自动驾驶中的行人及车辆行为意图建模、预测及规划总结
1 行人的行为意图建模和预测
主要的论述文章包括:
(1)行人的行为意图建模和预测(上);
(2)行人的行为意图建模和预测(下);
(3)自动驾驶中路上行人的行为和意图理解及预测;
上面文章基本对目前主流的对行人的行为意图预测(即对行人进行轨迹预测)的文章进行了阐述。
简单的归纳分析:
- 和驾驶行为一样,不确定性和多模态是行人行为建模的挑战;
- 大多方法采用递归神经网络,如RNN/LSTM/GRU模型;
- 有采用对抗理论GAN,比如social GAN和Social Ways;
- 有采用增强学习(RL),本身RL和GAN之间有联系;
- 大多考虑环境的交互(interaction)模型,不管局部或者全局,这是对行人的社会属性建模;
- 对人群(grouping)和单个行人,社会行为建模会不同;
- 一些采用注意机制,比如social attention和Sophie;
- 对行人意图和行人活动类型的理解。
2 车辆的行为意图建模和预测
自动驾驶里面很重要的就是估计和预测交通情况。预测的来源就是路上各种物体的姿态和速度历史,高级的预测会包括可能的行动轨迹。
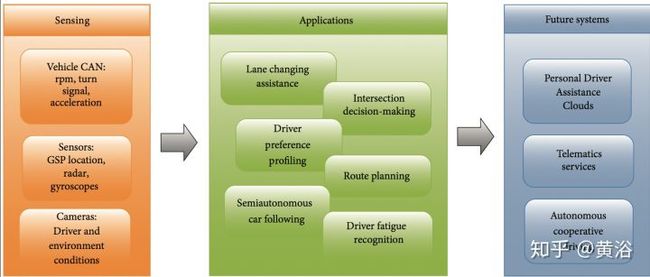
驾驶行为建模(DBM,driver behavior modeling)目的就是预测驾驶动作,预测驾驶员心思,还有环境因素,如下图所示:各种传感器和车载控制器CAN数据作为输入,预处理算法过滤数据,然后给各种应用提供预测模型。
基于深度学习的车辆行为意图建模和预测算法的论述文章包括:
(1)可以参考2019年12月25日英国的大学研究人员上传arXiv的综述《Deep Learning-based Vehicle Behaviour Prediction For Autonomous Driving Applications: A Review》;
(2)自动驾驶中的驾驶行为建模和预测方法;
(3)自动驾驶近期行为预测和规划的一些文章介绍(下);
(4)自动驾驶近期行为预测和规划的一些文章介绍(附录)。
3 运动预测(Motion prediction)
(1)建模参与者间相互作用(interactions )的机制总结
从科学上讲,运动预测对于理解人类行为和运动动力学很有用。这项任务的基本挑战之一是对场景约束进行建模,尤其是对角色之间的隐藏交互进行建模。 例如,在驾驶场景中,交通参与者(例如车辆和行人)以及交通条件和规则会相互影响,如下图所示。
参考论文《Collaborative Motion Prediction via Neural Motion Message Passing》中的论述,对交通参与者(traffic actors)间隐藏的相互作用进行建模的机制包括以下三种:
-
以空间为中心的机制( spatial-centric mechanism)
它在统一的空间域中表示交通参与者的轨迹,并使用空间关系隐式地建模参与者之间的相互作用。如:
Social Conv^[1]^和MATF^[2]^利用交通参与者的空间结构来学习交互作用;ChauffeurNet^[3]^和Motion Prediction^[4]^将交通参与者的轨迹和场景背景编码为鸟瞰图像; FMNet^[5]^使用轻量级的CNN来实现实时推断; IntentNet ^[6]^将LiDAR数据与图像结合在一起。
- 社会机制(the social mechanism)
它将邻近交通参与者的信息汇总为社会表征(social representation),并广播给每个参与者。 这样,每个交通参与者都知道邻近信息。如:
Social LSTM^[7]^将最大池化作用于的邻近交通参与者;考虑长期间的相互作用,Social GAN^[8]^将最大池化应用于所有参与者;CIDNN^[9]^则在交通参与者的先验的位置嵌入之间使用内积。 但是,最大池化操作会忽略每个参与者的独特性,而内积运算会将所有交通参与者同等对待。 注意力操作(attention operation)^[10,11]^,以便交通参与者可以专注于关键的影响因素。 然而不可避免地,注意力操作伴随着计算复杂性的增加。
-
基于图的策略(graph-based mechanism)
它构造了一个图以显式地建模参与者之间的成对交互作用。如:
Social-BiGAT^[12]^基于图注意力网络(GAT)学习全局嵌入来表示场景中的交互。 Social Attention^[13]^和STGAT^[14]^分别通过使用时空图和LSTM捕获了随时间变化动态交互作用的变化。
[1] Nachiket Deo and Mohan M Trivedi. Convolutional social pooling for vehicle trajectory prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pages 1468–1476, 2018.
[2] Tianyang Zhao, Yifei Xu, Mathew Monfort, Wongun Choi, Chris Baker, Yibiao Zhao, Yizhou Wang, and Ying Nian Wu. Multi-agent tensor fusion for contextual trajectory predic- tion. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 12126–12134, 2019.
[3] Mayank Bansal, Alex Krizhevsky, and Abhijit Ogale. Chauf- feurnet: Learning to drive by imitating the best and synthe- sizing the worst. arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.03079, 2018.
[4] Nemanja Djuric, Vladan Radosavljevic, Henggang Cui, Thi Nguyen, Fang-Chieh Chou, Tsung-Han Lin, and Jeff Schnei- der. Short-term motion prediction of traffic actors for au- tonomous driving using deep convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.05819, 2018.
[5] Fang-Chieh Chou, Tsung-Han Lin, Henggang Cui, Vladan Radosavljevic, Thi Nguyen, Tzu-Kuo Huang, Matthew Niedoba, Jeff Schneider, and Nemanja Djuric. Predicting motion of vulnerable road users using high-definition maps and efficient convnets. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.08469, 2019.
[6] Sergio Casas, Wenjie Luo, and Raquel Urtasun. Intentnet: Learning to predict intention from raw sensor data. In Con- ference on Robot Learning, pages 947–956, 2018.
[7] Alexandre Alahi, Kratarth Goel, Vignesh Ramanathan, Alexandre Robicquet, Li Fei-Fei, and Silvio Savarese. So- cial lstm: Human trajectory prediction in crowded spaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 961–971, 2016.
[8] Agrim Gupta, Justin Johnson, Li Fei-Fei, Silvio Savarese, and Alexandre Alahi. Social gan: Socially acceptable tra- jectories with generative adversarial networks. In Proceed- ings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 2255–2264, 2018.
[9] Yanyu Xu, Zhixin Piao, and Shenghua Gao. Encoding crowd interaction with deep neural network for pedestrian trajec- tory prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 5275– 5284, 2018.
[10] Anirudh V emula, Katharina Muelling, and Jean Oh. Social attention: Modeling attention in human crowds. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pages 1–7. IEEE, 2018.
[11] Amir Sadeghian, Vineet Kosaraju, Ali Sadeghian, Noriaki Hirose, Hamid Rezatofighi, and Silvio Savarese. Sophie: An attentive gan for predicting paths compliant to social and physical constraints. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 1349– 1358, 2019.
[12] Vineet Kosaraju, Amir Sadeghian, Roberto Mart´ ın-Mart´ ın, Ian Reid, S Hamid Rezatofighi, and Silvio Savarese. Social- bigat: Multimodal trajectory forecasting using bicycle-gan and graph attention networks. In Advances in Neural Infor- mation Processing Systems (NeurIPS) 32, 2019.
[13] Anirudh V emula, Katharina Muelling, and Jean Oh. Social attention: Modeling attention in human crowds. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pages 1–7. IEEE, 2018.
[14] Yingfan Huang, HuiKun Bi, Zhaoxin Li, Tianlu Mao, and Zhaoqi Wang. Stgat: Modeling spatial-temporal interactions for human trajectory prediction. In International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2019.