图解kubernetes资源扩展机制实现(上)
k8s目前主要支持CPU和内存两种资源,为了支持用户需要按需分配的其他硬件类型的资源的调度分配,k8s实现了设备插件框架(device plugin framework)来用于其他硬件类型的资源集成,比如现在机器学习要使用GPU等资源,今天来看下其内部的关键实现
1. 基础概念
1.1 集成方式
1.1.1 DaemonSet与服务
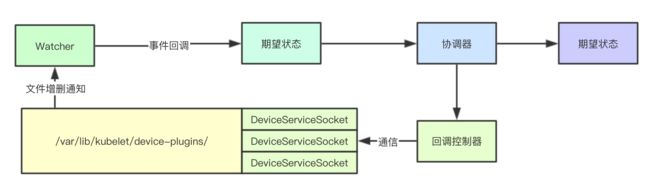
当我们要集成本地硬件的资源的时候,我们可以在当前节点上通过DaemonSet来运行一个GRPC服务,通过这个服务来进行本地硬件资源的上报与分配
1.1.2 服务注册设计
当提供硬件服务需要与kubelet进行通信的时候,则首先需要进行注册,注册的方式,则是通过最原始的底层的socket文件,并且通过Linux文件系统的inotify机制,来实现服务的注册
1.2 插件服务感知
1.2.1 Watcher
Watcher主要是负责感知当前节点上注册的服务,当发现新的要注册的插件服务,则会产生对应的事件,注册到当前的kubelet中
1.2.2 期望状态与实际状态
这里的状态主要是指的是否需要注册,因为kubelet与对应的插件服务是通过网络进行通信的,当网络出现问题、或者对应的插件服务故障,则可能会导致服务注册失败,但此时对应的服务的socket还依旧存在,即对应的插件服务依旧存在
此时就会有两种状态:期望状态与实际状态, 因为socket存在所以服务的期望状态其实是需要注册这个插件服务,但是实际上因为某些原因,这个插件服务并没有完成注册,后续会不断的通过期望状态,调整实际状态,从而达到一致
1.2.3 协调器
协调器则就是完成上述两种状态之间操作的核心,其通过调用对应插件的回调函数,其实就是调用对应的grpc接口,来完成期望状态与实际状态的一致性
1.2.4 插件控制器
针对每种类型的插件,都会有对应的控制器,其实也就是实现对应设备注册和反注册并且完成底层资源的分配(Allocate)和收集(ListWatch)操作
2. 插件服务发现
2.1 核心数据结构
type Watcher struct {
// 感知插件服务注册的socket的路径
path string
fs utilfs.Filesystem
// inotify监测插件服务socket变化
fsWatcher *fsnotify.Watcher
stopped chan struct{}
// 存储期望状态
desiredStateOfWorld cache.DesiredStateOfWorld
}2.2 初始化
初始化其实就是创建对应的目录
func (w *Watcher) init() error {
klog.V(4).Infof("Ensuring Plugin directory at %s ", w.path)
if err := w.fs.MkdirAll(w.path, 0755); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("error (re-)creating root %s: %v", w.path, err)
}
return nil
}2.3 插件服务发现核心
go func(fsWatcher *fsnotify.Watcher) {
defer close(w.stopped)
for {
select {
case event := <-fsWatcher.Events:
//如果发现对应目录的文件的变化,则会触发对应的事件
if event.Op&fsnotify.Create == fsnotify.Create {
err := w.handleCreateEvent(event)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("error %v when handling create event: %s", err, event)
}
} else if event.Op&fsnotify.Remove == fsnotify.Remove {
w.handleDeleteEvent(event)
}
continue
case err := <-fsWatcher.Errors:
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("fsWatcher received error: %v", err)
}
continue
case <-stopCh:
// In case of plugin watcher being stopped by plugin manager, stop
// probing the creation/deletion of plugin sockets.
// Also give all pending go routines a chance to complete
select {
case <-w.stopped:
case <-time.After(11 * time.Second):
klog.Errorf("timeout on stopping watcher")
}
w.fsWatcher.Close()
return
}
}
}(fsWatcher)2.4 补偿机制
其实补偿机制主要是在重新启动kubelet的时候,需要将之前已经存在的socket重新注册到当前的kubelet中
func (w *Watcher) traversePluginDir(dir string) error {
return w.fs.Walk(dir, func(path string, info os.FileInfo, err error) error {
if err != nil {
if path == dir {
return fmt.Errorf("error accessing path: %s error: %v", path, err)
}
klog.Errorf("error accessing path: %s error: %v", path, err)
return nil
}
switch mode := info.Mode(); {
case mode.IsDir():
if err := w.fsWatcher.Add(path); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to watch %s, err: %v", path, err)
}
case mode&os.ModeSocket != 0:
event := fsnotify.Event{
Name: path,
Op: fsnotify.Create,
}
//TODO: Handle errors by taking corrective measures
if err := w.handleCreateEvent(event); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("error %v when handling create event: %s", err, event)
}
default:
klog.V(5).Infof("Ignoring file %s with mode %v", path, mode)
}
return nil
})
}2.5 注册事件回调
注册其实就只需要感知到的socket文件路径传递给期望状态进行管理
func (w *Watcher) handlePluginRegistration(socketPath string) error {
if runtime.GOOS == "windows" {
socketPath = util.NormalizePath(socketPath)
}
// 调用期望状态进行更新
klog.V(2).Infof("Adding socket path or updating timestamp %s to desired state cache", socketPath)
err := w.desiredStateOfWorld.AddOrUpdatePlugin(socketPath)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("error adding socket path %s or updating timestamp to desired state cache: %v", socketPath, err)
}
return nil
}2.6 删除事件回调
注册其实就只需要感知到的socket文件路径传递给期望状态进行管理
func (w *Watcher) handleDeleteEvent(event fsnotify.Event) {
klog.V(6).Infof("Handling delete event: %v", event)
socketPath := event.Name
klog.V(2).Infof("Removing socket path %s from desired state cache", socketPath)
w.desiredStateOfWorld.RemovePlugin(socketPath)
}3.期望状态与实际状态
3.1 插件信息
插件信息其实只是存储了对应socket的路径和最近更新的时间
type PluginInfo struct {
SocketPath string
Timestamp time.Time
}3.2 期望状态
期望状态与实际状态在数据结构上都是一样的,因为本质上只是为了存储插件的当前的状态信息,即更新时间,这里不在赘述
type desiredStateOfWorld struct {
socketFileToInfo map[string]PluginInfo
sync.RWMutex
}type actualStateOfWorld struct {
socketFileToInfo map[string]PluginInfo
sync.RWMutex
}4.OperationExecutor
目前k8s中支持两大类的插件的管理一类是DevicePlugin即我们本文说的这些都是这种概念,一类是CSIPlugin,其中针对每一类DRiver的处理其实内部都是不一样的,那其实在操作之前就要先感知到当前的Driver是那种类型的
OperationExecutor主要就是做这件事的,其根据不同的plugin类型,生成不同的要执行的操作,即对应的Plugin类型获取对应的handler,就生成了一个要执行的操作
4.1 生成注册插件回调函数
4.1.1 通过socket连接对应的插件服务
registerPluginFunc := func() error {
client, conn, err := dial(socketPath, dialTimeoutDuration)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("RegisterPlugin error -- dial failed at socket %s, err: %v", socketPath, err)
}
defer conn.Close()
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), time.Second)
defer cancel()
infoResp, err := client.GetInfo(ctx, ®isterapi.InfoRequest{})
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("RegisterPlugin error -- failed to get plugin info using RPC GetInfo at socket %s, err: %v", socketPath, err)
}4.1.2 根据插件类型验证服务
handler, ok := pluginHandlers[infoResp.Type]
if !ok {
if err := og.notifyPlugin(client, false, fmt.Sprintf("RegisterPlugin error -- no handler registered for plugin type: %s at socket %s", infoResp.Type, socketPath)); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("RegisterPlugin error -- failed to send error at socket %s, err: %v", socketPath, err)
}
return fmt.Errorf("RegisterPlugin error -- no handler registered for plugin type: %s at socket %s", infoResp.Type, socketPath)
}
if infoResp.Endpoint == "" {
infoResp.Endpoint = socketPath
}
if err := handler.ValidatePlugin(infoResp.Name, infoResp.Endpoint, infoResp.SupportedVersions); err != nil {
if err = og.notifyPlugin(client, false, fmt.Sprintf("RegisterPlugin error -- plugin validation failed with err: %v", err)); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("RegisterPlugin error -- failed to send error at socket %s, err: %v", socketPath, err)
}
return fmt.Errorf("RegisterPlugin error -- pluginHandler.ValidatePluginFunc failed")
}4.1.3 注册插件到实际状态
err = actualStateOfWorldUpdater.AddPlugin(cache.PluginInfo{
SocketPath: socketPath,
Timestamp: timestamp,
})
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("RegisterPlugin error -- failed to add plugin at socket %s, err: %v", socketPath, err)
}
// 调用插件的注册回调函数
if err := handler.RegisterPlugin(infoResp.Name, infoResp.Endpoint, infoResp.SupportedVersions); err != nil {
return og.notifyPlugin(client, false, fmt.Sprintf("RegisterPlugin error -- plugin registration failed with err: %v", err))
}
4.1.4 通知对应的服务注册成功
if err := og.notifyPlugin(client, true, ""); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("RegisterPlugin error -- failed to send registration status at socket %s, err: %v", socketPath, err)
}4.2 通过socket构建注册client
func dial(unixSocketPath string, timeout time.Duration) (registerapi.RegistrationClient, *grpc.ClientConn, error) {
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), timeout)
defer cancel()
c, err := grpc.DialContext(ctx, unixSocketPath, grpc.WithInsecure(), grpc.WithBlock(),
grpc.WithContextDialer(func(ctx context.Context, addr string) (net.Conn, error) {
return (&net.Dialer{}).DialContext(ctx, "unix", addr)
}),
)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to dial socket %s, err: %v", unixSocketPath, err)
}
return registerapi.NewRegistrationClient(c), c, nil
}今天就先到这里,下一章会继续介绍如何组合上述组件以及默认的回调管理机制的实现,进探究到这里谢谢大家,感谢分享点赞,反转又不花钱
k8s源码阅读电子书地址: https://www.yuque.com/baxiaoshi/tyado3
更多文章关注 www.sreguide.com
本文由博客一文多发平台 OpenWrite 发布