《剑指offer》第10-20题:矩形覆盖到包含min函数的栈
《剑指offer》第10-20题
- 10 矩形覆盖
- 11 二进制中1的个数
- 12 数值的整数次方
- 13 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面.
- 14 链表中倒数第K个节点
- 15 反转链表
- 16 合并两个排序的链表
- 17树的子结构
- 18 二叉树的镜像
- 19 顺时针打印矩阵
- 20 包含min函数的栈
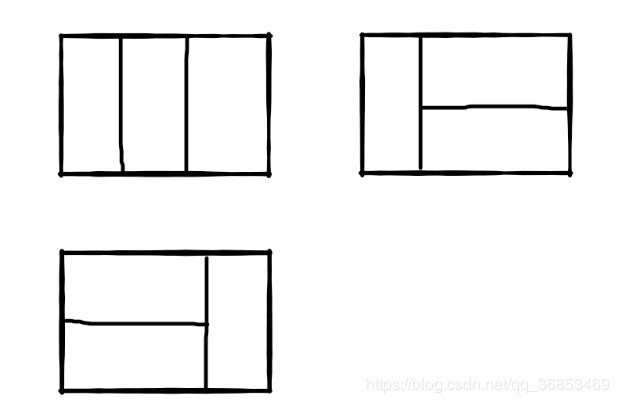
10 矩形覆盖
我们可以用21的小矩形横着或者竖着去覆盖更大的矩形。请问用n个21的小矩形无重叠地覆盖一个2n的大矩形,总共有多少种方法?比如n=3时,23的矩形块有3种覆盖方法:
'''
第一块有两种方式:横着放和竖着放
横着放对应为方法为f(n-2);
竖着放下一步的放方法为f(n-1);
所以总的放的方法为f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2);
和第7题一样,方法不外乎循环和递归两种
这里只写循环迭代法。其他方法查看第7题
'''
class Solution:
def rectCover(self, number):
# write code here
if number == 0:
return 0
pre,cur = 0,1
index = 0
while index < number:
pre,cur = cur,pre+cur
index += 1
return cur
11 二进制中1的个数
输入一个整数,输出该数32位二进制表示中1的个数。其中负数用补码表示
'''
python中 使用模将负数转化:n = n & 0xffffffff,然后再进行减1做与运算
先了解下计算机中原码反码补码
eg:十进制 3 转换为二进制: 00000011
原码:
是一种计算机中对数字的二进制定点表示方法。原码表示法在数值前面增加了一位符号位(即最高位为符号位):
正数该位为0,负数该位为1(0有两种表示:+0和-0),其余位表示数值的大小。
eg:十进制 3 转换为二进制的原码: 00000011,
-3的话:10000011
1的话: 00000001
-1的话:10000001
反码:
正数的反码是其本身
负数的反码是在其原码的基础上, 符号位不变,其余各个位取反.
eg: 十进制1:原码:00000001 反码:00000001
-1:原码:10000001 反码:11111110
补码:
正数的补码就是其本身
负数的补码是在其原码的基础上, 符号位不变, 其余各位取反, 最后+1. (即在反码的基础上+1)
eg: 十进制1:原码:00000001 反码:00000001 补码:00000001
-1:原码:10000001 反码:11111110 补码:11111111
'''
'''
方法一:内置函数
'''
class Solution1:
def NumberOf1(self, n):
# write code here
#整数转二进制
return str(bin(n)).count("1") if n >= 0 else str(bin(n & 0xffffffff)).count("1")
'''
方法二:位运算
负数的右移运算会在高位进行补1,如果没考虑这一点,可能导致程序陷入死循环
可以使用与运算实现1的个数统计
'''
class Solution3:
def NumberOf1(self, n):
maxNum = (1 << (32 - 1))
flag = 1
count = 0
while flag <= maxNum:
print(maxNum,flag,count,n & flag)
if n & flag:
count += 1
flag = flag << 1
return count
12 数值的整数次方
给定一个double类型的浮点数base和int类型的整数exponent。求base的exponent次方。
保证base和exponent不同时为0
'''
方法一:公式法 & 内置函数
'''
class Solution1:
def Power(self, base, exponent):
return pow(base,exponent)
# or
# return base ** exponent
'''
方法二:暴力法:次方累乘
'''
class Solution2:
def Power(self, base, exponent):
result = 1
for i in range(abs(exponent)):#次方的最初表达式
result *= base
return result if exponent >= 0 else 1/result #根据正负返回不同的值
'''
方法三:递归法
想了老半天没理清楚递归法,先略过...
'''
class Solution3:
def Power(self, base, exponent):
pass
13 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面.
输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后半部分,并保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。
'''
排序,奇奇 偶偶相对位置不变
'''
'''
方法一:暴力法
将奇数和偶数分别存放到新数组中,拼接
O(n)
'''
class Solution1:
def reOrderArray(self, array):
# write code here
odd,even = [],[]
for i in array:
even.append(i) if i%2 ==0 else odd.append(i)
return odd+even
14 链表中倒数第K个节点
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
'''
方法一:暴力法:将所有元素存到列表中
'''
class Solution1:
def FindKthToTail(self, head:ListNode, k):
nodeList = []
while head != None:
nodeList.append(head)
head = head.next
if k > len(nodeList) or k < 1:
return None
return nodeList[-k]
'''
方法二:先统计,再查询
'''
class Solution2:
def FindKthToTail(self, head, k):
if not head:
return None
nodeList = head
count = 0
while nodeList:
nodeList = nodeList.next
count += 1
if k > count:
return None
while count - k:
head = head.next
k += 1
return head
15 反转链表
输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
'''
方法一:
'''
class Solution1:
# 返回ListNode
def ReverseList(self, pHead):
# write code here
if not pHead:#空
return pHead
pre = pHead
cur = pHead.next
if cur is None:#一个节点
return pHead
next_p = cur.next
if next_p is None:#两个节点
pre.next = None
cur.next = pre
return cur
pre.next = None#节点数>=3
while next_p != None:
cur.next = pre
pre = cur#指针移动
cur = next_p
next_p = next_p.next
cur.next = pre
return cur
'''
方法二:
参考链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/75e878df47f24fdc9dc3e400ec6058ca?f=discussion
pHead始终指向要反转的结点
cur 指向反转后的首结点
每反转一个结点,把pHead结点的下一个结点指向cur, cur指向pHead成为反转后首结点, 再把pHead向前移动一个结点直至None结束
'''
class Solution2:
# 返回ListNode
def ReverseList(self, pHead):
cur = None
while pHead:
tmp = pHead.next
pHead.next = cur
cur = pHead
pHead = tmp
return cur
16 合并两个排序的链表
输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
''''
方法一:递归
'''
class Solution:
# 返回合并后列表
def Merge(self, pHead1, pHead2):
# write code here
if not pHead1:#判空
return pHead2
if not pHead2:
return pHead1
if pHead1.val < pHead2.val:
pHead1.next = self.Merge(pHead1.next, pHead2)
return pHead1
else:
pHead2.next = self.Merge(pHead1, pHead2.next)
return pHead2
'''
方法二:暴力法
'''
class Solution2:
# 返回合并后列表
def Merge(self, pHead1, pHead2):
# write code here
if not pHead1:
return pHead2
if not pHead2:
return pHead1
pNode1 = pHead1
pNode2 = pHead2
if pNode1.val <= pNode2.val:
pNode = pNode1
pNode1 = pNode1.next
else:
pNode = pNode2
pNode2 = pNode2.next
pHead = pNode
while pNode1 or pNode2:
if not pNode1:
pNode.next = pNode2
pNode2 = pNode2.next
elif not pNode2:
pNode.next = pNode1
pNode1 = pNode1.next
else:
if pNode1.val <= pNode2.val:
pNode.next = pNode1
pNode1 = pNode1.next
else:
pNode.next = pNode2
pNode2 = pNode2.next
pNode = pNode.next
return pHead
17树的子结构
输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(ps:我们约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
'''
方法一:递归遍历
'''
class Solution:
def HasSubtree(self, pRoot1, pRoot2):
# write code here
if not pRoot1 or not pRoot2:
return False
result = False
if pRoot1.val == pRoot2.val:
result = self.Tree1ContainTree2(pRoot1,pRoot2)
if not result:
if pRoot1.left:
result = self.HasSubtree(pRoot1.left,pRoot2)
if not result and pRoot1.right:
result = self.HasSubtree(pRoot1.right,pRoot2)
return result
def Tree1ContainTree2(self,pRoot1,pRoot2):
if not pRoot2:#遍历完,说明是A的子树,返回True
return True
if not pRoot1:
return False
if pRoot1.val != pRoot2.val:
return False
return self.Tree1ContainTree2(pRoot1.left, pRoot2.left) and self.Tree1ContainTree2(pRoot1.right,pRoot2.right)
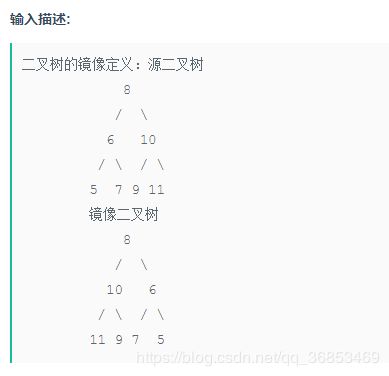
18 二叉树的镜像
操作给定的二叉树,将其变换为源二叉树的镜像。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
'''
方法一:递归
'''
class Solution1:
# 返回镜像树的根节点
def Mirror(self, root):
# write code here
if not root:
return root
#终止条件
if not root.left and not root.right:
return
if root.left and root.right:
root.left, root.right = root.right, root.left
self.Mirror(root.left)
self.Mirror(root.right)
elif root.left and not root.right:
root.left, root.right = None, root.left
self.Mirror(root.right)
elif not root.left and root.right:
root.left, root.right = root.right, None
self.Mirror(root.left)
return root
'''
方法二:递归简化
'''
class Solution2:
# 返回镜像树的根节点
def Mirror(self, root):
# write code here
if root:
root.left, root.right = root.right, root.left
self.Mirror(root.left)
self.Mirror(root.right)
return root
19 顺时针打印矩阵
输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字,例如,如果输入如下4 X 4矩阵:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
则依次打印出数字
1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11,10.
'''
方法一:
根据打印规则,第一次打印第一行,接着打印最后一列(除去第一个元素,后面类似),打印最后一行,打印第一列
第二圈第一行,依次打印,
'''
import numpy as np
class Solution1:
# matrix类型为二维列表,需要返回列表
def printMatrix(self, matrix):
# write code here
rowsTotal = len(matrix)
colsTotal = len(matrix[0])
if not rowsTotal and not colsTotal:
return None
left, right, top, bottom = 0, colsTotal - 1, 0, rowsTotal - 1#上下左右四个边界代表的行列值
result = []
while left <= right and top <= bottom:
#从左到右一行
for i in range(left,right+1):
result.append(matrix[top][i])
#从上到下一列
for j in range(top+1,bottom+1):
result.append(matrix[j][right])
#从右到左一行
if top != bottom:
for m in range(right-1,left-1,-1):
result.append(matrix[bottom][m])
#从下到上一列
if left != right:
for n in range(bottom-1,top,-1):
result.append(matrix[n][left])
left += 1
right -= 1
top += 1
bottom -= 1
return result
20 包含min函数的栈
定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈中所含最小元素的min函数(时间复杂度应为O(1))。
注意:保证测试中不会当栈为空的时候,对栈调用pop()或者min()或者top()方法。
'''
方法一:内置函数min()
...忽略题目O(1)的要求
'''
class Solution1:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = []
def push(self, node):
# write code here
self.stack.append(node)
def pop(self):
# write code here
return self.stack.pop()
def top(self):
# write code here
return self.stack[-1]
def min(self):
# write code here
return min(self.stack)
'''
方法二:借助一个辅助栈,辅助栈最后一个元素存放的一定是最小的元素
'''
class Solution2:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = []
self.minEleStack = []
def push(self, node):
# write code here
self.stack.append(node)
if not self.minEleStack:
self.minEleStack.append(node)
elif node < self.minEleStack[-1]:
self.minEleStack.append(node)
else:
self.minEleStack.append(self.minEleStack[-1])
def pop(self):
# write code here
if not self.stack:
return None
self.minEleStack.pop()
return self.stack.pop()
def top(self):
# write code here
if not self.stack:
return None
return self.stack[-1]
def min(self):
# write code here
return self.minEleStack[-1]