pytorch实现神经网络常见model(LeNet,GoogLeNet,AlexNet,VggNet)
神经网络常见model的实现
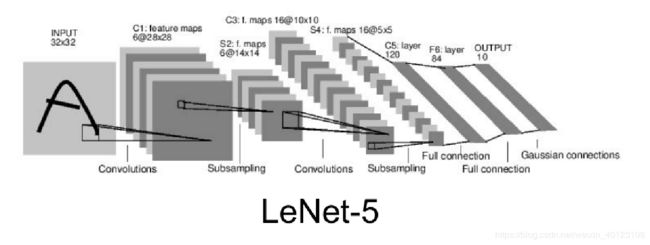
输入大小为32x32
class LenetNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LenetNet, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16*5*5, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2, 2))
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2)
x = x.view(x.size()[0], -1)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
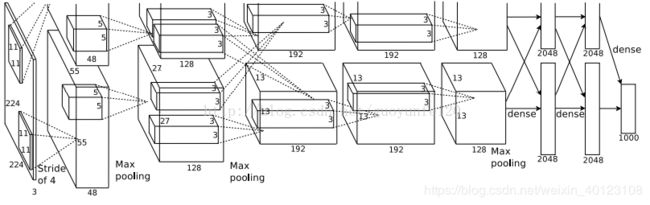
输入大小为224x224
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000):
super(AlexNet, self).__init__()
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(192, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(256 * 6 * 6, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(4096, num_classes),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), 256 * 6 * 6)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
查看模型输入大小:在Alexnet中尤其注意补充padding后的变化
conv1=nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=2)
pool=nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
test_x = Variable(torch.zeros(1, 3, 224, 224))
edge=pool(conv1(test_x))
print(edge.shape)
googlenet
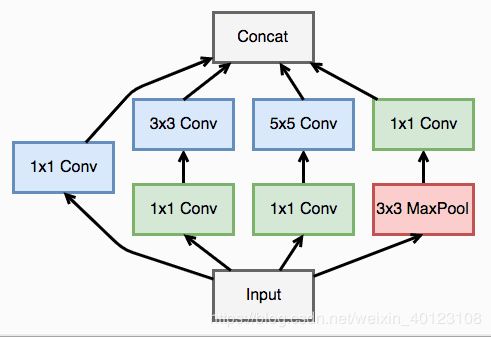
googlenet模型
定义一个卷积加一个 relu 激活函数和一个 batchnorm 作为一个基本的层结构,即inception模型
def conv_relu(in_channel, out_channel, kernel, stride=1, padding=0):
layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel, stride, padding),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel, eps=1e-3),
nn.ReLU(True)
)
return layer
class inception(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out1_1, out2_1, out2_3, out3_1, out3_5, out4_1):
super(inception, self).__init__()
# 第一条线路
self.branch1x1 = conv_relu(in_channel, out1_1, 1)
# 第二条线路
self.branch3x3 = nn.Sequential(
conv_relu(in_channel, out2_1, 1),
conv_relu(out2_1, out2_3, 3, padding=1)
)
# 第三条线路
self.branch5x5 = nn.Sequential(
conv_relu(in_channel, out3_1, 1),
conv_relu(out3_1, out3_5, 5, padding=2)
)
# 第四条线路
self.branch_pool = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=1, padding=1),
conv_relu(in_channel, out4_1, 1)
)
def forward(self, x):
f1 = self.branch1x1(x)
f2 = self.branch3x3(x)
f3 = self.branch5x5(x)
f4 = self.branch_pool(x)
output = torch.cat((f1, f2, f3, f4), dim=1)
return output
输入为224x224,模型中输入的图片大小多少无所谓,只需要将模型的全连接层处的大小匹配就好
class googlenet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, num_classes, verbose=False):
super(googlenet, self).__init__()
self.verbose = verbose
self.block1 = nn.Sequential(
conv_relu(in_channel, out_channel=64, kernel=7, stride=2, padding=3),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2)
)
self.block2 = nn.Sequential(
conv_relu(64, 64, kernel=1),
conv_relu(64, 192, kernel=3, padding=1),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2)
)
self.block3 = nn.Sequential(
inception(192, 64, 96, 128, 16, 32, 32),
inception(256, 128, 128, 192, 32, 96, 64),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2)
)
self.block4 = nn.Sequential(
inception(480, 192, 96, 208, 16, 48, 64),
inception(512, 160, 112, 224, 24, 64, 64),
inception(512, 128, 128, 256, 24, 64, 64),
inception(512, 112, 144, 288, 32, 64, 64),
inception(528, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2)
)
self.block5 = nn.Sequential(
inception(832, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128),
inception(832, 384, 182, 384, 48, 128, 128),
nn.AvgPool2d(2)
)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(9216, num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.block1(x)
if self.verbose:
print('block 1 output: {}'.format(x.shape))
x = self.block2(x)
if self.verbose:
print('block 2 output: {}'.format(x.shape))
x = self.block3(x)
if self.verbose:
print('block 3 output: {}'.format(x.shape))
x = self.block4(x)
if self.verbose:
print('block 4 output: {}'.format(x.shape))
x = self.block5(x)
if self.verbose:
print('block 5 output: {}'.format(x.shape))
x = x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
# 一个 vgg 的 block,传入三个参数,第一个是模型层数,第二个是输入的通道数,第三个是输出的通道数,第一
#层卷积接受的输入通道就是图片输入的通道数,然后输出最后的输出通道数,后面的卷积接受的通道数就是最后
#的输出通道数
def vgg_block(num_convs, in_channels, out_channels):
net = [nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(True)] # 定义第一层
for i in range(num_convs-1): # 定义后面的很多层
net.append(nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1))
net.append(nn.ReLU(True))
net.append(nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)) # 定义池化层
return nn.Sequential(*net)
#函数对 vgg block 进行堆叠
def vgg_stack(num_convs, channels):
net = []
for n, c in zip(num_convs, channels):
in_c = c[0]
out_c = c[1]
net.append(vgg_block(n, in_c, out_c))
return nn.Sequential(*net)
#vgg模型
class vgg(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(vgg, self).__init__()
self.feature = vgg_net
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(512, 100),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(100, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.feature(x)
x = x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x