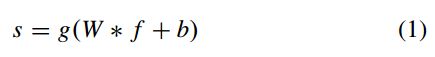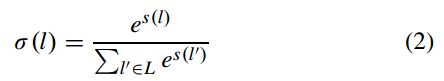【文献阅读】遥感图像中近海船舶的语义分割(H. Lin等人,IGRS Letter,2017)
一、背景
文章题目:《Fully Convolutional Network With Task Partitioning for Inshore Ship Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images》
IGRS Letter上的一篇文章,作者的第一单位是北航,好像这篇文章还获得了当年北航当年的优秀论文奖。
文章下载地址:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=8000357
文章引用格式:H. Lin, Z. Shi, and Z. Zou. "Fully Convolutional Network With Task Partitioning for Inshore Ship Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images." IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS, vol. 14, no. 10, pp, 1665-1669, 2017. DOI:10.1109/LGRS.2017.2727515
项目地址:暂时没有
二、文章导读
网上关于这篇文章几乎没怎么看到相关解读,我是从一篇介绍注意力的文章中看到的:
[1] 几篇不错的注意力机制文献
所以下面就自己来记录一下这篇文章。先来看下摘要部分:
Ship detection in optical remote sensing imagery has drawn much attention in recent years, especially with regards to the more challenging inshore ship detection. However, recent work on this subject relies heavily on hand-crafted features that require carefully tuned parameters and on complicated procedures. In this letter, we utilize a fully convolutional network (FCN) to tackle the problem of inshore ship detection and design a ship detection framework that possesses a more simplified procedure and a more robust performance. When tackling the ship detection problem with FCN, there are two major difficulties: 1) the long and thin shape of the ships and their arbitrary direction makes the objects extremely anisotropic and hard to be captured by network features and 2) ships can be closely docked side by side, which makes separating them difficult. Therefore, we implement a task partitioning model in the network, where layers at different depths are assigned different tasks. The deep layer in the network provides detection functionality and the shallow layer supplements with accurate localization. This approach mitigates the tradeoff of FCN between localization accuracy and feature representative ability, which is of importance in the detection of closely docked ships. The experiments demonstrate that this framework, with the advantages of FCN and the task partitioning model, provides robust and reliable inshore ship detection in complex contexts.
首先作者提到,传统的船舶提取都是通过手工设计的特征,这些特征必须经过精细调参且复杂度高。因此文章采用了一个全卷积网络FCN,在FCN中执行任务分割模型(task partitioning model),网络中不同深度的层执行不同的任务。深层提供目标检测功能,浅层提供精准定位功能。实验结果表明,该方法具有鲁棒性且能够准确检测船舶。
三、文章详细介绍
船舶检测不同与一般地物检测相比,具有一些难点,主要表现在两个方面:一是船舶的形状狭长且窄,且方向可以任意旋转,二是检测背景往往比较复杂,例如近岸的船只和码头。文章采用了FCN网络结构,同时引入了任务分割模型(task partitioning model),该模型类似于attention机制,但是又略有区别。
文章的主要贡献可以总结为以下两点:
(1)Focusing on the problem of inshore ship detection, we replace hand-crafted features with those learned by FCN, which allows unified optimization rather than individually tuned parameters and constitutes a more robust and scalable framework. (利用FCN网络进行船舶的检测)
(2)With the task partitioning model, the tasks of localization and detection are partitioned onto different layers of the network, thereby mitigating the localization accuracy/detection ability tradeoff common in FCNs and is of vital importance in ship detection tasks in remote sensing imagery. (采用了任务分割模型,定位和检测被分为了不同的task以传入网络)
这里要提一下为什么选择FCN,因为FCN可以输出一个预测的label map,而不是CNN经过softmax得到的scalar label。卷积网络的训练一般是采用的SGD(随机梯度下降)。而attention机制能够获得一个可视的feature map,文章采用的网络结构可表示为:
下面可以看一下实际的近岸船舶的遥感图:
可以看到,船舶之间的距离非常接近,这就导致仅用浅层网络是无法识别船舶之间的空隙这种非常细小的目标。作者网络借鉴ResNet-50,将其最后的全连接网络改为了全卷积网络(Res-FCN),并将这个模型分成了两部分——浅层和深层,作者在浅层网络后加了两个卷积层,使得其能够分出浅层通道和深层通道,浅层网络输出一个位置精度的检测结果,深层网络最终输出一个feature map,联合二者的最终结果。
训练数据的标签有4种:船头/船尾、船体、海洋、陆地。卷积操作能够提取图像的特征,通过attention model计算的特征图feature map可以表示为:
其中,g()表示非线性激活函数,W表示filter,*表示卷积操作。得到的s是一个C*H*W的变量。得到s之后,在进行一个softmax操作:
其中,l是特征的空间索引,这些特征是来自于特征图s中的二维坐标(x, y),L是l的邻域。
实验数据是来自于Google Earth 和GF-2。数据集包含24张图,每张图5000*5000像素,分辨率为1m,出于对数据的考虑(船舶之间需要比较接近,近海岸,船超过100m),最终选择了14张图,将这14图裁剪为321*321的patch作为训练集和测试集,同时还做了一些数据增广处理,包括数据的随机裁剪,旋转,轻微对比度调整等,最终测试集共有8800张图像。
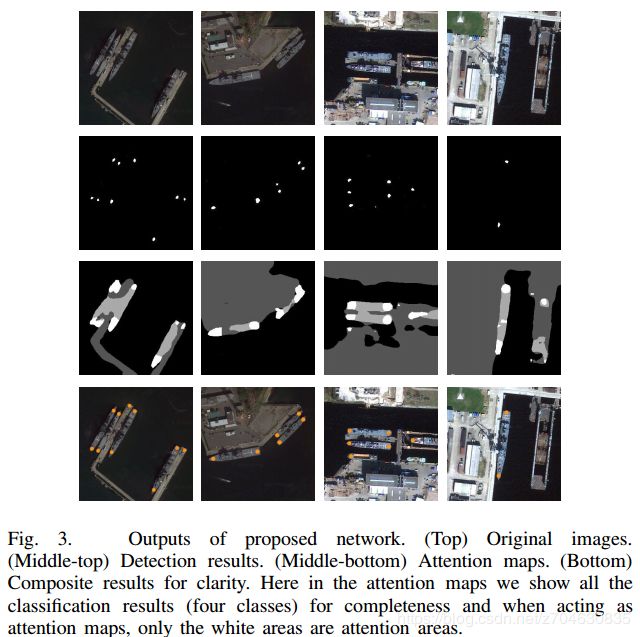
模型的处理结果:
最后为了说明任务分割模型的优势,作者又拿浅层模型做了一个对比,如下图:
可以看到,仅仅用浅层模型是没法准确提取船舶的。
四、小结
1. 这篇文章比较好的地方在于作者解释了他的网络为什么要这样设计,之前看到的很多网络结构的设计都没有详细介绍为何要这样设计。