Linux指令:grep指令详解1
grep可以完成不必打开ascii文件就可以搜索其内容,其帮助如下:
$ grep --help
用法: grep [选项]... PATTERN [FILE]...
在每个 FILE 或是标准输入中查找 PATTERN。
默认的 PATTERN 是一个基本正则表达式(缩写为 BRE)。
例如: grep -i 'hello world' menu.h main.c
正则表达式选择与解释:
-E, --extended-regexp PATTERN 是一个可扩展的正则表达式(缩写为 ERE)
-F, --fixed-strings PATTERN 是一组由断行符分隔的定长字符串。
-G, --basic-regexp PATTERN 是一个基本正则表达式(缩写为 BRE)
-P, --perl-regexp PATTERN 是一个 Perl 正则表达式
-e, --regexp=PATTERN 用 PATTERN 来进行匹配操作
-f, --file=FILE 从 FILE 中取得 PATTERN
-i, --ignore-case 忽略大小写
-w, --word-regexp 强制 PATTERN 仅完全匹配字词
-x, --line-regexp 强制 PATTERN 仅完全匹配一行
-z, --null-data 一个 0 字节的数据行,但不是空行
Miscellaneous:
-s, --no-messages suppress error messages
-v, --invert-match select non-matching lines
-V, --version display version information and exit
--help display this help text and exit
输出控制:
-m, --max-count=NUM NUM 次匹配后停止
-b, --byte-offset 输出的同时打印字节偏移
-n, --line-number 输出的同时打印行号
--line-buffered 每行输出清空
-H, --with-filename 为每一匹配项打印文件名
-h, --no-filename 输出时不显示文件名前缀
--label=LABEL 将LABEL 作为标准输入文件名前缀
-o, --only-matching show only the part of a line matching PATTERN
-q, --quiet, --silent suppress all normal output
--binary-files=TYPE assume that binary files are TYPE;
TYPE is 'binary', 'text', or 'without-match'
-a, --text equivalent to --binary-files=text
-I equivalent to --binary-files=without-match
-d, --directories=ACTION how to handle directories;
ACTION is 'read', 'recurse', or 'skip'
-D, --devices=ACTION how to handle devices, FIFOs and sockets;
ACTION is 'read' or 'skip'
-r, --recursive like --directories=recurse
-R, --dereference-recursive
likewise, but follow all symlinks
--include=FILE_PATTERN
search only files that match FILE_PATTERN
--exclude=FILE_PATTERN
skip files and directories matching FILE_PATTERN
--exclude-from=FILE skip files matching any file pattern from FILE
--exclude-dir=PATTERN directories that match PATTERN will be skipped.
-L, --files-without-match print only names of FILEs containing no match
-l, --files-with-matches print only names of FILEs containing matches
-c, --count print only a count of matching lines per FILE
-T, --initial-tab make tabs line up (if needed)
-Z, --null print 0 byte after FILE name
文件控制:
-B, --before-context=NUM 打印以文本起始的NUM 行
-A, --after-context=NUM 打印以文本结尾的NUM 行
-C, --context=NUM 打印输出文本NUM 行
-NUM same as --context=NUM
--group-separator=SEP use SEP as a group separator
--no-group-separator use empty string as a group separator
--color[=WHEN],
--colour[=WHEN] use markers to highlight the matching strings;
WHEN is 'always', 'never', or 'auto'
-U, --binary do not strip CR characters at EOL (MSDOS/Windows)
-u, --unix-byte-offsets report offsets as if CRs were not there
(MSDOS/Windows)
‘egrep’即‘grep -E’。‘fgrep’即‘grep -F’。
直接使用‘egrep’或是‘fgrep’均已不可行了。
若FILE 为 -,将读取标准输入。不带FILE,读取当前目录,除非命令行中指定了-r 选项。
如果少于两个FILE 参数,就要默认使用-h 参数。
如果有任意行被匹配,那退出状态为 0,否则为 1;
如果有错误产生,且未指定 -q 参数,那退出状态为 2。
请将错误报告给: [email protected]
GNU Grep 主页: 基本用法1:匹配字符串
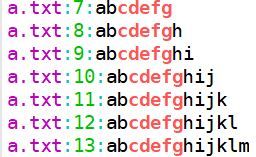
$ grep "cdefg" a.txt b.txt基本用法2:输出对应行号
$ grep "cdefg" a.txt -n基本用法3:输出不匹配的行
$ grep "cdefg" a.txt b.txt -n -v基本用法4:高光显示匹配的字符串
$ grep "cdefg" a.txt b.txt -n --color=auto基本用法5:只输出匹配的部分
$ grep "cdefg" a.txt b.txt -n -o --color=auto基本用法6:正则表达式
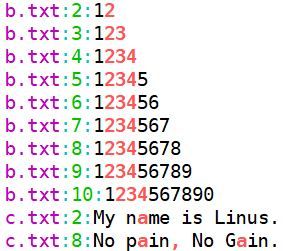
$ grep -E [a-c,2-4] b.txt c.txt -n --color=auto #或
$ egrep [a-c,2-4] b.txt c.txt -n --color=auto采用不同的正则表达式:
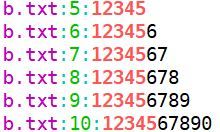
$ egrep [1-2]+[2-4] b.txt c.txt -n --color=auto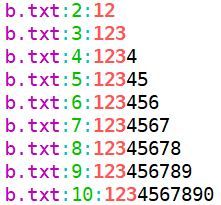
$ egrep [1-2]+[2-4]+5 b.txt c.txt -n --color=auto基本用法7:返回匹配的总行数
$ grep a b.txt c.txt -c基本用法8:字节偏移
$ grep -b -o "ab" a.txt b.txt
a.txt:2:ab
a.txt:5:ab
a.txt:9:ab
a.txt:14:ab
a.txt:20:ab
a.txt:27:ab
a.txt:35:ab
a.txt:44:ab
a.txt:54:ab
a.txt:65:ab
a.txt:77:ab
a.txt:90:ab基本用法9:返回字符串所在文件
$ grep -l "ab" a.txt b.txt c.txt
a.txt基本用法10:不区分大小写
$ grep -i "aB" a.txt b.txt c.txt基本用法11:管道
$ echo No Pain, No Gain | grep -i -e "nO" -e gA -n --color=auto![]()
$ echo No Pain, No Gain | grep -i -e "nO" -e gA -n --color=auto | tee d.txt
$ ls
a.txt b.txt c.txt d.txt
$ more d.txt
1:No Pain, No Gain基本用法12:《递归》--匹配当前目录下所有文件
$ grep "abc" . -r基本用法13:匹配多个字符(串)
$ grep -e "abc" -e "234" . -r多个字符串匹配也可以从文件中设定字符串
$ echo abc > e.txt
$ grep -f e.txt . -r
./a.txt:abc
./a.txt:abcd
./a.txt:abcde
./a.txt:abcdef
./a.txt:abcdefg
./a.txt:abcdefgh
./a.txt:abcdefghi
./a.txt:abcdefghij
./a.txt:abcdefghijk
./a.txt:abcdefghijkl
./a.txt:abcdefghijklm
./e.txt:abc基本用法14:搜索特定文件
$ grep -f e.txt . -r --include *.{txt,c} #搜索以txt和c结尾的文件
$ grep "abc" . -r --exclude *.{txt,c} #不搜索以txt和c结尾的文件
$ grep -f e.txt . -r --exclude-from d.txt #从文件中获取略过的文件名基本用法15:条件语句
$ grep -q "abc" a.txt #找到匹配字符则返回1,否则返回0$ more c.txt
Just Do it.
Hello World !
My name is Linus.
GNU is not UNIX.
GNU/Linux
Just For Fun.
Hello.
Just Do It.
Don't push me so hard.
We don't talk anymore.
To Be No.1.
No pain, No Gain.
One Day.
$ grep -i hello c.txt -A 3 --color=auto #显示后三行
Hello World !
My name is Linus.
GNU is not UNIX.
GNU/Linux
--
Hello.
Just Do It.
Don't push me so hard.
We don't talk anymore.
$ grep -i hello c.txt -B 3 --color=auto #显示前三行
Just Do it.
Hello World !
--
GNU is not UNIX.
GNU/Linux
Just For Fun.
Hello.
$ grep -i hello c.txt -C 3 --color=auto #显示前后三行
Just Do it.
Hello World !
My name is Linus.
GNU is not UNIX.
GNU/Linux
Just For Fun.
Hello.
Just Do It.
Don't push me so hard.
We don't talk anymore.