OpenCV学习笔记(4图像金字塔和轮廓检测)
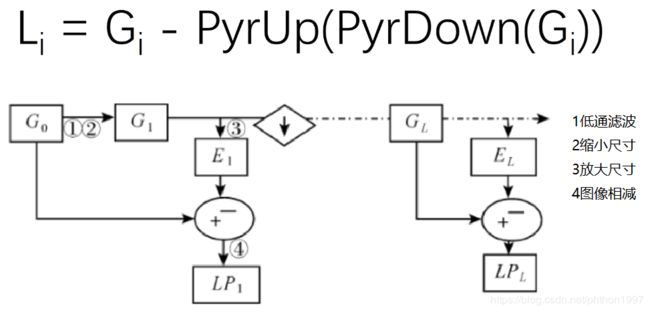
1.图像金字塔
高斯金字塔
拉普拉斯金字塔

高斯金字塔:向下采样方法(缩小)

高斯金字塔:向上采样方法(放大)

#pyrUp的作用是扩大像素值。
up=cv2.pyrUp(img)
cv_show(up,'up')
print (up.shape)
#pyrDown的作用是缩小像素值。
down=cv2.pyrDown(img)
cv_show(down,'down')
print (down.shape)
对于一个图像,如果你先扩大2倍,然后缩小2倍,图像和之前的一样吗?
答案是不一样的,因为它2种变换的方式是不一样的。变换过后的图像会损失一些精度,变模糊一些。
down=cv2.pyrDown(img)
down_up=cv2.pyrUp(down)
l_1=img-down_up
cv_show(l_1,'l_1')
2.图像轮廓
cv2.findContours(img,mode,method)
mode:轮廓检索模式
RETR_EXTERNAL :只检索最外面的轮廓;
RETR_LIST:检索所有的轮廓,并将其保存到一条链表当中;
RETR_CCOMP:检索所有的轮廓,并将他们组织为两层:顶层是各部分的外部边界,第二层是空洞的边界;
RETR_TREE:检索所有的轮廓,并重构嵌套轮廓的整个层次;
method:轮廓逼近方法
CHAIN_APPROX_NONE:以Freeman链码的方式输出轮廓,所有其他方法输出多边形(顶点的序列)。
CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE:压缩水平的、垂直的和斜的部分,也就是,函数只保留他们的终点部分。
img = cv2.imread('contours.png')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)#二值图像
cv_show(thresh,'thresh')
binary, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
绘制轮廓
cv_show(img,'img')
#传入绘制图像,轮廓,轮廓索引,颜色模式,线条厚度
# 注意需要copy,要不原图会变。。。
draw_img = img.copy()
res = cv2.drawContours(draw_img, contours, -1, (0, 0, 255), 2)#-1表示画所有的轮廓其他值画不同的轮廓,(R,G,B)
cv_show(res,'res')
轮廓特征
cnt = contours[0]
#面积
cv2.contourArea(cnt)
#周长,True表示闭合的
cv2.arcLength(cnt,True)
img = cv2.imread('contours2.png')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)#灰度图
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)#二值图
binary, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)#找轮廓
cnt = contours[0]
draw_img = img.copy()
res = cv2.drawContours(draw_img, [cnt], -1, (0, 0, 255), 2)#画图
cv_show(res,'res')
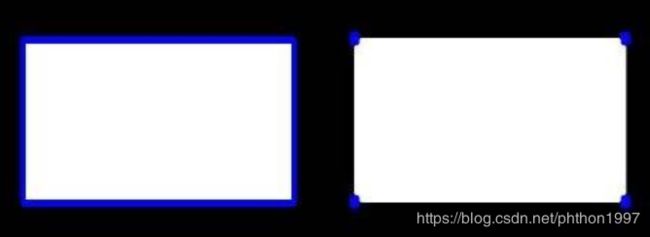
epsilon = 0.15*cv2.arcLength(cnt,True) #一般设置的阈值为周长的一个百分比
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(cnt,epsilon,True)
draw_img = img.copy()
res = cv2.drawContours(draw_img, [approx], -1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv_show(res,'res')
边界矩形
img = cv2.imread('contours.png')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
binary, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
cnt = contours[0]
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
img = cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,255,0),2)
cv_show(img,'img')
area = cv2.contourArea(cnt)
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
rect_area = w * h
extent = float(area) / rect_area
print ('轮廓面积与边界矩形比',extent)
外接圆
(x,y),radius = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(cnt)
center = (int(x),int(y))
radius = int(radius)
img = cv2.circle(img,center,radius,(0,255,0),2)
cv_show(img,'img')