用LSTM实现sin和tan的二分类
用LSTM实现sin和tan的二分类
- 读取数据(load_data.py)
- 定义RNN-LSTM模型(model.py)
- 定义训练过程(train_model.py)
- 主程序(main.py)
在基于CNN程序的基础上用长短时记忆网络对sin和tan离散数据进行了分类,采用单向单层LSTM网络,其中,对nn.LSTM()函数在程序中进行了详细解释。
读取数据(load_data.py)
可以调用此部分读取数据,数据的第一列为标签,用0,1表示类别
import pandas as pd
import torch
import torch.utils.data as Data
import numpy as np
class TrainDataset(Data.Dataset):
def __init__(self,path):
source = np.array(pd.read_csv(path, header=None))
col = len(source[0])
row = len(source.T[0])
source_data = source[0: row, 1: col]
source_label = source[0: row, 0: 1]
source = source_data.reshape(row,1,15200)
self.data = np.insert(source, 0, values=source_label, axis=2)
def __getitem__(self,idx):
data_ori = torch.from_numpy(self.data[idx].T) # torch.Size([15201, 1])
data = data_ori[1::].T # torch.Size([1, 15200])
label = data_ori[0] # 取data_ori的0行作为标签
return data, label # 返回数据和标签
def __len__(self): # 返回数据长度
return len(self.data)
定义RNN-LSTM模型(model.py)
此部分也可以调用,输出为类别数
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, lstm_output_size, hidden_size , output_size):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(input_size, lstm_output_size)
# input_size:输入特征的数目
# hidden_size:隐层的特征数目
# num_layers:这个是模型集成的LSTM的个数 记住这里是模型中有多少个LSTM摞起来 一般默认就1个
# bias:用不用偏置,默认是用
# batch_first:默认为假 若输入为二维数组,则应设此处为真
# dropout:默认0 若非0,则为dropout率;如果num_layers = 1 dropout应当为0
# bidirectional:是否为双向LSTM,默认为否(num_directions,默认为1)
self.r2h = nn.Linear(lstm_output_size, hidden_size )
self.h2o = nn.Linear(hidden_size , output_size)
def forward(self, input):
hidden, (hn,cn) = self.rnn(input)
# output, (h_n,c_n) = rnn(input, (h0,c0))
# input的格式为(seq_len, batch, input_size)这里默认batch_first为false,否则前两个换顺序
# h_0的格式为(num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size)
# c_0的格式为(seq_len, batch, input_size)
# 若h_0和c_0不提供,则默认为0
# output的格式为(seq_len, batch, num_directions * hidden_size)(num_directions,默认为1)
# h_n, c_n的格式为(num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size)
# self.rnn = nn.GRU(input_size, hidden_szie1, 1, dropout = 0.2)
# hidden = torch.Size([1, 32, 20])
# h_n = torch.Size([1, 32, 20])
# c_n = torch.Size([1, 32, 20])
fc1 = F.relu(self.r2h(hidden)) # torch.Size([1, 32, 5])
output = self.h2o(fc1) # torch.Size([1, 32, 2])
output = F.softmax(output,dim=2) # torch.Size([1, 32, 2]) (概率表示:行加起来为1)
output = output.transpose(0, 1).contiguous()
return output
定义训练过程(train_model.py)
此部分也可以调用,输出为交叉熵损失
import torch.nn as nn
def train(input_variable, target_variable, rnn, rnn_optimizer, criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()):
rnn_optimizer.zero_grad()
rnn_output = rnn(input_variable)
# print(cnn_output.shape) # torch.Size([32, 1, 2])
# print(target_variable)
loss = criterion(rnn_output, target_variable) # 交叉熵
loss.backward()
rnn_optimizer.step()
return loss
def test(input_variable, rnn):
rnn_output = rnn(input_variable)
top_n, top_i = rnn_output.data.topk(1,largest=False)
return top_i[0][0]
主程序(main.py)
import load_data
import model
import train_model
import torch
import torch.utils.data as Data
from torch.autograd import Variable
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
os.environ['CUDA_LAUNCH_BLOCKING'] = "0"
cuda = torch.cuda.is_available()
# 读取数据
train_path = 'F:/Data/QLX/0.csv'
test_path = 'F:/Data/QLX/1.csv'
trainset = load_data.TrainDataset(train_path)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
testset = load_data.TrainDataset(test_path)
test_loader = Data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=1, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
rnn = model.RNN(input_size = 7600, lstm_output_size = 20, hidden_size = 5, output_size = 2)
if cuda:
rnn = rnn.cuda()
LEARNING_RATE = 0.001
rnn_optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(rnn.parameters(), lr=LEARNING_RATE)
EPOCH = 1000
current_loss = 0
all_losses = []
err_rate = []
err = 0
accTemp = 0
for epoch in range(1, EPOCH + 1):
for step1, (batch_x, batch_y) in enumerate(train_loader):
batch_x = Variable(batch_x.type('torch.FloatTensor')) # torch.Size([32, 1, 15200])
batch_x = batch_x.reshape(32, 2, 7600)
batch_x = batch_x.transpose(0, 1).contiguous() # torch.Size([1, 32, 15200])
batch_y = Variable(batch_y.type('torch.LongTensor'))
batch_y = torch.zeros(32, 2).scatter_(1, batch_y, 1) # 标签实现one-hot编码
batch_y = Variable(batch_y.type('torch.LongTensor'))
if cuda:
batch_x = batch_x.cuda()
batch_y = batch_y.cuda()
loss = train_model.train(batch_x, batch_y, rnn, rnn_optimizer)
print(loss)
current_loss += loss
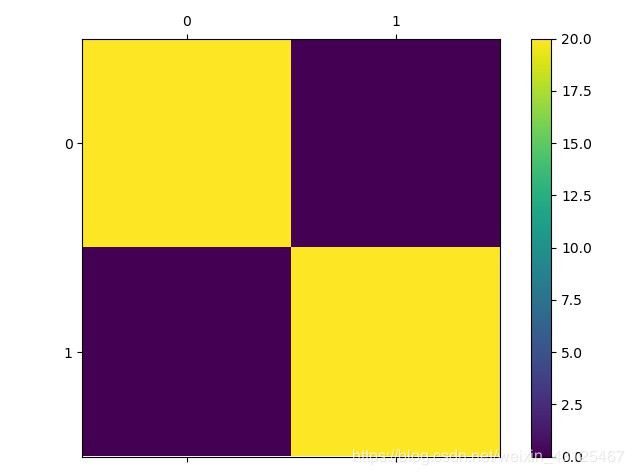
# 混淆矩阵
confusion = torch.zeros(2, 2)
for step2, (test_x, test_y) in enumerate(test_loader):
test_x = Variable(test_x.type('torch.FloatTensor')) # torch.Size([1, 8, 300])
test_x = test_x.reshape(1, 2, 7600)
test_x = test_x.transpose(0, 1).contiguous() # torch.Size([1, 32, 15200])
test_y = test_y.type('torch.LongTensor') # torch.Size([1, 300])
# test_y = torch.zeros(1, 2).scatter_(1, test_y, 1) # torch.Size([2, 2])
# test_y = Variable(test_y.type('torch.LongTensor')) # torch.Size([2, 2])
if cuda:
test_x = test_x.cuda()
test_y = test_y.cuda()
guess = train_model.test(test_x, rnn)
confusion[guess[0]][test_y[0][0]] += 1
print(confusion)
sen = (confusion[0][0]) / ((confusion[0][0] + confusion[0][1] + 1))
acc = (confusion[0][0] + confusion[1][1]) / (step2 + 1) # 准确率
all_losses.append(current_loss / step1)
err_rate.append(acc * 100)
if acc >= accTemp:
accTemp = acc
print(acc, accTemp)
print('%d epoch: acc = %.2f%%, sen = %.2f%%' % (epoch, acc * 100, sen * 100))
plt.figure()
plt.plot(all_losses)
plt.title('loss')
plt.figure()
plt.plot(err_rate)
plt.title('err')
print(confusion)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
cax = ax.matshow(confusion.numpy())
fig.colorbar(cax) # 颜色条
plt.show()