此分析过程基于Android 6.0源码,转载请注明来源地址http://www.jianshu.com/p/dae4efb744db
目录
1.概述
2.多媒体扫描过程分析
3.如何使用多媒体扫描
4.常见问题
1.概述
在Android系统中,多媒体文件通常在开机和SD卡挂载的时候进行扫描操作,目的是为了让多媒体应用便捷地使用和管理多媒体文件。设想一下如果进入多媒体应用才开始扫描,应用的可用性就很差,所以Android系统将这些媒体相关的信息扫描出来保存在数据库中,当打开应用的时候直接去数据库读取(或者所通过MediaProvider去从数据库读取)并展示给用户,这样用户体验会好很多。
下面是其具体的分析过程,分析了两种不同扫描方式的具体实现,和如何使用多媒体扫描,最后对常见的问题讲解。
2.多媒体扫描过程分析
多媒体扫描过程分为两种方式,一种是接收广播的方式,另一种是通过IPC方式。其中通过IPC的方式在底层实现的逻辑与前一种方式部分重合,所以不再重复介绍。
分析的代码层次为:
(1)Java层
(2)JNI层
(3)Native层
根据层级,结合流程图,逐渐深入底层进行分析,最终得出整套关于扫描过程的分析结论。
2.1 接收广播方式
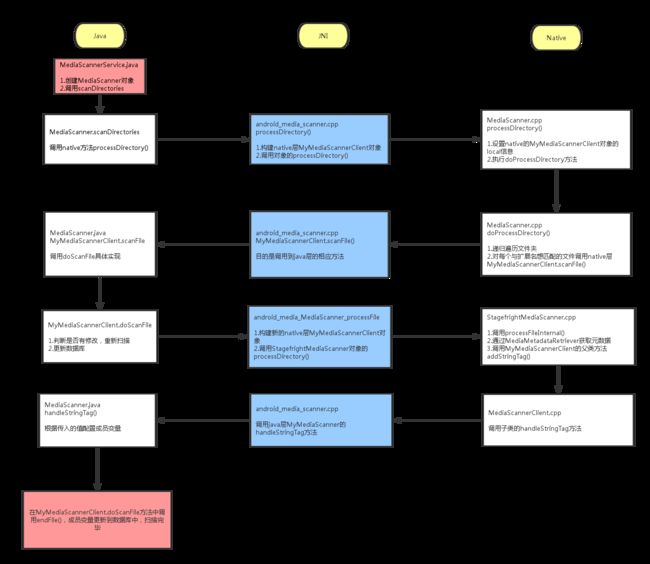
在扫描的具体实现中涉及到java层、JNI层和native层,其中MediaScanner.java对应java层,android_media_MediaScanner.cpp对应JNI层,MediaScanner.cpp对应Native层。下面进行逐层分析。
2.1.1 流程图
2.1.2 MediaScannerReceiver.java
在清单文件中注册的广播:
MediaScannerReceiver
android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED 开机广播
android.intent.action.MEDIA_MOUNTED 外部存储挂载
android.intent.action.MEDIA_UNMOUNTED 外部存储卸载
android.intent.action.MEDIA_SCANNER_SCAN_FILE 扫描单独的文件
接收开机广播的操作:
// Scan both internal and external storage
scan(context, MediaProvider.INTERNAL_VOLUME);
scan(context, MediaProvider.EXTERNAL_VOLUME);
对其他广播的操作。获取外部存储设备的路径,监听两种广播
一种是监听外部存储设备的挂载,另一种是接收指定文件的扫描。
// handle intents related to external storage
String path = uri.getPath();
//从log中的值为/storage/emulated/0
String externalStoragePath =
Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getPath();
//从log中的值为/sdcard
String legacyPath =
Environment.getLegacyExternalStorageDirectory().getPath();
try {
// An absolute path is one that begins at the root of the file system.
//A canonical path is an absolute path with symbolic links
path = new File(path).getCanonicalPath();
} catch (IOException e) {
return;
}
if (path.startsWith(legacyPath)) {
path = externalStoragePath + path.substring(legacyPath.length());
}
//对其他广播进行的处理
if (Intent.ACTION_MEDIA_MOUNTED.equals(action)||
ACTION_MEDIA_SCANNER_SCAN_ALL.equals(action)) {
//接收到外部存储挂载的广播之后扫描外部存储
// scan whenever any volume is mounted
scan(context, MediaProvider.EXTERNAL_VOLUME);
} else if (Intent.ACTION_MEDIA_SCANNER_SCAN_FILE.equals(action) &&
path != null && path.startsWith(externalStoragePath + "/")) {
//接收扫描单一文件的广播,扫描单一文件
scanFile(context, path);
}
在调用的scan方法去启动MediaScannerService,并且装填所对应的存储卷
private void scan(Context context, String volume) {
Bundle args = new Bundle();
args.putString("volume", volume);
context.startService(
new Intent(context, MediaScannerService.class).putExtras(args));
}
scanFile装填的参数是对应要扫描的路径
private void scanFile(Context context, String path) {
Bundle args = new Bundle();
args.putString("filepath", path);
context.startService(
new Intent(context, MediaScannerService.class).putExtras(args));
}
至此,MediaScannerReceiver分析完毕,内容较少,其作用主要就是:
(1) 接收广播
(2) 构造对应的扫描路径
(3) 启动MediaScannerService
2.1.3 MediaScannerService.java
分析Service首先分析其生命周期中所作的相关操作。先看onCreate函数中有哪些操作:
@Override
public void onCreate(){
PowerManager pm = (PowerManager)getSystemService(Context.POWER_SERVICE);
//新建电源锁,保证扫描过程中系统不会休眠
mWakeLock = pm.newWakeLock(PowerManager.PARTIAL_WAKE_LOCK, TAG);
StorageManager storageManager =
(StorageManager)getSystemService(Context.STORAGE_SERVICE);
//获取外部存储路径
mExternalStoragePaths = storageManager.getVolumePaths();
// Start up the thread running the service. Note that we create a
// separate thread because the service normally runs in the process's
// main thread, which we don't want to block.
Thread thr = new Thread(null, this, "MediaScannerService");
thr.start();
}
... ...
public void run(){
// reduce priority below other background threads to avoid interfering
// with other services at boot time.
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND +
Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_LESS_FAVORABLE);
//开启消息队列
Looper.prepare();
mServiceLooper = Looper.myLooper();
//创建Handler,在线程中处理相关操作
mServiceHandler = new ServiceHandler();
Looper.loop();
}
在正常情况下,Android系统会让程序和服务进入休眠状态以节约电量使用或者降低CPU消耗,而扫描任务可能会耗时较长,为了不让在扫描过程中出现系统休眠状态,要保证此时CPU一直不会休眠。
WakeLock是一种锁机制,只要有拿着这把锁,系统就无法进入休眠阶段。既然要保持应用程序一直在后台运行,那自然要获得这把锁才可以保证程序始终在后台运行。如果需要持有锁,需要调用acquire()方法,在不需要的时候即使释放,调用release()方法。
将工作线程的优先级降低是由于扫描过程中会很耗时,如果CPU一直被MediaScannerService占用就会影响其他的线程使用。
在onCreate中的操作有:
1. 获取WakeLock锁和外部存储路径
2. 新建工作线程
在service的生命周期中,onCreate只能调用一次,但是onStartCommand可以重复调用,也就是说每当启动一次startService,就会调用一次onStartCommand,下面分析onStartCommand函数。
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId){
//确保mServiceHandler已经被启动
while (mServiceHandler == null) {
synchronized (this) {
try {
wait(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
... ...
Message msg = mServiceHandler.obtainMessage();
msg.arg1 = startId;
msg.obj = intent.getExtras();
//向mServiceHandler发送消息
mServiceHandler.sendMessage(msg);
// Try again later if we are killed before we can finish scanning.
return Service.START_REDELIVER_INTENT;
}
在onStartCommand中主要的操作就是获取启动Intent的相关参数,并且发送给工作线程进行处理。
接下来分析mServiceHandler在接收消息之后是如何处理的:
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
Bundle arguments = (Bundle) msg.obj;
String filePath = arguments.getString("filepath");
try {
if (filePath != null) {
//处理扫描指定路径的操作
IBinder binder = arguments.getIBinder("listener");
IMediaScannerListener listener =
(binder == null ? null : IMediaScannerListener.Stub.asInterface(binder));
Uri uri = null;
try {
uri = scanFile(filePath, arguments.getString("mimetype"));
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Exception scanning file", e);
}
if (listener != null) {
listener.scanCompleted(filePath, uri);
}
} else {
//如果没有指定路径,就直接扫描对应的存储卷
String volume = arguments.getString("volume");
String[] directories = null;
if (MediaProvider.INTERNAL_VOLUME.equals(volume)) {
// scan internal media storage
//分别获取根目录和OEM分区的media
directories = new String[] {
Environment.getRootDirectory() + "/media",
Environment.getOemDirectory() + "/media",
};
if (RegionalizationEnvironment.isSupported()) {
final List regionalizationDirs = RegionalizationEnvironment
.getAllPackageDirectories();
if (regionalizationDirs.size() > 0) {
String[] mediaDirs =
new String[directories.length + regionalizationDirs.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < directories.length; i++) {
mediaDirs[i] = directories[i];
}
int j = directories.length;
for (File f : regionalizationDirs) {
mediaDirs[j] = f.getAbsolutePath() + "/system/media";
j++;
}
directories = mediaDirs;
}
}
}
else if (MediaProvider.EXTERNAL_VOLUME.equals(volume)) {
// scan external storage volumes
directories = mExternalStoragePaths;
}
if (directories != null) {
//调用scan函数,开始扫描文件
scan(directories, volume);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Exception in handleMessage", e);
}
//停止掉对应的service的id
stopSelf(msg.arg1);
}
handleMessage方法中主要的操作就是调用scan方法进行扫描。
private void scan(String[] directories, String volumeName) {
Uri uri = Uri.parse("file://" + directories[0]);
// don't sleep while scanning
mWakeLock.acquire();
try {
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put(MediaStore.MEDIA_SCANNER_VOLUME, volumeName);
//从 getContentResolver获得一个ContentResover,然后直接插入
//根据AIDL,这个ContentResover的另一端是MediaProvider。作用是让其做一些准备工作
Uri scanUri = getContentResolver().insert(MediaStore.getMediaScannerUri(), values);
//发送开始扫描的广播
sendBroadcast(new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MEDIA_SCANNER_STARTED, uri));
try {
if (volumeName.equals(MediaProvider.EXTERNAL_VOLUME)) {
openDatabase(volumeName);
}
//创建MediaScanner对象并开启扫描操作
MediaScanner scanner = createMediaScanner();
scanner.scanDirectories(directories, volumeName);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "exception in MediaScanner.scan()", e);
}
//通过特殊的Uri进行相关的清理工作
getContentResolver().delete(scanUri, null, null);
} finally {
//发送扫描完成的广播,释放锁
sendBroadcast(new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MEDIA_SCANNER_FINISHED, uri));
mWakeLock.release();
}
}
... ...
private void openDatabase(String volumeName) {
try {
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("name", volumeName);
//调用MediaProvider的insert方法,进行插值
getContentResolver().insert(Uri.parse("content://media/"), values);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
Log.w(TAG, "failed to open media database");
}
}
private MediaScanner createMediaScanner() {
MediaScanner scanner = new MediaScanner(this);
//获取语言信息,将文件转化成此时的语言
Locale locale = getResources().getConfiguration().locale;
if (locale != null) {
String language = locale.getLanguage();
String country = locale.getCountry();
String localeString = null;
if (language != null) {
if (country != null) {
//设置语言
scanner.setLocale(language + "_" + country);
} else {
scanner.setLocale(language);
}
}
}
return scanner;
}
在MediaScannerService中的onCreate和onStartCommand已经分析完成了,剩下的onDestory只是将Looper退出。
2.1.4 MediaScanner.java
在上面的分析中,MediaScannerService的createMediaScanner方法实例化MediaScanner对象,并且配置语言的。下面先从MediaScanner的创建分析,并且介绍相关的具体方法。
对于MediaScanner的初始化过程,首先执行的是静态代码块,然后是构造函数。
static {
//加载libmedia_jni.so
System.loadLibrary("media_jni");
native_init();
}
public MediaScanner(Context c) {
native_setup();
mContext = c;
mPackageName = c.getPackageName();
mBitmapOptions.inSampleSize = 1;
mBitmapOptions.inJustDecodeBounds = true;
setDefaultRingtoneFileNames();
mExternalStoragePath = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getAbsolutePath();
mExternalIsEmulated = Environment.isExternalStorageEmulated();
}
在初始化的过程中native_init();和native_setup();方法放在JNI层分析。
在MediaScannerService中调用了MediaScanner的scanDirectories方法,此方法是java层具体的扫描实现。
public void scanDirectories(String[] directories, String volumeName) {
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//扫描之前的初始化
initialize(volumeName);
//扫描之前的预处理
prescan(null, true);
long prescan = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (ENABLE_BULK_INSERTS) {
// create MediaInserter for bulk inserts
//A MediaScanner helper class which enables us to do lazy insertion on the given provider.
//参数500是每条Uri所占的buffer大小
mMediaInserter = new MediaInserter(mMediaProvider, mPackageName, 500);
}
for (int i = 0; i < directories.length; i++) {
//此方法是native方法,用来扫描文件,参数directories[i]是传入的路径数组
//mClient是MyMediaScannerClient的实例,之后会继续分析
processDirectory(directories[i], mClient);
}
if (ENABLE_BULK_INSERTS) {
// flush remaining inserts
// Note that you should call flushAll() after using this class.
mMediaInserter.flushAll();
mMediaInserter = null;
}
long scan = System.currentTimeMillis();
//处理扫描完成之后的操作
postscan(directories);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
}//catch各种异常
} finally {
// release the DrmManagerClient resources
releaseResources();
}
}
private void initialize(String volumeName) {
//获取MediaProvider对象
mMediaProvider = mContext.getContentResolver().acquireProvider("media");
//初始化不同类型数据的Uri,供之后根据不同的表进行插值
mAudioUri = Audio.Media.getContentUri(volumeName);
mVideoUri = Video.Media.getContentUri(volumeName);
mImagesUri = Images.Media.getContentUri(volumeName);
mThumbsUri = Images.Thumbnails.getContentUri(volumeName);
mFilesUri = Files.getContentUri(volumeName);
mFilesUriNoNotify = mFilesUri.buildUpon().appendQueryParameter("nonotify", "1").build();
//如果是外部存储,则可以获得播放列表的Uri
if (!volumeName.equals("internal")) {
// we only support playlists on external media
mProcessPlaylists = true;
mProcessGenres = true;
mPlaylistsUri = Playlists.getContentUri(volumeName);
mCaseInsensitivePaths = true;
}
}
private void prescan(String filePath, boolean prescanFiles) throws RemoteException {
Cursor c = null;
String where = null;
String[] selectionArgs = null;
if (mPlayLists == null) {
// mPlayLists的初始化
mPlayLists = new ArrayList();
} else {
mPlayLists.clear();
}
if (filePath != null) {
// query for only one file
//拼接where语句
where = MediaStore.Files.FileColumns._ID + ">?" +
" AND " + Files.FileColumns.DATA + "=?";
selectionArgs = new String[] { "", filePath };
} else {
where = MediaStore.Files.FileColumns._ID + ">?";
selectionArgs = new String[] { "" };
}
// Tell the provider to not delete the file.
// If the file is truly gone the delete is unnecessary, and we want to avoid
// accidentally deleting files that are really there (this may happen if the
// filesystem is mounted and unmounted while the scanner is running).
Uri.Builder builder = mFilesUri.buildUpon();
builder.appendQueryParameter(MediaStore.PARAM_DELETE_DATA, "false");
MediaBulkDeleter deleter = new MediaBulkDeleter(mMediaProvider, mPackageName,
builder.build());
// Build the list of files from the content provider
try {
if (prescanFiles) {
// First read existing files from the files table.
// Because we'll be deleting entries for missing files as we go,
// we need to query the database in small batches, to avoid problems
// with CursorWindow positioning.
long lastId = Long.MIN_VALUE;
//指定查询1000条数据
Uri limitUri =
mFilesUri.buildUpon().appendQueryParameter("limit", "1000").build();
mWasEmptyPriorToScan = true;
while (true) {
//拼装where查询的参数
selectionArgs[0] = "" + lastId;
if (c != null) {
c.close();
c = null;
}
//开始查询
c =
mMediaProvider.query(mPackageName, limitUri, FILES_PRESCAN_PROJECTION,
where, selectionArgs, MediaStore.Files.FileColumns._ID, null);
if (c == null) {
break;
}
int num = c.getCount();
if (num == 0) {
break;
}
mWasEmptyPriorToScan = false;
while (c.moveToNext()) {
//获取查询的数据
long rowId = c.getLong(FILES_PRESCAN_ID_COLUMN_INDEX);
String path = c.getString(FILES_PRESCAN_PATH_COLUMN_INDEX);
int format = c.getInt(FILES_PRESCAN_FORMAT_COLUMN_INDEX);
long lastModified =
c.getLong(FILES_PRESCAN_DATE_MODIFIED_COLUMN_INDEX);
lastId = rowId;
// Only consider entries with absolute path names.
// This allows storing URIs in the database without the
// media scanner removing them.
if (path != null && path.startsWith("/")) {
boolean exists = false;
try {
//获取此路径下是否有文件
exists = Os.access(path, android.system.OsConstants.F_OK);
} catch (ErrnoException e1) {
}
if (!exists && !MtpConstants.isAbstractObject(format)) {
// do not delete missing playlists, since they may have been
// modified by the user.
// The user can delete them in the media player instead.
// instead, clear the path and lastModified fields in the row
MediaFile.MediaFileType mediaFileType =
MediaFile.getFileType(path);
int fileType = (mediaFileType == null ? 0 :
mediaFileType.fileType);
if (!MediaFile.isPlayListFileType(fileType)) {
//删除掉指定的数据
deleter.delete(rowId);
if (path.toLowerCase(Locale.US).endsWith("/.nomedia")) {
deleter.flush();
String parent = new File(path).getParent();
**
* The method name used by the media scanner and mtp to tell the media provider to
* rescan and reclassify that have become unhidden because of renaming folders or
* removing nomedia files
* @hide
*/
mMediaProvider.call(mPackageName,
MediaStore.UNHIDE_CALL,parent, null);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
finally {
if (c != null) {
c.close();
}
deleter.flush();
}
// compute original size of images
mOriginalCount = 0;
c = mMediaProvider.query(mPackageName, mImagesUri, ID_PROJECTION, null, null, null, null);
if (c != null) {
mOriginalCount = c.getCount();
c.close();
}
}
private void postscan(String[] directories) throws RemoteException {
// handle playlists last, after we know what media files are on the storage.
if (mProcessPlaylists) {
processPlayLists();
}
//如果图片的数目为0,并且是外部存储,则清除掉无效的略缩图文件
if (mOriginalCount == 0 && mImagesUri.equals(Images.Media.getContentUri("external")))
pruneDeadThumbnailFiles();
// allow GC to clean up
mPlayLists = null;
mMediaProvider = null;
}
至此,关于java层的分析已经完成,剩下几个比较重要的JNI函数需要分析,分别是native_init,native_setup和processDirectory。接下来就开始分析JNI层。
Media Data之多媒体扫描过程分析(二)
Media Data之多媒体扫描过程分析(三)