概述
看Java NIO一篇文章的时候又看到了“异步非阻塞”这个概念,一直处于似懂非懂的状态,想解释下到底什么是异步 什么是非阻塞,感觉抓不住重点。决定仔细研究一下。
本文试图研究以下问题:
web server原理,bio的connector与nio的connector在架构上到底什么区别?
NIO的优势到底在哪里,是如何应用到实践中的?
同步/异步、阻塞/非阻塞到底是什么概念,引出的IO模型同步阻塞、同步非阻塞、异步阻塞、异步非阻塞的具体使用场景,适用的场景是怎样的?
bio nio也只是对内核的封装,Linux内核的支持是怎样的?再往下TCP的接口调用、参数的设置是否有异同?
这里就不浪费篇幅介绍基础,文中结论是学习、思考的记录 topic比较大,欢迎讨论
1. 数据的IO
1.1 IO模型
“一切皆文件”,Linux对于文件、字符设备、块设备、socket的访问都是以抽象为文件的方式进行。
Linux与Unix都提供了五种IO模型,在参考1 参考2中都涉及:
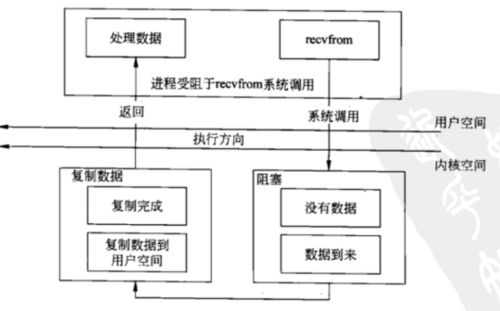
阻塞IO
非阻塞IO
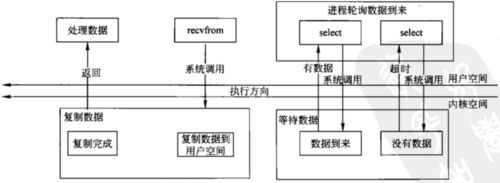
IO复用
信号驱动
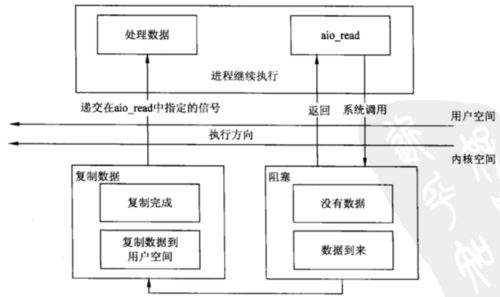
异步IO
但是在实际应用中,二、四很少使用。传统BIO使用1,Java NIO使用3,JDK7 提供了5的支持。
1.2 Java NIO被称为Non-block的疑问
Java NIO使用了事件驱动模型,以Linux为例 底层通过epoll支持,使用epoll的优点:
避免大量线程阻塞,避免浪费线程资源,避免线程上下文切换浪费CPU资源
打开的fd不受限制(还是受操作系统的限制但进程级不再受限)
IO效率不会随着fd数目增加而线性下降
使用mmap加速内核与用户空间消息传递
在参考3的最终模型中,称之为Non-block
但这里会造成混淆:
mainReactor、subReactor一直等待事件发生,是阻塞还是非阻塞?
ThreadPool中的worker一直处于wait状态,event发生收到Reactor的调度会触发后续操作,是阻塞还是非阻塞?
上面问题的答案貌似是阻塞。那为何叫这个模型为非阻塞?
我的理解是阻塞是对应用层而言,应用层并没有检测accept、read、write是否完成,而是等待调度所以叫非阻塞。避免应用层检测的好处上面已经提过 避免过多线程浪费资源、避免上下文切换
1.3 什么是异步
可以理解为应用程序调用了io函数后,继续执行,io操作完成后可以通过回调函数获取结果。
JDK7加入了对io的异步支持,如下面的例子:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
AsynchronousChannelGroup group = AsynchronousChannelGroup.withThreadPool(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10));
final AsynchronousServerSocketChannel server = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(group).bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8080));
server.accept(null, new CompletionHandler() {
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel channel, Void p_w_upload) {
server.accept(null, this);
try {
String now = new Date().toString();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(now.getBytes());
Future f = channel.write(buffer);
f.get();
channel.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Void p_w_upload) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
System.out.println("end........ ");
group.awaitTermination(Long.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
} 与此类似,使用多线程也可以实现异步。比如访问数据库,下游服务等会block主线程的操作,可以放在新的线程中执行。
JDK对异步的支持很早就出现了,JDK5就加入了concurrent包 对于多线程异步的支持:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//第一种方式
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Task task = new Task();
Future future = executor.submit(task);
executor.shutdown();
System.out.println("task运行结果"+future.get());
}
}
class Task implements Callable{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(3000);
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<100;i++)
sum += i;
return sum;
}
} 1.4 同步与异步
从上面的说明可以得出结论,实际应用中的IO模型:
同步阻塞:传统的BIO属于这种类型
同步非阻塞:使用IO复用(select epoll)。
异步非阻塞:使用AIO,基于回调或者阻塞等待异步操作完成后继续主程序。
2. Java NIO
2.1 核心概念
Channel
Buffer
Selector
2.2 NIO的优势
Nio与传统BIO相比的优势在于利用了IO多路复用
面向缓冲区
避免资源过高占用,BIO中等待线程过高会引发两类问题:一是占用过多线程资源,二是过多线程导致的上下问切换浪费CPU资源
高并发连接时,性能不会线性下降
epoll可以通过mmap加速内核空间与用户空间消息传递
文件锁
3. NIO应用
3.1 Tomcat connector
代码版本:6.0.44
tomcat实现NIOEndPoint提供对NIO的支持
Acceptor内部类实现接受用户请求
Poller实现对事件的处理
Tomcat的实现代码中包含不少Fixme注释,以及异常的特殊处理(捕获后仅打印堆栈 程序继续运行)
重点代码:
NioEndPoint.start()
public void start()
throws Exception {
// Initialize socket if not done before
if (!initialized) {
init();
}
if (!running) {
running = true;
paused = false;
// Create worker collection
if (getUseExecutor()) {
if ( executor == null ) {
TaskQueue taskqueue = new TaskQueue();
TaskThreadFactory tf = new TaskThreadFactory(getName() + "-exec-");
executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(getMinSpareThreads(), getMaxThreads(), 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,taskqueue, tf);
taskqueue.setParent( (ThreadPoolExecutor) executor, this);
}
} else if ( executor == null ) {//avoid two thread pools being created
workers = new WorkerStack(maxThreads);
}
// Start poller threads
pollers = new Poller[getPollerThreadCount()];
for (int i=0; i
Acceptor
protected class Acceptor implements Runnable {
/**
* The background thread that listens for incoming TCP/IP connections and
* hands them off to an appropriate processor.
*/
public void run() {
// Loop until we receive a shutdown command
while (running) {
// Loop if endpoint is paused
while (paused) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
try {
// Accept the next incoming connection from the server socket
SocketChannel socket = serverSock.accept();
// Hand this socket off to an appropriate processor
//TODO FIXME - this is currently a blocking call, meaning we will be blocking
//further accepts until there is a thread available.
if ( running && (!paused) && socket != null ) {
//processSocket(socket);
if (!setSocketOptions(socket)) {
try {
socket.socket().close();
socket.close();
} catch (IOException ix) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("", ix);
}
}
}
}catch (SocketTimeoutException sx) {
//normal condition
}catch ( IOException x ) {
if ( running ) log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), x);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError oom) {
try {
oomParachuteData = null;
releaseCaches();
log.error("", oom);
}catch ( Throwable oomt ) {
try {
try {
System.err.println(oomParachuteMsg);
oomt.printStackTrace();
}catch (Throwable letsHopeWeDontGetHere){}
}catch (Throwable letsHopeWeDontGetHere){}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), t);
}
}//while
}//run
}Poller:注册、处理事件
public void add(final NioChannel socket, final int interestOps) {
PollerEvent r = eventCache.poll();
if ( r==null) r = new PollerEvent(socket,null,interestOps);
else r.reset(socket,null,interestOps);
addEvent(r);
}
/**
* Processes events in the event queue of the Poller.
*
* @return true if some events were processed,
* false if queue was empty
*/
public boolean events() {
boolean result = false;
Runnable r = null;
while ( (r = (Runnable)events.poll()) != null ) {
result = true;
try {
r.run();
if ( r instanceof PollerEvent ) {
((PollerEvent)r).reset();
eventCache.offer((PollerEvent)r);
}
} catch ( Throwable x ) {
log.error("",x);
}
}
return result;
}
public void register(final NioChannel socket)
{
socket.setPoller(this);
KeyAttachment key = keyCache.poll();
final KeyAttachment ka = key!=null?key:new KeyAttachment();
ka.reset(this,socket,getSocketProperties().getSoTimeout());
PollerEvent r = eventCache.poll();
ka.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);//this is what OP_REGISTER turns into.
if ( r==null) r = new PollerEvent(socket,ka,OP_REGISTER);
else r.reset(socket,ka,OP_REGISTER);
addEvent(r);
}
public void cancelledKey(SelectionKey key, SocketStatus status, boolean dispatch) {
try {
if ( key == null ) return;//nothing to do
KeyAttachment ka = (KeyAttachment) key.p_w_upload();
if (ka != null && ka.getComet() && status != null) {
//the comet event takes care of clean up
//processSocket(ka.getChannel(), status, dispatch);
ka.setComet(false);//to avoid a loop
if (status == SocketStatus.TIMEOUT ) {
processSocket(ka.getChannel(), status, true);
return; // don't close on comet timeout
} else {
processSocket(ka.getChannel(), status, false); //don't dispatch if the lines below are cancelling the key
}
}
key.attach(null);
if (ka!=null) handler.release(ka.getChannel());
if (key.isValid()) key.cancel();
if (key.channel().isOpen()) try {key.channel().close();}catch (Exception ignore){}
try {if (ka!=null) ka.channel.close(true);}catch (Exception ignore){}
try {if (ka!=null && ka.getSendfileData()!=null && ka.getSendfileData().fchannel!=null && ka.getSendfileData().fchannel.isOpen()) ka.getSendfileData().fchannel.close();}catch (Exception ignore){}
if (ka!=null) ka.reset();
} catch (Throwable e) {
if ( log.isDebugEnabled() ) log.error("",e);
// Ignore
}
}
/**
* The background thread that listens for incoming TCP/IP connections and
* hands them off to an appropriate processor.
*/
public void run() {
// Loop until we receive a shutdown command
while (running) {
try {
// Loop if endpoint is paused
while (paused && (!close) ) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
boolean hasEvents = false;
hasEvents = (hasEvents | events());
// Time to terminate?
if (close) {
timeout(0, false);
break;
}
int keyCount = 0;
try {
if ( !close ) {
if (wakeupCounter.getAndSet(-1) > 0) {
//if we are here, means we have other stuff to do
//do a non blocking select
keyCount = selector.selectNow();
} else {
keyCount = selector.select(selectorTimeout);
}
wakeupCounter.set(0);
}
if (close) {
timeout(0, false);
selector.close();
break;
}
} catch ( NullPointerException x ) {
//sun bug 5076772 on windows JDK 1.5
if ( log.isDebugEnabled() ) log.debug("Possibly encountered sun bug 5076772 on windows JDK 1.5",x);
if ( wakeupCounter == null || selector == null ) throw x;
continue;
} catch ( CancelledKeyException x ) {
//sun bug 5076772 on windows JDK 1.5
if ( log.isDebugEnabled() ) log.debug("Possibly encountered sun bug 5076772 on windows JDK 1.5",x);
if ( wakeupCounter == null || selector == null ) throw x;
continue;
} catch (Throwable x) {
log.error("",x);
continue;
}
//either we timed out or we woke up, process events first
if ( keyCount == 0 ) hasEvents = (hasEvents | events());
Iterator iterator = keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null;
// Walk through the collection of ready keys and dispatch
// any active event.
while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey sk = (SelectionKey) iterator.next();
KeyAttachment p_w_upload = (KeyAttachment)sk.p_w_upload();
// Attachment may be null if another thread has called
// cancelledKey()
if (p_w_upload == null) {
iterator.remove();
} else {
p_w_upload.access();
iterator.remove();
processKey(sk, p_w_upload);
}
}//while
//process timeouts
timeout(keyCount,hasEvents);
if ( oomParachute > 0 && oomParachuteData == null ) checkParachute();
} catch (OutOfMemoryError oom) {
try {
oomParachuteData = null;
releaseCaches();
log.error("", oom);
}catch ( Throwable oomt ) {
try {
System.err.println(oomParachuteMsg);
oomt.printStackTrace();
}catch (Throwable letsHopeWeDontGetHere){}
}
}
}//while
synchronized (this) {
this.notifyAll();
}
stopLatch.countDown();
}
protected boolean processKey(SelectionKey sk, KeyAttachment p_w_upload) {
boolean result = true;
try {
if ( close ) {
cancelledKey(sk, SocketStatus.STOP, false);
} else if ( sk.isValid() && p_w_upload != null ) {
p_w_upload.access();//make sure we don't time out valid sockets
sk.attach(p_w_upload);//cant remember why this is here
NioChannel channel = p_w_upload.getChannel();
if (sk.isReadable() || sk.isWritable() ) {
if ( p_w_upload.getSendfileData() != null ) {
processSendfile(sk,p_w_upload,true, false);
} else if ( p_w_upload.getComet() ) {
//check if thread is available
if ( isWorkerAvailable() ) {
//set interest ops to 0 so we don't get multiple
//invokations for both read and write on separate threads
reg(sk, p_w_upload, 0);
//read goes before write
if (sk.isReadable()) {
//read notification
if (!processSocket(channel, SocketStatus.OPEN))
processSocket(channel, SocketStatus.DISCONNECT);
} else {
//future placement of a WRITE notif
if (!processSocket(channel, SocketStatus.OPEN))
processSocket(channel, SocketStatus.DISCONNECT);
}
} else {
result = false;
}
} else {
//later on, improve latch behavior
if ( isWorkerAvailable() ) {
unreg(sk, p_w_upload,sk.readyOps());
boolean close = (!processSocket(channel));
if (close) {
cancelledKey(sk,SocketStatus.DISCONNECT,false);
}
} else {
result = false;
}
}
}
} else {
//invalid key
cancelledKey(sk, SocketStatus.ERROR,false);
}
} catch ( CancelledKeyException ckx ) {
cancelledKey(sk, SocketStatus.ERROR,false);
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error("",t);
}
return result;
}
PollerEvent
public class PollerEvent implements Runnable {
protected NioChannel socket;
protected int interestOps;
protected KeyAttachment key;
public PollerEvent(NioChannel ch, KeyAttachment k, int intOps) {
reset(ch, k, intOps);
}
public void reset(NioChannel ch, KeyAttachment k, int intOps) {
socket = ch;
interestOps = intOps;
key = k;
}
public void reset() {
reset(null, null, 0);
}
public void run() {
if ( interestOps == OP_REGISTER ) {
try {
socket.getIOChannel().register(socket.getPoller().getSelector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ, key);
} catch (Exception x) {
log.error("", x);
}
} else {
final SelectionKey key = socket.getIOChannel().keyFor(socket.getPoller().getSelector());
try {
boolean cancel = false;
if (key != null) {
final KeyAttachment att = (KeyAttachment) key.p_w_upload();
if ( att!=null ) {
//handle callback flag
if (att.getComet() && (interestOps & OP_CALLBACK) == OP_CALLBACK ) {
att.setCometNotify(true);
} else {
att.setCometNotify(false);
}
interestOps = (interestOps & (~OP_CALLBACK));//remove the callback flag
att.access();//to prevent timeout
//we are registering the key to start with, reset the fairness counter.
int ops = key.interestOps() | interestOps;
att.interestOps(ops);
key.interestOps(ops);
att.setCometOps(ops);
} else {
cancel = true;
}
} else {
cancel = true;
}
if ( cancel ) socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key,SocketStatus.ERROR,false);
}catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) {
try {
socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key,SocketStatus.DISCONNECT,true);
}catch (Exception ignore) {}
}
}//end if
}//run
public String toString() {
return super.toString()+"[intOps="+this.interestOps+"]";
}
}3.2 Jetty NIO
3.3 Netty
编码解码:可以定制数据的编码解码方式,使用高效的二进制数据。
多协议开发:可以基于http或者私有协议
特性:
0拷贝
异步非阻塞
内存池ByteBuf
主从Reactor
无锁化的串行设计理念
TCP参数定制
3.4 总结
比较Tomcat、jetty与Netty可以发现,Tomcat、Jetty的connector只是对nio接口的简单实现,Netty提供了更方便使用的可编程API,提供了更丰富的高级功能。
参考
Unix网络编程 Volumn1
Linux网络编程
scale in java
Netty权威指南
Netty系列之Netty高性能之道