Netty进阶:浅析Read事件的处理过程
文章目录
- 1.read
- 2. ByteBufAllocator介绍
- 3.Handle
- 4. allocate 方法
- 5. 读取到ByteBuf
- 总结
上篇文章讲述了Accept事件的处理过程,本文将详细分析Read过程中的细节。按照accept事件的思路,当读事件进来的时候,会调用 unsafe 的 read 方法,这个方法的主要作用是读取 Socket 缓冲区的内存,并包装成 Netty 的 ByteBuf 对象,最后传递进 pipeline 中的所有节点完成处理。
1.read
进入AbstractNioByteChannel.NioByteUnsafe的read方法:
@Override
public final void read() {
final ChannelConfig config = config();
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
final ByteBufAllocator allocator = config.getAllocator();
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
ByteBuf byteBuf = null;
boolean close = false;
try {
do {
//分配内存
byteBuf = allocHandle.allocate(allocator);
//读取socketChannel数据到分配的byteBuf,对写入的大小进行一个累计叠加
allocHandle.lastBytesRead(doReadBytes(byteBuf));
if (allocHandle.lastBytesRead() <= 0) {
// nothing was read. release the buffer.
byteBuf.release();
byteBuf = null;
close = allocHandle.lastBytesRead() < 0;
if (close) {
// There is nothing left to read as we received an EOF.
readPending = false;
}
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(1);
readPending = false;
//触发pipeline的ChannelRead事件来对byteBuf进行后续处理
pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf);
byteBuf = null;
} while (allocHandle.continueReading());
// 记录总共读取的大小
allocHandle.readComplete();
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
if (close) {
closeOnRead(pipeline);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleReadException(pipeline, byteBuf, t, close, allocHandle);
} finally {
if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
removeReadOp();
}
}
}
}
- 获取到 Channel 的 config 对象,并从该对象中获取内存分配器ByteBufAllocator,还有计算内存分配器RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle
- 进入一个循环,循环体的作用是:使用内存分配器获取数据容器ByteBuf,调用 doReadBytes 方法将数据读取到容器中,如果这次读取什么都没有或远程连接关闭,则跳出循环。还有,如果满足了跳出推荐,也要结束循环,不能无限循环,默认16 次,默认参数来自 AbstractNioByteChannel 的 属性 ChannelMetadata 类型的 METADATA 实例。每读取一次就调用 pipeline 的 channelRead 方法,为什么呢?因为由于 TCP 传输如果包过大的话,丢失的风险会更大,导致重传,所以,大的数据流会分成多次传输。而 channelRead 方法也会被调用多次,因此,使用 channelRead 方法的时候需要注意,如果数据量大,最好将数据放入到缓存中,读取完毕后,再进行处理。
- 跳出循环后,调用 allocHandle 的 readComplete 方法,表示读取已完成,并记录读取记录,用于下次分配合理内存。
- 调用 pipeline 的fireChannelReadComplete方法。
下面一一介绍每一条内容
2. ByteBufAllocator介绍
该接口负责分配缓冲区。作用是创建 ByteBuf,这个 ByteBuf 是 Netty 用来替代 NIO 的 ByteBuffer 的,是存储数据的缓存区。其中,这个接口有一个默认实现 ByteBufUtil.DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR :该实现根据配置创建一个 池化或非池化的缓存区分配器。该参数是 io.netty.allocator.type。接口如下图所示:
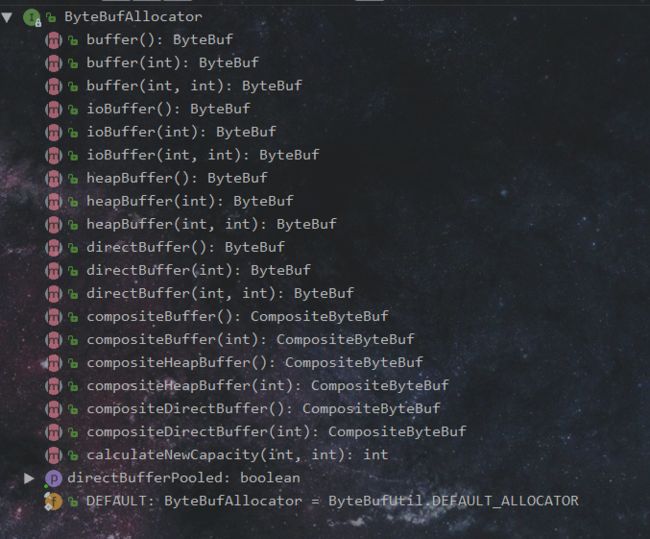
几个重要的方法定义:
buffer() // 返回一个 ByteBuf 对象,默认直接内存。如果平台不支持,返回堆内存。
heapBuffer()// 返回堆内存缓存区
directBuffer()// 返回直接内存缓冲区
compositeBuffer() // 返回一个复合缓冲区。可能同时包含堆内存和直接内存。
ioBuffer() // 当当支持 Unsafe 时,返回直接内存的 Bytebuf,否则返回返回基于堆内存,当使用 PreferHeapByteBufAllocator 时返回堆内存
ByteBufUtil的DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR常量初始化如下:
static {
String allocType = SystemPropertyUtil.get(
"io.netty.allocator.type", PlatformDependent.isAndroid() ? "unpooled" : "pooled");
allocType = allocType.toLowerCase(Locale.US).trim();
ByteBufAllocator alloc;
if ("unpooled".equals(allocType)) {
alloc = UnpooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT;
} else if ("pooled".equals(allocType)) {
alloc = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT;
} else {
alloc = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT;
}
DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR = alloc;
//...
}
获取io.netty.allocator.type的值,决定创建池化还是普通的内存分配器。现在分配有有了,该分配多少呢?所以还需要一个分配策略。RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle接口定义了如何分配的标准。也就是说分配大小合适的内存。
3.Handle
Handle 是 RecvByteBufAllocator 的内部接口。负责自适应调整当前缓存分配的大小,以防止缓存分配过多或过少,接口的定义如下图:
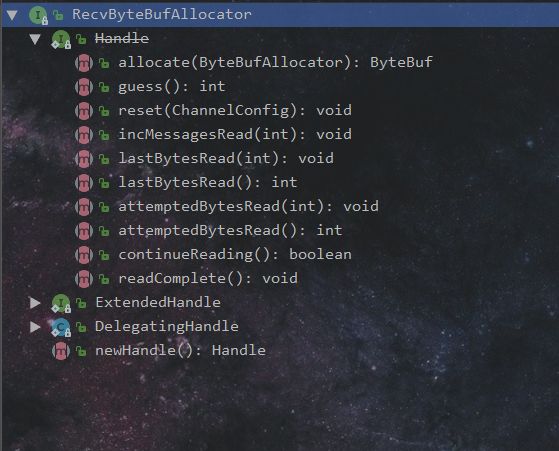
handle接口中的方法:
//创建一个新的接收缓冲区,其容量可能大到足以读取所有入站数据和小到数据足够不浪费它的空间。
ByteBuf allocate(ByteBufAllocator alloc);
// 猜测所需的缓冲区大小,不进行实际的分配
int guess();
// 每次开始读循环之前,重置相关属性
void reset(ChannelConfig config);
// 增加本地读循环的次数
void incMessagesRead(int numMessages);
// 设置最后一次读到的字节数
void lastBytesRead(int bytes);
// 最后一次读到的字节数
int lastBytesRead();
// 设置读操作尝试读取的字节数
void attemptedBytesRead(int bytes);
// 获取尝试读取的字节数
void attemptedBytesRead();
// 判断是否需要继续读
boolean continueReading();
// 读结束后调用
void readComplete();
该接口的主要作用就是计算字节数,如同 RecvByteBufAllocator 的文档说的那样,根据预测和计算最佳大小的缓存区,确保不浪费。
RecvByteBufAllocator中的newHandle方法创建一个Handle的实例。recvBufAllocHandle()方法的内部也调用了此方法。那么该方法的实现在哪呢?也就是Handle的实现在哪?
最终追踪到了RecvByteBufAllocator接口的实现类 AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator类,AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator 的具体内容如下图:
public class AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator extends DefaultMaxMessagesRecvByteBufAllocator {
// 缓存区最小值
static final int DEFAULT_MINIMUM = 64;
// 缓冲区初始值
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL = 1024;
// 缓冲区最大值
static final int DEFAULT_MAXIMUM = 65536;
// 当发现缓存过小,数组下标自增值
private static final int INDEX_INCREMENT = 4;
// 当发现缓冲区过大,数组下标自减值
private static final int INDEX_DECREMENT = 1;
private static final int[] SIZE_TABLE;
//minIndex是最小缓存在SIZE_TABLE中对应的下标
private final int minIndex;
//maxIndex是最大缓存在SIZE_TABLE中对应的下标
private final int maxIndex;
//initial为初始化缓存大小。
private final int initial;
static {
List<Integer> sizeTable = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 16; i < 512; i += 16) {
sizeTable.add(i);
}
for (int i = 512; i > 0; i <<= 1) {
sizeTable.add(i);
}
SIZE_TABLE = new int[sizeTable.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE_TABLE.length; i ++) {
SIZE_TABLE[i] = sizeTable.get(i);
}
}
}
//...
从 static 块中可以看到,显示创建一个List,逐渐添加16,32,48…到496,然后添加512,1024…,递增策略变为了每次 * 2,直到溢出,最后一个节点的值为int的最大值2^32-1,然后将list的值赋值到SIZE_TABLE数组中。
下面看下AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator的构造函数
public AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator(int minimum, int initial, int maximum) {
int minIndex = getSizeTableIndex(minimum);
if (SIZE_TABLE[minIndex] < minimum) {
this.minIndex = minIndex + 1;
} else {
this.minIndex = minIndex;
}
int maxIndex = getSizeTableIndex(maximum);
if (SIZE_TABLE[maxIndex] > maximum) {
this.maxIndex = maxIndex - 1;
} else {
this.maxIndex = maxIndex;
}
this.initial = initial;
}
该构造函数式对三个成员变量进行赋值,getSizeTableIndex内部是通过二分法查找对应值的位置。那么实例化了AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator终于可以使用newHandle方法了,newHandle方法内部构造了
public HandleImpl(int minIndex, int maxIndex, int initial) {
this.minIndex = minIndex;
this.maxIndex = maxIndex;
index = getSizeTableIndex(initial);
nextReceiveBufferSize = SIZE_TABLE[index];
}
此构造方法内部实现很直观,是对HandleImpl类的成员变量进行赋值。index是初始化内存大小的下标。下次需要分配的缓冲大小nextReceiveBufferSize,默认是初始化内存大小的值。guess()时返回的即是该值。每次读循环完成后,会根据实际读取到的字节数和当前缓冲大小重新设置下次需要分配的缓冲大小。record方法如下:
private void record(int actualReadBytes) {
if (actualReadBytes <= SIZE_TABLE[Math.max(0, index - INDEX_DECREMENT - 1)]) {
if (decreaseNow) { // 因为连续两次小于缓冲大小才会减小
index = Math.max(index - INDEX_DECREMENT, minIndex);
nextReceiveBufferSize = SIZE_TABLE[index];
decreaseNow = false;
} else {
decreaseNow = true;
}
} else if (actualReadBytes >= nextReceiveBufferSize) {//读到的值大于缓冲大小
index = Math.min(index + INDEX_INCREMENT, maxIndex); // INDEX_INCREMENT=4 index前进4
nextReceiveBufferSize = SIZE_TABLE[index];
decreaseNow = false;
}
}
@Override
public void readComplete() { //读取完成后调用
record(totalBytesRead());
}
4. allocate 方法
ok!Handle的实例也获取到了,那么终于可以分配内存了,但是我们在HandleImpl类中并没有看到allocate 方法,此方法的实现在DefaultMaxMessagesRecvByteBufAllocator.MaxMessageHandle
public ByteBuf allocate(ByteBufAllocator alloc) {
return alloc.ioBuffer(guess());
}
//AbstractByteBufAllocator类中
@Override
public ByteBuf ioBuffer(int initialCapacity) {
if (PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe()) {
return directBuffer(initialCapacity);
}
return heapBuffer(initialCapacity);
}
ioBuffer函数中主要逻辑为:如果平台支持 unSafe,就使用直接内存,否则使用堆内存,初始大小就是我们刚刚说的 1024。继续看看 directBuffer 方法的实现:
public ByteBuf directBuffer(int initialCapacity) {
return directBuffer(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_MAX_CAPACITY);
}
//
public ByteBuf directBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity == 0 && maxCapacity == 0) {
return emptyBuf;
}
validate(initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
return newDirectBuffer(initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
}
//
protected ByteBuf newDirectBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
final ByteBuf buf;
if (PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe()) {
buf = noCleaner ? new InstrumentedUnpooledUnsafeNoCleanerDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity) :
new InstrumentedUnpooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
} else {
buf = new InstrumentedUnpooledDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
}
return disableLeakDetector ? buf : toLeakAwareBuffer(buf);
}
最终调用的是 newDirectBuffer,根据 noCleaner 参数决定创建一个 ByteBuf,这个属性怎么来的呢?当 unsafe 不是 null 的时候,会尝试获取 DirectByteBuffer 的构造器,如果成功获取,则 noCleaner 属性为 true。
noCleaner默认情况下就是 true,那么,也就是创建了一个 InstrumentedUnpooledUnsafeNoCleanerDirectByteBuf 对象,该对象构造函数调用链如下:
InstrumentedUnpooledUnsafeNoCleanerDirectByteBuf(
UnpooledByteBufAllocator alloc, int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
super(alloc, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
}
UnpooledUnsafeNoCleanerDirectByteBuf(ByteBufAllocator alloc, int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
super(alloc, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
}
public UnpooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf(ByteBufAllocator alloc, int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
super(maxCapacity);
//...
this.alloc = alloc;
setByteBuffer(allocateDirect(initialCapacity), false);
}
static ByteBuffer newDirectBuffer(long address, int capacity) {
ObjectUtil.checkPositiveOrZero(capacity, "capacity");
return (ByteBuffer) DIRECT_BUFFER_CONSTRUCTOR.newInstance(address, capacity);
}
通过ByteBuffer的allocateDirect方法实现缓存的申请。最后根据 disableLeakDetector 属性判断释放进行自动内存回收(也就是当你忘记回收的时候,帮你回收),原理这里简单的说一下,使用虚引用进行跟踪。 FastThreadLocal 的内存回收类似。
可以说,大部分工作都是 allocator 做的,allocHandle 的作用就是提供了如何分配一个合理的内存的策略。
5. 读取到ByteBuf
回到doReadBytes(byteBuf)方法, 就是将 Channel 的内容读取到容器中,并返回一个读取到的字节数。
protected int doReadBytes(ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = unsafe().recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.attemptedBytesRead(byteBuf.writableBytes());
return byteBuf.writeBytes(javaChannel(), allocHandle.attemptedBytesRead());
}
获取到 handle,设置一个 attemptedBytesRead 属性为 ByteBuf 的可写字节数。这个参数可用于后面分配内存时的一些考量。然后调用 byteBuf.writeBytes()方法。传入了 NIO 的 channel,还有刚刚的可写字节数。进入到该方法查看:
@Override
public int writeBytes(ScatteringByteChannel in, int length) throws IOException {
ensureWritable(length);
int writtenBytes = setBytes(writerIndex, in, length);
if (writtenBytes > 0) {
writerIndex += writtenBytes;
}
return writtenBytes;
}
首先对长度进行校验,确保可写长度大于0,如果被并发了导致容量不够,则进行扩容。调用 setBytes 方法,将流中输入写入到缓冲区。方法如下
@Override
public int setBytes(int index, ScatteringByteChannel in, int length) throws IOException {
ensureAccessible();
ByteBuffer tmpBuf = internalNioBuffer();
tmpBuf.clear().position(index).limit(index + length);
try {
return in.read(tmpNioBuf);
} catch (ClosedChannelException ignored) {
return -1;
}
}
首先获取到内部 ByteBuffer 的共享缓冲区,赋值给临时的 tmpNioBuf 属性。然后返回这个引用。将这个引用清空,并将指针移动到给定 index 为止,然后 limit 方法设置缓存区大小。
最后调用 Channel 的 read 方法,将Channel 数据读入到 ByteBuffer 中。读的过程时线程安全的,内部使用了 synchronized 关键字控制写入 buffer 的过程。返回了读到的字节数。回到 writeBytes 方法,得到字节数之后,将这个字节数追加到 writerIndex 属性,表示可写字节变小了。
回到 最初的起点,allocHandle 得到读取到的字节数,调用 lastBytesRead 方法,该方法的作用时调整下一次分配内存的大小。
如果最后一次读取到字节数小于等于0,跳出循环,不做 channelRead 操作。反之,将 totalMessages 加1,这个就是用来记录循环次数,判断不能超过 16次。调用 fireChannelRead 方法,方法结束后,将这个 Buffer 的引用置为null,
总结
从 NioSocketChannel$NioSocketChannelUnsafe 的实现看 read 方法。每个 ByteBuf 都会由一个 Config 实例中的 ByteBufAllocator 对象创建,池化或非池化,直接内存或堆内存,这些都根据系统是否支持或参数设置,底层使用的是 NIO 的 API。今天我们看的是非池化的直接内存。同时,为了节省内存,为每个 ByteBufAllocator 配置了一个 handle,用于计算和预估缓冲区大小。
还有一个需要注意的地方就是 noCleaner 策略。这是 Netty 的一个优化。针对默认的直接内存创建和销毁做了优化--------不使用 JDK 的 cleaner 策略。
最终读取数据到封装了 NIO ByteBuffer 实例的 Netty 的 ByteBuf 中,其中,如果数据量超过 1024,则会读取超过两次,但最多不超过 16 次, 这个次数可以设置,也就是说,可能会调用超过2次 fireChannelRead 方法,使用的时候需要注意(存起来一起在 ChannelReadComplete 使用之类的方法)。