| 您的评价: |
|
|
如基本的单向加密算法:
-
BASE64 严格地说,属于编码格式,而非加密算法
-
MD5(Message Digest algorithm 5,信息摘要算法)
-
SHA(Secure Hash Algorithm,安全散列算法)
-
HMAC(Hash Message Authentication Code,散列消息鉴别码)
复杂的对称加密(DES、PBE)、非对称加密算法:
-
DES(Data Encryption Standard,数据加密算法)
-
PBE(Password-based encryption,基于密码验证)
-
RSA(算法的名字以发明者的名字命名:Ron Rivest, AdiShamir 和Leonard Adleman)
-
DH(Diffie-Hellman算法,密钥一致协议)
-
DSA(Digital Signature Algorithm,数字签名)
-
ECC(Elliptic Curves Cryptography,椭圆曲线密码编码学)
本篇内容简要介绍BASE64、MD5、SHA、HMAC几种方法。
MD5、SHA、HMAC这三种加密算法,可谓是非可逆加密,就是不可解密的加密方法。我们通常只把他们作为加密的基础。单纯的以上三种的加密并不可靠。
BASE64
按 照RFC2045的定义,Base64被定义为:Base64内容传送编码被设计用来把任意序列的8位字节描述为一种不易被人直接识别的形式。(The Base64 Content-Transfer-Encoding is designed to represent arbitrary sequences of octets in a form that need not be humanly readable.)
常见于邮件、http加密,截取http信息,你就会发现登录操作的用户名、密码字段通过BASE64加密的。
通过java代码实现如下:
08 |
public static byte[] decryptBASE64(String key) throws Exception { |
09 |
return (new BASE64Decoder()).decodeBuffer(key); |
19 |
public static String encryptBASE64(byte[] key) throws Exception { |
20 |
return (new BASE64Encoder()).encodeBuffer(key); |
主要就是BASE64Encoder、BASE64Decoder两个类,我们只需要知道使用对应的方法即可。另,BASE加密后产生的字节位数是8的倍数,如果不够位数以=符号填充。
MD5
MD5 -- message-digest algorithm 5 (信息-摘要算法)缩写,广泛用于加密和解密技术,常用于文件校验。校验?不管文件多大,经过MD5后都能生成唯一的MD5值。好比现在的ISO校验,都 是MD5校验。怎么用?当然是把ISO经过MD5后产生MD5的值。一般下载linux-ISO的朋友都见过下载链接旁边放着MD5的串。就是用来验证文 件是否一致的。
通过java代码实现如下:
08 |
public static byte[] encryptMD5(byte[] data) throws Exception { |
10 |
MessageDigest md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance(KEY_MD5); |
通常我们不直接使用上述MD5加密。通常将MD5产生的字节数组交给BASE64再加密一把,得到相应的字符串。
SHA
SHA(Secure Hash Algorithm,安全散列算法),数字签名等密码学应用中重要的工具,被广泛地应用于电子商务等信息安全领域。虽然,SHA与MD5通过碰撞法都被破解了, 但是SHA仍然是公认的安全加密算法,较之MD5更为安全。
通过java代码实现如下:
08 |
public static byte[] encryptSHA(byte[] data) throws Exception { |
10 |
MessageDigest sha = MessageDigest.getInstance(KEY_SHA); |
HMAC
HMAC(Hash Message Authentication Code,散列消息鉴别码,基于密钥的Hash算法的认证协议。消息鉴别码实现鉴别的原理是,用公开函数和密钥产生一个固定长度的值作为认证标识,用这个 标识鉴别消息的完整性。使用一个密钥生成一个固定大小的小数据块,即MAC,并将其加入到消息中,然后传输。接收方利用与发送方共享的密钥进行鉴别认证 等。
通过java代码实现如下:
07 |
public static String initMacKey() throws Exception { |
08 |
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance(KEY_MAC); |
10 |
SecretKey secretKey = keyGenerator.generateKey(); |
11 |
return encryptBASE64(secretKey.getEncoded()); |
22 |
public static byte[] encryptHMAC(byte[] data, String key) throws Exception { |
24 |
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(decryptBASE64(key), KEY_MAC); |
25 |
Mac mac = Mac.getInstance(secretKey.getAlgorithm()); |
28 |
return mac.doFinal(data); |
给出一个完整类,如下:
001 |
import java.security.MessageDigest; |
003 |
import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator; |
004 |
import javax.crypto.Mac; |
005 |
import javax.crypto.SecretKey; |
007 |
import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder; |
008 |
import sun.misc.BASE64Encoder; |
017 |
public abstract class Coder { |
018 |
public static final String KEY_SHA = "SHA"; |
019 |
public static final String KEY_MD5 = "MD5"; |
032 |
public static final String KEY_MAC = "HmacMD5"; |
041 |
public static byte[] decryptBASE64(String key) throws Exception { |
042 |
return (new BASE64Decoder()).decodeBuffer(key); |
052 |
public static String encryptBASE64(byte[] key) throws Exception { |
053 |
return (new BASE64Encoder()).encodeBuffer(key); |
063 |
public static byte[] encryptMD5(byte[] data) throws Exception { |
065 |
MessageDigest md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance(KEY_MD5); |
079 |
public static byte[] encryptSHA(byte[] data) throws Exception { |
081 |
MessageDigest sha = MessageDigest.getInstance(KEY_SHA); |
094 |
public static String initMacKey() throws Exception { |
095 |
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance(KEY_MAC); |
097 |
SecretKey secretKey = keyGenerator.generateKey(); |
098 |
return encryptBASE64(secretKey.getEncoded()); |
109 |
public static byte[] encryptHMAC(byte[] data, String key) throws Exception { |
111 |
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(decryptBASE64(key), KEY_MAC); |
112 |
Mac mac = Mac.getInstance(secretKey.getAlgorithm()); |
115 |
return mac.doFinal(data); |
再给出一个测试类:
01 |
import static org.junit.Assert.*; |
03 |
import org.junit.Test; |
11 |
public class CoderTest { |
14 |
public void test() throws Exception { |
15 |
String inputStr = "简单加密"; |
16 |
System.err.println("原文:\n" + inputStr); |
18 |
byte[] inputData = inputStr.getBytes(); |
19 |
String code = Coder.encryptBASE64(inputData); |
21 |
System.err.println("BASE64加密后:\n" + code); |
23 |
byte[] output = Coder.decryptBASE64(code); |
25 |
String outputStr = new String(output); |
27 |
System.err.println("BASE64解密后:\n" + outputStr); |
30 |
assertEquals(inputStr, outputStr); |
33 |
assertArrayEquals(Coder.encryptMD5(inputData), Coder |
34 |
.encryptMD5(inputData)); |
37 |
assertArrayEquals(Coder.encryptSHA(inputData), Coder |
38 |
.encryptSHA(inputData)); |
40 |
String key = Coder.initMacKey(); |
41 |
System.err.println("Mac密钥:\n" + key); |
44 |
assertArrayEquals(Coder.encryptHMAC(inputData, key), Coder.encryptHMAC( |
47 |
BigInteger md5 = new BigInteger(Coder.encryptMD5(inputData)); |
48 |
System.err.println("MD5:\n" + md5.toString(16)); |
50 |
BigInteger sha = new BigInteger(Coder.encryptSHA(inputData)); |
51 |
System.err.println("SHA:\n" + sha.toString(32)); |
53 |
BigInteger mac = new BigInteger(Coder.encryptHMAC(inputData, inputStr)); |
54 |
System.err.println("HMAC:\n" + mac.toString(16)); |
控制台输出:
原文:
简单加密
BASE64加密后:
566A5Y2V5Yqg5a+G
BASE64解密后:
简单加密
Mac密钥:
uGxdHC+6ylRDaik++leFtGwiMbuYUJ6mqHWyhSgF4trVkVBBSQvY/a22xU8XT1RUemdCWW155Bke
pBIpkd7QHg==
MD5:
-550b4d90349ad4629462113e7934de56
SHA:
91k9vo7p400cjkgfhjh0ia9qthsjagfn
HMAC:
2287d192387e95694bdbba2fa941009a
注意
编译时,可能会看到如下提示:
引用
警告:sun.misc.BASE64Decoder 是 Sun 的专用 API,可能会在未来版本中删除
import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder;
^
警告:sun.misc.BASE64Encoder 是 Sun 的专用 API,可能会在未来版本中删除
import sun.misc.BASE64Encoder;
^
BASE64Encoder 和BASE64Decoder是非官方JDK实现类。虽然可以在JDK里能找到并使用,但是在API里查不到。JRE 中 sun 和 com.sun 开头包的类都是未被文档化的,他们属于 java, javax 类库的基础,其中的实现大多数与底层平台有关,一般来说是不推荐使用的。
BASE64的加密解密是双向的,可以求反解。
MD5、SHA以及HMAC是单向加密,任何数据加密后只会产生唯一的一个加密串,通常用来校验数据在传输过程中是否被修改。其中HMAC算法有一个密钥,增强了数据传输过程中的安全性,强化了算法外的不可控因素。
单向加密的用途主要是为了校验数据在传输过程中是否被修改。
接下来我们介绍对称加密算法,最常用的莫过于DES数据加密算法。
DES
DES-Data Encryption Standard,即数据加密算法。是IBM公司于1975年研究成功并公开发表的。DES算法的入口参数有三个:Key、Data、Mode。其中 Key为8个字节共64位,是DES算法的工作密钥;Data也为8个字节64位,是要被加密或被解密的数据;Mode为DES的工作方式,有两种:加密 或解密。
DES算法把64位的明文输入块变为64位的密文输出块,它所使用的密钥也是64位。
通过java代码实现如下:Coder类见
001 |
import java.security.Key; |
002 |
import java.security.SecureRandom; |
004 |
import javax.crypto.Cipher; |
005 |
import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator; |
006 |
import javax.crypto.SecretKey; |
007 |
import javax.crypto.SecretKeyFactory; |
008 |
import javax.crypto.spec.DESKeySpec; |
015 |
* 支持 DES、DESede(TripleDES,就是3DES)、AES、Blowfish、RC2、RC4(ARCFOUR) |
016 |
* DES key size must be equal to 56 |
017 |
* DESede(TripleDES) key size must be equal to 112 or 168 |
018 |
* AES key size must be equal to 128, 192 or 256,but 192 and 256 bits may not be available |
019 |
* Blowfish key size must be multiple of 8, and can only range from 32 to 448 (inclusive) |
020 |
* RC2 key size must be between 40 and 1024 bits |
021 |
* RC4(ARCFOUR) key size must be between 40 and 1024 bits |
022 |
* 具体内容 需要关注 JDK Document http://.../docs/technotes/guides/security/SunProviders.html |
029 |
public abstract class DESCoder extends Coder { |
032 |
* 可替换为以下任意一种算法,同时key值的size相应改变。 |
035 |
* DES key size must be equal to 56 |
036 |
* DESede(TripleDES) key size must be equal to 112 or 168 |
037 |
* AES key size must be equal to 128, 192 or 256,but 192 and 256 bits may not be available |
038 |
* Blowfish key size must be multiple of 8, and can only range from 32 to 448 (inclusive) |
039 |
* RC2 key size must be between 40 and 1024 bits |
040 |
* RC4(ARCFOUR) key size must be between 40 and 1024 bits |
043 |
* 在Key toKey(byte[] key)方法中使用下述代码 |
044 |
* SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key, ALGORITHM); 替换 |
046 |
* DESKeySpec dks = new DESKeySpec(key); |
047 |
* SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance(ALGORITHM); |
048 |
* SecretKey secretKey = keyFactory.generateSecret(dks); |
051 |
public static final String ALGORITHM = "DES"; |
060 |
private static Key toKey(byte[] key) throws Exception { |
061 |
DESKeySpec dks = new DESKeySpec(key); |
062 |
SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance(ALGORITHM); |
063 |
SecretKey secretKey = keyFactory.generateSecret(dks); |
079 |
public static byte[] decrypt(byte[] data, String key) throws Exception { |
080 |
Key k = toKey(decryptBASE64(key)); |
082 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM); |
083 |
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, k); |
085 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
096 |
public static byte[] encrypt(byte[] data, String key) throws Exception { |
097 |
Key k = toKey(decryptBASE64(key)); |
098 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM); |
099 |
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, k); |
101 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
110 |
public static String initKey() throws Exception { |
111 |
return initKey(null); |
121 |
public static String initKey(String seed) throws Exception { |
122 |
SecureRandom secureRandom = null; |
125 |
secureRandom = new SecureRandom(decryptBASE64(seed)); |
127 |
secureRandom = new SecureRandom(); |
130 |
KeyGenerator kg = KeyGenerator.getInstance(ALGORITHM); |
131 |
kg.init(secureRandom); |
133 |
SecretKey secretKey = kg.generateKey(); |
135 |
return encryptBASE64(secretKey.getEncoded()); |
延续上一个类的实现,我们通过MD5以及SHA对字符串加密生成密钥,这是比较常见的密钥生成方式。
再给出一个测试类:
01 |
import static org.junit.Assert.*; |
04 |
import org.junit.Test; |
12 |
public class DESCoderTest { |
15 |
public void test() throws Exception { |
16 |
String inputStr = "DES"; |
17 |
String key = DESCoder.initKey(); |
18 |
System.err.println("原文:\t" + inputStr); |
20 |
System.err.println("密钥:\t" + key); |
22 |
byte[] inputData = inputStr.getBytes(); |
23 |
inputData = DESCoder.encrypt(inputData, key); |
25 |
System.err.println("加密后:\t" + DESCoder.encryptBASE64(inputData)); |
27 |
byte[] outputData = DESCoder.decrypt(inputData, key); |
28 |
String outputStr = new String(outputData); |
30 |
System.err.println("解密后:\t" + outputStr); |
32 |
assertEquals(inputStr, outputStr); |
得到的输出内容如下:
原文: DES
密钥: f3wEtRrV6q0=
加密后: C6qe9oNIzRY=
解密后: DES
由控制台得到的输出,我们能够比对加密、解密后结果一致。这是一种简单的加密解密方式,只有一个密钥。
其实DES有很多同胞兄弟,如DESede(TripleDES)、AES、Blowfish、RC2、RC4(ARCFOUR)。这里就不过多阐述了,大同小异,只要换掉ALGORITHM换成对应的值,同时做一个代码替换SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key, ALGORITHM);就可以了,此外就是密钥长度不同了。
2 |
* DES key size must be equal to 56 |
3 |
* DESede(TripleDES) key size must be equal to 112 or 168 |
4 |
* AES key size must be equal to 128, 192 or 256,but 192 and 256 bits may not be available |
5 |
* Blowfish key size must be multiple of 8, and can only range from 32 to 448 (inclusive) |
6 |
* RC2 key size must be between 40 and 1024 bits |
7 |
* RC4(ARCFOUR) key size must be between 40 and 1024 bits |
除了DES,我们还知道有DESede(TripleDES,就是3DES)、AES、Blowfish、RC2、RC4(ARCFOUR)等多种对称加密方式,其实现方式大同小异,这里介绍对称加密的另一个算法——PBE
PBE
PBE——Password-based encryption(基于密码加密)。其特点在于口令由用户自己掌管,不借助任何物理媒体;采用随机数(这里我们叫做盐)杂凑多重加密等方法保证数据的安全性。是一种简便的加密方式。
通过java代码实现如下:Coder类见
001 |
import java.security.Key; |
002 |
import java.util.Random; |
004 |
import javax.crypto.Cipher; |
005 |
import javax.crypto.SecretKey; |
006 |
import javax.crypto.SecretKeyFactory; |
007 |
import javax.crypto.spec.PBEKeySpec; |
008 |
import javax.crypto.spec.PBEParameterSpec; |
017 |
public abstract class PBECoder extends Coder { |
023 |
* PBEWithMD5AndTripleDES |
024 |
* PBEWithSHA1AndDESede |
025 |
* PBEWithSHA1AndRC2_40 |
028 |
public static final String ALGORITHM = "PBEWITHMD5andDES"; |
036 |
public static byte[] initSalt() throws Exception { |
037 |
byte[] salt = new byte[8]; |
038 |
Random random = new Random(); |
039 |
random.nextBytes(salt); |
050 |
private static Key toKey(String password) throws Exception { |
051 |
PBEKeySpec keySpec = new PBEKeySpec(password.toCharArray()); |
052 |
SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance(ALGORITHM); |
053 |
SecretKey secretKey = keyFactory.generateSecret(keySpec); |
067 |
public static byte[] encrypt(byte[] data, String password, byte[] salt) |
070 |
Key key = toKey(password); |
072 |
PBEParameterSpec paramSpec = new PBEParameterSpec(salt, 100); |
073 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM); |
074 |
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key, paramSpec); |
076 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
089 |
public static byte[] decrypt(byte[] data, String password, byte[] salt) |
092 |
Key key = toKey(password); |
094 |
PBEParameterSpec paramSpec = new PBEParameterSpec(salt, 100); |
095 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM); |
096 |
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key, paramSpec); |
098 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
再给出一个测试类:
01 |
import static org.junit.Assert.*; |
03 |
import org.junit.Test; |
11 |
public class PBECoderTest { |
14 |
public void test() throws Exception { |
15 |
String inputStr = "abc"; |
16 |
System.err.println("原文: " + inputStr); |
17 |
byte[] input = inputStr.getBytes(); |
20 |
System.err.println("密码: " + pwd); |
22 |
byte[] salt = PBECoder.initSalt(); |
24 |
byte[] data = PBECoder.encrypt(input, pwd, salt); |
26 |
System.err.println("加密后: " + PBECoder.encryptBASE64(data)); |
28 |
byte[] output = PBECoder.decrypt(data, pwd, salt); |
29 |
String outputStr = new String(output); |
31 |
System.err.println("解密后: " + outputStr); |
32 |
assertEquals(inputStr, outputStr); |
控制台输出:
原文: abc
密码: efg
加密后: iCZ0uRtaAhE=
解密后: abc
后续我们会介绍非对称加密算法,如RSA、DSA、DH、ECC等。
接下来我们介绍典型的非对称加密算法——RSA
RSA
这种算法1978年就出现了,它是第一个既能用于数据加密也能用于数字签名的算法。它易于理解和操作,也很流行。算法的名字以发明者的名字命名:Ron Rivest, AdiShamir 和Leonard Adleman。
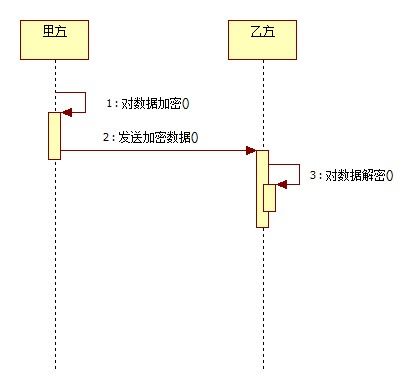
这种加密算法的特点主要是密钥的变化,上文我们看到DES只有一个密钥。相当于只有一把钥匙,如果这把钥匙丢了,数据也就不安全了。RSA同时有两把钥 匙,公钥与私钥。同时支持数字签名。数字签名的意义在于,对传输过来的数据进行校验。确保数据在传输工程中不被修改。
流程分析:
-
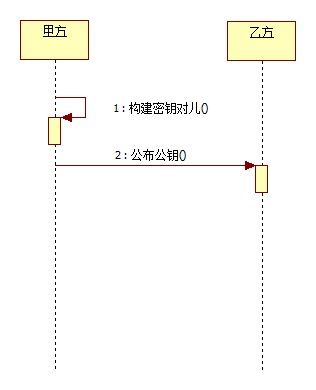
甲方构建密钥对儿,将公钥公布给乙方,将私钥保留。
-
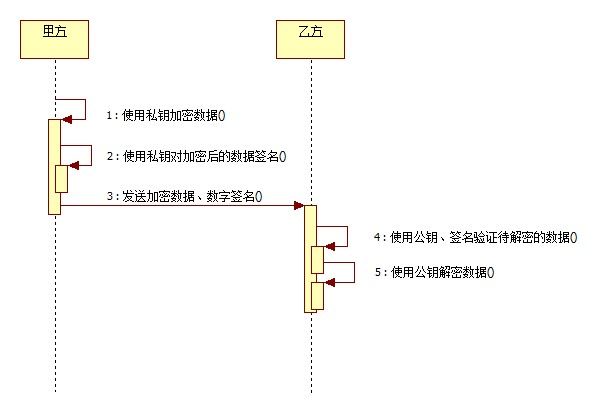
甲方使用私钥加密数据,然后用私钥对加密后的数据签名,发送给乙方签名以及加密后的数据;乙方使用公钥、签名来验证待解密数据是否有效,如果有效使用公钥对数据解密。
-
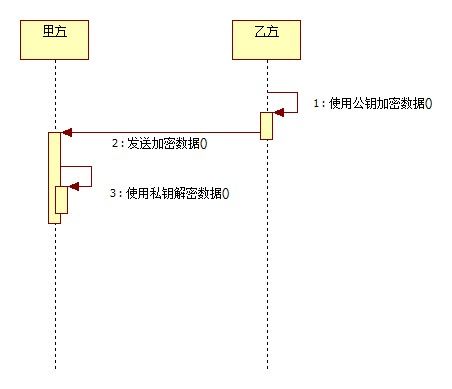
乙方使用公钥加密数据,向甲方发送经过加密后的数据;甲方获得加密数据,通过私钥解密。
按如上步骤给出序列图,如下:
-
-
-
通过java代码实现如下:Coder类见
001 |
import java.security.Key; |
002 |
import java.security.KeyFactory; |
003 |
import java.security.KeyPair; |
004 |
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator; |
005 |
import java.security.PrivateKey; |
006 |
import java.security.PublicKey; |
007 |
import java.security.Signature; |
008 |
import java.security.interfaces.RSAPrivateKey; |
009 |
import java.security.interfaces.RSAPublicKey; |
010 |
import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec; |
011 |
import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec; |
013 |
import java.util.HashMap; |
014 |
import java.util.Map; |
016 |
import javax.crypto.Cipher; |
025 |
public abstract class RSACoder extends Coder { |
026 |
public static final String KEY_ALGORITHM = "RSA"; |
027 |
public static final String SIGNATURE_ALGORITHM = "MD5withRSA"; |
029 |
private static final String PUBLIC_KEY = "RSAPublicKey"; |
030 |
private static final String PRIVATE_KEY = "RSAPrivateKey"; |
043 |
public static String sign(byte[] data, String privateKey) throws Exception { |
045 |
byte[] keyBytes = decryptBASE64(privateKey); |
048 |
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec pkcs8KeySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes); |
051 |
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM); |
054 |
PrivateKey priKey = keyFactory.generatePrivate(pkcs8KeySpec); |
057 |
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance(SIGNATURE_ALGORITHM); |
058 |
signature.initSign(priKey); |
059 |
signature.update(data); |
061 |
return encryptBASE64(signature.sign()); |
074 |
* @return 校验成功返回true 失败返回false |
078 |
public static boolean verify(byte[] data, String publicKey, String sign) |
082 |
byte[] keyBytes = decryptBASE64(publicKey); |
085 |
X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes); |
088 |
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM); |
091 |
PublicKey pubKey = keyFactory.generatePublic(keySpec); |
093 |
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance(SIGNATURE_ALGORITHM); |
094 |
signature.initVerify(pubKey); |
095 |
signature.update(data); |
098 |
return signature.verify(decryptBASE64(sign)); |
110 |
public static byte[] decryptByPrivateKey(byte[] data, String key) |
113 |
byte[] keyBytes = decryptBASE64(key); |
116 |
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec pkcs8KeySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes); |
117 |
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM); |
118 |
Key privateKey = keyFactory.generatePrivate(pkcs8KeySpec); |
121 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(keyFactory.getAlgorithm()); |
122 |
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey); |
124 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
136 |
public static byte[] decryptByPublicKey(byte[] data, String key) |
139 |
byte[] keyBytes = decryptBASE64(key); |
142 |
X509EncodedKeySpec x509KeySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes); |
143 |
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM); |
144 |
Key publicKey = keyFactory.generatePublic(x509KeySpec); |
147 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(keyFactory.getAlgorithm()); |
148 |
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, publicKey); |
150 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
162 |
public static byte[] encryptByPublicKey(byte[] data, String key) |
165 |
byte[] keyBytes = decryptBASE64(key); |
168 |
X509EncodedKeySpec x509KeySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes); |
169 |
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM); |
170 |
Key publicKey = keyFactory.generatePublic(x509KeySpec); |
173 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(keyFactory.getAlgorithm()); |
174 |
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey); |
176 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
188 |
public static byte[] encryptByPrivateKey(byte[] data, String key) |
191 |
byte[] keyBytes = decryptBASE64(key); |
194 |
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec pkcs8KeySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes); |
195 |
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM); |
196 |
Key privateKey = keyFactory.generatePrivate(pkcs8KeySpec); |
199 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(keyFactory.getAlgorithm()); |
200 |
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, privateKey); |
202 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
212 |
public static String getPrivateKey(Map keyMap) |
214 |
Key key = (Key) keyMap.get(PRIVATE_KEY); |
216 |
return encryptBASE64(key.getEncoded()); |
226 |
public static String getPublicKey(Map keyMap) |
228 |
Key key = (Key) keyMap.get(PUBLIC_KEY); |
230 |
return encryptBASE64(key.getEncoded()); |
239 |
public static Map initKey() throws Exception { |
240 |
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGen = KeyPairGenerator |
241 |
.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM); |
242 |
keyPairGen.initialize(1024); |
244 |
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGen.generateKeyPair(); |
247 |
RSAPublicKey publicKey = (RSAPublicKey) keyPair.getPublic(); |
250 |
RSAPrivateKey privateKey = (RSAPrivateKey) keyPair.getPrivate(); |
252 |
Map keyMap = new HashMap(2); |
254 |
keyMap.put(PUBLIC_KEY, publicKey); |
255 |
keyMap.put(PRIVATE_KEY, privateKey); |
再给出一个测试类:
01 |
import static org.junit.Assert.*; |
03 |
import org.junit.Before; |
04 |
import org.junit.Test; |
14 |
public class RSACoderTest { |
15 |
private String publicKey; |
16 |
private String privateKey; |
19 |
public void setUp() throws Exception { |
20 |
Map keyMap = RSACoder.initKey(); |
22 |
publicKey = RSACoder.getPublicKey(keyMap); |
23 |
privateKey = RSACoder.getPrivateKey(keyMap); |
24 |
System.err.println("公钥: \n\r" + publicKey); |
25 |
System.err.println("私钥: \n\r" + privateKey); |
29 |
public void test() throws Exception { |
30 |
System.err.println("公钥加密——私钥解密"); |
31 |
String inputStr = "abc"; |
32 |
byte[] data = inputStr.getBytes(); |
34 |
byte[] encodedData = RSACoder.encryptByPublicKey(data, publicKey); |
36 |
byte[] decodedData = RSACoder.decryptByPrivateKey(encodedData, |
39 |
String outputStr = new String(decodedData); |
40 |
System.err.println("加密前: " + inputStr + "\n\r" + "解密后: " + outputStr); |
41 |
assertEquals(inputStr, outputStr); |
46 |
public void testSign() throws Exception { |
47 |
System.err.println("私钥加密——公钥解密"); |
48 |
String inputStr = "sign"; |
49 |
byte[] data = inputStr.getBytes(); |
51 |
byte[] encodedData = RSACoder.encryptByPrivateKey(data, privateKey); |
53 |
byte[] decodedData = RSACoder |
54 |
.decryptByPublicKey(encodedData, publicKey); |
56 |
String outputStr = new String(decodedData); |
57 |
System.err.println("加密前: " + inputStr + "\n\r" + "解密后: " + outputStr); |
58 |
assertEquals(inputStr, outputStr); |
60 |
System.err.println("私钥签名——公钥验证签名"); |
62 |
String sign = RSACoder.sign(encodedData, privateKey); |
63 |
System.err.println("签名:\r" + sign); |
66 |
boolean status = RSACoder.verify(encodedData, publicKey, sign); |
67 |
System.err.println("状态:\r" + status); |
控制台输出:
公钥:
MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQCYU/+I0+z1aBl5X6DUUOHQ7FZpmBSDbKTtx89J
EcB64jFCkunELT8qiKly7fzEqD03g8ALlu5XvX+bBqHFy7YPJJP0ekE2X3wjUnh2NxlqpH3/B/xm
1ZdSlCwDIkbijhBVDjA/bu5BObhZqQmDwIxlQInL9oVz+o6FbAZCyHBd7wIDAQAB
私钥:
MIICdgIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAASCAmAwggJcAgEAAoGBAJhT/4jT7PVoGXlfoNRQ4dDsVmmY
FINspO3Hz0kRwHriMUKS6cQtPyqIqXLt/MSoPTeDwAuW7le9f5sGocXLtg8kk/R6QTZffCNSeHY3
GWqkff8H/GbVl1KULAMiRuKOEFUOMD9u7kE5uFmpCYPAjGVAicv2hXP6joVsBkLIcF3vAgMBAAEC
gYBvZHWoZHmS2EZQqKqeuGr58eobG9hcZzWQoJ4nq/CarBAjw/VovUHE490uK3S9ht4FW7Yzg3LV
/MB06Huifh6qf/X9NQA7SeZRRC8gnCQk6JuDIEVJOud5jU+9tyumJakDKodQ3Jf2zQtNr+5ZdEPl
uwWgv9c4kmpjhAdyMuQmYQJBANn6pcgvyYaia52dnu+yBUsGkaFfwXkzFSExIbi0MXTkhEb/ER/D
rLytukkUu5S5ecz/KBa8U4xIslZDYQbLz5ECQQCy5dutt7RsxN4+dxCWn0/1FrkWl2G329Ucewm3
QU9CKu4D+7Kqdj+Ha3lXP8F0Etaaapi7+EfkRUpukn2ItZV/AkEAlk+I0iphxT1rCB0Q5CjWDY5S
Df2B5JmdEG5Y2o0nLXwG2w44OLct/k2uD4cEcuITY5Dvi/4BftMCZwm/dnhEgQJACIktJSnJwxLV
o9dchENPtlsCM9C/Sd2EWpqISSUlmfugZbJBwR5pQ5XeMUqKeXZYpP+HEBj1nS+tMH9u2/IGEwJA
fL8mZiZXan/oBKrblAbplNcKWGRVD/3y65042PAEeghahlJMiYquV5DzZajuuT0wbJ5xQuZB01+X
nfpFpBJ2dw==
公钥加密——私钥解密
加密前: abc
解密后: abc
公钥:
MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQDdOj40yEB48XqWxmPILmJAc7UecIN7F32etSHF
9rwbuEh3+iTPOGSxhoSQpOED0vOb0ZIMkBXZSgsxLaBSin2RZ09YKWRjtpCA0kDkiD11gj4tzTiM
l9qq1kwSK7ZkGAgodEn3yIILVmQDuEImHOXFtulvJ71ka07u3LuwUNdB/wIDAQAB
私钥:
MIICdwIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAASCAmEwggJdAgEAAoGBAN06PjTIQHjxepbGY8guYkBztR5w
g3sXfZ61IcX2vBu4SHf6JM84ZLGGhJCk4QPS85vRkgyQFdlKCzEtoFKKfZFnT1gpZGO2kIDSQOSI
PXWCPi3NOIyX2qrWTBIrtmQYCCh0SffIggtWZAO4QiYc5cW26W8nvWRrTu7cu7BQ10H/AgMBAAEC
gYEAz2JWBizjI31bqhP4XiP9PuY5F3vqBW4T+L9cFbQiyumKJc58yzTWUAUGKIIn3enXLG7dNqGr
mbJro4JeFIJ3CiVDpXR9+FluIgI4SXm7ioGKF2NOMA9LR5Fu82W+pLfpTN2y2SaLYWEDZyp53BxY
j9gUxaxi1MQs+C1ZgDF2xmECQQDy70bQntbRfysP+ppCtd56YRnES1Tyekw0wryS2tr+ivQJl7JF
gp5rPAOXpgrq36xHDwUspQ0sJ0vj0O7ywxr1AkEA6SAaLhrJJrYucC0jxwAhUYyaPN+aOsWymaRh
9jA/Wc0wp29SbGTh5CcMuGpXm1g0M+FKW3dGiHgS3rVUKim4owJAbnxgapUzAgiiHxxMeDaavnHW
9C2GrtjsO7qtZOTgYI/1uT8itvZW8lJTF+9OW8/qXE76fXl7ai9dFnl5kzMk2QJBALfHz/vCsArt
mkRiwY6zApE4Z6tPl1V33ymSVovvUzHnOdD1SKQdD5t+UV/crb3QVi8ED0t2B0u0ZSPfDT/D7kMC
QDpwdj9k2F5aokLHBHUNJPFDAp7a5QMaT64gv/d48ITJ68Co+v5WzLMpzJBYXK6PAtqIhxbuPEc2
I2k1Afmrwyw=
私钥加密——公钥解密
加密前: sign
解密后: sign
私钥签名——公钥验证签名
签名:
ud1RsIwmSC1pN22I4IXteg1VD2FbiehKUfNxgVSHzvQNIK+d20FCkHCqh9djP3h94iWnIUY0ifU+
mbJkhAl/i5krExOE0hknOnPMcEP+lZV1RbJI2zG2YooSp2XDleqrQk5e/QF2Mx0Zxt8Xsg7ucVpn
i3wwbYWs9wSzIf0UjlM=
状态:
true
简要总结一下,使用公钥加密、私钥解密,完成了乙方到甲方的一次数据传递,通过私钥加密、公钥解密,同时通过私钥签名、公钥验证签名,完成了一次甲方到乙方的数据传递与验证,两次数据传递完成一整套的数据交互!
类似数字签名,数字信封是这样描述的:
数字信封
数字信封用加密技术来保证只有特定的收信人才能阅读信的内容。
流程:
信息发送方采用对称密钥来加密信息,然后再用接收方的公钥来加密此对称密钥(这部分称为数字信封),再将它和信息一起发送给接收方;接收方先用相应的私钥打开数字信封,得到对称密钥,然后使用对称密钥再解开信息。
接下来我们分析DH加密算法,一种适基于密钥一致协议的加密算法。
DH
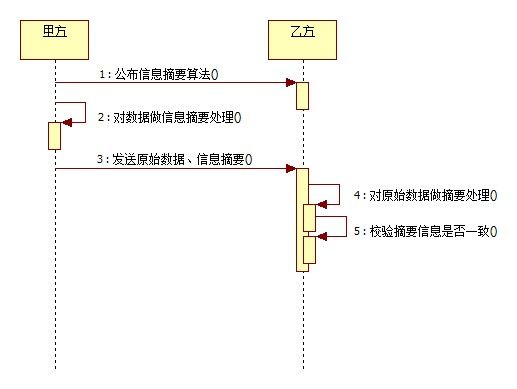
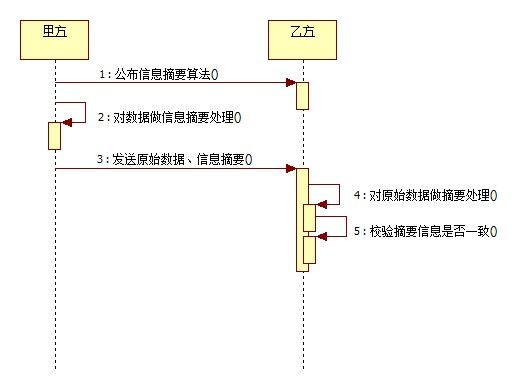
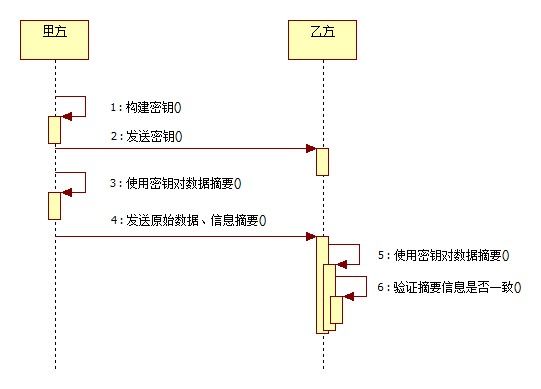
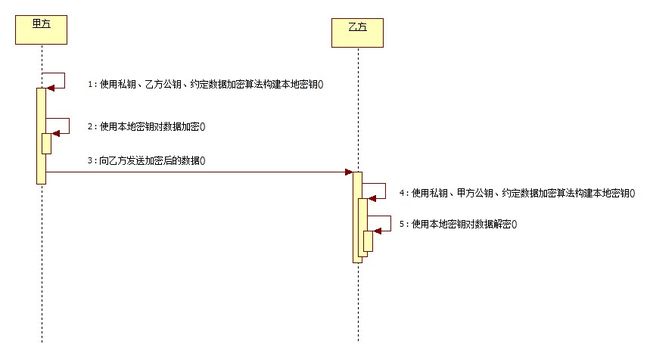
Diffie- Hellman算法(D-H算法),密钥一致协议。是由公开密钥密码体制的奠基人Diffie和Hellman所提出的一种思想。简单的说就是允许两名用 户在公开媒体上交换信息以生成"一致"的、可以共享的密钥。换句话说,就是由甲方产出一对密钥(公钥、私钥),乙方依照甲方公钥产生乙方密钥对(公钥、私 钥)。以此为基线,作为数据传输保密基础,同时双方使用同一种对称加密算法构建本地密钥(SecretKey)对数据加密。这样,在互通了本地密钥 (SecretKey)算法后,甲乙双方公开自己的公钥,使用对方的公钥和刚才产生的私钥加密数据,同时可以使用对方的公钥和自己的私钥对数据解密。不单 单是甲乙双方两方,可以扩展为多方共享数据通讯,这样就完成了网络交互数据的安全通讯!该算法源于中国的同余定理——中国馀数定理。
流程分析:
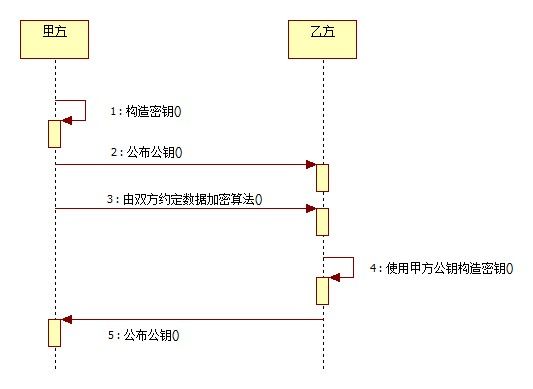
1.甲方构建密钥对儿,将公钥公布给乙方,将私钥保留;双方约定数据加密算法;乙方通过甲方公钥构建密钥对儿,将公钥公布给甲方,将私钥保留。
2.甲方使用私钥、乙方公钥、约定数据加密算法构建本地密钥,然后通过本地密钥加密数据,发送给乙方加密后的数据;乙方使用私钥、甲方公钥、约定数据加密算法构建本地密钥,然后通过本地密钥对数据解密。
3.乙方使用私钥、甲方公钥、约定数据加密算法构建本地密钥,然后通过本地密钥加密数据,发送给甲方加密后的数据;甲方使用私钥、乙方公钥、约定数据加密算法构建本地密钥,然后通过本地密钥对数据解密。
-
-
-

通过java代码实现如下:Coder类见
001 |
import java.security.Key; |
002 |
import java.security.KeyFactory; |
003 |
import java.security.KeyPair; |
004 |
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator; |
005 |
import java.security.PublicKey; |
006 |
import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec; |
007 |
import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec; |
008 |
import java.util.HashMap; |
009 |
import java.util.Map; |
011 |
import javax.crypto.Cipher; |
012 |
import javax.crypto.KeyAgreement; |
013 |
import javax.crypto.SecretKey; |
014 |
import javax.crypto.interfaces.DHPrivateKey; |
015 |
import javax.crypto.interfaces.DHPublicKey; |
016 |
import javax.crypto.spec.DHParameterSpec; |
025 |
public abstract class DHCoder extends Coder { |
026 |
public static final String ALGORITHM = "DH"; |
033 |
* Default Keysize 1024 |
034 |
* Keysize must be a multiple of 64, ranging from 512 to 1024 (inclusive). |
037 |
private static final int KEY_SIZE = 1024; |
040 |
* DH加密下需要一种对称加密算法对数据加密,这里我们使用DES,也可以使用其他对称加密算法。 |
042 |
public static final String SECRET_ALGORITHM = "DES"; |
043 |
private static final String PUBLIC_KEY = "DHPublicKey"; |
044 |
private static final String PRIVATE_KEY = "DHPrivateKey"; |
052 |
public static Map initKey() throws Exception { |
053 |
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator |
054 |
.getInstance(ALGORITHM); |
055 |
keyPairGenerator.initialize(KEY_SIZE); |
057 |
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair(); |
060 |
DHPublicKey publicKey = (DHPublicKey) keyPair.getPublic(); |
063 |
DHPrivateKey privateKey = (DHPrivateKey) keyPair.getPrivate(); |
065 |
Map keyMap = new HashMap(2); |
067 |
keyMap.put(PUBLIC_KEY, publicKey); |
068 |
keyMap.put(PRIVATE_KEY, privateKey); |
080 |
public static Map initKey(String key) throws Exception { |
082 |
byte[] keyBytes = decryptBASE64(key); |
083 |
X509EncodedKeySpec x509KeySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes); |
084 |
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(ALGORITHM); |
085 |
PublicKey pubKey = keyFactory.generatePublic(x509KeySpec); |
088 |
DHParameterSpec dhParamSpec = ((DHPublicKey) pubKey).getParams(); |
090 |
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator |
091 |
.getInstance(keyFactory.getAlgorithm()); |
092 |
keyPairGenerator.initialize(dhParamSpec); |
094 |
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair(); |
097 |
DHPublicKey publicKey = (DHPublicKey) keyPair.getPublic(); |
100 |
DHPrivateKey privateKey = (DHPrivateKey) keyPair.getPrivate(); |
102 |
Map keyMap = new HashMap(2); |
104 |
keyMap.put(PUBLIC_KEY, publicKey); |
105 |
keyMap.put(PRIVATE_KEY, privateKey); |
122 |
public static byte[] encrypt(byte[] data, String publicKey, |
123 |
String privateKey) throws Exception { |
126 |
SecretKey secretKey = getSecretKey(publicKey, privateKey); |
129 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(secretKey.getAlgorithm()); |
130 |
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey); |
132 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
147 |
public static byte[] decrypt(byte[] data, String publicKey, |
148 |
String privateKey) throws Exception { |
151 |
SecretKey secretKey = getSecretKey(publicKey, privateKey); |
153 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(secretKey.getAlgorithm()); |
154 |
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey); |
156 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
169 |
private static SecretKey getSecretKey(String publicKey, String privateKey) |
172 |
byte[] pubKeyBytes = decryptBASE64(publicKey); |
174 |
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(ALGORITHM); |
175 |
X509EncodedKeySpec x509KeySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(pubKeyBytes); |
176 |
PublicKey pubKey = keyFactory.generatePublic(x509KeySpec); |
179 |
byte[] priKeyBytes = decryptBASE64(privateKey); |
181 |
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec pkcs8KeySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(priKeyBytes); |
182 |
Key priKey = keyFactory.generatePrivate(pkcs8KeySpec); |
184 |
KeyAgreement keyAgree = KeyAgreement.getInstance(keyFactory |
186 |
keyAgree.init(priKey); |
187 |
keyAgree.doPhase(pubKey, true); |
190 |
SecretKey secretKey = keyAgree.generateSecret(SECRET_ALGORITHM); |
202 |
public static String getPrivateKey(Map keyMap) |
204 |
Key key = (Key) keyMap.get(PRIVATE_KEY); |
206 |
return encryptBASE64(key.getEncoded()); |
216 |
public static String getPublicKey(Map keyMap) |
218 |
Key key = (Key) keyMap.get(PUBLIC_KEY); |
220 |
return encryptBASE64(key.getEncoded()); |
再给出一个测试类:
01 |
import static org.junit.Assert.*; |
05 |
import org.junit.Test; |
13 |
public class DHCoderTest { |
16 |
public void test() throws Exception { |
18 |
Map aKeyMap = DHCoder.initKey(); |
19 |
String aPublicKey = DHCoder.getPublicKey(aKeyMap); |
20 |
String aPrivateKey = DHCoder.getPrivateKey(aKeyMap); |
22 |
System.err.println("甲方公钥:\r" + aPublicKey); |
23 |
System.err.println("甲方私钥:\r" + aPrivateKey); |
26 |
Map bKeyMap = DHCoder.initKey(aPublicKey); |
27 |
String bPublicKey = DHCoder.getPublicKey(bKeyMap); |
28 |
String bPrivateKey = DHCoder.getPrivateKey(bKeyMap); |
30 |
System.err.println("乙方公钥:\r" + bPublicKey); |
31 |
System.err.println("乙方私钥:\r" + bPrivateKey); |
33 |
String aInput = "abc "; |
34 |
System.err.println("原文: " + aInput); |
37 |
byte[] aCode = DHCoder.encrypt(aInput.getBytes(), aPublicKey, |
41 |
byte[] aDecode = DHCoder.decrypt(aCode, bPublicKey, aPrivateKey); |
42 |
String aOutput = (new String(aDecode)); |
44 |
System.err.println("解密: " + aOutput); |
46 |
assertEquals(aInput, aOutput); |
48 |
System.err.println(" ===============反过来加密解密================== "); |
49 |
String bInput = "def "; |
50 |
System.err.println("原文: " + bInput); |
53 |
byte[] bCode = DHCoder.encrypt(bInput.getBytes(), bPublicKey, |
57 |
byte[] bDecode = DHCoder.decrypt(bCode, aPublicKey, bPrivateKey); |
58 |
String bOutput = (new String(bDecode)); |
60 |
System.err.println("解密: " + bOutput); |
62 |
assertEquals(bInput, bOutput); |
控制台输出:
甲方公钥:
MIHfMIGXBgkqhkiG9w0BAwEwgYkCQQD8poLOjhLKuibvzPcRDlJtsHiwXt7LzR60ogjzrhYXrgHz
W5Gkfm32NBPF4S7QiZvNEyrNUNmRUb3EPuc3WS4XAkBnhHGyepz0TukaScUUfbGpqvJE8FpDTWSG
kx0tFCcbnjUDC3H9c9oXkGmzLik1Yw4cIGI1TQ2iCmxBblC+eUykAgIBgANDAAJAdAWBVmIzqcko
Ej6qFjLDL2+Y3FPq1iRbnOyOpDj71yKaK1K+FhTv04B0zy4DKcvAASV7/Gv0W+bgqdmffRkqrQ==
甲方私钥:
MIHRAgEAMIGXBgkqhkiG9w0BAwEwgYkCQQD8poLOjhLKuibvzPcRDlJtsHiwXt7LzR60ogjzrhYX
rgHzW5Gkfm32NBPF4S7QiZvNEyrNUNmRUb3EPuc3WS4XAkBnhHGyepz0TukaScUUfbGpqvJE8FpD
TWSGkx0tFCcbnjUDC3H9c9oXkGmzLik1Yw4cIGI1TQ2iCmxBblC+eUykAgIBgAQyAjACJRfy1LyR
eHyD+4Hfb+xR0uoIGR1oL9i9Nk6g2AAuaDPgEVWHn+QXID13yL/uDos=
乙方公钥:
MIHfMIGXBgkqhkiG9w0BAwEwgYkCQQD8poLOjhLKuibvzPcRDlJtsHiwXt7LzR60ogjzrhYXrgHz
W5Gkfm32NBPF4S7QiZvNEyrNUNmRUb3EPuc3WS4XAkBnhHGyepz0TukaScUUfbGpqvJE8FpDTWSG
kx0tFCcbnjUDC3H9c9oXkGmzLik1Yw4cIGI1TQ2iCmxBblC+eUykAgIBgANDAAJAVEYSfBA+I9nr
dWw3OBv475C+eBrWBBYqt0m6/eu4ptuDQHwV4MmUtKAC2wc2nNrdb1wmBhY1X8RnWkJ1XmdDbQ==
乙方私钥:
MIHSAgEAMIGXBgkqhkiG9w0BAwEwgYkCQQD8poLOjhLKuibvzPcRDlJtsHiwXt7LzR60ogjzrhYX
rgHzW5Gkfm32NBPF4S7QiZvNEyrNUNmRUb3EPuc3WS4XAkBnhHGyepz0TukaScUUfbGpqvJE8FpD
TWSGkx0tFCcbnjUDC3H9c9oXkGmzLik1Yw4cIGI1TQ2iCmxBblC+eUykAgIBgAQzAjEAqaZiCdXp
2iNpdBlHRaO9ir70wo2n32xNlIzIX19VLSPCDdeUWkgRv4CEj/8k+/yd
原文: abc
解密: abc
===============反过来加密解密==================
原文: def
解密: def
如我所言,甲乙双方在获得对方公钥后可以对发送给对方的数据加密,同时也能对接收到的数据解密,达到了数据安全通信的目的!
接下来我们介绍DSA数字签名,非对称加密的另一种实现。
DSA
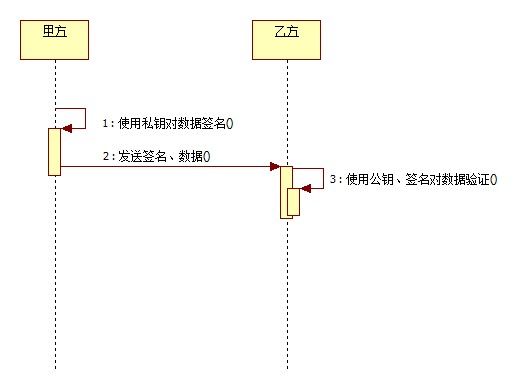
DSA-Digital Signature Algorithm 是Schnorr和ElGamal签名算法的变种,被美国NIST作为DSS(DigitalSignature Standard)。简单的说,这是一种更高级的验证方式,用作数字签名。不单单只有公钥、私钥,还有数字签名。私钥加密生成数字签名,公钥验证数据及签 名。如果数据和签名不匹配则认为验证失败!数字签名的作用就是校验数据在传输过程中不被修改。数字签名,是单向加密的升级!
-

-
通过java代码实现如下:Coder类见
001 |
import java.security.Key; |
002 |
import java.security.KeyFactory; |
003 |
import java.security.KeyPair; |
004 |
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator; |
005 |
import java.security.PrivateKey; |
006 |
import java.security.PublicKey; |
007 |
import java.security.SecureRandom; |
008 |
import java.security.Signature; |
009 |
import java.security.interfaces.DSAPrivateKey; |
010 |
import java.security.interfaces.DSAPublicKey; |
011 |
import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec; |
012 |
import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec; |
013 |
import java.util.HashMap; |
014 |
import java.util.Map; |
023 |
public abstract class DSACoder extends Coder { |
025 |
public static final String ALGORITHM = "DSA"; |
032 |
* Default Keysize 1024 |
033 |
* Keysize must be a multiple of 64, ranging from 512 to 1024 (inclusive). |
036 |
private static final int KEY_SIZE = 1024; |
041 |
private static final String DEFAULT_SEED = "0f22507a10bbddd07d8a3082122966e3"; |
043 |
private static final String PUBLIC_KEY = "DSAPublicKey"; |
044 |
private static final String PRIVATE_KEY = "DSAPrivateKey"; |
057 |
public static String sign(byte[] data, String privateKey) throws Exception { |
059 |
byte[] keyBytes = decryptBASE64(privateKey); |
062 |
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec pkcs8KeySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes); |
065 |
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(ALGORITHM); |
068 |
PrivateKey priKey = keyFactory.generatePrivate(pkcs8KeySpec); |
071 |
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance(keyFactory.getAlgorithm()); |
072 |
signature.initSign(priKey); |
073 |
signature.update(data); |
075 |
return encryptBASE64(signature.sign()); |
088 |
* @return 校验成功返回true 失败返回false |
092 |
public static boolean verify(byte[] data, String publicKey, String sign) |
096 |
byte[] keyBytes = decryptBASE64(publicKey); |
099 |
X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes); |
102 |
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(ALGORITHM); |
105 |
PublicKey pubKey = keyFactory.generatePublic(keySpec); |
107 |
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance(keyFactory.getAlgorithm()); |
108 |
signature.initVerify(pubKey); |
109 |
signature.update(data); |
112 |
return signature.verify(decryptBASE64(sign)); |
123 |
public static Map initKey(String seed) throws Exception { |
124 |
KeyPairGenerator keygen = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance(ALGORITHM); |
126 |
SecureRandom secureRandom = new SecureRandom(); |
127 |
secureRandom.setSeed(seed.getBytes()); |
128 |
keygen.initialize(KEY_SIZE, secureRandom); |
130 |
KeyPair keys = keygen.genKeyPair(); |
132 |
DSAPublicKey publicKey = (DSAPublicKey) keys.getPublic(); |
133 |
DSAPrivateKey privateKey = (DSAPrivateKey) keys.getPrivate(); |
135 |
Map map = new HashMap(2); |
136 |
map.put(PUBLIC_KEY, publicKey); |
137 |
map.put(PRIVATE_KEY, privateKey); |
148 |
public static Map initKey() throws Exception { |
149 |
return initKey(DEFAULT_SEED); |
159 |
public static String getPrivateKey(Map keyMap) |
161 |
Key key = (Key) keyMap.get(PRIVATE_KEY); |
163 |
return encryptBASE64(key.getEncoded()); |
173 |
public static String getPublicKey(Map keyMap) |
175 |
Key key = (Key) keyMap.get(PUBLIC_KEY); |
177 |
return encryptBASE64(key.getEncoded()); |
再给出一个测试类:
01 |
import static org.junit.Assert.*; |
05 |
import org.junit.Test; |
13 |
public class DSACoderTest { |
16 |
public void test() throws Exception { |
17 |
String inputStr = "abc"; |
18 |
byte[] data = inputStr.getBytes(); |
21 |
Map keyMap = DSACoder.initKey(); |
24 |
String publicKey = DSACoder.getPublicKey(keyMap); |
25 |
String privateKey = DSACoder.getPrivateKey(keyMap); |
27 |
System.err.println("公钥:\r" + publicKey); |
28 |
System.err.println("私钥:\r" + privateKey); |
31 |
String sign = DSACoder.sign(data, privateKey); |
32 |
System.err.println("签名:\r" + sign); |
35 |
boolean status = DSACoder.verify(data, publicKey, sign); |
36 |
System.err.println("状态:\r" + status); |
控制台输出:
公钥:
MIIBtzCCASwGByqGSM44BAEwggEfAoGBAP1/U4EddRIpUt9KnC7s5Of2EbdSPO9EAMMeP4C2USZp
RV1AIlH7WT2NWPq/xfW6MPbLm1Vs14E7gB00b/JmYLdrmVClpJ+f6AR7ECLCT7up1/63xhv4O1fn
xqimFQ8E+4P208UewwI1VBNaFpEy9nXzrith1yrv8iIDGZ3RSAHHAhUAl2BQjxUjC8yykrmCouuE
C/BYHPUCgYEA9+GghdabPd7LvKtcNrhXuXmUr7v6OuqC+VdMCz0HgmdRWVeOutRZT+ZxBxCBgLRJ
FnEj6EwoFhO3zwkyjMim4TwWeotUfI0o4KOuHiuzpnWRbqN/C/ohNWLx+2J6ASQ7zKTxvqhRkImo
g9/hWuWfBpKLZl6Ae1UlZAFMO/7PSSoDgYQAAoGAIu4RUlcQLp49PI0MrbssOY+3uySVnp0TULSv
5T4VaHoKzsLHgGTrwOvsGA+V3yCNl2WDu3D84bSLF7liTWgOj+SMOEaPk4VyRTlLXZWGPsf1Mfd9
21XAbMeVyKDSHHVGbMjBScajf3bXooYQMlyoHiOt/WrCo+mv7efstMM0PGo=
私钥:
MIIBTAIBADCCASwGByqGSM44BAEwggEfAoGBAP1/U4EddRIpUt9KnC7s5Of2EbdSPO9EAMMeP4C2
USZpRV1AIlH7WT2NWPq/xfW6MPbLm1Vs14E7gB00b/JmYLdrmVClpJ+f6AR7ECLCT7up1/63xhv4
O1fnxqimFQ8E+4P208UewwI1VBNaFpEy9nXzrith1yrv8iIDGZ3RSAHHAhUAl2BQjxUjC8yykrmC
ouuEC/BYHPUCgYEA9+GghdabPd7LvKtcNrhXuXmUr7v6OuqC+VdMCz0HgmdRWVeOutRZT+ZxBxCB
gLRJFnEj6EwoFhO3zwkyjMim4TwWeotUfI0o4KOuHiuzpnWRbqN/C/ohNWLx+2J6ASQ7zKTxvqhR
kImog9/hWuWfBpKLZl6Ae1UlZAFMO/7PSSoEFwIVAIegLUtmm2oQKQJTOiLugHTSjl/q
签名:
MC0CFQCMg0J/uZmF8GuRpr3TNq48w60nDwIUJCyYNah+HtbU6NcQfy8Ac6LeLQs=
状态:
true
注意状态为true,就验证成功!
ECC
ECC-Elliptic Curves Cryptography,椭圆曲线密码编码学,是目前已知的公钥体制中,对每比特所提供加密强度最高的一种体制。在软件注册保护方面起到很大的作用,一般的序列号通常由该算法产生。
当我开始整理《Java加密技术(二)》的时候,我就已经在开始研究ECC了,但是关于Java实现ECC算法的资料实在是太少了,无论是国内还是国外的 资料,无论是官方还是非官方的解释,最终只有一种答案——ECC算法在jdk1.5后加入支持,目前仅仅只能完成密钥的生成与解析。 如果想要获得ECC算法实现,需要调用硬件完成加密/解密(ECC算法相当耗费资源,如果单纯使用CPU进行加密/解密,效率低下),涉及到Java Card领域,PKCS#11。 其实,PKCS#11配置很简单,但缺乏硬件设备,无法尝试!
尽管如此,我照旧提供相应的Java实现代码,以供大家参考。
通过java代码实现如下:Coder类见
001 |
import java.math.BigInteger; |
002 |
import java.security.Key; |
003 |
import java.security.KeyFactory; |
004 |
import java.security.interfaces.ECPrivateKey; |
005 |
import java.security.interfaces.ECPublicKey; |
006 |
import java.security.spec.ECFieldF2m; |
007 |
import java.security.spec.ECParameterSpec; |
008 |
import java.security.spec.ECPoint; |
009 |
import java.security.spec.ECPrivateKeySpec; |
010 |
import java.security.spec.ECPublicKeySpec; |
011 |
import java.security.spec.EllipticCurve; |
012 |
import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec; |
013 |
import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec; |
014 |
import java.util.HashMap; |
015 |
import java.util.Map; |
017 |
import javax.crypto.Cipher; |
018 |
import javax.crypto.NullCipher; |
020 |
import sun.security.ec.ECKeyFactory; |
021 |
import sun.security.ec.ECPrivateKeyImpl; |
022 |
import sun.security.ec.ECPublicKeyImpl; |
031 |
public abstract class ECCCoder extends Coder { |
033 |
public static final String ALGORITHM = "EC"; |
034 |
private static final String PUBLIC_KEY = "ECCPublicKey"; |
035 |
private static final String PRIVATE_KEY = "ECCPrivateKey"; |
046 |
public static byte[] decrypt(byte[] data, String key) throws Exception { |
048 |
byte[] keyBytes = decryptBASE64(key); |
051 |
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec pkcs8KeySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes); |
052 |
KeyFactory keyFactory = ECKeyFactory.INSTANCE; |
054 |
ECPrivateKey priKey = (ECPrivateKey) keyFactory |
055 |
.generatePrivate(pkcs8KeySpec); |
057 |
ECPrivateKeySpec ecPrivateKeySpec = new ECPrivateKeySpec(priKey.getS(), |
062 |
Cipher cipher = new NullCipher(); |
064 |
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, priKey, ecPrivateKeySpec.getParams()); |
066 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
078 |
public static byte[] encrypt(byte[] data, String privateKey) |
081 |
byte[] keyBytes = decryptBASE64(privateKey); |
084 |
X509EncodedKeySpec x509KeySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes); |
085 |
KeyFactory keyFactory = ECKeyFactory.INSTANCE; |
087 |
ECPublicKey pubKey = (ECPublicKey) keyFactory |
088 |
.generatePublic(x509KeySpec); |
090 |
ECPublicKeySpec ecPublicKeySpec = new ECPublicKeySpec(pubKey.getW(), |
095 |
Cipher cipher = new NullCipher(); |
097 |
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, pubKey, ecPublicKeySpec.getParams()); |
099 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
109 |
public static String getPrivateKey(Map keyMap) |
111 |
Key key = (Key) keyMap.get(PRIVATE_KEY); |
113 |
return encryptBASE64(key.getEncoded()); |
123 |
public static String getPublicKey(Map keyMap) |
125 |
Key key = (Key) keyMap.get(PUBLIC_KEY); |
127 |
return encryptBASE64(key.getEncoded()); |
136 |
public static Map initKey() throws Exception { |
137 |
BigInteger x1 = new BigInteger( |
138 |
"2fe13c0537bbc11acaa07d793de4e6d5e5c94eee8", 16); |
139 |
BigInteger x2 = new BigInteger( |
140 |
"289070fb05d38ff58321f2e800536d538ccdaa3d9", 16); |
142 |
ECPoint g = new ECPoint(x1, x2); |
145 |
BigInteger n = new BigInteger( |
146 |
"5846006549323611672814741753598448348329118574063", 10); |
150 |
int[] ks = { 7, 6, 3 }; |
151 |
ECFieldF2m ecField = new ECFieldF2m(m, ks); |
153 |
BigInteger a = new BigInteger("1", 2); |
154 |
BigInteger b = new BigInteger("1", 2); |
156 |
EllipticCurve ellipticCurve = new EllipticCurve(ecField, a, b); |
158 |
ECParameterSpec ecParameterSpec = new ECParameterSpec(ellipticCurve, g, |
161 |
ECPublicKey publicKey = new ECPublicKeyImpl(g, ecParameterSpec); |
163 |
BigInteger s = new BigInteger( |
164 |
"1234006549323611672814741753598448348329118574063", 10); |
166 |
ECPrivateKey privateKey = new ECPrivateKeyImpl(s, ecParameterSpec); |
168 |
Map keyMap = new HashMap(2); |
170 |
keyMap.put(PUBLIC_KEY, publicKey); |
171 |
keyMap.put(PRIVATE_KEY, privateKey); |
请注意上述代码中的TODO内容,再次提醒注意,Chipher不支持EC算法 ,以上代码仅供参考。Chipher、Signature、KeyPairGenerator、KeyAgreement、SecretKey均不支持EC算法。为了确保程序能够正常执行,我们使用了NullCipher类,验证程序。
照旧提供一个测试类:
01 |
import static org.junit.Assert.*; |
03 |
import java.math.BigInteger; |
04 |
import java.security.spec.ECFieldF2m; |
05 |
import java.security.spec.ECParameterSpec; |
06 |
import java.security.spec.ECPoint; |
07 |
import java.security.spec.ECPrivateKeySpec; |
08 |
import java.security.spec.ECPublicKeySpec; |
09 |
import java.security.spec.EllipticCurve; |
12 |
import org.junit.Test; |
20 |
public class ECCCoderTest { |
23 |
public void test() throws Exception { |
24 |
String inputStr = "abc"; |
25 |
byte[] data = inputStr.getBytes(); |
27 |
Map keyMap = ECCCoder.initKey(); |
29 |
String publicKey = ECCCoder.getPublicKey(keyMap); |
30 |
String privateKey = ECCCoder.getPrivateKey(keyMap); |
31 |
System.err.println("公钥: \n" + publicKey); |
32 |
System.err.println("私钥: \n" + privateKey); |
34 |
byte[] encodedData = ECCCoder.encrypt(data, publicKey); |
36 |
byte[] decodedData = ECCCoder.decrypt(encodedData, privateKey); |
38 |
String outputStr = new String(decodedData); |
39 |
System.err.println("加密前: " + inputStr + "\n\r" + "解密后: " + outputStr); |
40 |
assertEquals(inputStr, outputStr); |
控制台输出:
公钥:
MEAwEAYHKoZIzj0CAQYFK4EEAAEDLAAEAv4TwFN7vBGsqgfXk95ObV5clO7oAokHD7BdOP9YMh8u
gAU21TjM2qPZ
私钥:
MDICAQAwEAYHKoZIzj0CAQYFK4EEAAEEGzAZAgEBBBTYJsR3BN7TFw7JHcAHFkwNmfil7w==
加密前: abc
解密后: abc
本篇的主要内容为Java证书体系的实现。
在构建Java代码实现前,我们需要完成证书的制作。
1.生成keyStroe文件
在命令行下执行以下命令:
keytool -genkey -validity 36000 -alias www.zlex.org -keyalg RSA -keystore d:\zlex.keystore
其中
-genkey表示生成密钥
-validity指定证书有效期,这里是36000天
-alias指定别名,这里是www.zlex.org
-keyalg指定算法,这里是RSA
-keystore指定存储位置,这里是d:\zlex.keystore
在这里我使用的密码为 123456
控制台输出:
输入keystore密码:
再次输入新密码:
您的名字与姓氏是什么?
[Unknown]: www.zlex.org
您的组织单位名称是什么?
[Unknown]: zlex
您的组织名称是什么?
[Unknown]: zlex
您所在的城市或区域名称是什么?
[Unknown]: BJ
您所在的州或省份名称是什么?
[Unknown]: BJ
该单位的两字母国家代码是什么
[Unknown]: CN
CN=www.zlex.org, OU=zlex, O=zlex, L=BJ, ST=BJ, C=CN 正确吗?
[否]: Y
输入的主密码
(如果和 keystore 密码相同,按回车):
再次输入新密码:
这时,在D盘下会生成一个zlex.keystore的文件。
2.生成自签名证书
光有keyStore文件是不够的,还需要证书文件,证书才是直接提供给外界使用的公钥凭证。
导出证书:
keytool -export -keystore d:\zlex.keystore -alias www.zlex.org -file d:\zlex.cer -rfc
其中
-export指定为导出操作
-keystore指定keystore文件
-alias指定导出keystore文件中的别名
-file指向导出路径
-rfc以文本格式输出,也就是以BASE64编码输出
这里的密码是 123456
控制台输出:
输入keystore密码:
保存在文件中的认证
当然,使用方是需要导入证书的!
可以通过自签名证书完成CAS单点登录系统的构建!
Ok,准备工作完成,开始Java实现!
通过java代码实现如下:Coder类见
001 |
import java.io.FileInputStream; |
002 |
import java.security.KeyStore; |
003 |
import java.security.PrivateKey; |
004 |
import java.security.PublicKey; |
005 |
import java.security.Signature; |
006 |
import java.security.cert.Certificate; |
007 |
import java.security.cert.CertificateFactory; |
008 |
import java.security.cert.X509Certificate; |
009 |
import java.util.Date; |
011 |
import javax.crypto.Cipher; |
020 |
public abstract class CertificateCoder extends Coder { |
024 |
* Java密钥库(Java Key Store,JKS)KEY_STORE |
026 |
public static final String KEY_STORE = "JKS"; |
028 |
public static final String X509 = "X.509"; |
033 |
* @param keyStorePath |
039 |
private static PrivateKey getPrivateKey(String keyStorePath, String alias, |
040 |
String password) throws Exception { |
041 |
KeyStore ks = getKeyStore(keyStorePath, password); |
042 |
PrivateKey key = (PrivateKey) ks.getKey(alias, password.toCharArray()); |
049 |
* @param certificatePath |
053 |
private static PublicKey getPublicKey(String certificatePath) |
055 |
Certificate certificate = getCertificate(certificatePath); |
056 |
PublicKey key = certificate.getPublicKey(); |
063 |
* @param certificatePath |
067 |
private static Certificate getCertificate(String certificatePath) |
069 |
CertificateFactory certificateFactory = CertificateFactory |
071 |
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(certificatePath); |
073 |
Certificate certificate = certificateFactory.generateCertificate(in); |
082 |
* @param keyStorePath |
088 |
private static Certificate getCertificate(String keyStorePath, |
089 |
String alias, String password) throws Exception { |
090 |
KeyStore ks = getKeyStore(keyStorePath, password); |
091 |
Certificate certificate = ks.getCertificate(alias); |
099 |
* @param keyStorePath |
104 |
private static KeyStore getKeyStore(String keyStorePath, String password) |
106 |
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(keyStorePath); |
107 |
KeyStore ks = KeyStore.getInstance(KEY_STORE); |
108 |
ks.load(is, password.toCharArray()); |
117 |
* @param keyStorePath |
123 |
public static byte[] encryptByPrivateKey(byte[] data, String keyStorePath, |
124 |
String alias, String password) throws Exception { |
126 |
PrivateKey privateKey = getPrivateKey(keyStorePath, alias, password); |
129 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(privateKey.getAlgorithm()); |
130 |
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, privateKey); |
132 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
140 |
* @param keyStorePath |
146 |
public static byte[] decryptByPrivateKey(byte[] data, String keyStorePath, |
147 |
String alias, String password) throws Exception { |
149 |
PrivateKey privateKey = getPrivateKey(keyStorePath, alias, password); |
152 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(privateKey.getAlgorithm()); |
153 |
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey); |
155 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
163 |
* @param certificatePath |
167 |
public static byte[] encryptByPublicKey(byte[] data, String certificatePath) |
171 |
PublicKey publicKey = getPublicKey(certificatePath); |
173 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(publicKey.getAlgorithm()); |
174 |
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey); |
176 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
184 |
* @param certificatePath |
188 |
public static byte[] decryptByPublicKey(byte[] data, String certificatePath) |
191 |
PublicKey publicKey = getPublicKey(certificatePath); |
194 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(publicKey.getAlgorithm()); |
195 |
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, publicKey); |
197 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
204 |
* @param certificatePath |
207 |
public static boolean verifyCertificate(String certificatePath) { |
208 |
return verifyCertificate(new Date(), certificatePath); |
212 |
* 验证Certificate是否过期或无效 |
215 |
* @param certificatePath |
218 |
public static boolean verifyCertificate(Date date, String certificatePath) { |
219 |
boolean status = true; |
222 |
Certificate certificate = getCertificate(certificatePath); |
224 |
status = verifyCertificate(date, certificate); |
225 |
} catch (Exception e) { |
238 |
private static boolean verifyCertificate(Date date, Certificate certificate) { |
239 |
boolean status = true; |
241 |
X509Certificate x509Certificate = (X509Certificate) certificate; |
242 |
x509Certificate.checkValidity(date); |
243 |
} catch (Exception e) { |
252 |
* @param keyStorePath |
259 |
public static String sign(byte[] sign, String keyStorePath, String alias, |
260 |
String password) throws Exception { |
262 |
X509Certificate x509Certificate = (X509Certificate) getCertificate( |
263 |
keyStorePath, alias, password); |
265 |
KeyStore ks = getKeyStore(keyStorePath, password); |
267 |
PrivateKey privateKey = (PrivateKey) ks.getKey(alias, password |
271 |
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance(x509Certificate |
273 |
signature.initSign(privateKey); |
274 |
signature.update(sign); |
275 |
return encryptBASE64(signature.sign()); |
283 |
* @param certificatePath |
287 |
public static boolean verify(byte[] data, String sign, |
288 |
String certificatePath) throws Exception { |
290 |
X509Certificate x509Certificate = (X509Certificate) getCertificate(certificatePath); |
292 |
PublicKey publicKey = x509Certificate.getPublicKey(); |
294 |
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance(x509Certificate |
296 |
signature.initVerify(publicKey); |
297 |
signature.update(data); |
299 |
return signature.verify(decryptBASE64(sign)); |
306 |
* @param keyStorePath |
311 |
public static boolean verifyCertificate(Date date, String keyStorePath, |
312 |
String alias, String password) { |
313 |
boolean status = true; |
315 |
Certificate certificate = getCertificate(keyStorePath, alias, |
317 |
status = verifyCertificate(date, certificate); |
318 |
} catch (Exception e) { |
327 |
* @param keyStorePath |
332 |
public static boolean verifyCertificate(String keyStorePath, String alias, |
334 |
return verifyCertificate(new Date(), keyStorePath, alias, password); |
再给出一个测试类:
01 |
import static org.junit.Assert.*; |
03 |
import org.junit.Test; |
11 |
public class CertificateCoderTest { |
12 |
private String password = "123456"; |
13 |
private String alias = "www.zlex.org"; |
14 |
private String certificatePath = "d:/zlex.cer"; |
15 |
private String keyStorePath = "d:/zlex.keystore"; |
18 |
public void test() throws Exception { |
19 |
System.err.println("公钥加密——私钥解密"); |
20 |
String inputStr = "Ceritifcate"; |
21 |
byte[] data = inputStr.getBytes(); |
23 |
byte[] encrypt = CertificateCoder.encryptByPublicKey(data, |
26 |
byte[] decrypt = CertificateCoder.decryptByPrivateKey(encrypt, |
27 |
keyStorePath, alias, password); |
28 |
String outputStr = new String(decrypt); |
30 |
System.err.println("加密前: " + inputStr + "\n\r" + "解密后: " + outputStr); |
33 |
assertArrayEquals(data, decrypt); |
36 |
assertTrue(CertificateCoder.verifyCertificate(certificatePath)); |
41 |
public void testSign() throws Exception { |
42 |
System.err.println("私钥加密——公钥解密"); |
44 |
String inputStr = "sign"; |
45 |
byte[] data = inputStr.getBytes(); |
47 |
byte[] encodedData = CertificateCoder.encryptByPrivateKey(data, |
48 |
keyStorePath, alias, password); |
50 |
byte[] decodedData = CertificateCoder.decryptByPublicKey(encodedData, |
53 |
String outputStr = new String(decodedData); |
54 |
System.err.println("加密前: " + inputStr + "\n\r" + "解密后: " + outputStr); |
55 |
assertEquals(inputStr, outputStr); |
57 |
System.err.println("私钥签名——公钥验证签名"); |
59 |
String sign = CertificateCoder.sign(encodedData, keyStorePath, alias, |
61 |
System.err.println("签名:\r" + sign); |
64 |
boolean status = CertificateCoder.verify(encodedData, sign, |
66 |
System.err.println("状态:\r" + status); |
控制台输出:
公钥加密——私钥解密
加密前: Ceritificate
解密后: Ceritificate
私钥加密——公钥解密
加密前: sign
解密后: sign
私钥签名——公钥验证签名
签名:
pqBn5m6PJlfOjH0A6U2o2mUmBsfgyEY1NWCbiyA/I5Gc3gaVNVIdj/zkGNZRqTjhf3+J9a9z9EI7
6F2eWYd7punHx5oh6hfNgcKbVb52EfItl4QEN+djbXiPynn07+Lbg1NOjULnpEd6ZhLP1YwrEAuM
OfvX0e7/wplxLbySaKQ=
状态:
true
由此完成了证书验证体系!
同样,我们可以对代码做签名——代码签名!
通过工具JarSigner可以完成代码签名。
这里我们对tools.jar做代码签名,命令如下:
jarsigner -storetype jks -keystore zlex.keystore -verbose tools.jar www.zlex.org
控制台输出:
输入密钥库的口令短语:
正在更新: META-INF/WWW_ZLEX.SF
正在更新: META-INF/WWW_ZLEX.RSA
正在签名: org/zlex/security/Security.class
正在签名: org/zlex/tool/Main$1.class
正在签名: org/zlex/tool/Main$2.class
正在签名: org/zlex/tool/Main.class
警告:
签名者证书将在六个月内过期。
此时,我们可以对签名后的jar做验证!
验证tools.jar,命令如下:
jarsigner -verify -verbose -certs tools.jar
控制台输出:
402 Sat Jun 20 16:25:14 CST 2009 META-INF/MANIFEST.MF
532 Sat Jun 20 16:25:14 CST 2009 META-INF/WWW_ZLEX.SF
889 Sat Jun 20 16:25:14 CST 2009 META-INF/WWW_ZLEX.RSA
sm 590 Wed Dec 10 13:03:42 CST 2008 org/zlex/security/Security.class
X.509, CN=www.zlex.org, OU=zlex, O=zlex, L=BJ, ST=BJ, C=CN
[证书将在 09-9-18 下午3:27 到期]
sm 705 Tue Dec 16 18:00:56 CST 2008 org/zlex/tool/Main$1.class
X.509, CN=www.zlex.org, OU=zlex, O=zlex, L=BJ, ST=BJ, C=CN
[证书将在 09-9-18 下午3:27 到期]
sm 779 Tue Dec 16 18:00:56 CST 2008 org/zlex/tool/Main$2.class
X.509, CN=www.zlex.org, OU=zlex, O=zlex, L=BJ, ST=BJ, C=CN
[证书将在 09-9-18 下午3:27 到期]
sm 12672 Tue Dec 16 18:00:56 CST 2008 org/zlex/tool/Main.class
X.509, CN=www.zlex.org, OU=zlex, O=zlex, L=BJ, ST=BJ, C=CN
[证书将在 09-9-18 下午3:27 到期]
s = 已验证签名
m = 在清单中列出条目
k = 在密钥库中至少找到了一个证书
i = 在身份作用域内至少找到了一个证书
jar 已验证。
警告:
此 jar 包含签名者证书将在六个月内过期的条目。
代码签名认证的用途主要是对发布的软件做验证,支持 Sun Java .jar (Java Applet) 文件(J2SE)和 J2ME MIDlet Suite 文件。
在中,我们模拟了一个基于RSA非对称加密网络的安全通信。现在我们深度了解一下现有的安全网络通信——SSL。
我们需要构建一个由CA机构签发的有效证书,这里我们使用上文中生成的自签名证书zlex.cer
这里,我们将证书导入到我们的密钥库。
keytool -import -alias www.zlex.org -file d:/zlex.cer -keystore d:/zlex.keystore
其中
-import表示导入
-alias指定别名,这里是www.zlex.org
-file指定算法,这里是d:/zlex.cer
-keystore指定存储位置,这里是d:/zlex.keystore
在这里我使用的密码为654321
控制台输出:
输入keystore密码:
再次输入新密码:
所有者:CN=www.zlex.org, OU=zlex, O=zlex, L=BJ, ST=BJ, C=CN
签发人:CN=www.zlex.org, OU=zlex, O=zlex, L=BJ, ST=BJ, C=CN
序列号:4a1e48df
有效期: Thu May 28 16:18:39 CST 2009 至Wed Aug 26 16:18:39 CST 2009
证书指纹:
MD5:19:CA:E6:36:E2:DF:AD:96:31:97:2F:A9:AD:FC:37:6A
SHA1:49:88:30:59:29:45:F1:69:CA:97:A9:6D:8A:CF:08:D2:C3:D5:C0:C4
签名算法名称:SHA1withRSA
版本: 3
信任这个认证? [否]: y
认证已添加至keystore中
OK,最复杂的准备工作已经完成。
接下来我们将域名www.zlex.org定位到本机上。打开C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts文件,将www.zlex.org绑定在本机上。在文件末尾追加127.0.0.1 www.zlex.org。现在通过地址栏访问http://www.zlex.org,或者通过ping命令,如果能够定位到本机,域名映射就搞定了。
现在,配置tomcat。先将zlex.keystore拷贝到tomcat的conf目录下,然后配置server.xml。将如下内容加入配置文件
注意clientAuth="false"测试阶段,置为false,正式使用时建议使用true。现在启动tomcat,访问https://www.zlex.org/。
显然,证书未能通过认证,这个时候你可以选择安装证书(上文中的zlex.cer文件就是证书),作为受信任的根证书颁发机构导入,再次重启浏览器(IE,其他浏览器对于域名www.zlex.org不支持本地方式访问),访问https://www.zlex.org/,你会看到地址栏中会有个小锁 ,就说明安装成功。所有的浏览器联网操作已经在RSA加密解密系统的保护之下了。但似乎我们感受不到。 ,就说明安装成功。所有的浏览器联网操作已经在RSA加密解密系统的保护之下了。但似乎我们感受不到。
这个时候很多人开始怀疑,如果我们要手工做一个这样的https的访问是不是需要把浏览器的这些个功能都实现呢?不需要!
接着上篇内容,给出如下代码实现:
001 |
import java.io.FileInputStream; |
002 |
import java.security.KeyStore; |
003 |
import java.security.PrivateKey; |
004 |
import java.security.PublicKey; |
005 |
import java.security.Signature; |
006 |
import java.security.cert.Certificate; |
007 |
import java.security.cert.CertificateFactory; |
008 |
import java.security.cert.X509Certificate; |
009 |
import java.util.Date; |
011 |
import javax.crypto.Cipher; |
012 |
import javax.net.ssl.HttpsURLConnection; |
013 |
import javax.net.ssl.KeyManagerFactory; |
014 |
import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext; |
015 |
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory; |
016 |
import javax.net.ssl.TrustManagerFactory; |
025 |
public abstract class CertificateCoder extends Coder { |
028 |
* Java密钥库(Java Key Store,JKS)KEY_STORE |
030 |
public static final String KEY_STORE = "JKS"; |
032 |
public static final String X509 = "X.509"; |
033 |
public static final String SunX509 = "SunX509"; |
034 |
public static final String SSL = "SSL"; |
039 |
* @param keyStorePath |
045 |
private static PrivateKey getPrivateKey(String keyStorePath, String alias, |
046 |
String password) throws Exception { |
047 |
KeyStore ks = getKeyStore(keyStorePath, password); |
048 |
PrivateKey key = (PrivateKey) ks.getKey(alias, password.toCharArray()); |
055 |
* @param certificatePath |
059 |
private static PublicKey getPublicKey(String certificatePath) |
061 |
Certificate certificate = getCertificate(certificatePath); |
062 |
PublicKey key = certificate.getPublicKey(); |
069 |
* @param certificatePath |
073 |
private static Certificate getCertificate(String certificatePath) |
075 |
CertificateFactory certificateFactory = CertificateFactory |
077 |
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(certificatePath); |
079 |
Certificate certificate = certificateFactory.generateCertificate(in); |
088 |
* @param keyStorePath |
094 |
private static Certificate getCertificate(String keyStorePath, |
095 |
String alias, String password) throws Exception { |
096 |
KeyStore ks = getKeyStore(keyStorePath, password); |
097 |
Certificate certificate = ks.getCertificate(alias); |
105 |
* @param keyStorePath |
110 |
private static KeyStore getKeyStore(String keyStorePath, String password) |
112 |
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(keyStorePath); |
113 |
KeyStore ks = KeyStore.getInstance(KEY_STORE); |
114 |
ks.load(is, password.toCharArray()); |
123 |
* @param keyStorePath |
129 |
public static byte[] encryptByPrivateKey(byte[] data, String keyStorePath, |
130 |
String alias, String password) throws Exception { |
132 |
PrivateKey privateKey = getPrivateKey(keyStorePath, alias, password); |
135 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(privateKey.getAlgorithm()); |
136 |
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, privateKey); |
138 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
146 |
* @param keyStorePath |
152 |
public static byte[] decryptByPrivateKey(byte[] data, String keyStorePath, |
153 |
String alias, String password) throws Exception { |
155 |
PrivateKey privateKey = getPrivateKey(keyStorePath, alias, password); |
158 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(privateKey.getAlgorithm()); |
159 |
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey); |
161 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
169 |
* @param certificatePath |
173 |
public static byte[] encryptByPublicKey(byte[] data, String certificatePath) |
177 |
PublicKey publicKey = getPublicKey(certificatePath); |
179 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(publicKey.getAlgorithm()); |
180 |
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey); |
182 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
190 |
* @param certificatePath |
194 |
public static byte[] decryptByPublicKey(byte[] data, String certificatePath) |
197 |
PublicKey publicKey = getPublicKey(certificatePath); |
200 |
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(publicKey.getAlgorithm()); |
201 |
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, publicKey); |
203 |
return cipher.doFinal(data); |
210 |
* @param certificatePath |
213 |
public static boolean verifyCertificate(String certificatePath) { |
214 |
return verifyCertificate(new Date(), certificatePath); |
218 |
* 验证Certificate是否过期或无效 |
221 |
* @param certificatePath |
224 |
public static boolean verifyCertificate(Date date, String certificatePath) { |
225 |
boolean status = true; |
228 |
Certificate certificate = getCertificate(certificatePath); |
230 |
status = verifyCertificate(date, certificate); |
231 |
} catch (Exception e) { |
244 |
private static boolean verifyCertificate(Date date, Certificate certificate) { |
245 |
boolean status = true; |
247 |
X509Certificate x509Certificate = (X509Certificate) certificate; |
248 |
x509Certificate.checkValidity(date); |
249 |
} catch (Exception e) { |
258 |
* @param keyStorePath |
265 |
public static String sign(byte[] sign, String keyStorePath, String alias, |
266 |
String password) throws Exception { |
268 |
X509Certificate x509Certificate = (X509Certificate) getCertificate( |
269 |
keyStorePath, alias, password); |
271 |
KeyStore ks = getKeyStore(keyStorePath, password); |
273 |
PrivateKey privateKey = (PrivateKey) ks.getKey(alias, password |
277 |
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance(x509Certificate |
279 |
signature.initSign(privateKey); |
280 |
signature.update(sign); |
281 |
return encryptBASE64(signature.sign()); |
289 |
* @param certificatePath |
293 |
public static boolean verify(byte[] data, String sign, |
294 |
String certificatePath) throws Exception { |
296 |
X509Certificate x509Certificate = (X509Certificate) getCertificate(certificatePath); |
298 |
PublicKey publicKey = x509Certificate.getPublicKey(); |
300 |
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance(x509Certificate |
302 |
signature.initVerify(publicKey); |
303 |
signature.update(data); |
305 |
return signature.verify(decryptBASE64(sign)); |
312 |
* @param keyStorePath |
317 |
public static boolean verifyCertificate(Date date, String keyStorePath, |
318 |
String alias, String password) { |
319 |
boolean status = true; |
321 |
Certificate certificate = getCertificate(keyStorePath, alias, |
323 |
status = verifyCertificate(date, certificate); |
324 |
} catch (Exception e) { |
333 |
* @param keyStorePath |
338 |
public static boolean verifyCertificate(String keyStorePath, String alias, |
340 |
return verifyCertificate(new Date(), keyStorePath, alias, password); |
348 |
* @param keyStorePath |
351 |
* @param trustKeyStorePath |
356 |
private static SSLSocketFactory getSSLSocketFactory(String password, |
357 |
String keyStorePath, String trustKeyStorePath) throws Exception { |
359 |
KeyManagerFactory keyManagerFactory = KeyManagerFactory |
360 |
.getInstance(SunX509); |
361 |
KeyStore keyStore = getKeyStore(keyStorePath, password); |
362 |
keyManagerFactory.init(keyStore, password.toCharArray()); |
365 |
TrustManagerFactory trustManagerFactory = TrustManagerFactory |
366 |
.getInstance(SunX509); |
367 |
KeyStore trustkeyStore = getKeyStore(trustKeyStorePath, password); |
368 |
trustManagerFactory.init(trustkeyStore); |
371 |
SSLContext ctx = SSLContext.getInstance(SSL); |
372 |
ctx.init(keyManagerFactory.getKeyManagers(), trustManagerFactory |
373 |
.getTrustManagers(), null); |
374 |
SSLSocketFactory sf = ctx.getSocketFactory(); |
380 |
* 为HttpsURLConnection配置SSLSocketFactory |
386 |
* @param keyStorePath |
389 |
* @param trustKeyStorePath |
393 |
public static void configSSLSocketFactory(HttpsURLConnection conn, |
394 |
String password, String keyStorePath, String trustKeyStorePath) |
396 |
conn.setSSLSocketFactory(getSSLSocketFactory(password, keyStorePath, |
增加了configSSLSocketFactory方法供外界调用,该方法为 HttpsURLConnection配置了SSLSocketFactory。当HttpsURLConnection配置了 SSLSocketFactory后,我们就可以通过HttpsURLConnection的getInputStream、 getOutputStream,像往常使用HttpURLConnection做操作了。尤其要说明一点,未配置SSLSocketFactory 前,HttpsURLConnection的getContentLength()获得值永远都是-1。
给出相应测试类:
001 |
import static org.junit.Assert.*; |
003 |
import java.io.DataInputStream; |
004 |
import java.io.InputStream; |
007 |
import javax.net.ssl.HttpsURLConnection; |
009 |
import org.junit.Test; |
017 |
public class CertificateCoderTest { |
018 |
private String password = "123456"; |
019 |
private String alias = "www.zlex.org"; |
020 |
private String certificatePath = "d:/zlex.cer"; |
021 |
private String keyStorePath = "d:/zlex.keystore"; |
022 |
private String clientKeyStorePath = "d:/zlex-client.keystore"; |
023 |
private String clientPassword = "654321"; |
026 |
public void test() throws Exception { |
027 |
System.err.println("公钥加密——私钥解密"); |
028 |
String inputStr = "Ceritifcate"; |
029 |
byte[] data = inputStr.getBytes(); |
031 |
byte[] encrypt = CertificateCoder.encryptByPublicKey(data, |
034 |
byte[] decrypt = CertificateCoder.decryptByPrivateKey(encrypt, |
035 |
keyStorePath, alias, password); |
036 |
String outputStr = new String(decrypt); |
038 |
System.err.println("加密前: " + inputStr + "\n\r" + "解密后: " + outputStr); |
041 |
assertArrayEquals(data, decrypt); |
044 |
assertTrue(CertificateCoder.verifyCertificate(certificatePath)); |
049 |
public void testSign() throws Exception { |
050 |
System.err.println("私钥加密——公钥解密"); |
052 |
String inputStr = "sign"; |
053 |
byte[] data = inputStr.getBytes(); |
055 |
byte[] encodedData = CertificateCoder.encryptByPrivateKey(data, |
056 |
keyStorePath, alias, password); |
058 |
byte[] decodedData = CertificateCoder.decryptByPublicKey(encodedData, |
061 |
String outputStr = new String(decodedData); |
062 |
System.err.println("加密前: " + inputStr + "\n\r" + "解密后: " + outputStr); |
063 |
assertEquals(inputStr, outputStr); |
065 |
System.err.println("私钥签名——公钥验证签名"); |
067 |
String sign = CertificateCoder.sign(encodedData, keyStorePath, alias, |
069 |
System.err.println("签名:\r" + sign); |
072 |
boolean status = CertificateCoder.verify(encodedData, sign, |
074 |
System.err.println("状态:\r" + status); |
080 |
public void testHttps() throws Exception { |
081 |
URL url = new URL("https://www.zlex.org/examples/"); |
082 |
HttpsURLConnection conn = (HttpsURLConnection) url.openConnection(); |
084 |
conn.setDoInput(true); |
085 |
conn.setDoOutput(true); |
087 |
CertificateCoder.configSSLSocketFactory(conn, clientPassword, |
088 |
clientKeyStorePath, clientKeyStorePath); |
090 |
InputStream is = conn.getInputStream(); |
092 |
int length = conn.getContentLength(); |
094 |
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is); |
095 |
byte[] data = new byte[length]; |
099 |
System.err.println(new String(data)); |
注意testHttps方法,几乎和我们往常做HTTP访问没有差别,我们来看控制台输出:
Apache Tomcat Examples
Apache Tomcat Examples
- Servlets examples
- JSP Examples
通过浏览器直接访问https://www.zlex.org/examples/你 也会获得上述内容。也就是说应用甲方作为服务器构建tomcat服务,乙方可以通过上述方式访问甲方受保护的SSL应用,并且不需要考虑具体的加密解密问 题。甲乙双方可以经过相应配置,通过双方的tomcat配置有效的SSL服务,简化上述代码实现,完全通过证书配置完成SSL双向认证!
我们使用自签名证书完成了认证。接下来,我们使用第三方CA签名机构完成证书签名。
这里我们使用thawte提供的测试用21天免费ca证书。
1.要在该网站上注明你的域名,这里使用www.zlex.org作为测试用域名(请勿使用该域名作为你的域名地址,该域名受法律保护!请使用其他非注册域名!)。
2.如果域名有效,你会收到邮件要求你访问https://www.thawte.com/cgi/server/try.exe获得ca证书。
3.复述密钥库的创建。
keytool -genkey -validity 36000 -alias www.zlex.org -keyalg RSA -keystore d:\zlex.keystore
在这里我使用的密码为 123456
控制台输出:
输入keystore密码:
再次输入新密码:
您的名字与姓氏是什么?
[Unknown]: www.zlex.org
您的组织单位名称是什么?
[Unknown]: zlex
您的组织名称是什么?
[Unknown]: zlex
您所在的城市或区域名称是什么?
[Unknown]: BJ
您所在的州或省份名称是什么?
[Unknown]: BJ
该单位的两字母国家代码是什么
[Unknown]: CN
CN=www.zlex.org, OU=zlex, O=zlex, L=BJ, ST=BJ, C=CN 正确吗?
[否]: Y
输入的主密码
(如果和 keystore 密码相同,按回车):
再次输入新密码:
4.通过如下命令,从zlex.keystore中导出CA证书申请。
keytool -certreq -alias www.zlex.org -file d:\zlex.csr -keystore d:\zlex.keystore -v
你会获得zlex.csr文件,可以用记事本打开,内容如下格式:
-----BEGIN NEW CERTIFICATE REQUEST-----
MIIBnDCCAQUCAQAwXDELMAkGA1UEBhMCQ04xCzAJBgNVBAgTAkJKMQswCQYDVQQHEwJCSjENMAsG
A1UEChMEemxleDENMAsGA1UECxMEemxleDEVMBMGA1UEAxMMd3d3LnpsZXgub3JnMIGfMA0GCSqG
SIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQCR6DXU9Mp+mCKO7cv9JPsj0n1Ec/GpM09qvhpgX3FNad/ZWSDc
vU77YXZSoF9hQp3w1LC+eeKgd2MlVpXTvbVwBNVd2HiQPp37ic6BUUjSaX8LHtCl7l0BIEye9qQ2
j8G0kak7e8ZA0s7nb3Ymq/K8BV7v0MQIdhIc1bifK9ZDewIDAQABoAAwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEFBQAD
gYEAMA1r2fbZPtNx37U9TRwadCH2TZZecwKJS/hskNm6ryPKIAp9APWwAyj8WJHRBz5SpZM4zmYO
oMCI8BcnY2A4JP+R7/SwXTdH/xcg7NVghd9A2SCgqMpF7KMfc5dE3iygdiPu+UhY200Dvpjx8gmJ
1UbH3+nqMUyCrZgURFslOUY=
-----END NEW CERTIFICATE REQUEST-----
5.将上述文件内容拷贝到https://www.thawte.com/cgi/server/try.exe中,点击next,获得回应内容,这里是p7b格式。
内容如下:
-----BEGIN PKCS7-----
MIIF3AYJKoZIhvcNAQcCoIIFzTCCBckCAQExADALBgkqhkiG9w0BBwGgggWxMIID
EDCCAnmgAwIBAgIQA/mx/pKoaB+KGX2hveFU9zANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQUFADCBhzEL
MAkGA1UEBhMCWkExIjAgBgNVBAgTGUZPUiBURVNUSU5HIFBVUlBPU0VTIE9OTFkx
HTAbBgNVBAoTFFRoYXd0ZSBDZXJ0aWZpY2F0aW9uMRcwFQYDVQQLEw5URVNUIFRF
U1QgVEVTVDEcMBoGA1UEAxMTVGhhd3RlIFRlc3QgQ0EgUm9vdDAeFw0wOTA1Mjgw
MDIxMzlaFw0wOTA2MTgwMDIxMzlaMFwxCzAJBgNVBAYTAkNOMQswCQYDVQQIEwJC
SjELMAkGA1UEBxMCQkoxDTALBgNVBAoTBHpsZXgxDTALBgNVBAsTBHpsZXgxFTAT
BgNVBAMTDHd3dy56bGV4Lm9yZzCBnzANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOBjQAwgYkCgYEA
keg11PTKfpgiju3L/ST7I9J9RHPxqTNPar4aYF9xTWnf2Vkg3L1O+2F2UqBfYUKd
8NSwvnnioHdjJVaV0721cATVXdh4kD6d+4nOgVFI0ml/Cx7Qpe5dASBMnvakNo/B
tJGpO3vGQNLO5292JqvyvAVe79DECHYSHNW4nyvWQ3sCAwEAAaOBpjCBozAMBgNV
HRMBAf8EAjAAMB0GA1UdJQQWMBQGCCsGAQUFBwMBBggrBgEFBQcDAjBABgNVHR8E
OTA3MDWgM6Axhi9odHRwOi8vY3JsLnRoYXd0ZS5jb20vVGhhd3RlUHJlbWl1bVNl
cnZlckNBLmNybDAyBggrBgEFBQcBAQQmMCQwIgYIKwYBBQUHMAGGFmh0dHA6Ly9v
Y3NwLnRoYXd0ZS5jb20wDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEFBQADgYEATPuxZbtJJSPmXvfrr1yz
xqM06IwTZ6UU0lZRG7I0WufMjNMKdpn8hklUhE17mxAhGSpewLVVeLR7uzBLFkuC
X7wMXxhoYdJZtNai72izU6Rd1oknao7diahvRxPK4IuQ7y2oZ511/4T4vgY6iRAj
q4q76HhPJrVRL/sduaiu+gYwggKZMIICAqADAgECAgEAMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBBAUA
MIGHMQswCQYDVQQGEwJaQTEiMCAGA1UECBMZRk9SIFRFU1RJTkcgUFVSUE9TRVMg
T05MWTEdMBsGA1UEChMUVGhhd3RlIENlcnRpZmljYXRpb24xFzAVBgNVBAsTDlRF
U1QgVEVTVCBURVNUMRwwGgYDVQQDExNUaGF3dGUgVGVzdCBDQSBSb290MB4XDTk2
MDgwMTAwMDAwMFoXDTIwMTIzMTIxNTk1OVowgYcxCzAJBgNVBAYTAlpBMSIwIAYD
VQQIExlGT1IgVEVTVElORyBQVVJQT1NFUyBPTkxZMR0wGwYDVQQKExRUaGF3dGUg
Q2VydGlmaWNhdGlvbjEXMBUGA1UECxMOVEVTVCBURVNUIFRFU1QxHDAaBgNVBAMT
E1RoYXd0ZSBUZXN0IENBIFJvb3QwgZ8wDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADgY0AMIGJAoGB
ALV9kG+Os6x/DOhm+tKUQfzVMWGhE95sFmEtkMMTX2Zi4n6i6BvzoReJ5njzt1LF
cqu4EUk9Ji20egKKfmqRzmQFLP7+1niSdfJEUE7cKY40QoI99270PTrLjJeaMcCl
+AYl+kD+RL5BtuKKU3PurYcsCsre6aTvjMcqpTJOGeSPAgMBAAGjEzARMA8GA1Ud
EwEB/wQFMAMBAf8wDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEEBQADgYEAgozj7BkD9O8si2V0v+EZ/t7E
fz/LC8y6mD7IBUziHy5/53ymGAGLtyhXHvX+UIE6UWbHro3IqVkrmY5uC93Z2Wew
A/6edK3KFUcUikrLeewM7gmqsiASEKx2mKRKlu12jXyNS5tXrPWRDvUKtFC1uL9a
12rFAQS2BkIk7aU+ghYxAA==
-----END PKCS7-----
将其存储为zlex.p7b
6.将由CA签发的证书导入密钥库。
keytool -import -trustcacerts -alias www.zlex.org -file d:\zlex.p7b -keystore d:\zlex.keystore -v
在这里我使用的密码为 123456
控制台输出:
输入keystore密码:
回复中的最高级认证:
所有者:CN=Thawte Test CA Root, OU=TEST TEST TEST, O=Thawte Certification, ST=FOR
TESTING PURPOSES ONLY, C=ZA
签发人:CN=Thawte Test CA Root, OU=TEST TEST TEST, O=Thawte Certification, ST=FOR
TESTING PURPOSES ONLY, C=ZA
序列号:0
有效期: Thu Aug 01 08:00:00 CST 1996 至Fri Jan 01 05:59:59 CST 2021
证书指纹:
MD5:5E:E0:0E:1D:17:B7:CA:A5:7D:36:D6:02:DF:4D:26:A4
SHA1:39:C6:9D:27:AF:DC:EB:47:D6:33:36:6A:B2:05:F1:47:A9:B4:DA:EA
签名算法名称:MD5withRSA
版本: 3
扩展:
#1: ObjectId: 2.5.29.19 Criticality=true
BasicConstraints:[
CA:true
PathLen:2147483647
]
... 是不可信的。 还是要安装回复? [否]: Y
认证回复已安装在 keystore中
[正在存储 d:\zlex.keystore]
7.域名定位
将域名www.zlex.org定位到本机上。打开C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts文件,将 www.zlex.org绑定在本机上。在文件末尾追加127.0.0.1 www.zlex.org。现在通过地址栏访问http://www.zlex.org,或者通过ping命令,如果能够定位到本机,域名映射就搞定 了。
8.配置server.xml
将文件zlex.keystore拷贝到tomcat的conf目录下,重新启动tomcat。访问https://www.zlex.org/,我们发现联网有些迟钝。大约5秒钟后,网页正常显示,同时有如下图所示:
浏览器验证了该CA机构的有效性。
打开证书,如下图所示:
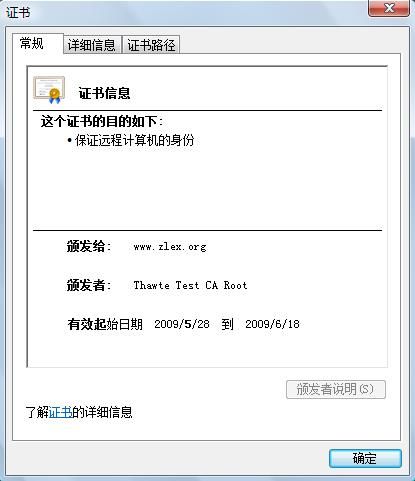
调整测试类:
001 |
import static org.junit.Assert.*; |
003 |
import java.io.DataInputStream; |
004 |
import java.io.InputStream; |
007 |
import javax.net.ssl.HttpsURLConnection; |
009 |
import org.junit.Test; |
017 |
public class CertificateCoderTest { |
018 |
private String password = "123456"; |
019 |
private String alias = "www.zlex.org"; |
020 |
private String certificatePath = "d:/zlex.cer"; |
021 |
private String keyStorePath = "d:/zlex.keystore"; |
024 |
public void test() throws Exception { |
025 |
System.err.println("公钥加密——私钥解密"); |
026 |
String inputStr = "Ceritifcate"; |
027 |
byte[] data = inputStr.getBytes(); |
029 |
byte[] encrypt = CertificateCoder.encryptByPublicKey(data, |
032 |
byte[] decrypt = CertificateCoder.decryptByPrivateKey(encrypt, |
033 |
keyStorePath, alias, password); |
034 |
String outputStr = new String(decrypt); |
036 |
System.err.println("加密前: " + inputStr + "\n\r" + "解密后: " + outputStr); |
039 |
assertArrayEquals(data, decrypt); |
042 |
assertTrue(CertificateCoder.verifyCertificate(certificatePath)); |
047 |
public void testSign() throws Exception { |
048 |
System.err.println("私钥加密——公钥解密"); |
050 |
String inputStr = "sign"; |
051 |
byte[] data = inputStr.getBytes(); |
053 |
byte[] encodedData = CertificateCoder.encryptByPrivateKey(data, |
054 |
keyStorePath, alias, password); |
056 |
byte[] decodedData = CertificateCoder.decryptByPublicKey(encodedData, |
059 |
String outputStr = new String(decodedData); |
060 |
System.err.println("加密前: " + inputStr + "\n\r" + "解密后: " + outputStr); |
061 |
assertEquals(inputStr, outputStr); |
063 |
System.err.println("私钥签名——公钥验证签名"); |
065 |
String sign = CertificateCoder.sign(encodedData, keyStorePath, alias, |
067 |
System.err.println("签名:\r" + sign); |
070 |
boolean status = CertificateCoder.verify(encodedData, sign, |
072 |
System.err.println("状态:\r" + status); |
078 |
public void testHttps() throws Exception { |
079 |
URL url = new URL("https://www.zlex.org/examples/"); |
080 |
HttpsURLConnection conn = (HttpsURLConnection) url.openConnection(); |
082 |
conn.setDoInput(true); |
083 |
conn.setDoOutput(true); |
085 |
CertificateCoder.configSSLSocketFactory(conn, password, keyStorePath, |
088 |
InputStream is = conn.getInputStream(); |
090 |
int length = conn.getContentLength(); |
092 |
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is); |
093 |
byte[] data = new byte[length]; |
098 |
System.err.println(new String(data)); |
再次执行,验证通过!
由此,我们了基于SSL协议的认证过程。测试类的testHttps方法模拟了一次浏览器的HTTPS访问。
|