum'])
# Batch norm requires update ops to be added as a dependency to the train_op
update_ops = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS)
with tf.control_dependencies(update_ops):
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss, global_step, var_list=train_var_list)
else:
train_op = None
3、evaluation
连个评价指标:px_accuracy和mean_iou
accuracy = tf.metrics.accuracy(
valid_labels, valid_preds)
mean_iou = tf.metrics.mean_iou(valid_labels, valid_preds, params['num_classes'])
metrics = {'px_accuracy': accuracy, 'mean_iou': mean_iou}
# Create a tensor named train_accuracy for logging purposes
tf.identity(accuracy[1], name='train_px_accuracy')
tf.summary.scalar('train_px_accuracy', accuracy[1])
def compute_mean_iou(total_cm, name='mean_iou'):
"""Compute the mean intersection-over-union via the confusion matrix."""
sum_over_row = tf.to_float(tf.reduce_sum(total_cm, 0))
sum_over_col = tf.to_float(tf.reduce_sum(total_cm, 1))
cm_diag = tf.to_float(tf.diag_part(total_cm))
denominator = sum_over_row + sum_over_col - cm_diag
# The mean is only computed over classes that appear in the
# label or prediction tensor. If the denominator is 0, we need to
# ignore the class.
num_valid_entries = tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(
tf.not_equal(denominator, 0), dtype=tf.float32))
# If the value of the denominator is 0, set it to 1 to avoid
# zero division.
denominator = tf.where(
tf.greater(denominator, 0),
denominator,
tf.ones_like(denominator))
iou = tf.div(cm_diag, denominator)
for i in range(params['num_classes']):
tf.identity(iou[i], name='train_iou_class{}'.format(i))
tf.summary.scalar('train_iou_class{}'.format(i), iou[i])
# If the number of valid entries is 0 (no classes) we return 0.
result = tf.where(
tf.greater(num_valid_entries, 0),
tf.reduce_sum(iou, name=name) / num_valid_entries,
0)
return result
train_mean_iou = compute_mean_iou(mean_iou[1])
tf.identity(train_mean_iou, name='train_mean_iou')
tf.summary.scalar('train_mean_iou', train_mean_iou)
return tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(
mode=mode,
predictions=predictions,
loss=loss,
train_op=train_op,
eval_metric_ops=metrics)
至此我们的model_fn已经完整的建立好了,要开始训练了!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
step5 开始训练
#使用循环训练,共训练这么多个epoch
for _ in range(FLAGS.train_epochs // FLAGS.epochs_per_eval):
tensors_to_log = {
'learning_rate': 'learning_rate',
'cross_entropy': 'cross_entropy',
'train_px_accuracy': 'train_px_accuracy',
'train_mean_iou': 'train_mean_iou',
}
#每迭代10次,打印一次状态:learning_rate,cross_entropy,train_px_accuracy,train_mean_iou
logging_hook = tf.train.LoggingTensorHook(
tensors=tensors_to_log, every_n_iter=10)
train_hooks = [logging_hook]
eval_hooks = None
if FLAGS.debug:
debug_hook = tf_debug.LocalCLIDebugHook()
train_hooks.append(debug_hook)
eval_hooks = [debug_hook]
#开始训练,由于没有制定steps和max_iters,所以模型会一直训练,直到这个epoch都参与了训练
#train使用了tf.data API,可以参考我的另一篇博客:https://blog.csdn.net/wangdongwei0/article/details/82991048
tf.logging.info("Start training.")
model.train(
input_fn=lambda: input_fn(True, FLAGS.data_dir, FLAGS.batch_size, FLAGS.epochs_per_eval),
hooks=train_hooks,
# steps=1 # For debug
)
#每个epoch训练完后,开始验证训练结果
tf.logging.info("Start evaluation.")
# Evaluate the model and print results
eval_results = model.evaluate(
# Batch size must be 1 for testing because the images' size differs
input_fn=lambda: input_fn(False, FLAGS.data_dir, 1),
hooks=eval_hooks,
# steps=1 # For debug
)
print(eval_results)
#model.train使用了tf.data API,可以参考我的另一篇博客:https://blog.csdn.net/wangdongwei0/article/details/82991048
完!