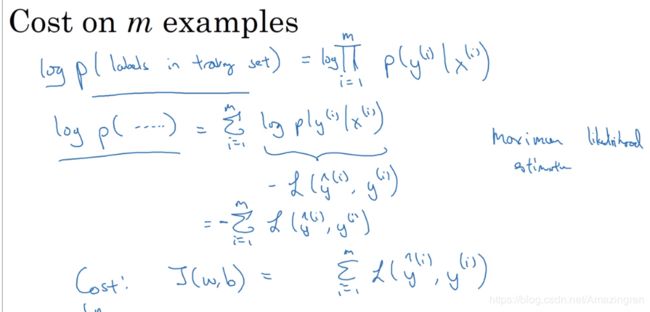【Neural Networks and Deep Learning2019吴恩达最新Coursera课程学习】——第二周—Neural Networks Basics
Neural Networks Basics(神经网络的基础知识)
这一周的学习内容主要就是围绕神经网络基础以及Python以及向量化操作进行的
所以这一周过后我自己就应该获得扎实的神经网络的基础以及基本的Python编程能力!
这次的课程是以逻辑回归为例子来逐步进行的。希望可以通过这样的方式学习更多东西,而且这个例子非常有助于理解
1. Binary Classification(二分类,逻辑回归就是一个二分类问题)——2019-06-11
这一节我觉得自己最重要的收货就是:
输入的图片(3个通道RGB,美格尔channel都是64X64),那么当把这样的图像送入到计算机进行处理的时候(比如这里的识别猫咪的方案,如果是猫咪就是1,没有猫咪就是0)
那么计算机会把这样的数据挤压成一个列向量(64X64X3, 1),该向量就被称之为特征向量。

在二元分类问题中,就是需要学习一个分类器,
输入:一副图的特征向量
输出:0,1向量
还有一点需要说的就是这里的Notation了,输入最后会以矩阵的形式送进去
每一列是一个样本的输入,列的长度是特诊的维度(也就是矩阵的行数),列的个数是特征向量的个数(也就是矩阵的列数)
输出也是一维向量(1Xm),(y1, y2, y3, y4, y5, ……, yn)
每一个y代表的是相应的x对应的输出。
2. Logistics Regression(逻辑回归)——2019-06-11
从线性回归开始,引入sigmoid()函数

就是之前五角星的地方会是实数系列,并不能以是(1)否(0)的形式来告诉我们图片中是不是有猫咪,但是经过sogmoid之后就会把输出的具体数值拉到(0,1)之间。约接近1,就说明是猫的可能性越大。
另外需要说明的是有时候会把参数写在一起.比如:

这里x0就是一个额外的特征,相当于b,这个时候的拟合函数也就不是wx+b了而是wx了!
但是这个课程中还是以分开的形式进行,吴恩达说这样分开会让网络简单!
3. Logistic Regression Cost Function(逻辑回归的代价函数)——2019-06-11
目的:为了求解参数w和b
办法:定义代价函数
里的Loss Function并没有选择平方的形式,而是这种交叉熵形式,后面的视频中会详细的介绍。
然后要注意区分y=0以及y=1的情况下这个损失 函数的形式以及相应的变化的趋势
上面的形式是对单一的优化示例进行的描述:这里叫做loss function
下面的是对所有的样本进行描述的代价函数,叫做Cost Function:检测优化组的整体运行情况,是一个平均损失
loss函数适用于 单一的优化示例,
cost函数反应的是你的参数成本;
所以由此,我们的目的就是寻找合适的W和B来使得整体的J变得更小。
总结:逻辑回归可以被视为非常小的神经网络。
4. Gradient Descent(梯度下降)——2019-06-13
这一次的课程主要就是梯度下降的知识点,基本没有什么特别的东西,很基础,
大概就是下面的这样的一个思路:
- 我们需要让代价函数最小
- 我们需要更新参数w和b
- 那么要使得J变得最小就需要朝着J减小的最快的方向进行,也就是梯度的方向,所以朝着这个方向去更新w和b
- 得到使得J最小的参数w和b
这个大概就是梯度下降的只是,这里还区分了倒数和偏导数的概念,对这些要有基本的认识,在高等数学里就学过了!
5. Derivatives(倒数) —— 2019-06-13
高中知识
6. More Derivative Examples(非线性函数的倒数)—— 2019-06-13
高中知识
7. Computation Graph(计算图)——2019-06-13
我的立理解这里更像是复合函数的东西,把小 的变量组装成小函数,然后小函数再组成搭函数,方便后面的链式求导吧!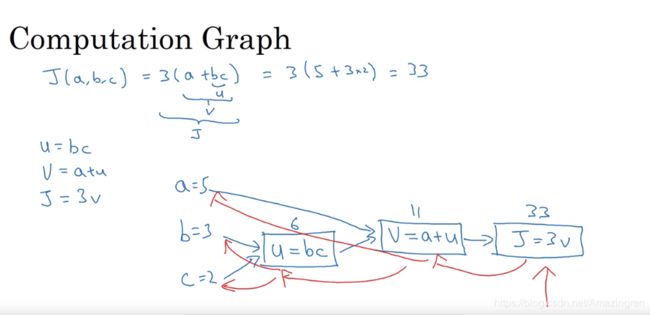
8. Derivatives with a computation graph(对计算图的求导)——2019-06-13
所以这里就是上面那个步骤的反向的过程了!
反向的链式求导法则!
9. Logistic Regression Gradient Descent(逻辑回归中的梯度下降)——2019-06-13
逻辑回归中的梯度下降是如何进行的!
还是链式法则,一个一个求导,dL/dz = a-y
高中基础知识!
10. Gradient Descent on m Examples(多个样例上的梯度下降)——2019-06-13
主要思想:在深度学习算法中,数据的特征非常多,如果用for循环的话,那么计算量会非常大,这样就非常低效,所以要引入矢量化的计算!
接下来的Python and Vectorization 就是用来说明这些问题的的!
————————————————Python and Vectorization————————————————————
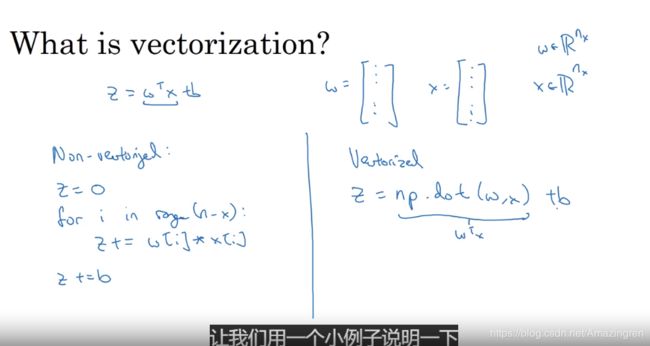
1. Vectorization(向量化)——2019-06-13
在jupyter notebook中随便来两个例子就显而易见的发现问题所在了:
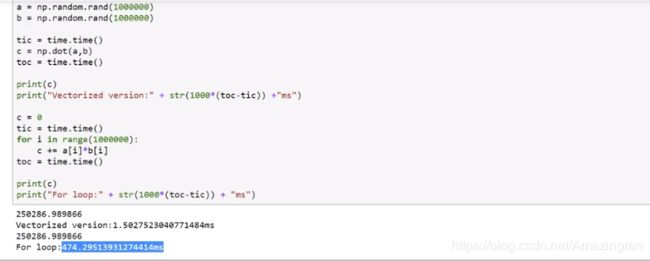
先验向量化的操作要快几个数量级!(相比于for循环!)
2. More Vectorization Examples(更多的向量化的例子)——2019-06-13
这里将的还是把直接的for循环要变换成矩阵运算!
这样的话几行代码就能训练整个数据集!
3. Vectorizing Logistic Regression(逻辑回归的向量化)——2019-06-15
对于逻辑回归:
z = wx +b
这只是一个这样的还有很多个从1到n
如果用for循环来计算的话,那将非常的耗费计算能力
但是用矩阵运算就会消除这个问题,直接一行代码就能解决!
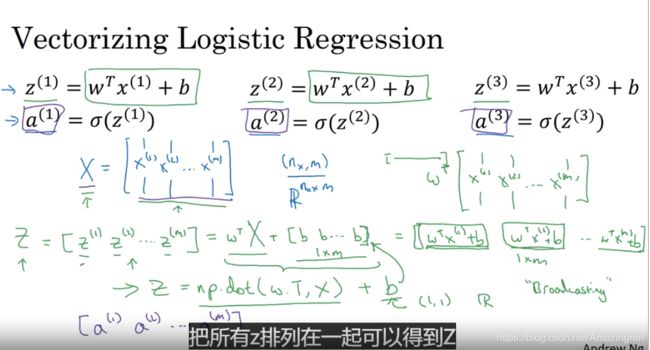
加油鸭!
4. Vectorizing Logistic Regression’s Gradient Output(梯度上的向量化!)——2019-06-15
高效的实现Logistic Regression

这里的变化就是如上面的PPT讲的一样,关于dz的推导有点忘记了,但是结果就是a-y
这里分别就是把单个计算db和dw的问题用向量化的计算去除了for循环,不然计算起来运算量太大了!时间复杂度太高了!
然后这里就是整体的运用了:

一个大的for循环来控制epoch的次数,然后就可以更新参数,就是一个网络更新的过程!
5. Broadcasting in Python(广播机制)——2019-06-16
6. A Note on python/numpy vectors(一些小点子)——2019-06-16
从源头消除Python的bug,也让编程的练习变得更容易!
一定要知道运算背后的机制,比如广播机制这种非常灵活的特点有时候也是会带来一些奇奇怪怪的bug,所以要自己脑子很清楚的去处理这些东西!
下面就是一些防止写出奇奇怪怪代码的点子!记录一下!
- 不要使用秩为1的数组,那样会出现奇怪的bug,要指定维度,使用n1的矩阵或者1n的矩阵,本质上还是向量!!这样才好一点!
- 自由使用断言语句assert(a.shape ==(5,1))来查询数矩阵和数组的维度!没什么代价,随便使用!
7. Quick tour of Jupyter/iPython Notebooks(简单的上手介绍)——2019-06-16
就是正常的使用就好了,直接在coursera上面学习的好处真的多,很方便,不用折腾环境!这样就好多了!直接在网页打开那边配置好环境的jupyter!
最小化代价函数就是最大似然估计(寻找一个参数使得所有的乘机最大!)
8. Explanation of logistic regression cost function(对逻辑回归代价函数的解释)——2019-06-16
最小化代价函数就是最大似然估计(寻找一个参数使得所有的乘机最大!)
因为去了负对数!当然这里的样本都得是iid独立同分布的!
—————————————————Practice Question—————————————————————
这个还是不妨出来比较好吧,既然学了课程就要遵守约定!
感兴趣的可以自己在coursera上面报名参加课程实际体验!
下面的programming Assignment 也是一样的!
包含了下面这些东西:
加油鸭!!!
————————————练习题:Logistic Regression with a Neural Network mindset v5——————————————
学习心得:
General Architecture of learning algorithm
- Logistic Regression is actually a very simple Neural Network!(A direct understanding of the flow!)
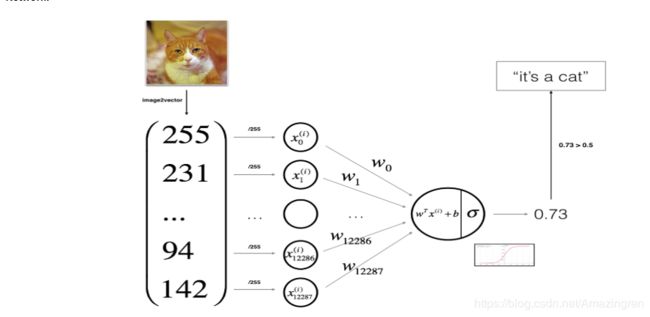
- Mathematical expression of the algorithm:
Building the parts of our algorithm:
# GRADED FUNCTION: sigmoid
def sigmoid(z):
"""
Compute the sigmoid of z
Arguments:
z -- A scalar or numpy array of any size.
Return:
s -- sigmoid(z)
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
s = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
### END CODE HERE ###
return s
print ("sigmoid([0, 2]) = " + str(sigmoid(np.array([0,2]))))
# 这里代码比较重要,记录下,主要是维度
# GRADED FUNCTION: initialize_with_zeros
def initialize_with_zeros(dim):
"""
This function creates a vector of zeros of shape (dim, 1) for w and initializes b to 0.
Argument:
dim -- size of the w vector we want (or number of parameters in this case)
Returns:
w -- initialized vector of shape (dim, 1)
b -- initialized scalar (corresponds to the bias)
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
w = np.zeros(shape=(dim,1))
b = 0
### END CODE HERE ###
assert(w.shape == (dim, 1))
assert(isinstance(b, float) or isinstance(b, int))
return w, b
dim = 2
w, b = initialize_with_zeros(dim)
print ("w = " + str(w))
print ("b = " + str(b))
# GRADED FUNCTION: propagate
import numpy as np
def propagate(w, b, X, Y):
"""
Implement the cost function and its gradient for the propagation explained above
Arguments:
w -- weights, a numpy array of size (num_px * num_px * 3, 1)
b -- bias, a scalar
X -- data of size (num_px * num_px * 3, number of examples)
Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat) of size (1, number of examples)
Return:
cost -- negative log-likelihood cost for logistic regression
dw -- gradient of the loss with respect to w, thus same shape as w
db -- gradient of the loss with respect to b, thus same shape as b
Tips:
- Write your code step by step for the propagation. np.log(), np.dot()
"""
m = X.shape[1]
# FORWARD PROPAGATION (FROM X TO COST)
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
A = sigmoid(np.dot(w.T, X) + b) # compute activation
cost = -np.sum(np.dot(Y,np.log(A).T) + np.dot(1-Y, np.log(1-A).T)) / m # compute cost
### END CODE HERE ###
# BACKWARD PROPAGATION (TO FIND GRAD)
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
dw = np.dot(X, (A-Y).T)/ m
db = np.sum(A-Y) / m
### END CODE HERE ###
assert(dw.shape == w.shape)
assert(db.dtype == float)
cost = np.squeeze(cost)
assert(cost.shape == ())
grads = {"dw": dw,
"db": db}
return grads, cost
w, b, X, Y = np.array([[1.],[2.]]), 2., np.array([[1.,2.,-1.],[3.,4.,-3.2]]), np.array([[1,0,1]])
grads, cost = propagate(w, b, X, Y)
print ("dw = " + str(grads["dw"]))
print ("db = " + str(grads["db"]))
print ("cost = " + str(cost))
# GRADED FUNCTION: optimize
def optimize(w, b, X, Y, num_iterations, learning_rate, print_cost = False):
"""
This function optimizes w and b by running a gradient descent algorithm
Arguments:
w -- weights, a numpy array of size (num_px * num_px * 3, 1)
b -- bias, a scalar
X -- data of shape (num_px * num_px * 3, number of examples)
Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat), of shape (1, number of examples)
num_iterations -- number of iterations of the optimization loop
learning_rate -- learning rate of the gradient descent update rule
print_cost -- True to print the loss every 100 steps
Returns:
params -- dictionary containing the weights w and bias b
grads -- dictionary containing the gradients of the weights and bias with respect to the cost function
costs -- list of all the costs computed during the optimization, this will be used to plot the learning curve.
Tips:
You basically need to write down two steps and iterate through them:
1) Calculate the cost and the gradient for the current parameters. Use propagate().
2) Update the parameters using gradient descent rule for w and b.
"""
costs = []
for i in range(num_iterations):
# Cost and gradient calculation (≈ 1-4 lines of code)
### START CODE HERE ###
grads, cost = propagate(w,b,X,Y)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Retrieve derivatives from grads
dw = grads["dw"]
db = grads["db"]
# update rule (≈ 2 lines of code)
### START CODE HERE ###
w = w - learning_rate * dw
b = b - learning_rate * db
### END CODE HERE ###
# Record the costs
if i % 100 == 0:
costs.append(cost)
# Print the cost every 100 training iterations
if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:
print ("Cost after iteration %i: %f" %(i, cost))
params = {"w": w,
"b": b}
grads = {"dw": dw,
"db": db}
return params, grads, costs
params, grads, costs = optimize(w, b, X, Y, num_iterations= 100, learning_rate = 0.009, print_cost = False)
print ("w = " + str(params["w"]))
print ("b = " + str(params["b"]))
print ("dw = " + str(grads["dw"]))
print ("db = " + str(grads["db"]))
# GRADED FUNCTION: predict
def predict(w, b, X):
'''
Predict whether the label is 0 or 1 using learned logistic regression parameters (w, b)
Arguments:
w -- weights, a numpy array of size (num_px * num_px * 3, 1)
b -- bias, a scalar
X -- data of size (num_px * num_px * 3, number of examples)
Returns:
Y_prediction -- a numpy array (vector) containing all predictions (0/1) for the examples in X
'''
m = X.shape[1]
Y_prediction = np.zeros((1,m))
w = w.reshape(X.shape[0], 1)
# Compute vector "A" predicting the probabilities of a cat being present in the picture
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
A = sigmoid(np.dot(w.T, X) + b)
### END CODE HERE ###
#print(Y_prediction.shape)
for i in range(A.shape[1]):
# Convert probabilities A[0,i] to actual predictions p[0,i]
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)
if(A[0][i] <=0.5):
Y_prediction[0][i] = 0
else:
Y_prediction[0][i] = 1
### END CODE HERE ###
assert(Y_prediction.shape == (1, m))
return Y_prediction
w = np.array([[0.1124579],[0.23106775]])
b = -0.3
X = np.array([[1.,-1.1,-3.2],[1.2,2.,0.1]])
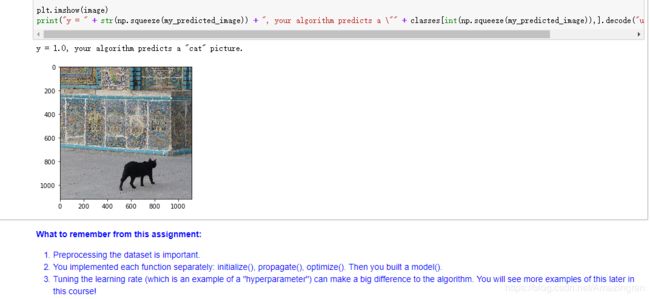
print ("predictions = " + str(predict(w, b, X)))
维度真的很重要!
Heroes of Deep Learning ——Pieter Abbeel
- 当时让我觉得很着迷的是 就是一个简单的许多随机变量的组合分布 然后在一些变量上 加上限定条件 并在其它变量上做出结论 就能让你获得如此丰富的结论 只要它是可被计算的 能让图模型的计算变得可行!
- 对于初学者的建议:一定要动手去做去尝试,而不是一味的看视频,读文章,比如现在很多深度学习的框架,可有很快的跑起来一些东西,然后英国16岁的少年在Kaggle比赛上就已经取得了很好的成绩,所以一定要自学!
- 然后对于导师和教授的理解:导师和教授就是将花费时间加速学生的成长和进步当做自己的责任的人,这么来看,我身边的这些大多数的导师和教授都是一坨狗屎!妈的还是要自己好好学习!好好自学!开源的世界真的太美好了!