Qt:MySQL数据库总结(表的创建,插入,各种查询方式,删除,封装时需要的dll)
Qt:MySQL数据库总结(表的创建,插入,各种查询方式,删除,封装时需要的dll)更新中.....
参考:
mysql选择指定范围行的记录:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35462323/article/details/82775242
MySQL系列操作(非常全):https://www.cnblogs.com/whgk/p/6149009.html
封装需要的dll:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41605114/article/details/86612264
SQL相关介绍合集:
SQL介绍(一)创建数据库,表的操作(创建,更新,删除):https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41605114/article/details/97292616
SQL介绍(二)完整性约束,数据类型,索引(创建,更新,删除):https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41605114/article/details/97392269
SQL介绍(三)触发器:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41605114/article/details/97794131
SQL介绍(四)单表查询:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41605114/article/details/97934605
Qt:MySQL数据库总结(表的创建,插入,各种查询方式,删除,封装时需要的dll):https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41605114/article/details/90671791
Qt封装调用MySQL的软件时所需的依赖项:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41605114/article/details/86612264
目录
1.表的创建
2.数据插入(读取excel中的文本,并插入数据库)
3.单表查询
3.1查询所有字段数据
3.2查询指定字段数据
3.3避免重复数据查询——DISTINCT
3.4实现数学四则运算数据查询
3.5单条件数据查询
3.6多条件数据查询
3.7带BETWEEN AND关键字的范围查询
3.7.1符合范围的数据记录查询
3.7.2不符合范围的数据记录查询
3.8在集合中数据记录查询
3.9排序数据记录查询
3.9.1按照单字段排序
升序排序
降序排序
3.9.2按照多字段排序
3.10限制数据记录查询数据
3.10.1指定初始位置
3.11统计函数和分组数据记录查询
统计数据记录条数-COUNT()
4.表的删除
Qt封装带MySQL数据库的程序时,需要的依赖项
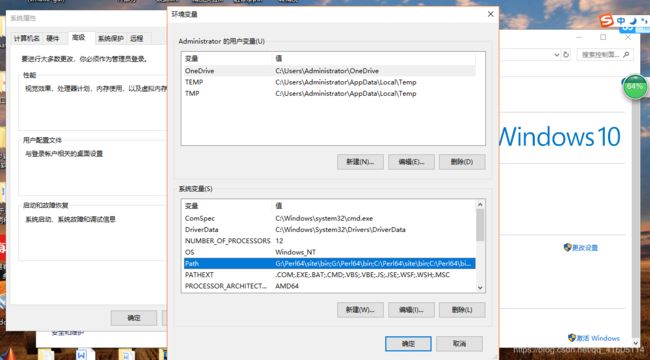
MySQL环境变量配置(不进行配置无法进行连接):
修改path
增加环境变量:
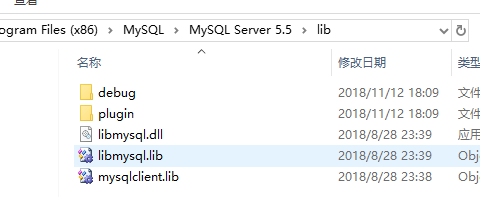
之后需要将MySQL的libmysql的.dll文件和.lib文件拷贝到Qt的相关文件夹下:
MySQL需要的文件路径如下:
并将其拷贝到你需要的编译器下的bin和lib文件夹下即可。
需要包含的头文件
//数据库
#include
#include
#include
#include//互斥锁,保持数据库的原子性 需要的连接操作
mutex.lock();//保持原子性
QSqlDatabase db = QSqlDatabase::addDatabase("QMYSQL","a");//可以不加“a”第二个参数
db.setHostName("localhost");//数据库服务器IP
db.setUserName("root");//用户名
db.setPassword("xxxxxx"); //这里输入你的密码
db.setDatabaseName("test");//这里输入你的数据库名
bool flagdb=db.open();
if (flagdb==false)
{
QMessageBox::critical(NULL, QObject::tr("无法打开数据库"),"无法创建数据库连接! ", QMessageBox::Cancel);
return;
}
mutex.unlock();
query = QSqlQuery ("",db);
//如果QSqlDatabase::addDatabase时,省略了第二个参数,则此处也应该省略第一个参数数据库的操作,返回值均为bool变量
1.表的创建
query.exec("create table Aksscomb(Ak_num_one double,Ak_num_two double,Ak_num_three double)");创建表的语法:create table name_for_table(name_one type,num_two type,num_three type)
创建表的形式(包含主键):create table name_for_table(name_one type primary key,num_two type,num_three type)
加入约束——主键的作用:当字段加上了primary key(主键),则该字段必须非空且唯一,可以作为单表查询的索引。
name_one表示列的名称,type表示此列要保存的数据类型,后面跟上primary key表示主键
2.数据插入(读取excel中的文本,并插入数据库)
部分头文件:
public:
explicit insert(QWidget *parent = nullptr);
QList num_primary;
QList other_data;
void read_execel();
void DB_insert_toMySQL(); 对应源文件中的公共接口:
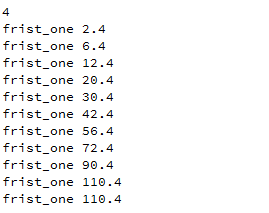
excel中的文本内容(示例):
读取excel中的内容:将第一列压入int类型的链表中,其余压入double类型的链表中
void insert::read_execel()
{
qDebug()<<"进入数据读取部分";
QString path = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this,"open","../","execl(*.xlsx *.xls)");
//指定父对象(this),“open”具体操作,打开,“../”默认,之后可以添加要打开文件的格式
if(path.isEmpty()==false)
{
//文件对象
QFile file(path);
//打开文件,默认为utf8变量,
bool flag = file.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly);
if(flag == true)//打开成功
{
QAxObject *excel = new QAxObject(this);//建立excel操作对象
excel->setControl("Excel.Application");//连接Excel控件
excel->setProperty("Visible", false);//不显示窗体看效果
excel->setProperty("DisplayAlerts", false);//不显示警告看效果
/*********获取COM文件的一种方式************/
QAxObject *workbooks = excel->querySubObject("WorkBooks");
//获取工作簿(excel文件)集合
workbooks->dynamicCall("Open(const QString&)", path);//path至关重要,获取excel文件的路径
//打开一个excel文件
QAxObject *workbook = excel->querySubObject("ActiveWorkBook");
QAxObject *worksheet = workbook->querySubObject("WorkSheets(int)",1);//访问excel中的工作表中第一个单元格
QAxObject *usedRange = worksheet->querySubObject("UsedRange");//sheet的范围
/*********获取COM文件的一种方式************/
//获取打开excel的起始行数和列数和总共的行数和列数
int intRowStart = usedRange->property("Row").toInt();//起始行数
int intColStart = usedRange->property("Column").toInt(); //起始列数
QAxObject *rows, *columns;
rows = usedRange->querySubObject("Rows");//
columns = usedRange->querySubObject("Columns");//
int intRow = rows->property("Count").toInt();//
int intCol = columns->property("Count").toInt();//
//起始行列号
qDebug()<<"intRowStart起始行数"<querySubObject("Cells(Int, Int)", i, intColStart );
QVariant cellValue_int = cellStructPara_int->dynamicCall("value");
num_primary.append( cellValue_int.toDouble() );//转化为double类型,能储存下来,小于1的数都变成
for (int j = intColStart+1; j < intColStart + intCol; j++)//列
{
QAxObject *cellStructPara = new QAxObject(this);
cellStructPara = excel->querySubObject("Cells(Int, Int)", i, j );
QVariant cellValue = cellStructPara->dynamicCall("value");
other_data.append( cellValue.toDouble() );//转化为double类型,能储存下来,小于1的数都变成
}
}
workbook->dynamicCall( "Close(Boolean)", false );
excel->dynamicCall( "Quit(void)" );
delete excel;
QMessageBox::warning(this,tr("warning"),tr("数据库参数导入成功"),QMessageBox::Yes);
}
file.close();
}
qDebug()<<"完成数据读取部分";
}
将读取进链表的数据,插入数据库中:
void insert::DB_insert_toMySQL()
{
read_execel();
QString insert="insert into testfordb "
"(id,frist_one,second_two,thrid_three) "
"values(:id,:frist_one,:second_two,:thrid_three);";
bool insertfalg =create_DB_insert->query.prepare(insert);//插入操作
if(insertfalg == false)
{
qDebug()<query.lastError();
}
else
{
qDebug()<<"insert succeed!";
}
int size_double = 0;
for(int i = 0;iquery.bindValue(":id",num_primary.at(i));
create_DB_insert->query.bindValue(":frist_one",other_data.at(size_double));
create_DB_insert->query.bindValue(":second_two",other_data.at(size_double+1));
create_DB_insert->query.bindValue(":thrid_three",other_data.at(size_double+2));
create_DB_insert->query.exec();
size_double+=3;
}
qDebug()<<"插入完成";
}
注意:
- 表有多少字段,插入的时候必须一次全部插入数值,如上,不能第一次只插入frist_one,第二次再插入second_two
这样会失效,字段是没有办法分开插入的,但是可以分开查询。
- 一次插入后,需要加入结束句:query.exec();否则数据只会停留在第一行,不会累计将数据插入
3.单表查询
注意:查询中,使用 query.value("Ak_num_one")前,必须有query.next(),否则查询不成功
3.1查询所有字段数据
查询语法如下:
SELECT *
FROM table_name;查询之后,使用以下语法进行字段内容的输出:
query.value("字段名称").toDouble();具体实施方案如下:
void inquiry::num1_inquiry_all()
{
qDebug()<<"1";
QString compren = QString("select * from testfordb;");//全表查询
bool fflag = create_DB_inquiry->query.exec(compren);//只进行enfrist的查询
if(fflag==false)
{
qDebug() <<"Error: Fail to SELECT * FORM testfordb:" << create_DB_inquiry->query.lastError();
}
else
{
while(create_DB_inquiry->query.next())
{
// id int primary key,frist_one double,second_two double,thrid_three double
qDebug()<<"id"<query.value("id").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"frist_one"<query.value("frist_one").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"second_two"<query.value("second_two").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"thrid_three"<query.value("thrid_three").toDouble();
}
}
} 查询结果,按行输出:
3.2查询指定字段数据
语法如下:
SELECT field1,field2,field3
FROM table_name;只查询table_name(假设有5个字段)中field1,field2,field3字段的数据。
具体实施方案如下,只查询testfordb中的id字段和frist_one字段:
void inquiry::num2_inquiry_all()
{
qDebug()<<"2";
QString compren = QString("select id,frist_one from testfordb;");//分段提取
bool fflag = create_DB_inquiry->query.exec(compren);//只进行enfrist的查询
if(fflag==false)
{
qDebug() <<"Error: Fail to SELECT * FROM testfordb:" << create_DB_inquiry->query.lastError();
}
else
{
while(create_DB_inquiry->query.next())
{
// id int primary key,frist_one double,second_two double,thrid_three double
qDebug()<<"id"<query.value("id").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"frist_one"<query.value("frist_one").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"second_two"<query.value("second_two").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"thrid_three"<query.value("thrid_three").toDouble();
}
}
} 查询结果,按行输出:
3.3避免重复数据查询——DISTINCT
当在MySQL软件中执行简单数据查询时,有时会显示出重复数据。为了实现查询不重复的数据,MySQL软件提供了关键字——DISTINCT。
语法如下:
SELECT DISTINCT field1 field2 ...fieldn
FROM table_name;查询table_name中字段的数据,同时实现去除重复数据。
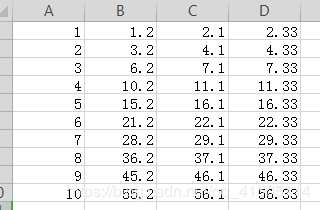
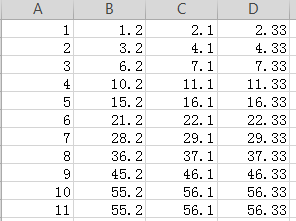
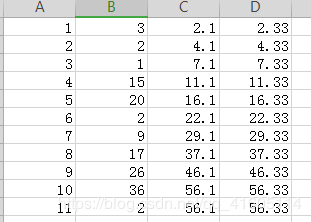
为了演示,将输入内容增加一行,第十一行,除去id,其余和第十行的内容完全相同
查询frist_one,second_two,third_three;
void inquiry::num3_inquiry_all()
{
qDebug()<<"3";
QString compren = QString("select distinct frist_one,second_two,thrid_three from testfordb;");//分段提取SELECT DISTINCT job FROM t_employee;
bool fflag = create_DB_inquiry->query.exec(compren);//只进行enfrist的查询
if(fflag==false)
{
qDebug() <<"Error: Fail to SELECT DISTINCT FROM testfordb:" << create_DB_inquiry->query.lastError();
}
else
{
while(create_DB_inquiry->query.next())
{
// id int primary key,frist_one double,second_two double,thrid_three double
// qDebug()<<"id"<query.value("id").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"frist_one"<query.value("frist_one").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"second_two"<query.value("second_two").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"thrid_three"<query.value("thrid_three").toDouble();
}
}
} 从结果可以看出,没有对重复的数据进行查询。
3.4实现数学四则运算数据查询
当在MySQL软件中执行简单数据查询时,有时会需要实现数学四则运算(+,-,*,/,%)加减乘除取余;
由于字段sal表示每月的工资,所以在查询字段sal的值时需要进行简单的四则运算。
SELECT field1,field2*12
FROM table_name;具体输出时,不能使用field2,而是使用field2*12进行查询。
在MySQL软件中,提供一种机制来实现字段名,具体语法如下:
SELECT field1 [AS] otherfield1,field2 [AS] otherfield2
FROM table_name;在上述语句中,参数field为字段原来的名字,参数otherfield为字段的新名字,设置新的名字是为了更加方便直观和方便。
具体实施方案如下:
SELECT frist_one*12 AS yearsalary
FROM testforab;
void inquiry::num4_inquiry_all()
{
qDebug()<<"4";
QString compren = QString("select frist_one*2 AS double_frist from testfordb;");//分段提取
bool fflag = create_DB_inquiry->query.exec(compren);//只进行enfrist的查询
if(fflag==false)
{
qDebug() <<"Error: Fail to SELECT frist_one*2 FROM testfordb:" << create_DB_inquiry->query.lastError();
}
else
{
while(create_DB_inquiry->query.next())
{
// id int primary key,frist_one double,second_two double,thrid_three double
// qDebug()<<"id"<query.value("id").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"frist_one"<query.value("double_frist").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"second_two"<query.value("second_two").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"thrid_three"<query.value("thrid_three").toDouble();
}
}
} 输出结果如下:全部的frist_one的数组全部乘上了2;
3.5单条件数据查询
在MySQL软件中,可以通过关系运算符和逻辑运算符来编写“条件表达式”。
SELECT field1,field2
FORM table_name
WHERE field1=...;查询表中jfield1=...表达式。
为了查询效果,将输入内容进行更改:
具体语法如下,将frist_one等于2的内容找出,并输出id和frist_one的内容:
void inquiry::num5_inquiry_all()
{
qDebug()<<"5";
QString compren = QString("select id,frist_one from testfordb where frist_one = 2;");//分段提取
bool fflag = create_DB_inquiry->query.exec(compren);//只进行enfrist的查询
if(fflag==false)
{
qDebug() <<"Error: Fail to SELECT id from testfordb where frist_one = 2:" << create_DB_inquiry->query.lastError();
}
else
{
while(create_DB_inquiry->query.next())
{
// id int primary key,frist_one double,second_two double,thrid_three double
qDebug()<<"id"<query.value("id").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"frist_one"<query.value("frist_one").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"second_two"<query.value("second_two").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"thrid_three"<query.value("thrid_three").toDouble();
}
}
} 输出结果如图:
3.6多条件数据查询
SELECT field1,field2,field3
FORM table_name
WHERE field1=‘...’&&field2>...;查询符合field1=‘...’&&field2>...条件的,字段field1,field2,field3的内容;
查询符合frist_one = 2,second_two <12的id,frist_one,second_two三个字段。
void inquiry::num6_inquiry_all()
{
qDebug()<<"6";
QString compren = QString("select id,frist_one,second_two from testfordb where frist_one = 2&&second_two < 12;");//分段提取
bool fflag = create_DB_inquiry->query.exec(compren);//只进行enfrist的查询
if(fflag==false)
{
qDebug() <<"Error: Fail to SELECT * FROM testfordb:" << create_DB_inquiry->query.lastError();
}
else
{
while(create_DB_inquiry->query.next())
{
// id int primary key,frist_one double,second_two double,thrid_three double
qDebug()<<"id"<query.value("id").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"frist_one"<query.value("frist_one").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"second_two"<query.value("second_two").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"thrid_three"<query.value("thrid_three").toDouble();
}
}
} 输出结果如下:
3.7带BETWEEN AND关键字的范围查询
MySQL软件提供了关键字BETWEEN AND ,用来实现判断字段的数值是否在指定范围内
SELECT field1 field2 ...fieldn
FROM table_name
WHERE field BETWEEN VALUE1 AND VALUE2;在上述语句中,通过关键字BETWEEN AND来设置字段field的取值范围,如果字段field的值在指定范围内,则满足查询条件,该记录就会被查询出来
3.7.1符合范围的数据记录查询
SELECT ename
FROM t_employee
WHERE sal BETWEEN 1000 AND 2000;查询符合frist_one的值在2和12之间,id和frist_one两个字段的内容,
void inquiry::num7_inquiry_all()
{
qDebug()<<"7";
QString compren = QString("select id,frist_one from testfordb where frist_one between 2 and 12;");//分段提取
bool fflag = create_DB_inquiry->query.exec(compren);//只进行enfrist的查询
if(fflag==false)
{
qDebug() <<"Error: Fail to SELECT id,frist_one from testfordb where frist_one between 2 and 12:" << create_DB_inquiry->query.lastError();
}
else
{
while(create_DB_inquiry->query.next())
{
// id int primary key,frist_one double,second_two double,thrid_three double
qDebug()<<"id"<query.value("id").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"frist_one"<query.value("frist_one").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"second_two"<query.value("second_two").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"thrid_three"<query.value("thrid_three").toDouble();
}
}
}
输出结果如下:
3.7.2不符合范围的数据记录查询
SELECT ename
FROM t_employee
WHERE sal NOT BETWEEN 1000 AND 2000;查询不在frist_one的值在2和12之间,id和frist_one两个字段的内容,
void inquiry::num7_inquiry_all()
{
qDebug()<<"7";
// QString compren = QString("select id,frist_one from testfordb where frist_one between 2 and 12;");//分段提取
QString compren = QString("select id,frist_one from testfordb where frist_one not between 2 and 12;");//分段提取
bool fflag = create_DB_inquiry->query.exec(compren);//只进行enfrist的查询
if(fflag==false)
{
qDebug() <<"Error: Fail to SELECT id,frist_one from testfordb where frist_one between 2 and 12:" << create_DB_inquiry->query.lastError();
}
else
{
while(create_DB_inquiry->query.next())
{
// id int primary key,frist_one double,second_two double,thrid_three double
qDebug()<<"id"<query.value("id").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"frist_one"<query.value("frist_one").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"second_two"<query.value("second_two").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"thrid_three"<query.value("thrid_three").toDouble();
}
}
} 输出结果如下:
3.8在集合中数据记录查询
查询员工编号为7521,7782,7566,7788的雇员
SELECT field1,field2...fieldn
FROM table_name
WHERE field1=... or field1=... or field1=... or field1=...;使用IN
查询员工编号为...,###,@@@,&&&的字段
SELECT field1,field2...fieldn
FROM table_name
WHERE field1 IN (...,###,@@@,&&&);具体实施方案如下:
void inquiry::num8_inquiry_all()
{
qDebug()<<"8";
QString compren = QString("select id,frist_one from testfordb where frist_one = 11 or frist_one = 26;");//分段提取
bool fflag = create_DB_inquiry->query.exec(compren);//只进行enfrist的查询
if(fflag==false)
{
qDebug() <<"Error: Fail to SELECT id,frist_one from testfordb where frist_one = 11 or frist_one = 26:" << create_DB_inquiry->query.lastError();
}
else
{
while(create_DB_inquiry->query.next())
{
// id int primary key,frist_one double,second_two double,thrid_three double
qDebug()<<"id"<query.value("id").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"frist_one"<query.value("frist_one").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"second_two"<query.value("second_two").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"thrid_three"<query.value("thrid_three").toDouble();
}
}
} 输出结果如下:
使用IN
void inquiry::num8_inquiry_all()
{
qDebug()<<"8";
// QString compren = QString("select id,frist_one from testfordb where frist_one = 11 or frist_one = 26;");//分段提取
QString compren = QString("select id,frist_one from testfordb where frist_one IN (11,26);");//分段提取
bool fflag = create_DB_inquiry->query.exec(compren);//只进行enfrist的查询
if(fflag==false)
{
qDebug() <<"Error: Fail to SELECT id,frist_one from testfordb where frist_one = 11 or frist_one = 26:" << create_DB_inquiry->query.lastError();
}
else
{
while(create_DB_inquiry->query.next())
{
// id int primary key,frist_one double,second_two double,thrid_three double
qDebug()<<"id"<query.value("id").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"frist_one"<query.value("frist_one").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"second_two"<query.value("second_two").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"thrid_three"<query.value("thrid_three").toDouble();
}
}
} 输出结果如下:
3.9排序数据记录查询
通过条件数据查询,虽然可以查询到符合用户需求的数据记录,但是查询到的记录在默认情况下,都是按照数据记录最初添加到表中的顺序来显示。默认的查询结果顺序并不满足用户的需求。于是MySQL软件提供了关键字ORDER BY来设置查询结果的顺序。
SELECT field1 field2 ...fieldn
FROM table_name
WHERE CONDITION
ORDER BY fieldm1 [ASC|DESC] [,fieldm2[ASC|DESC],];在上述语句中,通过参数fieldm表示按照该字段进行排序,参数ASC表示按升序的顺序进行排序,参数DESC表示按照降序的顺序进行排序。
在默认情况下按照ASC(升序)进行排序,还可以在关键字ORDER BY后面设置多个不同的字段进行排序。
关于排序数据查询结果语句包含如下功能:
- 按照单字段排序
- 按照多字段排序
为了演示效果,输入如图所示:
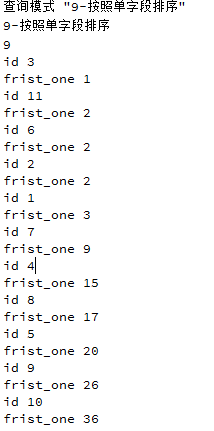
3.9.1按照单字段排序
MySQL软件中如果想实现按照单字段进行排序,关键字ORDER BY后面将只有一个字段
升序排序
SELECT *
FROM table_name
ORDER BY field1 ASC;
-ORDER BY sal;按照关键字ORDER BY的操作字段sal,同时通过关键字ASC设置为升序排序。 也可以省略升序ASC通配符,默认为升序。
降序排序
SELECT *
FROM table_name
ORDER BY field1 DESC;按照关键字ORDER BY的操作字段mgr,同时通过关键字DESC设置为降序排序。
查询字段id和frist_one,以frist_one升序排列
具体实施如下:
void inquiry::num9_inquiry_all()
{
qDebug()<<"9";
QString compren = QString("select id,frist_one from testfordb order by frist_one;");//分段提取
bool fflag = create_DB_inquiry->query.exec(compren);//只进行enfrist的查询
if(fflag==false)
{
qDebug() <<"Error: Fail to SELECT * FROM testfordb:" << create_DB_inquiry->query.lastError();
}
else
{
while(create_DB_inquiry->query.next())
{
// id int primary key,frist_one double,second_two double,thrid_three double
qDebug()<<"id"<query.value("id").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"frist_one"<query.value("frist_one").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"second_two"<query.value("second_two").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"thrid_three"<query.value("thrid_three").toDouble();
}
}
} 输出结果:
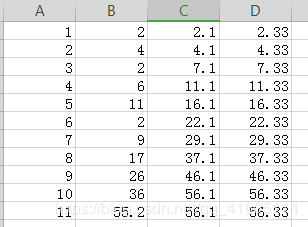
3.9.2按照多字段排序
如果字段mgr中存在值相同的数据记录,为了解决该问题,可以按照多字段进行排序,首先按照第一个字段进行排序,如果遇到值相同的字段则会按照第二个字段进行排序。
SELECT *
FROM t_employee
ORDER BY mgr DESC,
hiredata ASC;查询字段id和frist_one,second_two,以frist_one升序,如果元素相同,再以second_two升序排列
具体实施如下:
qDebug()<<"10";
QString compren = QString("select id,frist_one,second_two from testfordb order by frist_one,second_two;");//分段提取
bool fflag = create_DB_inquiry->query.exec(compren);//只进行enfrist的查询
if(fflag==false)
{
qDebug() <<"Error: Fail to SELECT * FROM testfordb:" << create_DB_inquiry->query.lastError();
}
else
{
while(create_DB_inquiry->query.next())
{
// id int primary key,frist_one double,second_two double,thrid_three double
qDebug()<<"id"<query.value("id").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"frist_one"<query.value("frist_one").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"second_two"<query.value("second_two").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"thrid_three"<query.value("thrid_three").toDouble();
}
}
输出结果:frist_one按照升序排列,如果需要frist_one相同的元素,则按照second_two进行升序排列
3.10限制数据记录查询数据
通过条件数据查询,虽然可以查询到符合用户需求的数据记录,但是有时所查询到的数据记录太多,对于这么多数据记录,如果全部显示则不符合实际需求,这时可以通过MySQL软件提供的关键字LIMIT来限制查询结果的数量。
SELECT field1 field2 ...fieldn
FROM table_name
WHERE CONDITION
LIMIT OFFSET_START,ROW_COUNT;3.10.1指定初始位置
LIMIT关键字经常被应用在分页系统中,对于第一项的数据记录,可以通过不指定初始位置来实现,但是对于第二页等其他页面则必须指定初始位置(OFFSET_START),否则将无法实现分页功能,除此之外,LIMIT关键字还经常与OREDER BY关键字一起使用,即先对查询结果进行排序,然后显示其中部分数据记录。
语法如下:
SELECT field1 field2 ...fieldn
FROM table_name
WHERE CONDITION
ORDER BY fieldm1 [ASC|DESC] [,fieldm2[ASC|DESC],]
LIMIT OFFSET_START,ROW_COUNT;查询tbale_name中,查询字段field1的所有元素,然后对排序结果根据入职时间(字段field2)进行从早到晚排序,并从第一条数据开始显示,共显示5条记录。
SELECT *
FROM table_name
WHERE field1 is NULL
ORDER BY field2 LIMIT 0,5;在MySQL中,LIMIT中参数OFFSET_START的值默认为0,所以上述SQL语句可以修改如下:
SELECT *
FROM t_employee
WHERE comm is NULL
ORDER BY hiredate LIMIT 5;具体实施情况如下:
查询id,frist_one,second_two字段,限制条件为frist_one为2,以second_two升序排列,从第一个位置开始,查询6个符合要求的字段,不够6个,则查询并显示所有。
void inquiry::num11_inquiry_all()
{
qDebug()<<"11";
QString compren = QString("select id,frist_one,second_two from testfordb where frist_one = 2 order by second_two limit 0,6 ;");//分段提取
bool fflag = create_DB_inquiry->query.exec(compren);//只进行enfrist的查询
if(fflag==false)
{
qDebug() <<"Error: Fail to SELECT * FROM testfordb:" << create_DB_inquiry->query.lastError();
}
else
{
while(create_DB_inquiry->query.next())
{
// id int primary key,frist_one double,second_two double,thrid_three double
qDebug()<<"id"<query.value("id").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"frist_one"<query.value("frist_one").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"second_two"<query.value("second_two").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"thrid_three"<query.value("thrid_three").toDouble();
}
}
} 输出结果如下:
3.11统计函数和分组数据记录查询
在MySQL软件中,很多情况下都需要进行一些统计汇总操作,比如,统计整个公司的人数或整个部门的人数,这时候就会用到该软件所支持的统计函数,分别为:
COUNT()函数:该统计函数实现统计表中记录的条数
AVG()函数:该统计函数实现计算字段值的平均值
SUM()函数:该统计函数实现计算字段值的总和
MAX()函数:该统计函数实现查询字段值的最大值
MIN()函数:该统计函数实现查询字段值的最小值
统计数据记录条数-COUNT()
COUNT(*):这种方式可以实现对表中记录进行统计,不管表字段中包含的是NULL值还是非NULL值。
COUNT(field):这种方式可以实现对指定字段的记录进行统计,在具体统计时将忽略NULL值。
SELECT COUNT(*) number
FROM t_employee;除此之外,还可以对相应的字段进行操作。
SELECT COUNT(comm) number
FROM t_employee;也可以在查询的时候加入限制条件:
比如不算入comm为零的记录,对comm进行统计:
SELECT COUNT(comm) number
FROM t_employee
WHERE NOT comm = 0;具体实施如下:查询的时候,注意, query.value("number").toDouble()才能成功查询。
void inquiry::num12_inquiry_all()
{
qDebug()<<"12";
QString compren = QString("select count(frist_one) number from testfordb where NOT frist_one = 0;");//分段提取
bool fflag = create_DB_inquiry->query.exec(compren);//只进行enfrist的查询
if(fflag==false)
{
qDebug() <<"Error: Fail to SELECT * FROM testfordb:" << create_DB_inquiry->query.lastError();
}
else
{
while(create_DB_inquiry->query.next())
{
// id int primary key,frist_one double,second_two double,thrid_three double
// qDebug()<<"id"<query.value("id").toDouble();
qDebug()<<"frist_one"<query.value("number").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"second_two"<query.value("second_two").toDouble();
// qDebug()<<"thrid_three"<query.value("thrid_three").toDouble();
}
}
} 输出结果如下:
4.表的删除
关闭程序时,可以进行表的删除操作:
closeEvent关闭事件:
void Widget::closeEvent(QCloseEvent *event)
{
int ret = QMessageBox::question(this,"退出","是否退出?",QMessageBox::Yes,QMessageBox::No);
if(ret == QMessageBox::Yes)
{
event->accept();
//删除数据库
function_delete_ALL();
qDebug()<<"退出程序";
}
else if(ret == QMessageBox::No)
{
event->ignore();
qDebug()<<"忽略退出摁键";
}
}function_delete_ALL():
void delete_data::function_delete_ALL()
{
bool clearfalg = create_DB_delete->query.exec("DROP table testfordb");//删除是使用DROP
if(clearfalg==false)
{
qDebug()<< create_DB_delete->query.lastError();
}
else
{
qDebug() << "delete all table!";
}
}
语法:DROP table name_for_table
-
Qt封装带MySQL数据库的程序时,需要的依赖项
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41605114/article/details/86612264