实验八---有向不带权图的遍历以及简单路径的求解
【目的】
1. 领会图的两种存储结构和图的基本运算算法设计;领会图的两种遍历算法。
2. 掌握图的深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历算法在求解图路径搜索问题中的应用。
**
【内容】
**建立有向图的邻接矩阵和邻接表存储结构,并实现两种遍历运算、简单路径求解:
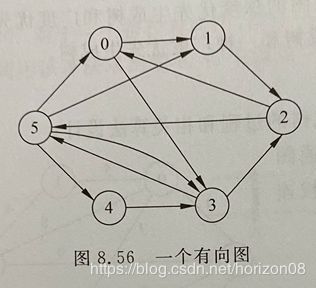
(1)建立如图8.56所示的有向图G的邻接矩阵和邻接表存储结构,并输出这两种结构。
(2)根据邻接表,实现图G的从顶点0开始的深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历运算。
(3)根据邻接表,输出:
①从顶点5到顶点2的所有长度为3的
简单路径;
②从顶点5到顶点2的最短路径。
(4)销毁图G的邻接表。
#include