JDK源码阅读——HashMap(1.7)
HashMap
- 使用到的位运算
使用到的位运算解释:
异或运算:1 ^ 2==01^10==11
1 << 4: 1*2的4次幂
8>>2 :8除以2的2次幂(无符号)
8>>>2 :8除以2的2次幂(有符号)
-8 >> 2 等于-2
8 >> 2 等于2
-8 >>> 2等于1073741822
8 >>> 2等于2
- HashMap jdoc概要翻译:
1.HashMap 实现了Map所有的操作,允许null作为 key/value;无序(因为h&length-1,也就是bucket数组索引无序)
2.HashMap 除了非同步性,k\v 允许null, HashTable与之相反,为线程安全(但效率不如ConcurrentHashMap),key与value都不允许null值。
3.两个因素影响HashMap性能:”initial capacity”、”load factor” . threshold=(capacity * load factor),当size超过threshold,会产生rehash
initial capacity:is the number of buckets in the hash table
load factor :is a measure of how full the hash table is allowed to
get before its capacity is automatically increased
4.当HashMap中的entry超过了,capacity(.75 defautl,更高的值导致 空间占用-,检索耗时+)与
loadFactor的计算值,rehashed(内部数据结构重新构建) twice the number of buckets.
5.如果一个Map中非常多的mapping隐射,考虑给Map一个足够大的初始值,减少rehash操作
6.HashMap是非同步的,如果多个线程访问这个HashMap,至少其中有一个对这个HashMap做了结构修改
(add\remove),那必须在外部完成“同步”!一般使用
Collections.synchronized(new Hash())
7.Fail-fast iterators:
当你从HashMap中遍历出来的 一个对象,然后这个HashMap结构变化,这个对象会fail-fast立即失效(throw ConcurrentModificationException).除非你使用Iterator.remove
- HashMap成员变量:
/**
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
*
* 注意capacity与size的区别:
* 成员变量capacity(必须为2的次幂,为什么??见后文)实际就是table的size(buckets的size);
* 成员变量size时k-v映射关系的个数
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;
/**
* The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified by
* either of the constructors with arguments. MUST be a power of two <=
* 1<<30.
*
* 最大容量值
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
/**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/**
* An empty table instance to share when the table is not inflated.
* Entry[] 实现bucket数组,Entry对象又实现了链表。
* 整体实现了hashMap底层存储结构
*/
static final Entry[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};
/**
* The table, resized as necessary. Length MUST Always be a power of two.
* 散列链表,HashMap的底层数据结构实现,为什么是transient?
* table数组维护了buckets,其中的Entry实现了链表
*/
transient Entry[] table = (Entry[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
/**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
*
* k/v隐射关系的数量
*/
transient int size;
/**
* The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor).
* @serial
*
* 阈值,当HashMap的下一个元素size>=threshold时,rehash
*/
// If table == EMPTY_TABLE then this is the initial capacity at which the
// table will be created when inflated.
int threshold;
/**
* The load factor for the hash table.
*
* @serial
*/
final float loadFactor;
/**
* The number of times this HashMap has been structurally modified
* Structural modifications are those that change the number of mappings in
* the HashMap or otherwise modify its internal structure (e.g., rehash).
* This field is used to make iterators on Collection-views of the HashMap
* fail-fast. (See ConcurrentModificationException).
*
* 这个HashMap结构变化(k\v映射关系数量改变,或者rehash都算)的次数,
* 用来实现HashMap的iterator的fail-fast特点
*/
transient int modCount; 为什么 capacity 必须为2的次幂?
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*
* h& (length-1)运算等价于对length取模,也就是h%length,但是&比%具有更高的效.
*
* capacity 必须为2的n次幂,则length-1肯定为奇数,在位运算h & (length -
* 1)唯一性更高,减少了collision的发生,也就是保证bucketIndex低重复性.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 :
// "length must be a non-zero power of 2";
return h & (length - 1);
}为什么使用transient (transient Entry
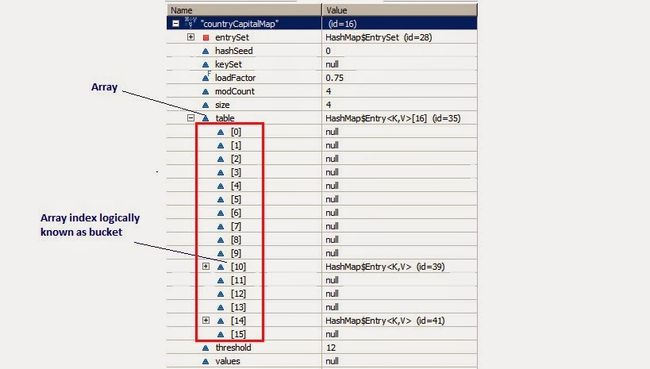
散列Hash结构
请点击这个链接,动态演示了散列Hash(注意总是从链表的表头处插入新结点)
hashCode
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
// 通过使用这个hash函数去获取一个hashCode.通过位运算,
// key通过hash算法,获得具体bucket的索引,但可能出现不同的key,通过hash算法后,出现一样的索引,为了避免这种冲突,
// 使用如下hash函数 降低冲突
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}Entry单向链表实现
……
// 实现了单向链表
static class Entry<K, V> implements Map.Entry<K, V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry next;
int hash;
/**
* Creates new entry.
* Map.Entry保存一个键值对 和这个键值对持有指向下一个键值对的引用,如此就构成了链表了。
*/
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
……
get()
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
Entry entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
private V getForNullKey() {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
// Null keys map to index
// 0(bucketIndex=0*table.length-1,也是0),但是table[0]可能有多个value(index都是0)
// 所以遍历链表
for (Entry e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
final Entry getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
// 1 indexFor(hash, table.length):获取bucketIndex
// 2 遍历具体bucket[indexFor(hash, table.length)]下的单向链表
// 3 如果这个key的hashCode一样同时key值一样,或者key对象相同,则返回
for (Entry e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}
Put
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);// 通过key获取key的 hash code
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);// 通过hashCode&table.length-1获得table中的bucketIndex
for (Entry e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {// 遍历链表
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {// 如果发现链表上的数据一样,则replace
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
// Map结构变化次数累计,fail-fast的实现.
// 如果多个线程访问,得到Iterator后,当发现modCount变化,抛出ConcurrentModificationException
modCount++;
/**
* 如果没有个这个key,则插入
*
* hash:key 的HashCode
*
* i:talbe数组的索引(buckets的编号)
*/
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
} void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//这里与JDK1.6不同,这里先判断—>resize—>再插入新结点
// 是否需要resize
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {// 当前存在的k\v映射数目>=threshold(默认为16*0.75=12)
resize(2 * table.length);// 增大一倍
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
// 在链表上加入k\v结点
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*
* h& (length-1)运算等价于对length取模,也就是h%length,但是&比%具有更高的效.
*
* capacity 必须为2的n次幂,则length-1肯定为奇数,在位运算h & (length -
* 1)唯一性更高,减少了collision的发生,也就是保证bucketIndex低重复性.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 :
// "length must be a non-zero power of 2";
return h & (length - 1);
} void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 断开链表,add结点,注意总是从链表的表头处插入新结点,详细请参看数据结构单向链表
Entry e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
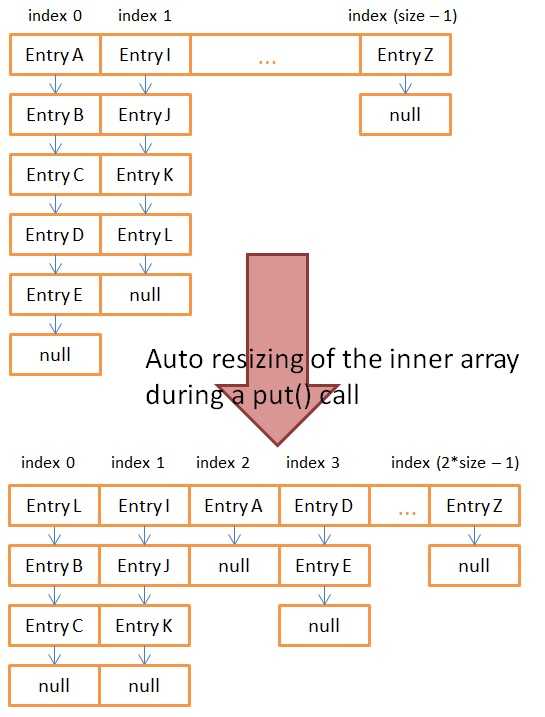
} /*
* 1.初始化newTable Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
* newCapacity增加的幅度是之前的1倍
* 2.把oldTable里的元素拷贝到 newTable
*/
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable;
threshold = (int) Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
} /**
* Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
*/
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry e : table) {// 遍历这个hash table(桶数组)
while (null != e) {// 遍历数组中的链表结构
// 可能导致原来的k\v在不同的桶中
Entry next = e.next;
if (rehash) {// hashSeed变化,需要重新执行hash函数
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);// hash函数返回值
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);// 计算新的bucket index
// 这里就是经典的hashMap出现死循环的地方,resize后形成环链表。以下两行代码的意思是:
// 1.newTable[i]==null表示首次进入这个桶,那么清空e.next的引用。
// 2,然后仅仅放入单个结点e
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 1.newTable[i]!=null表示这个桶已经放入了元素,那么开始形成链表。并且准备把首结点后移,从头部插入一个新结点
// 2.把首结点后移,从头部插入一个新结点
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;// 遍历 继续
}
}
} HashIterator
private abstract class HashIterator<E> implements Iterator<E> {
Entry next; // next entry to return
int expectedModCount; // For fast-fail
int index; // current slot
Entry current; // current entry
HashIterator() {
expectedModCount = modCount;
if (size > 0) { // advance to first entry
// 找到table数组中第一个存在的结点,即找到第一个具有元素的bucket
Entry[] t = table;
while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null)
;
}
}
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
final Entry nextEntry() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
Entry e = next;
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if ((next = e.next) == null) {
Entry[] t = table;
while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null)
;
}
current = e;
return e;
}
public void remove() {
if (current == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
Object k = current.key;
current = null;
HashMap.this.removeEntryForKey(k);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
}
1.8中对链表进行了优化,如果链表上的数据结点超过了8个就会将链表转换为红黑树,提高查询效率
TreeMap
TreeMap实现了红黑树。为什么要实现红黑树?
因为二叉树的一个结点大于它的左子结点,小于它的右子结点,按照这个规律,很容易出现失衡的状态,即根结点一边的树可能很长,另一边很短,这样可能会造成检索效率低下(O(n)。所以红黑树就是一种平衡二叉树。红黑树通过“左旋、右旋、着色”三大特点维持了树的平衡。
与HashMap比较,最大的特点就是TreeMap中的k\v有序.效率不如HashMap
http://www.cnblogs.com/vamei/archive/2013/03/17/2962290.html
推荐阅读:
http://coolshell.cn/articles/9606.html
https://tech.meituan.com/archives