需求
实现一个温度变化曲线
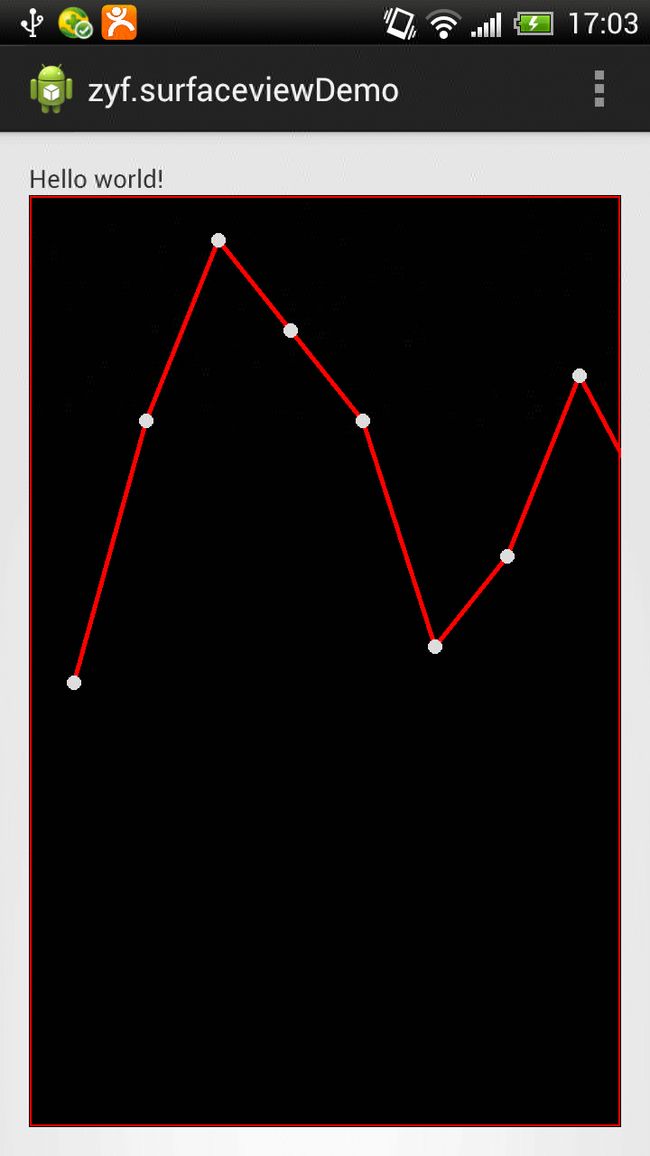
该曲线的数据时不断加载的,如下图。
支持手势,当不断向左拖动时,图形曲线要随着拖动移动,并在拖动到边界时需要加载更多数据。
步骤:
1.在Activity里放一个surfaceView
2.为surfaceView 添加监听器
surfaceHolder = surfaceView1.getHolder();
mMySurfaceCallback = new MySurfaceCallback();
surfaceHolder.addCallback(mMySurfaceCallback);
3.实现监听器。
class MySurfaceCallback implements android.view.SurfaceHolder.Callback {
MyDraw mMyDraw;
@Override
public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder holder, int format, int width,
int height) {
mMyDraw.onSurfaceChanged();
}
@Override
public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder holder) {
mMyDraw = new MyDraw();
mMyDraw.draw();
}
@Override
public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder holder) {
}
}
4.编写绘制图形的方法
class MyDraw {
Paint p;
Canvas canvas;
int unit_x = 80; // 单位 宽度,根据要 绘制的个数不同而计算
int unit_y = 10;// 单位高度 ,固定
final int preInit_x = 50;// 开始位置
final int preInit_y = 550;// 最大的Y顶点。
Point origin;
final int MAX_Fliing_X = unit_x * 20;// 最大20个
public MyDraw() {
super();
p = new Paint(); // 创建画笔
origin = new Point(preInit_x, preInit_y);// 坐标系的原点
}
/**
* 拖动的范围,x > 0说明是 从左到右拖动。 x<0是从右向左拖动
*
* @param x_changed
*/
public void onFliing(float x_changed) {
float newX = origin.x + x_changed;
if (newX > preInit_x)
newX = preInit_x;
int minNewX = -((result.length) * unit_x - surfaceView1.getWidth());
boolean isToEnd = false;// 是否到达了最后一个点。即拖到最右侧极限处。
if (newX < minNewX) {
newX = minNewX;
isToEnd = true;
}
int x = (int) newX;
if (x == origin.x)
return;
origin = new Point(x, origin.y);//更改坐标系原点的位置
draw();
if (isToEnd) {// 触发 到达顶点的方法。
raiseScrollToEnd();
}
}
public void draw() {
canvas = surfaceHolder.lockCanvas();
onDdraw(canvas);
surfaceHolder.unlockCanvasAndPost(canvas);
}
public void onDdraw(Canvas c) {
Log.i("PDWY", String.format("新原点位置 :(%s, %s)", origin.x, origin.y));
Rect r;
int height = c.getHeight();
int width = c.getWidth();
c.drawColor(Color.BLACK);
p.setColor(Color.RED);
p.setStrokeWidth(2);
p.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
r = new Rect(2, 2, width - 2, height - 2);
c.drawRect(r, p);
p.reset();
p.setColor(Color.RED);
p.setStrokeWidth(5);
float[] lines = new float[max_unit];
lines = evalPosition(result, unit_x, unit_y, origin);
// lines = new float[]{0,0,50,500,100,400,100,400,150,500,0,0};
// drawLines方法用一组float表示要绘制的直线,每个直线用4个点表示,前两个为起端点,后两个为终端点
c.drawLines(lines, 2, lines.length - 2, p);
p.reset();
p.setColor(Color.parseColor("#dcdcdc"));
drawEndPoint(lines, 2, lines.length - 2, p, c);
}
private void drawEndPoint(float[] lines, int offset, int count,
Paint p2, Canvas c) {
for (int i = offset; i < count; i += 2) {
float x = lines[i];
float y = lines[i + 1];
c.drawCircle(x, y, 8, p2);
}
}
private float[] evalPosition(float[] result2, int unit_widht,
int unit_height, Point origin) {
if (result2 == null)
return new float[0];
float[] val = new float[result2.length * 4];
for (int i = 0; i < result2.length; i++) {
float y = origin.y - result2[i] * unit_height;
float x = origin.x + unit_widht * i;
val[i * 4 + 0] = x;
val[i * 4 + 1] = y;
val[i * 4 + 2] = x;
val[i * 4 + 3] = y;
}
return val;
}
final int max_unit = 6;
public void onSurfaceChanged() {
}
}
-
注册 手势 ,当手指拖动时,曲线要随着变化。
surfaceView1.setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener() { int state = 0; float x_start; @Override public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) { // mGestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event); if (event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) { state = 1; x_start = event.getX(); } if (event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP) { state = 0; x_start = 0; } if (event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE) { if (state == 1) { if (mMySurfaceCallback != null && mMySurfaceCallback.mMyDraw != null) { float xEnd = event.getX(); float x_changed = (float) ((xEnd - x_start) / 1.3); if (Math.abs(x_changed) > 5) { Log.i("PDWY", "移动了 " + x_changed); mMySurfaceCallback.mMyDraw.onFliing(x_changed); x_start = xEnd; } } } } return true; } });
6。记得计算坐标位置,当不断向左拖动,拖动到 最后时,触发一个 自定义的 事件 onScrollToEnd。订阅了该事件的对象可以在 适当的时机 “加载更多的数据”
/**
* 拖动的范围,x > 0说明是 从左到右拖动。 x<0是从右向左拖动
*
* @param x_changed
*/
public void onFliing(float x_changed) {
float newX = origin.x + x_changed;
if (newX > preInit_x)
newX = preInit_x;
int minNewX = -((result.length) * unit_x - surfaceView1.getWidth());
boolean isToEnd = false;// 是否到达了最后一个点。即拖到最右侧极限处。
if (newX < minNewX) {
newX = minNewX;
isToEnd = true;
}
int x = (int) newX;
if (x == origin.x)
return;
origin = new Point(x, origin.y);//更改坐标系原点的位置
draw();
if (isToEnd) {// 触发 到达顶点的方法。
raiseScrollToEnd();
}
}
自定义事件的实现
ScrollToEndListener mScrollToEndListener;
private void raiseScrollToEnd() {
if (mScrollToEndListener != null)
mScrollToEndListener.onScrollToEnd();
}
public void setScrollToEndListener(ScrollToEndListener scrollToEndListener) {
mScrollToEndListener = scrollToEndListener;
}
public static interface ScrollToEndListener {
public void onScrollToEnd();
}
最后,如何使用它:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
SurfaceView surfaceView1;
MyCustomCurve mMyCustomCurve;
float[] result;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Package pck = Package.getPackage(this.getPackageName());
Resources resource = this.getResources();
surfaceView1 = (SurfaceView)findViewById(resource.getIdentifier("surfaceView1", "id", pck.getName()));
mMyCustomCurve = new MyCustomCurve(this,surfaceView1);
result = new float[] { 1, 30, 50, 40, 30, 5, 15, 35, 20,3,12,15,31, 30, 50, 40, 30, 5, 15, 35, 20,3,12,15,15};
mMyCustomCurve.setResult(result);
//当读取到数据的终点时
mMyCustomCurve.setScrollToEndListener(new ScrollToEndListener() {
@Override
public void onScrollToEnd() {
ArrayList lst = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
lst.add(result[i]);
}
//追加新的数据,随机添加10个数字,值不大于50.
Random r = new Random();
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
lst.add(r.nextFloat() * 50);
}
float[] newArray = new float[lst.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < lst.size(); i++) {
newArray[i] = lst.get(i);
}
result = newArray;
//设置新的数据源
mMyCustomCurve.setResult(result);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "加载了一次新的数据", 0).show();
}
});
}
代码下载 提取码:883c