Swagger使用简介
一、Swagger的作用
Swagger 是一个规范和完整的框架,用于生成、描述、调用和可视化 RESTful 风格的 Web 服务。总体目标是使客户端和文件系统作为服务器以同样的速度来更新。文件的方法,参数和模型紧密集成到服务器端的代码,允许API来始终保持同步。
作用:
1. 接口的文档在线自动生成。
2. 功能测试。
二、Swagger的主要项目
Swagger是一组开源项目,其中主要项目如下:
- Swagger-tools:提供各种与Swagger进行集成和交互的工具。例如模式检验、Swagger 1.2文档转换成Swagger 2.0文档等功能。
- Swagger-core: 用于Java/Scala的的Swagger实现。与JAX-RS(Jersey、Resteasy、CXF…)、Servlets和Play框架进行集成。
- Swagger-js: 用于JavaScript的Swagger实现。
- Swagger-node-express: Swagger模块,用于node.js的Express web应用框架。
- Swagger-ui:一个无依赖的HTML、JS和CSS集合,可以为Swagger兼容API动态生成优雅文档。
- Swagger-codegen:一个模板驱动引擎,通过分析用户Swagger资源声明以各种语言生成客户端代码。
三、引入Swagger依赖
在pom.xml中加入swagger2的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfoxgroupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2artifactId>
<version>2.9.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfoxgroupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-uiartifactId>
<version>2.9.2version>
dependency>
四、创建Swagger2配置类
在Application.java同级目录下创建Swagger2的配置类Swagger2.java
@Configuration:表明它是一个配置类。
@EnableSwagger2:开启swagger2。
createRestApi():创建Docket的Bean。
apiInfo():创建该API的基本信息,这些基本信息会展现在文档页面中。
apis():指定扫描的包会生成文档。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
/**
* Swagger2配置类
* 在与spring boot集成时,放在与Application.java同级的目录下。
* 通过@Configuration注解,让Spring来加载该类配置。
* 再通过@EnableSwagger2注解来启用Swagger2。
*/
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class Swagger2 {
/**
* 创建API应用
* apiInfo() 增加API相关信息
* 通过select()函数返回一个ApiSelectorBuilder实例,用来控制哪些接口暴露给Swagger来展现,
* 本例采用指定扫描的包路径来定义指定要建立API的目录。
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.test.helloworld.controller"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
/**
* 创建该API的基本信息(这些基本信息会展现在文档页面中)
* 访问地址:http://项目实际地址/swagger-ui.html
*
* @return
*/
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("Spring Boot中使用Swagger2构建RESTful APIs")
.description("更多请关注http://www.baidu.com")
.termsOfServiceUrl("http://www.baidu.com")
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
}
五、添加文档内容
swagger通过注解表明该接口会生成文档,包括接口名、请求方法、参数、返回信息的等等。
Swagger使用的注解及其说明:
swagger通过注解表明该接口会生成文档,包括接口名、请求方法、参数、返回信息的等等。
Swagger使用的注解及其说明:
1、@Api:用在请求的类上,表示对类的说明
tags="说明该类的作用,可以在UI界面上看到的注解"
value="该参数没什么意义,在UI界面上也看不到,所以不需要配置"
示例:
@Api(tags="APP用户注册Controller")
2、@ApiOperation:用在请求的方法上,说明方法的用途、作用
value="说明方法的用途、作用"
notes="方法的备注说明"
示例:
@ApiOperation(value="用户注册",notes="手机号、密码都是必输项,年龄随边填,但必须是数字")
3、@ApiImplicitParams:用在请求的方法上,表示一组参数说明
@ApiImplicitParam:用在@ApiImplicitParams注解中,指定一个请求参数的各个方面
name:参数名
value:参数的汉字说明、解释
required:参数是否必须传(true | false)
paramType:参数放在哪个地方
· header --> 请求参数的获取:@RequestHeader
· query --> 请求参数的获取:@RequestParam
· path(用于restful接口)--> 请求参数的获取:@PathVariable
· body(不常用)
· form(不常用)
dataType:参数类型,默认String,其它值dataType="Integer"
defaultValue:参数的默认值
示例:
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name="mobile",value="手机号",required=true,paramType="form"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name="password",value="密码",required=true,paramType="form"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name="age",value="年龄",required=true,paramType="form",dataType="Integer")
})
4、@ApiResponses:用在请求的方法上,表示一组响应
@ApiResponse:用在@ApiResponses中,一般用于表达一个错误的响应信息
code:数字,例如400
message:信息,例如"请求参数没填好"
response:抛出异常的类
示例:
@ApiOperation(value = "select1请求",notes = "多个参数,多种的查询参数类型")
@ApiResponses({
@ApiResponse(code=400,message="请求参数没填好"),
@ApiResponse(code=404,message="请求路径没有或页面跳转路径不对")
})
5、@ApiModel:用于响应类上,表示一个返回响应数据的信息
(这种一般用在post创建的时候,使用@RequestBody这样的场景,请求参数无法使用@ApiImplicitParam注解进行描述的时候)
@ApiModelProperty:用在属性上,描述响应类的属性
示例:
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import java.io.Serializable;
@ApiModel(description= "返回响应数据")
public class RestMessage implements Serializable{
@ApiModelProperty(value = "是否成功")
private boolean success=true;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "返回对象")
private Object data;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "错误编号")
private Integer errCode;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "错误信息")
private String message;
/* getter/setter */
}
六、示例说明
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
/**
* 一个用来测试swagger注解的控制器
* 注意@ApiImplicitParam的使用会影响程序运行,如果使用不当可能造成控制器收不到消息
*
* @author
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/say")
@Api(value = "SayController|一个用来测试swagger注解的控制器")
public class SayController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/getUserName", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ApiOperation(value = "根据用户编号获取用户姓名", notes = "test: 仅1和2有正确返回")
@ApiImplicitParam(paramType = "query", name = "userNumber", value = "用户编号", required = true, dataType = "Integer")
public String getUserName(@RequestParam Integer userNumber) {
if (userNumber == 1) {
return "小浦";
} else if (userNumber == 2) {
return "小招";
} else {
return "未知";
}
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/updatePassword")
@ApiOperation(value = "修改用户密码", notes = "根据用户id修改密码")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(paramType = "query", name = "userId", value = "用户ID", required = true, dataType = "Integer"),
@ApiImplicitParam(paramType = "query", name = "password", value = "旧密码", required = true, dataType = "String"),
@ApiImplicitParam(paramType = "query", name = "newPassword", value = "新密码", required = true, dataType = "String")
})
public String updatePassword(@RequestParam(value = "userId") Integer userId,
@RequestParam(value = "password") String password,
@RequestParam(value = "newPassword") String newPassword) {
if (userId <= 0 || userId > 2) {
return "未知的用户";
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(password) || StringUtils.isEmpty(newPassword)) {
return "密码不能为空";
}
if (password.equals(newPassword)) {
return "新旧密码不能相同";
}
return "密码修改成功!";
}
}
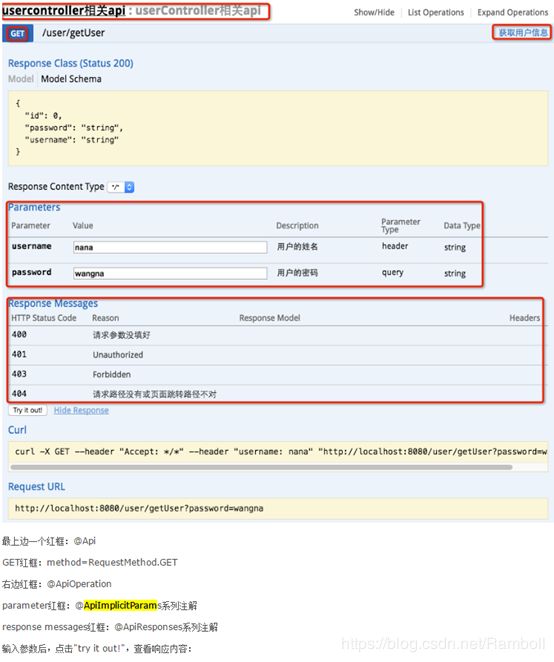
七、查看接口信息
完成上述代码添加后,启动Spring Boot程序,访问:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
如上图,可以看到接口的控制器信息,点击进入可以看到详细信息。

八、注意事项
- paramType会直接影响程序的运行,如果paramType与方法参数获取使用的注解不一致,会影响参数的接收。
例如:
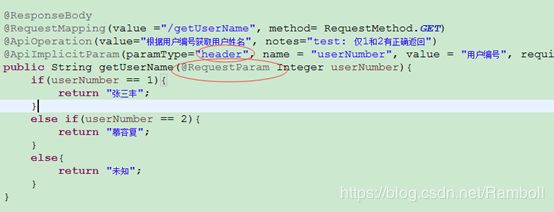
在使用Sawgger UI进行测试时,接收不到参数。
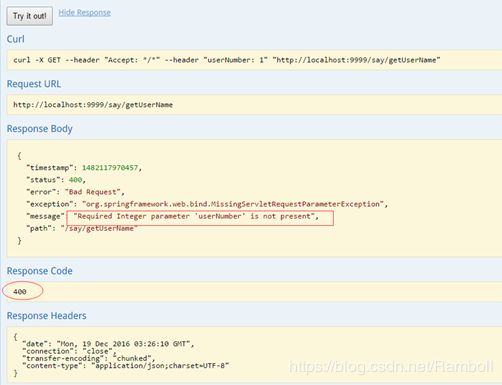
- Conntroller中定义的方法必须在@RequestMapper中显示的指定RequestMethod类型,否则SawggerUI会默认为全类型皆可访问, API列表中会生成多条项目。
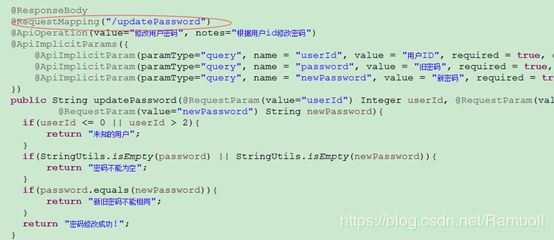
如上图updatePassword()未指定requestMethod,结果生成了7条API信息(如下图)。所以如果没有特殊需求,建议根据实际情况加上requestMethod。
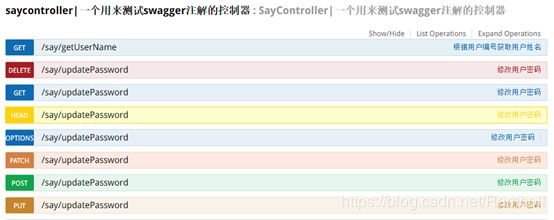
九、Swagger UI面板说明
十、接收对象传参
在POJO上增加@ApiModel注解
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* 医生对象模型
*
* @author
*/
@ApiModel(value = "医生对象模型")
@Data
public class DemoDoctor {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "id", required = true)
private Integer id;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "医生姓名", required = true)
private String name;
}
注意: 在后台采用对象接收参数时,Swagger自带的工具采用的是JSON传参,测试时需要在参数上加上@RequestBody注解,正常运行采用form或URL提交时候请删除。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import com.forezp.helloworld.javaBean.DemoDoctor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.github.pagehelper.PageInfo;
import com.forezp.api.exception.HttpStatus401Exception;
import com.forezp.api.model.base.DemoDoctor;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
/**
* 医生类
*
* @author
*/
@RequestMapping("/api/v1")
@Controller
@Api(value = "DoctorTestController-医生信息接口")
public class DoctorTestController {
/**
* 添加医生
*
* 在使用对象封装参数进行传参时,需要在该对象添加注解,将其注册到swagger中
*
* @param doctor 医生类对象
* @return
* @throws Exception
* @link com.zhongying.api.model.base.DemoDoctor
*
* 注意: 在后台采用对象接收参数时,Swagger自带的工具采用的是JSON传参,
* 测试时需要在参数上加入@RequestBody,正常运行采用form或URL提交时候请删除。
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/doctor", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ApiOperation(value = "添加医生信息", notes = "")
public String addDoctor(@RequestBody DemoDoctor doctor) throws Exception {
if (null == doctor || doctor.getId() == null) {
throw new HttpStatus401Exception("添加医生失败", "DT3388", "未知原因", "请联系管理员");
}
try {
System.out.println("成功----------->" + doctor.getName());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new HttpStatus401Exception("添加医生失败", "DT3388", "未知原因", "请联系管理员");
}
return doctor.getId().toString();
}
/**
* 删除医生
*
* @param doctorId 医生ID
* @return
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/doctor/{doctorId}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ApiOperation(value = "删除医生信息", notes = "")
@ApiImplicitParam(paramType = "query", name = "doctorId", value = "医生ID", required = true, dataType = "Integer")
public String deleteDoctor(@RequestParam Integer doctorId) {
if (doctorId > 2) {
return "删除失败";
}
return "删除成功";
}
/**
* 修改医生信息
*
* @param doctorId 医生ID
* @param doctor 医生信息
* @return
* @throws HttpStatus401Exception
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/doctor/{doctorId}", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ApiOperation(value = "修改医生信息", notes = "")
@ApiImplicitParam(paramType = "query", name = "doctorId", value = "医生ID", required = true, dataType = "Integer")
public String updateDoctor(@RequestParam Integer doctorId, @RequestBody DemoDoctor doctor) throws HttpStatus401Exception {
if (null == doctorId || null == doctor) {
throw new HttpStatus401Exception("修改医生信息失败", "DT3391", "id不能为空", "请修改");
}
if (doctorId > 5) {
throw new HttpStatus401Exception("医生不存在", "DT3392", "错误的ID", "请更换ID");
}
System.out.println(doctorId);
System.out.println(doctor);
return "修改成功";
}
/**
* 获取医生详细信息
*
* @param doctorId 医生ID
* @return
* @throws HttpStatus401Exception
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/doctor/{doctorId}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ApiOperation(value = "获取医生详细信息", notes = "仅返回姓名..")
@ApiImplicitParam(paramType = "query", name = "doctorId", value = "医生ID", required = true, dataType = "Integer")
public DemoDoctor getDoctorDetail(@RequestParam Integer doctorId) throws HttpStatus401Exception {
System.out.println(doctorId);
if (null == doctorId) {
throw new HttpStatus401Exception("查看医生信息失败", "DT3390", "未知原因", "请联系管理员");
}
if (doctorId > 3) {
throw new HttpStatus401Exception("医生不存在", "DT3392", "错误的ID", "请更换ID");
}
DemoDoctor doctor = new DemoDoctor();
doctor.setId(1);
doctor.setName("测试员");
return doctor;
}
/**
* 获取医生列表
*
* @param pageIndex 当前页数
* @param pageSize 每页记录数
* @param request
* @return
* @throws HttpStatus401Exception
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/doctor", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ApiOperation(value = "获取医生列表", notes = "目前一次全部取,不分页")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(paramType = "header", name = "token", value = "token", required = true, dataType = "String"),
@ApiImplicitParam(paramType = "query", name = "pageIndex", value = "当前页数", required = false, dataType = "String"),
@ApiImplicitParam(paramType = "query", name = "pageSize", value = "每页记录数", required = true, dataType = "String"),
})
public PageInfo<DemoDoctor> getDoctorList(@RequestParam(value = "pageIndex", required = false, defaultValue = "1") Integer pageIndex,
@RequestParam(value = "pageSize", required = false) Integer pageSize,
HttpServletRequest request) throws HttpStatus401Exception {
String token = request.getHeader("token");
if (null == token) {
throw new HttpStatus401Exception("没有权限", "SS8888", "没有权限", "请查看操作文档");
}
if (null == pageSize) {
throw new HttpStatus401Exception("每页记录数不粗安在", "DT3399", "不存在pageSize", "请查看操作文档");
}
DemoDoctor doctor1 = new DemoDoctor();
doctor1.setId(1);
doctor1.setName("测试员1");
DemoDoctor doctor2 = new DemoDoctor();
doctor2.setId(2);
doctor2.setName("测试员2");
List<DemoDoctor> doctorList = new ArrayList<DemoDoctor>();
doctorList.add(doctor1);
doctorList.add(doctor2);
return new PageInfo<DemoDoctor>(doctorList);
}
}
如请求需要在header增加额外参数,可以参考getDoctorList()的做法,使用request接收。
@ApiImplicitParam(paramType = “header”, name = “token”, value = “token”, required = true, dataType = “String”)
String token = request.getHeader(“token”);
十一、参考资料
https://blog.csdn.net/sanyaoxu_2/article/details/80555328
https://blog.csdn.net/jia20003/article/details/50700736
http://blog.didispace.com/springbootswagger2/
Swagger官网 :http://swagger.io/
Spring Boot & Swagger UI : http://fruzenshtein.com/spring-boot-swagger-ui/
Github:https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-core/wiki/Annotations