嵌入式软件开发QT-01-helloworld工程的几种编写方式以及详解
1.使用纯代码方式编写helloworld
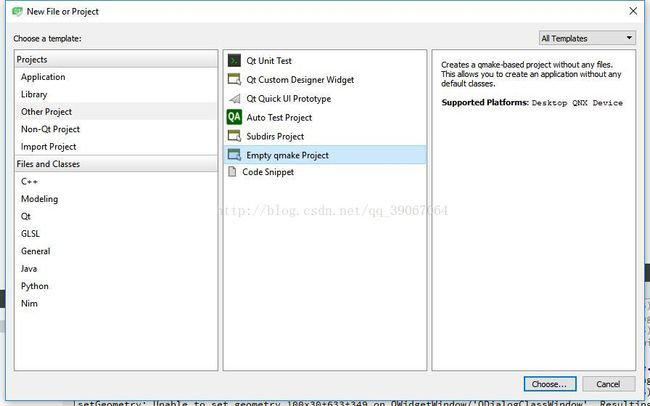
新建一个空工程
此时目录中只有一个pro文件
右键工程目录,新建c++源文件并且加入工程
此时工程目录为
在改写pro文件为
SOURCES += \
main.cpp
#为高版本模块添加widgets模块
greaterThan(QT_MAJOR_VERSION, 4): QT += widgets然后改写main.cpp文件为
#include
#include
#include
//主函数
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
//QApplication类用于管理应用程序资源,所有Qt Widgets程序必有
QApplication a(argc, argv);
//声明QDialog对象,生成对话框
QDialog w;
//设置对话框大小
w.resize(400, 300);
//声明QLabel对象,此对象继承自QDialog类
QLabel label(&w);
//设置标签位置
label.move(120, 120);
//设置标签内的内容,通过QObject::tr()函数实现多语言支持
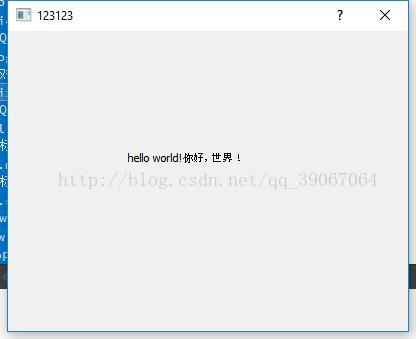
label.setText(QObject::tr("hello world!你好,世界!"));
//显示w对象
w.show();
//使QApplication进入事件循环,可以接收事件,否则将会秒退
return a.exec();
}
编译运行
如果使用命令行编译程序,复制刚刚的main.cpp到一个新目录
打开Qt 5.9.1 for Desktop (MinGW 5.3.0 32 bit)
cd到工程目录
qmake -project生成pro文件,在生成的pro文件中加入
greaterThan(QT_MAJOR_VERSION, 4): QT += widgets然后
qmake最后
mingw32-makedir一下看看文件名字,直接执行
2.使用ui文件
在上一个工程中,添加ui文件
这样可以生成一个ui文件,名字默认即可,也可以不默认,但是这个名字将会写入主函数中
使用qt设计师拖拽设计ui界面
然后点击构建,发现在工程文件的ddebug目录中多了一个h文件
简单解释一下
/********************************************************************************
** Form generated from reading UI file 'dialog.ui'
**
** Created by: Qt User Interface Compiler version 5.9.1
**
** WARNING! All changes made in this file will be lost when recompiling UI file!
********************************************************************************/
//预防多重包含的宏定义
#ifndef UI_DIALOG_H
#define UI_DIALOG_H
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
//QT命名空间开始
QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
//添加Ui_前缀,实现一个模板的父类
class Ui_Dialog
{
public:
//添加的label部件
QLabel *label;
//生成界面函数
void setupUi(QDialog *Dialog)
{
if (Dialog->objectName().isEmpty())
Dialog->setObjectName(QStringLiteral("Dialog"));
//大小、位置属性设置
Dialog->resize(400, 300);
label = new QLabel(Dialog);
label->setObjectName(QStringLiteral("label"));
label->setGeometry(QRect(120, 120, 128, 32));
retranslateUi(Dialog);
//添加信号与槽功能
QMetaObject::connectSlotsByName(Dialog);
} // setupUi
//添加编码转换功能
void retranslateUi(QDialog *Dialog)
{
Dialog->setWindowTitle(QApplication::translate("Dialog", "Dialog", Q_NULLPTR));
label->setText(QApplication::translate("Dialog", "hello, world!", Q_NULLPTR));
} // retranslateUi
};
namespace Ui {
//继承自父类的可用的类
class Dialog: public Ui_Dialog {};
} // namespace Ui
QT_END_NAMESPACE
#endif // UI_DIALOG_H //头文件名为debug文件夹中自动生成的文件
#include "ui_dialog.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
QApplication a (argc, argv);
QDialog w;
//此处注意,Ui命名空间中的类,查看ui_dialog.h文件中的类名,一般与ui文件名字相同,并且首字母大写
Ui::Dialog ui;
ui.setupUi(&w);
w.show();
return a.exec();
}3.使用自定义c++类
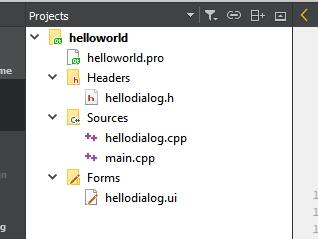
建立空工程,然后添加c++类,以hellodialog命名,再新建ui文件,添加main.cpp
最终工程目录为
修改hellodialog.cpp文件为
#include "hellodialog.h"
#include "ui_hellodialog.h"
HelloDialog::HelloDialog(QWidget *parent) :
QDialog(parent),
ui(new Ui::HelloDialog)
{
//为当前对话框创建界面
ui->setupUi(this);
}
HelloDialog::~HelloDialog()
{
delete ui;
}
修改h文件为
#ifndef HELLODIALOG_H
#define HELLODIALOG_H
#include
namespace Ui {
class HelloDialog;
}
class HelloDialog : public QDialog
{
//扩展普通c++类功能
Q_OBJECT
public:
//显示构造函数,指定父窗口
explicit HelloDialog(QWidget *parent = 0);
~HelloDialog();
private:
Ui::HelloDialog *ui;
};
#endif // HELLODIALOG_H
最后编译,即可完成
4.使用qt设计师类
新建空工程,添加qt设计师类
这个类建立了一整套的文件
添加主函数,修改为
#include
#include "dialog.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
QApplication a (argc, argv);
Dialog w;
w.show();
return a.exec();
}
编译运行
以上就是4种编写代码的方式。