数据结构与算法 -- 队列 ADT
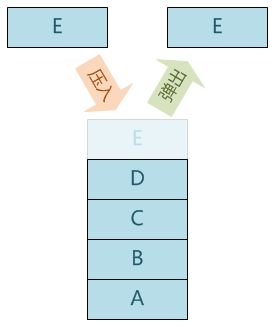
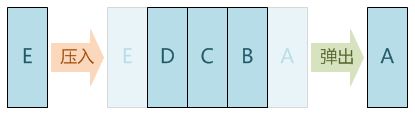
像栈一样,队列(queue)也是表。然而,使用队列时插入在一端进行而删除则在另一端进行,也就是先进先出(FIFO)。队列的基本操作是EnQueue(入队),它是在表的末端(叫做队尾(rear))插入一个元素;还有DeQueue(出队),它是删除(或返回)在表的开头(叫做队头(front))的元素。队列中没有元素时,称为空队列。
队列需要两个指针,一个指向队头,一个指向队尾。对栈的操作永远都是针对栈顶(top)进行的。但是,当队列的元素插入和删除时,它所使用的是数组中的不同的元素。
队列一般有链式队列和顺序队列两种。链式队列相当于我们在银行中排队,后来的人排到队伍的最后,前面的人办理完业务后就会离开,让下一个人进去;顺序队列则是采用循环数组实现,让队列的尾部“环绕”到数组的头部,这样新元素就可以存储到以前删除元素所留出来的空间中。
一、顺序队列
和栈类似,其中又分为静态数组和动态数组两类。
静态数组:特点是要求结构的长度固定,而且长度在编译时候就得确定。其优点是结构简单,实现起来方便而不容易出错。而缺点就是不够灵活以及固定长度不容易控制,适用于知道明确长度的场合。
动态数组:特点是长度可以在运行时候才确定以及可以更改原来数组的长度。优点是灵活,缺点是由此会增加程序的复杂性。
前面提到顺序队列采用循环数组实现,但是使用循环数组自身也会引入一个问题。当front 和 rear的值相同时,这和队列已满时的情况是一样的。当队列空或者满时对 front 和 rear 进行比较,其结果都是真。所以,我们无法通过比较 front 和 rear 来测试队列是否为空。
有两种方法可以解决这个问题:
第一种方法:对这个变量的值进行测试就可以很容易分清队列空间为空还是为满。
第二种方法:重定义“满”的含义。如果使数组中的一个元素始终保留不用,这样当队列“满”时 front 和 rear 的值便不相同,可以和队列为空时的情况区分开来。
代码实现说明:
首先我们来说下取余,之前有讲过的,参看:C语言再学习 -- 运算符与表达式
取余运算符用于整数运算,该运算符计算出用它右边的整数去除它左边的整数得到的余数。
注意:不要对浮点数使用该运算符,那将是无效的。
负数取余规则:
如果第一个操作数为负数,那么得到的余数也为负数;如果第一个操作数为正数,那么得到的余数也为正数。
11 % 5 = 1;11 % -5 = 1;-11 % 5 = -1;-11 % -5 = -1;
4、自增和自减:++和--
后缀: a++; a--; 使用a的值之后改变a;
前缀: ++a; --a; 使用a的值之前改变a;
在队列中我们用不到负数的,不过还是让你看一下取余的结果:
#include
int main (void)
{
printf ("0%%5 = %d\n", 0%5);
printf ("1%%5 = %d\n", 1%5);
printf ("2%%5 = %d\n", 2%5);
printf ("3%%5 = %d\n", 3%5);
printf ("4%%5 = %d\n", 4%5);
printf ("5%%5 = %d\n", 5%5);
printf ("6%%5 = %d\n", 6%5);
printf ("7%%5 = %d\n", 7%5);
return 0;
}
输出结果:
0%5 = 0
1%5 = 1
2%5 = 2
3%5 = 3
4%5 = 4
5%5 = 0
6%5 = 1
7%5 = 2 了解了取余后,就不难理解顺序队列了,其实也是操作的数组下标,只不过使用了前/后两个下标表示。
下面静态数组和动态数组参看于 C 和指针,你有没有看出来有什么问题?
首先,数组第一元素 queue[0],未赋值!! 不过宏定义的时候数组长度加 1 了。不过你最好是知道数组第一个元素是queue[0] 而不是 queue[1]。
最后它的判空判满,不够鲁棒。
1、静态数组
#include
#include
#include
#define QUEUE_TYPE int /* 队列元素的类型 */
#define QUEUE_SIZE 100 /* 队列中元素的最大数量 */
#define ARRAY_SIZE (QUEUE_SIZE + 1) /* 数组的长度 */
/* 用于存储队列元素的数组和指向队列头和尾的指针 */
static QUEUE_TYPE queue[ARRAY_SIZE];
static size_t front = 1;
static size_t rear = 0;
/* 向队列添加一个新元素,参数就是需要添加的元素 */
void insert (QUEUE_TYPE value);
/* 从队列中移除一个元素并将其丢弃 */
void delete (void);
/* 返回队列中第一个元素的值,但不修改队列本身 */
QUEUE_TYPE first (void);
/* 如果队列为空,返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE */
int is_empty (void);
/* 如果队列已满,返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE */
int is_full (void);
/* 自定义函数实现遍历操作 */
void travel (void);
/* 计算队列中元素的个数 */
int size (void);
int main (void)
{
travel ();
delete ();
printf("%s\n", is_empty() ? "队列已空" : "队列未空");
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
insert (i);
}
puts ("经过 insert 入队后的元素值为: ");
travel ();
printf ("此时队列首元素为:%d\n", first ());
printf ("此时队列元素个数为:%d\n", size ());
delete ();
delete ();
puts ("经过 delete 出队几个元素后的队列元素: ");
travel ();
printf("%s\n", is_full() ? "队列已满" : "队列未满");
printf("%s\n", is_empty() ? "队列已空" : "队列未空");
printf ("此时队列首元素为:%d\n", first ());
printf ("此时队列元素个数为:%d\n", size ());
return 0;
}
void insert (QUEUE_TYPE value)
{
//assert (!is_full ());
if (is_full ())
{
printf ("队列已满,入队列失败\n");
return ;
}
rear = (rear + 1) % ARRAY_SIZE;
queue[rear] = value;
}
void delete (void)
{
//assert (!is_empty ());
if (is_empty ())
{
printf ("队列已空,出队列失败\n");
return ;
}
front = (front + 1) % ARRAY_SIZE;
}
QUEUE_TYPE first (void)
{
assert (!is_empty ());
if (is_empty ())
return ;
return queue[front];
}
int is_empty (void)
{
return (rear + 1) % ARRAY_SIZE == front;
}
int is_full (void)
{
return (rear + 2) % ARRAY_SIZE == front;
}
void travel (void)
{
printf ("队列中的元素有:");
int i = 0;
for (i = front; i < rear; i++)
printf ("%d ", queue[i % ARRAY_SIZE]);
printf ("\n");
}
int size (void)
{
return rear - front;
}
队列中的元素有:
队列已空,出队列失败
队列已空
经过 insert 入队后的元素值为:
队列中的元素有:0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
此时队列首元素为:0
此时队列元素个数为:9
经过 delete 出队几个元素后的队列元素:
队列中的元素有:2 3 4 5 6 7 8
队列未满
队列未空
此时队列首元素为:2
此时队列元素个数为:7 2、动态数组
#include
#include
#include
#define QUEUE_TYPE int /* 队列元素的类型 */
/* 用于存储队列元素的数组和指向队列头和尾的指针 */
static QUEUE_TYPE *queue;
static int queue_size;
static int array_size;
static size_t front = 1;
static size_t rear = 0;
/*
创建一个队列,参数指定队列可以存储的元素的最大数量
注意:这个函数只适用于使用动态分配数组的队列
*/
void create_queue (size_t size);
/*
销毁一个队列
注意:这个函数只适用于链式和动态分配数组的队列
*/
void destroy_queue (void);
/* 向队列添加一个新元素,参数就是需要添加的元素 */
void insert (QUEUE_TYPE value);
/* 从队列中移除一个元素并将其丢弃 */
void delete (void);
/* 返回队列中第一个元素的值,但不修改队列本身 */
QUEUE_TYPE first (void);
/* 如果队列为空,返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE */
int is_empty (void);
/* 如果队列已满,返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE */
int is_full (void);
/* 自定义函数实现遍历操作 */
void travel (void);
/* 计算队列中元素的个数 */
int size (void);
int main (void)
{
create_queue (50);
travel ();
delete ();
printf("%s\n", is_empty() ? "队列已空" : "队列未空");
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
insert (i);
}
puts ("经过 insert 入队后的元素值为: ");
travel ();
printf ("此时队列首元素为:%d\n", first ());
printf ("此时队列元素个数为:%d\n", size ());
delete ();
delete ();
puts ("经过 delete 出队几个元素后的队列元素: ");
travel ();
printf("%s\n", is_full() ? "队列已满" : "队列未满");
printf("%s\n", is_empty() ? "队列已空" : "队列未空");
printf ("此时队列首元素为:%d\n", first ());
printf ("此时队列元素个数为:%d\n", size ());
destroy_queue ();
printf ("此时队列元素个数为:%d\n", size ());
return 0;
}
void create_queue (size_t size)
{
//assert (array_size == 0);
if (size < array_size)
{
printf ("队列元素太少\n");
}
array_size = size;
queue = malloc (sizeof (QUEUE_TYPE) * array_size);
if (NULL == queue)
perror ("malloc分配失败"), exit (1);
}
void destroy_queue (void)
{
//assert (queue_size > 0);
if (queue != NULL)
{
printf ("销毁队列\n");
array_size = 0;
free (queue);
queue = NULL;
front = 0;
rear = 0;
}
}
void insert (QUEUE_TYPE value)
{
//assert (!is_full ());
if (is_full ())
{
printf ("队列已满,入队列失败\n");
return ;
}
rear = (rear + 1) % array_size;
queue[rear] = value;
}
void delete (void)
{
//assert (!is_empty ());
if (is_empty ())
{
printf ("队列已空,出队列失败\n");
return ;
}
front = (front + 1) % array_size;
}
QUEUE_TYPE first (void)
{
assert (!is_empty ());
if (is_empty ())
return ;
return queue[front];
}
int is_empty (void)
{
//assert (queue_size > 0);
if (queue != NULL)
{
return (rear + 1) % array_size == front;
}
}
int is_full (void)
{
//assert (queue_size > 0);
if (queue != NULL)
{
return (rear + 2) % array_size == front;
}
}
void travel (void)
{
printf ("队列中的元素有:");
int i = 0;
for (i = front; i < rear; i++)
printf ("%d ", queue[i % array_size]);
printf ("\n");
}
int size (void)
{
return rear - front;
}
输出结果:
队列中的元素有:
队列已空,出队列失败
队列已空
经过 insert 入队后的元素值为:
队列中的元素有:0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
此时队列首元素为:0
此时队列元素个数为:9
经过 delete 出队几个元素后的队列元素:
队列中的元素有:2 3 4 5 6 7 8
队列未满
队列未空
此时队列首元素为:2
此时队列元素个数为:7
销毁队列
此时队列元素个数为:0 3、自写顺序队列
//采用顺序存储结构实现队列的操作
#include
#define SIZE 5
//定义队列的数据类型
int arr[SIZE]; //存储元素的位置
int front; //记录队首元素的下标
int rear; //下一个可以存放元素下标
//入队操作 值传递 址传递
void push (int data);
//遍历队列中的所有元素
void travel (void);
//出队操作
int pop (void);
//判断队列是否为空
int empty (void);
//判断队列是否为满
int full (void);
//查看队首元素
int get_head (void);
//查看队尾元素
int get_tail (void);
//计算队列中元素个数
int size (void);
int main (void)
{
//创建队列,并且进行初始化
push(11);
travel(); //11
push(22);
travel(); //11 22
push(33);
travel(); //11 22 33
push(44);
travel(); //11 22 33 44
push(55);
travel(); //11 22 33 44 55
printf("出队的元素是:%d\n",pop());
travel(); //22 33 44 55
printf("出队的元素是:%d\n",pop());
travel(); //33 44 55
push(66);
travel(); //33 44 55 66
push(77);
travel(); //33 44 55 66 77
printf("------------------\n");
printf("队首元素是:%d\n",get_head());
printf("队尾元素是:%d\n",get_tail());
printf("队列中元素个数是:%d\n",size());
printf("%s\n",empty()?"队列已经空了":"队列没有空");
printf("%s\n",full()?"队列已经满了":"队列没有满");
return 0;
}
void push (int data)
{
if (full ())
return ;
arr[rear % 5] = data;
rear++;
}
void travel (void)
{
printf ("队列中的元素有:");
int i = 0;
for (i = front; i < rear; i++)
{
printf ("%d ", arr[i % 5]);
}
printf ("\n");
}
int pop (void)
{
if (empty ())
return ;
int temp = arr[front % 5];
front++;
return temp;
}
int size (void)
{
return rear - front;
}
int get_tail (void)
{
if (empty ())
return ;
return arr[(rear - 1) % 5];
}
int get_head (void)
{
if (empty ())
return ;
return arr[front %5];
}
int full (void)
{
return SIZE == rear - front;
}
int empty (void)
{
return 0 == rear - front;
}
输出结果:
队列中的元素有:11
队列中的元素有:11 22
队列中的元素有:11 22 33
队列中的元素有:11 22 33 44
队列中的元素有:11 22 33 44 55
出队的元素是:11
队列中的元素有:22 33 44 55
出队的元素是:22
队列中的元素有:33 44 55
队列中的元素有:33 44 55 66
队列中的元素有:33 44 55 66 77
------------------
队首元素是:33
队尾元素是:77
队列中元素个数是:5
队列没有空
队列已经满了 4、顺序队列总结
二、链式队列
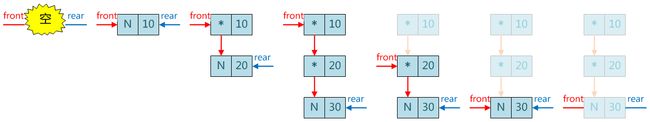
1、链式队列
#include
#include
#define QUEUE_TYPE int /* 队列所存储的值的数据类型 */
/* 定义一个结构以存储队列元素。 */
typedef struct node
{
QUEUE_TYPE value;
struct node *next;
}QueNode, *QuePtr;
typedef struct
{
QuePtr front, rear;
}Queue;
/*初始化队列*/
void init_queue (Queue *q);
/*创建队列,由于没有长度限制,故不需要create_stack函数*/
void create_queue (Queue *q);
//入队操作
void push (Queue *q, QUEUE_TYPE value);
//出队操作
int pop (Queue *q);
//判断队列是否为满
int is_full (Queue *q);
//判断队列是否为空
int is_empty (Queue *q);
//计算队列中节点的个数
int size (Queue *q);
//遍历操作
void travel (Queue *q);
//清空队列中所有的元素
void destroy_queue (Queue *q);
//获取队首元素的值
int top (Queue *q);
//获取队尾元素的值
int tail (Queue *q);
int main (void)
{
Queue queue;
init_queue (&queue);
push (&queue, 11);
travel (&queue);
push (&queue, 22);
travel (&queue);
push (&queue, 33);
travel (&queue);
push (&queue, 44);
travel (&queue);
push (&queue, 55);
travel (&queue);
printf("出队的元素是:%d\n",pop(&queue));
travel (&queue);
printf("出队的元素是:%d\n",pop(&queue));
travel (&queue);
push(&queue,66);
travel(&queue); //33 44 55 66
push(&queue,77);
travel(&queue); //33 44 55 66 77
printf("------------------\n");
printf("%s\n",is_empty(&queue)?"队列已经空了":"队列没有空");
printf("%s\n",is_full(&queue)?"队列已经满了":"队列没有满");
printf("队首元素是:%d\n",top (&queue));
printf("队尾元素是:%d\n",tail(&queue));
printf("队列中的元素个数是:%d\n",size(&queue));
printf("---------------------\n");
travel(&queue);
printf("出队的元素是:%d\n",pop(&queue));
destroy_queue (&queue);
travel(&queue);
return 0;
}
void init_queue (Queue *q)
{
q->front = (QuePtr)malloc (sizeof (QueNode));
if (NULL == q->front)
perror ("malloc分配失败"), exit (1);
q->front->next = NULL;
q->rear = q->front;
}
void create_queue (Queue *q)
{
}
void destroy_queue (Queue *q)
{
QuePtr temp, p;
if (q->front != NULL)
{
p = q->front->next;
while (p != NULL)
{
temp = p->next;
free (p);
p = temp;
}
q->front->next = NULL;
q->rear = q->front;
}
}
void push (Queue *q, QUEUE_TYPE value)
{
QuePtr p = (QuePtr)malloc (sizeof (QueNode));
if (NULL == p)
perror ("malloc分配失败");
p->value = value;
p->next = NULL;
if (q->rear != NULL)
q->rear->next = p;
q->rear = p;
if (q->front == NULL)
q->front = q->rear;
}
int pop (Queue *q)
{
if (is_empty (q))
return ;
QuePtr p = q->front->next;
QUEUE_TYPE i = p->value;
q->front->next = p->next;
if (q->rear == p)
q->rear = q->front;
free (p);
p = NULL;
return i;
}
int is_full (Queue *q)
{
return 0;
}
int is_empty (Queue *q)
{
return q->front == q->rear;
}
int size (Queue *q)
{
QuePtr p = q->front;
int i = 0;
while (p != q->rear)
{
++i;
p = p->next;
}
return i;
}
void travel (Queue *q)
{
printf ("队列中的元素有:");
if (NULL == q->front)
{
printf ("队列不存在\n");
return ;
}
else if (q->front == q->rear)
{
printf ("队列已空\n");
return ;
}
else
{
QuePtr p = NULL;
p = q->front->next;
while (p != q->rear)
{
printf ("%d ", p->value);
p = p->next;
}
printf ("%d ", p->value);
printf ("\n");
}
}
int top (Queue *q)
{
if (is_empty (q))
return ;
return q->front->next->value;
}
int tail (Queue *q)
{
if (is_empty (q))
return ;
return q->rear->value;
}
输出结果:
队列中的元素有:11
队列中的元素有:11 22
队列中的元素有:11 22 33
队列中的元素有:11 22 33 44
队列中的元素有:11 22 33 44 55
出队的元素是:11
队列中的元素有:22 33 44 55
出队的元素是:22
队列中的元素有:33 44 55
队列中的元素有:33 44 55 66
队列中的元素有:33 44 55 66 77
------------------
队列没有空
队列没有满
队首元素是:33
队尾元素是:77
队列中的元素个数是:5
---------------------
队列中的元素有:33 44 55 66 77
出队的元素是:33
队列中的元素有:队列已空 2、自写链式队列
//基于链式结构的队列操作
#include
#include
//定义节点的数据类型
typedef struct Node
{
int data; //存放具体的数据内容
struct Node *next; //下一个节点地址
}Node;
//定义队列的数据类型
typedef struct
{
Node *head; //保存第一个节点的地址
}Queue;
//入队操作
void push (Queue *pq, int data);
//遍历操作
void travel (Queue *pq);
//判断队列是否为空
int empty (Queue *pq);
//判断队列是否为满
int full (Queue *pq);
//获取队首元素的值
int get_head (Queue *pq);
//获取队尾元素的值
int get_tail (Queue *pq);
//计算队列中节点的个数
int size (Queue *pq);
//出队操作
int pop (Queue *pq);
//清空队列中所有的元素
void clear (Queue *pq);
int main (void)
{
//1.创建队列并且进行初始化
Queue queue;
queue.head = NULL;
push(&queue,11);
travel(&queue); //11
push(&queue,22);
travel(&queue); //11 22
push(&queue,33);
travel(&queue); //11 22 33
push(&queue,44);
travel(&queue); //11 22 33 44
push(&queue,55);
travel(&queue); //11 22 33 44 55
printf("出队的元素是:%d\n",pop(&queue));
travel(&queue); //22 33 44 55
printf("出队的元素是:%d\n",pop(&queue));
travel(&queue); //33 44 55
push(&queue,66);
travel(&queue); //33 44 55 66
push(&queue,77);
travel(&queue); //33 44 55 66 77
printf("------------------\n");
printf("%s\n",empty(&queue)?"队列已经空了":"队列没有空");
printf("%s\n",full(&queue)?"队列已经满了":"队列没有满");
printf("队首元素是:%d\n",get_head(&queue));
printf("队尾元素是:%d\n",get_tail(&queue));
printf("队列中的元素个数是:%d\n",size(&queue));
printf("---------------------\n");
travel(&queue);
printf("出队的元素是:%d\n",pop(&queue));
clear(&queue);
travel(&queue);
return 0;
}
void push (Queue *pq, int data)
{
//1.创建新节点
Node *pn = (Node *)malloc (sizeof (Node));
pn->data = data;
pn->next = NULL;
//2.挂接新节点到队列的尾部
//2.1 如果队列为空,则直接连接
if (NULL == pq->head)
pq->head = pn;
//2.2 如果队列不为空,使用尾节点连接新节点
else
{
Node *p = pq->head;
// p指向的节点不是尾节点,则寻找下一个节点 再比较
while (p->next != NULL)
//指向下一个节点
p = p->next;
//使用尾节点连接新节点
p->next = pn;
}
}
void travel (Queue *pq)
{
printf ("队列中的元素有:");
Node *p = pq->head;
while (p != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf ("\n");
}
int size (Queue *pq)
{
int count = 0;
Node *p = pq->head;
while (p != NULL)
{
count++;
p = p->next;
}
return count;
}
int get_tail (Queue *pq)
{
if (empty (pq))
return ;
Node *p = pq->head;
while (p->next != NULL)
p = p->next;
return p->data;
}
int get_head (Queue *pq)
{
if (empty (pq))
return ;
return pq->head->data;
}
int full (Queue *pq)
{
return 0;
}
int empty (Queue *pq)
{
return NULL == pq->head;
}
int pop (Queue *pq)
{
if (empty (pq))
return ;
//保存第一个节点的地址
Node *p = pq->head;
//头指针指向第二个节点
pq->head = pq->head->next;
//保存要删除的节点数据
int temp = p->data;
//删除第一个节点
free (p);
p = NULL;
return temp;
}
void clear (Queue *pq)
{
while (pq->head != NULL)
{
//保存第一个节点地址
Node *p = pq->head;
//头指针指向下一个节点
pq->head = pq->head->next;
//释放第一个节点
free (p);
p = NULL;
}
}
输出结果:
队列中的元素有:11
队列中的元素有:11 22
队列中的元素有:11 22 33
队列中的元素有:11 22 33 44
队列中的元素有:11 22 33 44 55
出队的元素是:11
队列中的元素有:22 33 44 55
出队的元素是:22
队列中的元素有:33 44 55
队列中的元素有:33 44 55 66
队列中的元素有:33 44 55 66 77
------------------
队列没有空
队列没有满
队首元素是:33
队尾元素是:77
队列中的元素个数是:5
---------------------
队列中的元素有:33 44 55 66 77
出队的元素是:33
队列中的元素有: