面7-多线程
1、线程简介
1.1 多任务、多线程
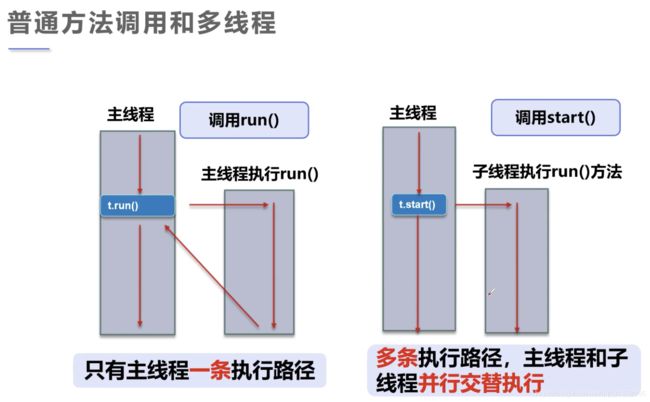
1.2 普通方法和多线程
1.3 process和Thread
1、程序:指令和数据的有序集合,无任何运行意义,是一个静态的概念
2、进程:执行程序的一次执行过程
3、通常一个进程中包含若干个线程,线程是cpu调度和执行的单位
4、线程是cpu执行的基本单位,进程是cpu分配资源的基本单位
2、线程创建
2.1 继承Thread类
1、代码
class FirstThread extends Thread{
/**
* 自定义线程类继承Thread类
* 重写run方法,编写线程执行体
* 创建线程对象,调用start方法启动线程
*/
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("我在看代码--");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) { //主线程
FirstThread ft = new FirstThread();
/**
* 两个线程同时执行,交替执行
* 线程开启不一定立即执行,由cpu调度执行
*/
ft.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("我在学习多线程--");
}
}
}
2、图片下载:
package Thread.java_thread_day1;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
/**
* @author houbj
* @date 2020/4/13 09:10
*/
public class DownloadTest extends Thread {
private String name;
private String url;
public DownloadTest(String url, String name){
this.name = name;
this.url = url;
}
@Override
public void run() {
DownloadPic dp = new DownloadPic();
dp.DownLoad(url, name);
System.out.println("download : " + name);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DownloadTest dt1 = new DownloadTest("https://i1.hdslb.com/bfs/archive/086a03610c465b930699c5ab80dc31fb4d808f83.jpg@336w_190h.webp","pic/pic1.jpg");
DownloadTest dt2 = new DownloadTest("https://i1.hdslb.com/bfs/archive/086a03610c465b930699c5ab80dc31fb4d808f83.jpg@336w_190h.webp","pic/pic2.jpg");
DownloadTest dt3 = new DownloadTest("https://i1.hdslb.com/bfs/archive/086a03610c465b930699c5ab80dc31fb4d808f83.jpg@336w_190h.webp","pic/pic3.jpg");
dt1.start();
dt2.start();
dt3.start();
}
}
class DownloadPic{
public void DownLoad(String url, String name) {
try {
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url),new File(name));
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("异常----");
}
}
}
2.2 实现runable接口
1、代码
public class CreateThreadByRunnable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 定义xx类实现Runnable接口
* 实现run()方法
* 创建线程对象,利用start方法启动线程
*/
RunnableThread rt = new RunnableThread();
//创建线程对象,通过线程对象来开启我们的线程,代理
Thread thread = new Thread(rt);
//利用start方法启动线程
thread.start();
//简化为
new Thread(rt).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 3000; i++) {
System.out.println("CreateThreadByRunnable -- ");
}
}
}
class RunnableThread implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 2000; i++) {
System.out.println("RunnableThread -- ");
}
}
}
2.3 两者之间的区别
继承Thread:不建议使用,避免使用OOP单继承局限性
实现Runnable接口,避免单继承局限性,灵活方便,方便同一个对象被多个线程使用
2.4 实现Callable接口
1、代码实现
public class DownLoadPicByCallable implements Callable<Boolean> {
// * 实现Callable接口,需要返回值类型
// * 重写 call方法,需要抛出异常
// * 创建目标对象
// * 创建执行服务:ExecutorService ser = Executors.newFixedThreadPoll(1)
// * 提交执行:Future result1 = ser.submit(t1);
// * 获取结果:boolean r1 = result1.get();
// * 关闭服务:ser.shutdownNow();
private String url;
private String name;
public DownLoadPicByCallable(String url, String name){
this.url = url;
this.name = name;
}
// * 重写 call方法,需要抛出异常
@Override
public Boolean call() {
DownLoadPic dl = new DownLoadPic();
dl.Download(this.url,this.name);
System.out.println("下载名字为 : " + this.name);
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
DownLoadPicByCallable dpbc1 = new DownLoadPicByCallable("https://i1.hdslb.com/bfs/archive/086a03610c465b930699c5ab80dc31fb4d808f83.jpg@336w_190h.webp","pic/CalPic1.jpg");
DownLoadPicByCallable dpbc2 = new DownLoadPicByCallable("https://i1.hdslb.com/bfs/archive/086a03610c465b930699c5ab80dc31fb4d808f83.jpg@336w_190h.webp","pic/CalPic2.jpg");
DownLoadPicByCallable dpbc3 = new DownLoadPicByCallable("https://i1.hdslb.com/bfs/archive/086a03610c465b930699c5ab80dc31fb4d808f83.jpg@336w_190h.webp","pic/CalPic3.jpg");
// * 创建执行服务
ExecutorService ser = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// * 提交执行:
Future<Boolean> result1 = ser.submit(dpbc1);
Future<Boolean> result2 = ser.submit(dpbc2);
Future<Boolean> result3 = ser.submit(dpbc3);
// * 获取结果:
boolean r1 = result1.get();
boolean r2 = result2.get();
boolean r3 = result3.get();
// * 关闭服务:
ser.shutdownNow();
}
}
class DownLoadPic{
public void Download(String url, String name){
try {
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url), new File(name));
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("下载异常");
}
}
}
2、使用Callable的好处:
可以定义返回值
可以抛出异常
3、相关知识
3.1 并发
1、代码
public class TicketTest implements Runnable {
private int ticketNum = 100;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
if (ticketNum <=0) break;
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
System.out.println("异常--");
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +" ->拿到了,第 "+ ticketNum -- + "张票");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 多个线程操作同一资源的情况下,线程不安全,数据紊乱(并发问题)
*/
TicketTest tt = new TicketTest();
new Thread(tt,"小明").start();
new Thread(tt,"张三").start();
new Thread(tt,"李四").start();
}
}
2、发现问题:
多个线程操作同一资源的情况下,线程不安全,数据紊乱(并发问题)
3、龟兔赛跑
public class RabbitAndTortoiseRace implements Runnable{
private int step = 100;
private String athlete;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i<= 100 ;i ++ ) {
// if (Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("rabbit")) {
// try {
// Thread.sleep(5);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// }
if (winner(i)){
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 跑了 "+ i+ "步");
}
}
public boolean winner(int step){
if (athlete != null) {
return true;
}
if (step >= 100) {
athlete = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(athlete +"胜利了!!!");
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
RabbitAndTortoiseRace rat = new RabbitAndTortoiseRace();
new Thread(rat,"rabbit").start();
new Thread(rat,"tortoise").start();
}
}
3.2 静态代理
3.3 lambda表达式
4、线程状态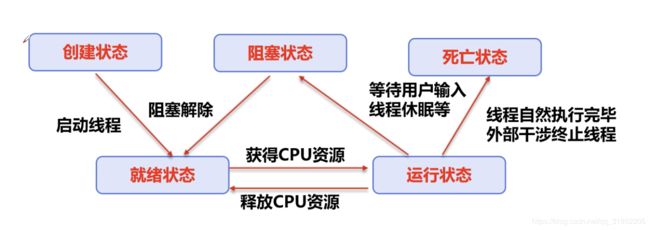
4.1 五种状态
setPriority(); // 更改线程优先级
void join(); // 等待该线程终止
static void yield(); // 暂停当前正在执行的线程对象,并执行其他线程
void interrupt() ; // 中断线程
boolean isAlive(); // 测试线程是否处于活动状态
4.2 线程停止
1、线程停止(不要使用stop或者destroy等过时的方法)
通过一个外部标志,使线程停止
public class ThreadStop{
/**
* 五种状态
* setPriority(); // 更改线程优先级
* void join(); // 等待该线程终止
* static void yield(); // 暂停当前正在执行的线程对象,并执行其他线程
* void interrupt() ; // 中断线程
* boolean isAlive(); // 测试线程是否处于活动状态
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 线程停止(不要使用stop或者destroy等过时的方法)
*/
/**
* 通过一个外部标志,使线程停止
*/
ThreadStopTest t = new ThreadStopTest();
new Thread(t).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("ThreadStatus --- " + i);
if(i >=80) {
t.stop();
break;
}
}
}
}
class ThreadStopTest implements Runnable{
private boolean flag =true;
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0;
while (flag) {
System.out.println("ThreadStatusTest --- :" + i++);
}
}
public void stop(){
this.flag = false;
System.out.println("该线程停止了 ---- ");
}
}
4.3 线程休眠——sleep
1、模拟倒计时
4.4 线程礼让——yield
1、 礼让线程,让当前正在执行的线程暂停,但不阻塞
2、将线程从运行状态转为就绪状态
3、让cpu重新调度,礼让不一定成功!看cpu心情
4.5 线程强制执行——join
1、 合并线程:待此线程执行完成之后,再执行其他线程
2、可以想象成插队
4.6 观察线程的状态
1、new:尚未启动的线程处于此状态
2、runnable:在Java虚拟机中执行的线程处于此状态
3、blocked:被阻塞等待监视器锁定的线程处于此状态
4、waiting:正在等待另一个线程执行特定动作的线程
5、timed_waiting:正在等待另一个线程执行动作达到指定等待时间的线程处于此状态
6、terminated:已退出的线程处于此状态
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
4.7 线程的优先级
1、 java提供一个线程调度器来监控程序中启动后进入就绪状态的所有线程,线程调度器按照优先级决定应该调度哪个线程来执行
2、线程优先级用数字表示,范围从1-10
thread2.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
4.8 守护线程
public class ThreadDaemon {
/**
* 线程分为用户线程和守护线程
* 虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕
* 虚拟机不用等待守护线程执行完毕
* 如,后台记录操作日志,监控内存,垃圾回收、、
* thread.setDaemon(false); 默认false都是用户线程,正常线程都是用户线程。true为守护线程
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
God god = new God();
You you = new You();
Thread thread = new Thread(god);
thread.setDaemon(true); //设置为守护线程
thread.start();
new Thread(you).start(); // 默认为用户线程
}
}
class God implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
int num = 1;
while (true) {
System.out.println("God bless you! --- " + num ++ );
}
}
}
class You implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 365; i++) {
System.out.println("i still alive! --- " + i);
}
}
}
5、同步
5.1 并发
1、同一个对象被多个线程同时操作
5.2 线程同步
1、多个线程操作同一个资源,一种等待机制,多个需要同时访问此对象的线程进入这个对象的等待池形成队列,等前面的线程使用完毕之后,下一个线程再使用
2、多个线程访问同一个对象,并且某些线程还想修改这个对象,这时候我们就需要线程同步,
3、多个需要同时访问此对象的线程进入这个对象的等待池形成队列,等前面的线程使用完毕之后,下一个线程再使用
5.3 锁
锁:由于同一进程的多个线程共享同一块存储空间,在带来方便的同时,也带来了访问冲突的问题,为保证数据在方法中被访问时的正确性,在访问时加入 锁机制 ,当一个
线程获得对象的排它锁,独占资源,其他线程必须等待,使用后释放锁即可,存在以下问题:
1、一个线程持有锁会导致其他所有需要此锁的线程挂起
2、再多线程竞争下,加锁,释放锁会导致比较多的上下文切换 和 延时调度,引起性能问题
3、如果一个优先级高的线程等待一个优先级低的线程释放锁,会导致优先级倒置,引起性能问题
4、锁对象
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (people) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
drawingMoney();
}
}
5、锁方法
public synchronized void drawingMoney(){
if (people.getBankMoney() - this.drawMoney <0) {
System.out.println( Thread.currentThread().getName() +people.getName() + " 余额不足");
return;
}
people.setBankMoney(people.getBankMoney() - this.drawMoney);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 已经在 "+ people.getName()+"账户取走 " + this.drawMoney + " 余额为 :" + people.getBankMoney());
}
5.4 死锁
1、 死锁 :多个线程各自占有一些共享资源,并且互相等待其他线程占有的资源才能运行,而导致两个或者多个线程都在等待对方释放资源,都停止执行的情况
某一个同步块同时拥有两个以上对象锁时,就可能发生死锁的问题
2、产生死锁的四个条件:
(1)互斥条件:一个资源每次只能被一个进程占用
(2)请求与保持条件:一个进程因请求资源而阻塞时,对与获得的资源保持不放
(3)不剥夺条件:进程已经获得的资源,在未使用完之前,不能强行剥夺
(4)循环等待条件,若干进程之间形成一种头尾相接的循环等待资源的关系
/**
* 不会发生死锁
*/
@Override
public void run() {
if (choice ==0 ){
synchronized (mirror) {
System.out.println(this.name + "获得 mirror");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
synchronized (lipstick) {
System.out.println(this.name + "获得 lipstick");
}
} else {
synchronized (lipstick) {
System.out.println(this.name + "获得 lipstick");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
synchronized (mirror) {
System.out.println(this.name + "获得 mirror");
}
}
}
/**
* 会发生死锁
*/
@Override
public void run() {
if (choice ==0 ){
synchronized (mirror) {
System.out.println(this.name + "获得 mirror");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (lipstick) {
System.out.println(this.name + "获得 lipstick");
}
}
} else {
synchronized (lipstick) {
System.out.println(this.name + "获得 lipstick");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (mirror) {
System.out.println(this.name + "获得 mirror");
}
}
}
}
5.5 lock锁
1、juc包下的Lock接口是控制多个线程对共享资源进行访问的工具。锁提供了对共享资源的独占访问,每次只能有一个线程对Lock对象加锁,线程开始访问共享资源之前应先获得Lock对象
2、ReentrantLock类实现了Lock,它拥有与synchronized相同的并发性和内存语义。
3、在实现线程安全的控制中,比较常用的是ReentrantLock,可以显式加锁、释放锁。
4、显示的加锁和解锁
class BuyTicketsSafe implements Runnable{
int ticketNum = 10;
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
//加锁
lock.lock();
try {
if (ticketNum > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("safe :" + ticketNum --);
} else {
break;
}
}finally {
//解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
5.6 synchronized与lock的对比
1、Lock是显示锁(手动开启和关闭锁),synchronized是隐式锁,出了作用域自动释放
2、Lock只有代码块锁,synchronized有代码块锁和方法锁
3、使用Lock锁,jvm将花费较少的时间来调度线程,性能更好。并且具有更好的扩展性
6、线程协作
6.1 生产者消费者模式
6.2 线程协作
6.3 线程通信
1、wait(),线程一直等待,直到其他线程通知,与sleep不同,会释放锁
2、notify(),唤醒一个处于等待状态的线程
3、notifyAll(),优先级别高于线程优先级
6.4 管程法
生产者将生产好的数据放入缓冲区,消费者从缓冲区中拿出数据
public class ThreadCope {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SyncContainer syncContainer = new SyncContainer();
new Producer(syncContainer).start();
new Consumer(syncContainer).start();
}
}
/**
* 生产者
*/
class Producer extends Thread{
SyncContainer container;
public Producer(SyncContainer container){
this.container = container;
}
//生产
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
container.push(new Chicken(i));
System.out.println("生产了 : " + i );
}
}
}
/**
* 消费者
*/
class Consumer extends Thread{
SyncContainer container;
public Consumer(SyncContainer container){
this.container = container;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("消费了 - 》》 " + container.pop().id );
}
}
}
class Chicken{
int id; //编号
public Chicken(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
class SyncContainer{
// 需要一个容器大小
Chicken[] chickens = new Chicken[10];
int count = 0 ; //容器计数器
// 生产者放入产品
public synchronized void push(Chicken chicken) {
// 如果容器满了,我们就需要消费者消费
if (count >= this.chickens.length) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//如果容器没有满,我们就需要生产者生产
chickens[count] = chicken;
count ++;
//可以通知消费者消费了
this.notifyAll();
}
// 消费者消费产品
public synchronized Chicken pop(){
// 判断能否消费
if(count ==0) {
// 等待生产者生产,消费者等待
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
count --;
Chicken chicken = chickens[count];
// 吃完了,通知生产者生产
this.notifyAll();
return chicken;
}
}
6.5 信号灯法
public class ThreadSign {
/**
* 信号灯法:通过标志位解决
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
TV tv = new TV();
new Player(tv).start();
new Watcher(tv).start();
}
}
//生产者 -》演员
class Player extends Thread{
TV tv ;
public Player (TV tv) {
this.tv = tv;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
if (i%2 == 0) {
this.tv.play("大本营");
} else {
this.tv.play("斗鱼");
}
}
}
}
//消费者 -》观众
class Watcher extends Thread{
TV tv ;
public Watcher (TV tv) {
this.tv = tv;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
tv.watch();
}
}
}
class TV{
// 演员表演,观众等待
// 观众观看,演员等待
String voice; //节目
boolean flag = true;
//表演
public synchronized void play(String voice){
if (!flag){
try {
this.wait();
System.out.println("演员等待 ------");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//通知观众观看
System.out.println("演员表演了 -- " + voice);
this.notifyAll(); //通知唤醒
this.voice = voice;
this.flag = ! this.flag;
}
//观看
public synchronized void watch(){
if (flag) { //flag为真:等待 观众在观看
try {
this.wait();
System.out.println("观众观看 ------");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("观看了 : " + this.voice);
//通知演员表演
this.notifyAll();
this.flag = ! this.flag;
}
}