ServerBootstrap和Bootstrap都是Netty的启动类,他们的主要作用就是配置相关参数(IP,端口等)并启动整个Netty服务,不同的是ServerBootstrap用于服务端服务启动,Bootstrap用于客户端。
我们先看一段最简单的ServerBootstrap启动代码
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);//用于接受accept事件的group serverSocketChannel
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); //用于真正读写事件的group socketChannel
try {
//create ServerBootstrap instance
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); //启动装载器,用于转载配置
//Specifies NIO transport, local socket address
//Adds handler to channel pipeline
//使用NIO通道
//保持连接,如果不设置则一次通讯后自动断开
b.group(bossGroup,group).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true).localAddress(port)
.handler(new SimpleServerHandler())//服务端handler
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() { //channel使用的handler
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoServerHandler2(),new EchoServerHandler());
}
});
//Binds server, waits for server to close, and releases resources
ChannelFuture f = b.bind().sync();
System.out.println(EchoServer.class.getName() + "started and listen on �" + f.channel().localAddress());
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
ServerBootstrap和Bootstrap相比最大的区别,是拥有2个EventLoopGroup,一个用于ServerSocketChannel的accept,一个用于SocketChannel的读写事件。
private volatile EventLoopGroup childGroup;
private volatile ChannelHandler childHandler;
...
public ServerBootstrap group(EventLoopGroup parentGroup, EventLoopGroup childGroup) {
super.group(parentGroup);
...
this.childGroup = childGroup;
return this;
}
public ServerBootstrap childHandler(ChannelHandler childHandler) {
...
this.childHandler = childHandler;
return this;
}
ServerBootstrap多了一个childGroup和childHandler
对比下ServerBootstrap和Bootstrap的主要差别:
ServerBootstrap.initChannel()
void init(Channel channel) throws Exception {
//设置channel参数
final Map, Object> options = options0();
synchronized (options) {
channel.config().setOptions(options);
}
final Map, Object> attrs = attrs0();
synchronized (attrs) {
for (Entry, Object> e: attrs.entrySet()) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
AttributeKey Bootstrap.initChannel()
void init(Channel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();
p.addLast(config.handler());
//设置channel参数
final Map, Object> options = options0();
synchronized (options) {
for (Entry, Object> e: options.entrySet()) {
try {
if (!channel.config().setOption((ChannelOption) e.getKey(), e.getValue())) {
logger.warn("Unknown channel option: " + e);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to set a channel option: " + channel, t);
}
}
}
final Map, Object> attrs = attrs0();
synchronized (attrs) {
for (Entry, Object> e: attrs.entrySet()) {
channel.attr((AttributeKey) e.getKey()).set(e.getValue());
}
}
}
看到ServerBootstrap比Bootstrap最大的区别是多了ServerBootstrapAcceptor
再看ServerBootstrapAcceptor,它继承了ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter,并且重写了channelRead函数:
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
//这里的msg实际上是SocketChannel
final Channel child = (Channel) msg;
//给这个channel增加handler
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler);
//设置参数,可以看到和Bootstrap的一样
for (Entry, Object> e: childOptions) {
try {
if (!child.config().setOption((ChannelOption) e.getKey(), e.getValue())) {
logger.warn("Unknown channel option: " + e);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to set a channel option: " + child, t);
}
}
for (Entry, Object> e: childAttrs) {
child.attr((AttributeKey) e.getKey()).set(e.getValue());
}
//注册child事件,增加监听操作完成后的关闭事件
try {
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
forceClose(child, t);
}
}
这里也许会有疑问,为什么会在读操作的时候在childGroup
里注册了channel呢?
先放一下这个疑问,回顾一下前几节内容,在什么时候触发的这个channelRead函数在。
http://www.jianshu.com/p/c998e29be549
NioEventLoop的run循环中,processSelectedKey的时候是这么设置的,注意这里是accept和read共用了一个事件:
//当accept或read事件时触发read函数
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
if (!ch.isOpen()) {
// Connection already closed - no need to handle write.
return;
}
}
NioServerSocketChannel(中间省略的步骤可以在前几节找到):
protected int doReadMessages(List buf) throws Exception {
SocketChannel ch = javaChannel().accept();
try {
if (ch != null) {
//
buf.add(new NioSocketChannel(this, ch));
return 1;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
return 0;
}
所以当一个client注册上来产生一个accept事件的时候,Netty会为这个事件新生成一个NioSocketChannel,并且为它添加childHandler,后续的读写事件便基于这个NioSocketChannel。
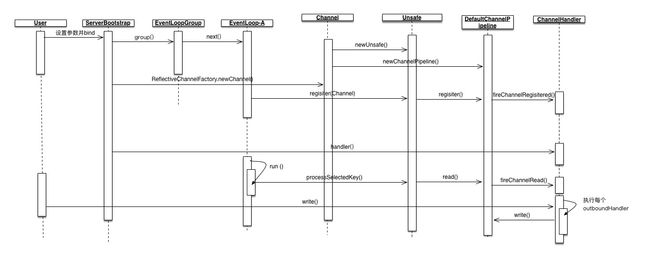
基于上述,整理时序图:
补上group和childGroup的关系。group用于接收accept事件,当有新事件上报后,group会委派给childGroup中的一个eventloop(如果该loop未启动则start),改loop会执行真正的select及handler。