netty NioEventLoop中run()方法执行流程分析
NioEventLoop的run方法的执行过程
在创建线程对象的任务中调用了SingleThreadEventExecutor.this#run()方法,使NioEventLoop开始运行,开始处理任务。
NioEventLoop#run()方法如下所示,可以看到run()方法是一个无限循环,直到NioEventLoop被关闭。
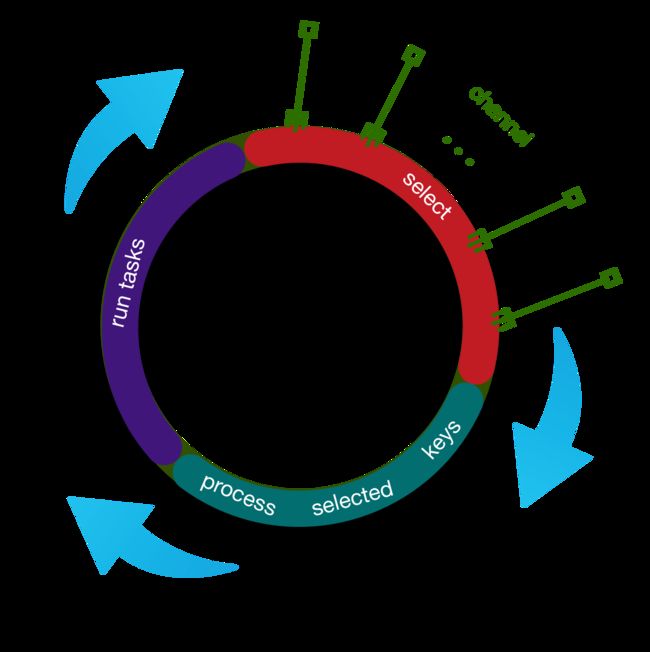
run()方法中的逻辑主要分为以下三大步骤
- select 选择任务
- processSelectedKeys 处理Channel 感兴趣的就绪 IO 事件
- runAllTasks 运行所有普通任务和定时任务
run()方法的执行流程如下图所示:
@Override
protected void run() {
for (;;) {
try {
switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:// 默认实现下,不存在这个情况。
continue;
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
//将wakenUp字段设置为false,标识当前状态为阻塞
//调用select查询任务
select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false));
if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
default:
}
cancelledKeys = 0;//已取消的key的数量
needsToSelectAgain = false;//是否需要再次选择
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;//IO比率
if (ioRatio == 100) {
try {
processSelectedKeys();//处理Channel 感兴趣的就绪 IO 事件
} finally {
runAllTasks();
}
} else {
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
//运行所有普通任务和定时任务,不限制时间
processSelectedKeys();//Channel 感兴趣的就绪 IO 事件
} finally {
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
//运行所有普通任务和定时任务,限制时间
runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
try {
if (isShuttingDown()) {
closeAll();
if (confirmShutdown()) {
return;
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
}
}
1.1select 选择任务
selectNowSupplier
调用Selector的selectNow()方法,此方法执行非阻塞的选择操作。如果自从前一次选择操作后,没有通道变成可选择的,则此方法直接返回零。
private final IntSupplier selectNowSupplier = new IntSupplier() {
@Override
public int get() throws Exception {
return selectNow();
}
};
int selectNow() throws IOException {
try {
return selector.selectNow();
} finally {
if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
}
}
hasTasks()
返回当前任务队列是否不为空
@Override
protected boolean hasTasks() {
return super.hasTasks() || !tailTasks.isEmpty();
}
protected boolean hasTasks() {
assert inEventLoop();
return !taskQueue.isEmpty();
}
SelectStrategy
NioEventLoop中的SelectStrategy的实现类为DefaultSelectStrategy,可以看到,DefaultSelectStrategy是一个单例的
final class DefaultSelectStrategy implements SelectStrategy {
static final SelectStrategy INSTANCE = new DefaultSelectStrategy();
//私有构造函数,保证单例
private DefaultSelectStrategy() { }
@Override
public int calculateStrategy(IntSupplier selectSupplier, boolean hasTasks) throws Exception {
//队列中有任务则调用selectNow返回当前已就绪IO事件的数量,否则继续select
return hasTasks ? selectSupplier.get() : SelectStrategy.SELECT;
}
}
select(boolean oldWakenUp)
select(boolean oldWakenUp)方法中的主要逻辑为
1、计算定时任务队列中最近要执行的任务和当前时间的差值(selectDeadLineNanos)
2、判断任务队列中是否有任务没有执行。如果有,则退出select循环,执行任务
3、如果队列中没有任务要执行,则调用jdk底层的select(timeoutMillis)方法继续阻塞
private void select(boolean oldWakenUp) throws IOException {
Selector selector = this.selector;//JDK原生的Selector
try {
int selectCnt = 0;//已轮训次数
long currentTimeNanos = System.nanoTime();
//计算本次轮询的截止时间,delayNanos方法用于计算定时任务队列中最近要执行的任务距离当前时间的差值
long selectDeadLineNanos = currentTimeNanos + delayNanos(currentTimeNanos);
for (;;) {
//timeoutMillis为本次轮询的超时时间
//加500000L为了方便四舍五入
//除以1000000L是为了将纳秒换算成毫秒
long timeoutMillis = (selectDeadLineNanos - currentTimeNanos + 500000L) / 1000000L;
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
if (selectCnt == 0) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
}
break;
}
//如果任务队列中有任务
if (hasTasks() && wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;//将已轮训次数重置为1
break;
}
//执行到这里表示任务队列中没有要执行的任务,故将selector阻塞timeoutMillis毫秒
int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis);
selectCnt ++;//已轮训次数加一
/**
* selectedKeys != 0 表示轮询到有已经就绪的IO事件
* wakenUp.get() 表示是否被用户唤醒
* hasTasks() 表示普通任务队列中有未完成的任务
* hasScheduledTasks() 表示定时任务队列中有未完成的任务
* 上述条件任何一个条件为真,则退出select,准备处理对应任务
*/
if (selectedKeys != 0 || oldWakenUp || wakenUp.get() || hasTasks() || hasScheduledTasks()) {
break;
}
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely because " +
"Thread.currentThread().interrupt() was called. Use " +
"NioEventLoop.shutdownGracefully() to shutdown the NioEventLoop.");
}
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
long time = System.nanoTime();
//执行时间大于阻塞超时时间,表示正常执行,则将已轮训次数重置为1
//否则则视为触发了JDK空轮训的bug,如果空轮训的次数大于事先设定的阈值
//SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD,则执行rebuildSelector()避免该bug
//避免jdk空轮训bug的方法后面展开分析
if (time - TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(timeoutMillis) >= currentTimeNanos) {
selectCnt = 1;
} else if (SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD > 0 &&
selectCnt >= SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD) {
logger.warn(
"Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row; rebuilding Selector {}.",
selectCnt, selector);
rebuildSelector();
selector = this.selector;
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
currentTimeNanos = time;
}
if (selectCnt > MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row for Selector {}.",
selectCnt - 1, selector);
}
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(CancelledKeyException.class.getSimpleName() + " raised by a Selector {} - JDK bug?",
selector, e);
}
}
}
1.2 processSelectedKeys 处理Channel 感兴趣的就绪 IO 事件
processSelectedKeys()方法的定义如下:
如果配置io.netty.noKeySetOptimization为false,则selectedKeys == null,netty对SelectedKeys做了优化。优化内容后面分析。
private void processSelectedKeys() {
if (selectedKeys != null) {
processSelectedKeysOptimized();
} else {
processSelectedKeysPlain(selector.selectedKeys());
}
}
如果io.netty.noKeySetOptimization不为false,即对selectedKeys进行优化
private void processSelectedKeysOptimized() {
for (int i = 0; i < selectedKeys.size; ++i) {
final SelectionKey k = selectedKeys.keys[i];
selectedKeys.keys[i] = null;
final Object a = k.attachment();
if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) {
processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a);
} else {
//io.netty.channel.nio.NioTask ,用于自定义 Nio 事件处理接口
//对于每个 Nio 事件,可以认为是一个任务( Task )
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
NioTask<SelectableChannel> task = (NioTask<SelectableChannel>) a;
processSelectedKey(k, task);
}
if (needsToSelectAgain) {
selectedKeys.reset(i + 1);
selectAgain();
i = -1;
}
}
}
这里只分析是AbstractNioChannel子类的情况
private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) {
final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe();//获取channel中Unsafe接口的实现类
// 如果 SelectionKey 是不合法的,则关闭 Channel
if (!k.isValid()) {
final EventLoop eventLoop;
try {
eventLoop = ch.eventLoop();
} catch (Throwable ignored) {
return;
}
if (eventLoop != this || eventLoop == null) {
return;
}
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
return;
}
try {
int readyOps = k.readyOps();//获取就绪事件类型
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) {//客户端连接事件
int ops = k.interestOps();
ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;
k.interestOps(ops);
unsafe.finishConnect();
}
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {//写事件
ch.unsafe().forceFlush();//上面已经获取到了unsafe,为什么还要再获取一次???
}
//读事件或者ACCEPT事件
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) {
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
}
}
1.3 runAllTasks 运行所有普通任务和定时任务
运行任务队列中所有的任务
protected boolean runAllTasks() {
assert inEventLoop();//断言当前线程就是Channel对应的EventLoop中的线程
boolean fetchedAll;//是否取全部任务
boolean ranAtLeastOne = false;//是否至少运行了一个
do {
fetchedAll = fetchFromScheduledTaskQueue();
//运行任务队列中的所有任务
if (runAllTasksFrom(taskQueue)) {
ranAtLeastOne = true;
}
} while (!fetchedAll); // keep on processing until we fetched all scheduled tasks.
if (ranAtLeastOne) {
//记录当前的时间
lastExecutionTime = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime();
}
//运行tailQueue里的所有任务
afterRunningAllTasks();
return ranAtLeastOne;
}
private boolean fetchFromScheduledTaskQueue() {
//获取系统当前时间(是一个相对值)
long nanoTime = AbstractScheduledEventExecutor.nanoTime();
//获取deadline<=nanoTime的定时任务
Runnable scheduledTask = pollScheduledTask(nanoTime);
while (scheduledTask != null) {
//将上面获取的定时任务添加到任务队列的队首
if (!taskQueue.offer(scheduledTask)) {
//如果添加失败则循环添加
scheduledTaskQueue().add((ScheduledFutureTask<?>) scheduledTask);
return false;
}
scheduledTask = pollScheduledTask(nanoTime);
}
return true;
}
从定时任务队列中获取定时任务
protected final Runnable pollScheduledTask(long nanoTime) {
assert inEventLoop();
Queue<ScheduledFutureTask<?>> scheduledTaskQueue = this.scheduledTaskQueue;
ScheduledFutureTask<?> scheduledTask = scheduledTaskQueue == null ? null : scheduledTaskQueue.peek();
if (scheduledTask == null) {
return null;
}
if (scheduledTask.deadlineNanos() <= nanoTime) {
scheduledTaskQueue.remove();
return scheduledTask;
}
return null;
}
带超时时间的版本
protected boolean runAllTasks(long timeoutNanos) {
fetchFromScheduledTaskQueue();//将定时队列中需要执行的定时任务添加到任务队列中
Runnable task = pollTask();//获取队列中队首的任务
if (task == null) {
afterRunningAllTasks();//运行所有tailQueue中的任务
return false;
}
//计算任务执行的超时时间
final long deadline = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime() + timeoutNanos;
long runTasks = 0;//已经执行的任务的数量
long lastExecutionTime;
for (;;) {
safeExecute(task);//执行队列中的任务
runTasks ++;
//如果执行的任务数量达到64且超时,则停止执行,目的是防止有过多的任务需要执行,从而导致无法处理IO事件
if ((runTasks & 0x3F) == 0) {
lastExecutionTime = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime();//记录最后执行的时间
if (lastExecutionTime >= deadline) {
break;
}
}
task = pollTask();
if (task == null) {
lastExecutionTime = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime();
break;
}
}
afterRunningAllTasks();
this.lastExecutionTime = lastExecutionTime;
return true;
}