常见设计模式之(一):单例模式
文章目录
- 常见设计模式之(一):单例模式
- 1 什么是单例模式(singleton pattern)?
- 2 单例模式的使用场景、优缺点
- 2.1 使用场景
- 2.2 优点
- 2.3 缺点
- 2.4 懒汉与饿汉
- 2.5 单例模式的线程安全问题
- 3 单例模式的c++实现
- 3.1 饿汉模式的实现
- 3.2 懒汉模式的实现
- 3.2.1 版本1 【适合单线程的场景,在多线程下存在线程安全问题】
- 3.2.2 版本2 通过加锁保证线程安全
- 3.2.3 版本3 双检查锁(DCL)机制
- 3.2.4 版本4x 利用c++11 中 std:: call_once进行实现
- 3.2.5 版本5 利用POSIX中pthread_once进行实现
- 4 结束语
常见设计模式之(一):单例模式
1 什么是单例模式(singleton pattern)?
摘自 java 设计模式官网 中 有关单例模式的定义:
Ensures that only one object of a particular class is ever created, and provide a global point of access to it
确保某个特定的类只被创建一次,并且提供一个全局的接口去访问实例。
提炼几点主要内容
- 需要提供一个全局的接口去访问改实例
- 确保该类只被创建一次(禁用赋值、拷贝等构造函数)
- 该实例为全局资源,如果涉及多线程,还需考虑同步问题
2 单例模式的使用场景、优缺点
2.1 使用场景
系统中要求一个类只有一个对象时可采取单例模式,具体的以下场景:
- 配置文件模块
- 生成唯一序列号时,比如说:设备的ID
- 获取系统状态信息,比如说:Windows的资源管理器 获取cpu 内存等信息
- 当创建一个对象需要的资源过多时,可以采用单例模式
- 资源池类的场景:线程池、连接池等
- 日志模块
大家可以自己实际情况进行分析,采用符合自己实际情况的模式
2.2 优点
- 单例在内存中只有一个实例,节省内存、减少创建实例带来的系统消耗。
2.3 缺点
- 单例类职责比较多,在某种程度上违反“单一职责原则”,不利于进行软件测试
- 单例类没有做抽象,所以扩展很不方便。
- 在单线程的情况下基本上不存在问题,在多线程中必须考虑线程安全的问题。 2.5 小节会进行单独讨论
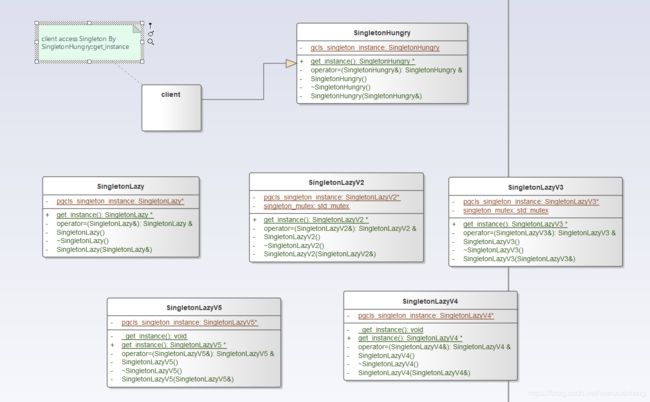
2.4 懒汉与饿汉
设计模式是Java中最经常使用的,而大多数的设计模式通常也是用Java实现的,设计模式更是一种编程思想,可以用任何的编程语言进行实现,只不过有的语言简单有的语言麻烦而已,本小结主要介绍单例模式的c++实现。
提到单例就不得不提到单例模式的两种实现方法:懒汉 和 饿汉
- 懒汉:不到万不得已就不会去实例化类,换而言之在第一次用到类实例的时候才会去实例化,这是一种时间换空间的方式
- 饿汉:即类产生的时候就创建好实例对象,这是一种空间换时间的方式
2.5 单例模式的线程安全问题
单例模式在单线程下不存在线程安全的问题,然而在多线程下就涉及到全局资源竞争问题,主要存在以下两个方面:
- 单例类在进行实例化时确保线程安全:在懒汉模式下存在线程安全问题,而饿汉模式线程安全不存在,至于原因稍后给出相关的代码
- 多线程对单例这种全局资源进行读写时会存在线程安全问题,这种情况无论是懒汉还是饿汉都存在此问题。这也是多线程程序设计不可避免的问题。如果多线程对于单例的全局资源只进行读操作时,则不存在此问题。
本博文主要讨论上述第一种线程安全问题。
3 单例模式的c++实现
3.1 饿汉模式的实现
利用static静态全局变量实现饿汉模式,代码如下:
SingletonHungry.h
#ifndef SINGLETON_HUNGRY_H
#define SINGLETON_HUNGRY_H
#include单例的使用
SingletonHungryMain.cpp
#include "SingletonHungry.h"
SingletonHungry SingletonHungry :: gcls_singleton_instance;
int main(void)
{
printf("Singleton Hungry test \n");
return 0;
}
编译运行:
root@wan:/wan/01singleton# make SingletonHungryMain
g++ SingletonHungryMain.cpp -o SingletonHungryMain
root@wan:/wan/01singleton# ./SingletonHungryMain
SingletonHungry 20 create Singleton Hungry
Singleton Hungry test
~SingletonHungry 24 destroy Singleton Hungry
通过上面代码可以饿汉模式是不需要考虑在创建时的线程安全问题,因为在程序启动之前,内存就已经分配完成,程序退出时自动进行析构;同样内存可以分配在堆上,同样是程序加载main函数之前进行new 等程序结束运行之前进行delete 这里就不进行详细的介绍,有一些可以自动释放堆内存的一些方法(智能指针、通过内部类的方式等),有机会进行详细介绍。
3.2 懒汉模式的实现
3.2.1 版本1 【适合单线程的场景,在多线程下存在线程安全问题】
SingletonLazyV1.h
#ifndef SINGLETON_LAZY_H
#define SINGLETON_LAZY_H
#include
class SingletonLazy
{
public:
/*
多个线程同时调用该接口时存在线程安全问题:
问题出在 pgcls_singleton_instance = new SingletonLazy();
线程1 检查 pgcls_singleton_instance = NULL 然后进行 new 然而new还没有完成
此时线程2 同样也检测到 pgcls_singleton_instance = NULL 同样又去进行new,这样就会造成:
1、new了两次 造成内存泄漏
2、pgcls_singleton_instance被赋值了两次,从而早晨内存错乱。
*/
static SingletonLazy * get_instance()
{
if(NULL == pgcls_singleton_instance)
{
pgcls_singleton_instance = new SingletonLazy();
printf("%s %d new Singleton Lazy\n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
}
else
{
printf("%s %d Singleton Lazy already \n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
}
return pgcls_singleton_instance;
}
private:
// 静态的全局变量 声明为 私有 static 变量 防止外部进行访问
static SingletonLazy * pgcls_singleton_instance;
// 构造函数 析构函数 赋值 拷贝 函数 防止外部进行创建
SingletonLazy()
{
printf("%s %d create Singleton Lazy\n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
};
~SingletonLazy()
{
printf("%s %d destroy Singleton Lazy\n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
};
SingletonLazy(const SingletonLazy &);
SingletonLazy & operator=(const SingletonLazy &);
};
SingletonLazy * SingletonLazy :: pgcls_singleton_instance = NULL;
#endif
主程序
SingletonLazyV1Main.cpp
#include "SingletonLazyV1.h"
int main(void)
{
SingletonLazy:: get_instance();
SingletonLazy:: get_instance();
SingletonLazy:: get_instance();
return 0;
}
编译并运行
root@wan:/wan/01singleton# make SingletonLazyV1Main
g++ SingletonLazyV1Main.cpp -o SingletonLazyV1Main
root@wan:/wan/01singleton# ./SingletonLazyV1Main
SingletonLazy 30 create Singleton Lazy
get_instance 15 new Singleton Lazy
get_instance 19 Singleton Lazy already
get_instance 19 Singleton Lazy already
3.2.2 版本2 通过加锁保证线程安全
SingletonLazyV2.h
#ifndef SINGLETON_LAZY_H
#define SINGLETON_LAZY_H
#include
#include
class SingletonLazy
{
public:
/*
解决多线程调用时线程安全问题采用加锁的形式。
*/
static SingletonLazy * get_instance()
{
singleton_mutex.lock();
if(NULL == pgcls_singleton_instance)
{
pgcls_singleton_instance = new SingletonLazy();
printf("%s %d new Singleton Lazy\n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
}
else
{
printf("%s %d Singleton Lazy already \n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
}
singleton_mutex.unlock();
return pgcls_singleton_instance;
}
private:
static std::mutex singleton_mutex;
// 静态的全局变量 声明为 私有 static 变量 防止外部进行访问
static SingletonLazy * pgcls_singleton_instance;
// 构造函数 析构函数 赋值 拷贝 函数 防止外部进行创建
SingletonLazy()
{
printf("%s %d create Singleton Lazy\n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
};
~SingletonLazy()
{
printf("%s %d destroy Singleton Lazy\n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
};
SingletonLazy(const SingletonLazy &);
SingletonLazy & operator=(const SingletonLazy &);
};
SingletonLazy * SingletonLazy :: pgcls_singleton_instance = NULL;
std::mutex SingletonLazy ::singleton_mutex;
#endif
SingletonLazyV2Main.cpp
#include "SingletonLazyV2.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void* thread_func(void *arg)
{
int i = 0;
while(i < 100)
{
SingletonLazy:: get_instance();
i++;
}
}
int main(void)
{
struct timeval start_time, end_time;
//运行计时开始
gettimeofday(&start_time, NULL);
int proc = 100;
pthread_t *threadId = (pthread_t *)malloc(proc*sizeof(pthread_t));
for (int i = 0; i < proc; i++)
{
pthread_create(&threadId[i], NULL, thread_func, NULL);
}
for (int i = 0; i < proc; i++)
{
pthread_join(threadId[i], NULL);
}
//运行计时结束
gettimeofday(&end_time, NULL);
//打印相关信息
printf("thread number = %d cost time msecond = %ld\n",proc,
(long)((end_time.tv_sec - start_time.tv_sec)*1000 + (end_time.tv_usec - start_time.tv_usec)/1000));
return 0;
}
编译并运行
root@wan:/wan/01singleton# g++ SingletonLazyV2Main.cpp -o SingletonLazyV2Main -lpthread -std=c++11
root@wan:/wan/01singleton# ./SingletonLazyV2Main
SingletonLazy 38 create Singleton Lazy
get_instance 20 new Singleton Lazy
get_instance 24 Singleton Lazy already
thread number = 100 cost time msecond = 1432
3.2.3 版本3 双检查锁(DCL)机制
SingletonLazyV3.h
#ifndef SINGLETON_LAZY_H
#define SINGLETON_LAZY_H
#include
#include
class SingletonLazy
{
public:
/*
先判断下 if (NULL == pgcls_singleton_instance),如果条件不满足则直接返回,提高效率
采用双检查锁(DCL),即:double-checked locking
*/
static SingletonLazy * get_instance()
{
if(NULL == pgcls_singleton_instance)
{
singleton_mutex.lock();
if(NULL == pgcls_singleton_instance)
{
pgcls_singleton_instance = new SingletonLazy();
//printf("%s %d new Singleton Lazy\n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
}
else
{
//printf("%s %d Singleton Lazy already \n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
}
singleton_mutex.unlock();
}
else
{
//printf("%s %d Singleton Lazy already \n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
}
return pgcls_singleton_instance;
}
private:
static std::mutex singleton_mutex;
// 静态的全局变量 声明为 私有 static 变量 防止外部进行访问
static SingletonLazy * pgcls_singleton_instance;
// 构造函数 析构函数 赋值 拷贝 函数 防止外部进行创建
SingletonLazy()
{
printf("%s %d create Singleton Lazy\n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
};
~SingletonLazy()
{
printf("%s %d destroy Singleton Lazy\n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
};
SingletonLazy(const SingletonLazy &);
SingletonLazy & operator=(const SingletonLazy &);
};
SingletonLazy * SingletonLazy :: pgcls_singleton_instance = NULL;
std::mutex SingletonLazy ::singleton_mutex;
#endif
SingletonLazyV3Main
#include "SingletonLazyV3.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void* thread_func(void *arg)
{
int i = 0;
while(i < 100)
{
SingletonLazy:: get_instance();
i++;
}
}
int main(void)
{
struct timeval start_time, end_time;
//运行计时开始
gettimeofday(&start_time, NULL);
int proc = 10000;
pthread_t *threadId = (pthread_t *)malloc(proc*sizeof(pthread_t));
for (int i = 0; i < proc; i++)
{
pthread_create(&threadId[i], NULL, thread_func, NULL);
}
for (int i = 0; i < proc; i++)
{
pthread_join(threadId[i], NULL);
}
//运行计时结束
gettimeofday(&end_time, NULL);
//打印相关信息
printf("thread number = %d cost time msecond = %ld\n",proc,
(long)((end_time.tv_sec - start_time.tv_sec)*1000 + (end_time.tv_usec - start_time.tv_usec)/1000));
return 0;
}
编译并运行
root@wan:/wan/01singleton# g++ SingletonLazyV3Main.cpp -o SingletonLazyV3Main -lpthread -std=c++11
root@wan:/wan/01singleton# ./SingletonLazyV3Main
SingletonLazy 45 create Singleton Lazy
thread number = 10000 cost time msecond = 1210
3.2.4 版本4x 利用c++11 中 std:: call_once进行实现
SingletonLazyV4.h
#ifndef SINGLETON_LAZY_H
#define SINGLETON_LAZY_H
#include
#include
std::once_flag once_singleton;
class SingletonLazy
{
public:
static SingletonLazy * get_instance()
{
std::call_once(once_singleton,&SingletonLazy::_get_instance);
return pgcls_singleton_instance;
}
private:
static SingletonLazy * pgcls_singleton_instance;
static void _get_instance()
{
pgcls_singleton_instance = new SingletonLazy();
}
// 构造函数 析构函数 赋值 拷贝 函数 防止外部进行创建
SingletonLazy()
{
printf("%s %d create Singleton Lazy\n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
};
~SingletonLazy()
{
printf("%s %d destroy Singleton Lazy\n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
};
SingletonLazy(const SingletonLazy &);
SingletonLazy & operator=(const SingletonLazy &);
};
SingletonLazy * SingletonLazy :: pgcls_singleton_instance = NULL;
#endif
调用方式以及编译方法同上
3.2.5 版本5 利用POSIX中pthread_once进行实现
SingletonLazyV5.h
#ifndef SINGLETON_LAZY_H
#define SINGLETON_LAZY_H
#include
#include
pthread_once_t once_singleton = PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT;
class SingletonLazy
{
public:
static SingletonLazy * get_instance()
{
pthread_once(&once_singleton,&SingletonLazy::_get_instance);
return pgcls_singleton_instance;
}
private:
static SingletonLazy * pgcls_singleton_instance;
static void _get_instance()
{
pgcls_singleton_instance = new SingletonLazy();
}
// 构造函数 析构函数 赋值 拷贝 函数 防止外部进行创建
SingletonLazy()
{
printf("%s %d create Singleton Lazy\n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
};
~SingletonLazy()
{
printf("%s %d destroy Singleton Lazy\n",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
};
SingletonLazy(const SingletonLazy &);
SingletonLazy & operator=(const SingletonLazy &);
};
SingletonLazy * SingletonLazy :: pgcls_singleton_instance = NULL;
#endif
**针对 std::call_once 和pthread_once 单独进行讨论
4 结束语
写到这里单例模式介绍的基本差不多了,读者可以根据自己的情况进行调整,此外由于有篇幅有限,有关单例单例模式的扩展没有涉及到:
- 将上述单例类提炼成模板
- 实例数量固定的类(单例类的扩展)
- 单例模式的实际应用
这些内容将在后续博文中就行讲解。