源代码:spark-shell解读
1.spark-shell启动指定master
./bin/spark-shell --master local[4] --jars code.jar 2.错误:System memory 239075328 must be at least 471859200
[root@biluos spark-2.2.0-bin-hadoop2.7]# bin/spark-shell
Setting default log level to "WARN".
To adjust logging level use sc.setLogLevel(newLevel). For SparkR, use setLogLevel(newLevel).
18/03/30 15:46:14 WARN NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
18/03/30 15:46:15 ERROR SparkContext: Error initializing SparkContext.
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: System memory 239075328 must be at least 471859200. Please increase heap size using the --driver-memory option or spark.driver.memory in Spark configuration.
at org.apache.spark.memory.UnifiedMemoryManager$.getMaxMemory(UnifiedMemoryManager.scala:217)
org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit$.org$apache$spark$deploy$SparkSubmit$$runMain(SparkSubmit.scala:755)
at org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit$.doRunMain$1(SparkSubmit.scala:180)
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: System memory 239075328 must be at least 471859200. Please increase heap size using the --driver-memory option or spark.driver.memory in Spark configuration.
at org.apache.spark.memory.UnifiedMemoryManager$.getMaxMemory(UnifiedMemoryManager.scala:217)
:14: error: not found: value spark
import spark.implicits._
^
:14: error: not found: value spark
import spark.sql
^
Welcome to
____ __
/ __/__ ___ _____/ /__
_\ \/ _ \/ _ `/ __/ '_/
/___/ .__/\_,_/_/ /_/\_\ version 2.2.0
/_/
Using Scala version 2.11.8 (Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM, Java 1.8.0_121)
Type in expressions to have them evaluated.
Type :help for more information. 这个原因是内存不够,修改spark-env.sh
SPARK_DRIVER_MEMORY=1024M2.源码解析
2.1 spark-shell.sh
#
# Shell script for starting the Spark Shell REPL
cygwin=false
case "$(uname)" in
CYGWIN*) cygwin=true;;
esac
# Enter posix mode for bash
set -o posix
# set 是显示所有变量 -o 选项名 打开该选项
# +o 选项名 关闭该选项
# 如果不写选项名,列出所有选项的状态
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
source "$(dirname "$0")"/find-spark-home
fi
export _SPARK_CMD_USAGE="Usage: ./bin/spark-shell [options]"
# SPARK-4161: scala does not assume use of the java classpath,
# so we need to add the "-Dscala.usejavacp=true" flag manually. We
# do this specifically for the Spark shell because the scala REPL
# has its own class loader, and any additional classpath specified
# through spark.driver.extraClassPath is not automatically propagated.
SPARK_SUBMIT_OPTS="$SPARK_SUBMIT_OPTS -Dscala.usejavacp=true"
# 修改为:
# SPARK_SUBMIT_OPTS="$SPARK_SUBMIT_OPTS -Dscala.usejavacp=true -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=10207 -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false"
function main() {
if $cygwin; then
# Workaround for issue involving JLine and Cygwin
# (see http://sourceforge.net/p/jline/bugs/40/).
# If you're using the Mintty terminal emulator in Cygwin, may need to set the
# "Backspace sends ^H" setting in "Keys" section of the Mintty options
# (see https://github.com/sbt/sbt/issues/562).
stty -icanon min 1 -echo > /dev/null 2>&1
export SPARK_SUBMIT_OPTS="$SPARK_SUBMIT_OPTS -Djline.terminal=unix"
# 这里执行了spark-submit脚本
"${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-submit --class org.apache.spark.repl.Main --name "Spark shell" "$@"
stty icanon echo > /dev/null 2>&1
else
export SPARK_SUBMIT_OPTS
"${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-submit --class org.apache.spark.repl.Main --name "Spark shell" "$@"
fi
}
# Copy restore-TTY-on-exit functions from Scala script so spark-shell exits properly even in
# binary distribution of Spark where Scala is not installed
exit_status=127
saved_stty=""
# restore stty settings (echo in particular)
function restoreSttySettings() {
stty $saved_stty
saved_stty=""
}
function onExit() {
if [[ "$saved_stty" != "" ]]; then
restoreSttySettings
fi
exit $exit_status
}
# to reenable echo if we are interrupted before completing.
trap onExit INT
# save terminal settings
saved_stty=$(stty -g 2>/dev/null)
# clear on error so we don't later try to restore them
if [[ ! $? ]]; then
saved_stty=""
fi
main "$@"
# record the exit status lest it be overwritten:
# then reenable echo and propagate the code.
exit_status=$?
onExit
这里执行了spark-submit脚本
然后看spark-submit脚本
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
source "$(dirname "$0")"/find-spark-home
fi
# disable randomized hash for string in Python 3.3+
export PYTHONHASHSEED=0
# 这里可以看到执行了spark-class脚本
exec "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-class org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit "$@"
继续看spark-class脚本
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
source "$(dirname "$0")"/find-spark-home
fi
. "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/load-spark-env.sh
# Find the java binary 这一段,主要是寻找java命令
if [ -n "${JAVA_HOME}" ]; then
RUNNER="${JAVA_HOME}/bin/java"
else
if [ "$(command -v java)" ]; then
RUNNER="java"
else
echo "JAVA_HOME is not set" >&2
exit 1
fi
# Find Spark jars. 寻找spark的jar包 这里如果我们的jar包数量多,而且内容大,可以事先放到每个机器的对应目录下,这里是一个优化点
if [ -d "${SPARK_HOME}/jars" ]; then
SPARK_JARS_DIR="${SPARK_HOME}/jars"
else
SPARK_JARS_DIR="${SPARK_HOME}/assembly/target/scala-$SPARK_SCALA_VERSION/jars"
fi
if [ ! -d "$SPARK_JARS_DIR" ] && [ -z "$SPARK_TESTING$SPARK_SQL_TESTING" ]; then
echo "Failed to find Spark jars directory ($SPARK_JARS_DIR)." 1>&2
echo "You need to build Spark with the target \"package\" before running this program." 1>&2
exit 1
else
LAUNCH_CLASSPATH="$SPARK_JARS_DIR/*"
fi
# Add the launcher build dir to the classpath if requested.
if [ -n "$SPARK_PREPEND_CLASSES" ]; then
LAUNCH_CLASSPATH="${SPARK_HOME}/launcher/target/scala-$SPARK_SCALA_VERSION/classes:$LAUNCH_CLASSPATH"
fi
# For tests
if [[ -n "$SPARK_TESTING" ]]; then
unset YARN_CONF_DIR
unset HADOOP_CONF_DIR
fi
# The launcher library will print arguments separated by a NULL character, to allow arguments with
# characters that would be otherwise interpreted by the shell. Read that in a while loop, populating
# an array that will be used to exec the final command.
# 启动程序库将打印由NULL字符分隔的参数,以允许与shell进行其他解释的字符进行参数。在while循环中读取它,填充将用于执行最终命令的数组。
#
# The exit code of the launcher is appended to the output, so the parent shell removes it from the
# command array and checks the value to see if the launcher succeeded.
# 启动程序的退出代码被追加到输出,因此父shell从命令数组中删除它,并检查其值,看看启动器是否成功。
# 这里spark启动了以SparkSubmit为主类的JVM进程。
build_command() {
"$RUNNER" -Xmx128m -cp "$LAUNCH_CLASSPATH" org.apache.spark.launcher.Main "$@"
printf "%d\0" $?
}
# Turn off posix mode since it does not allow process substitution
# 关闭posix模式,因为它不允许进程替换。
set +o posix
CMD=()
while IFS= read -d '' -r ARG; do
CMD+=("$ARG")
done < <(build_command "$@")
COUNT=${#CMD[@]}
LAST=$((COUNT - 1))
LAUNCHER_EXIT_CODE=${CMD[$LAST]}
# Certain JVM failures result in errors being printed to stdout (instead of stderr), which causes
# the code that parses the output of the launcher to get confused. In those cases, check if the
# exit code is an integer, and if it's not, handle it as a special error case.
# 某些JVM失败会导致错误被打印到stdout(而不是stderr),这会导致解析启动程序输出的代码变得混乱。
# 在这些情况下,检查退出代码是否为整数,如果不是,将其作为特殊的错误处理。
if ! [[ $LAUNCHER_EXIT_CODE =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]]; then
echo "${CMD[@]}" | head -n-1 1>&2
exit 1
fi
if [ $LAUNCHER_EXIT_CODE != 0 ]; then
exit $LAUNCHER_EXIT_CODE
fi
CMD=("${CMD[@]:0:$LAST}")
exec "${CMD[@]}"
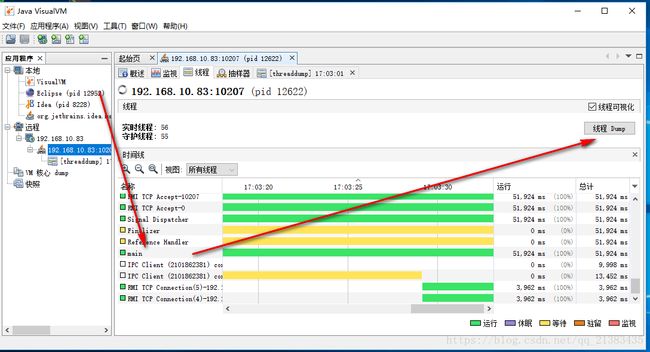
2.2 远程监控
为了方便在本地对Spark进行远程监控,在spark-shell.sh脚本中,添加一些配置
# 修改为:
# SPARK_SUBMIT_OPTS="$SPARK_SUBMIT_OPTS -Dscala.usejavacp=true -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=10207 -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false"
然后远程执行spark-shell
[root@bigdata02 spark]# bin/spark-shell
Setting default log level to "WARN".
To adjust logging level use sc.setLogLevel(newLevel). For SparkR, use setLogLevel(newLevel).
SLF4J: Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings.
SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/opt/hzjs/spark-2.1.1-bin-hadoop2.7/jars_test/slf4j-log4j12-1.7.16.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/opt/hzjs/spark-2.1.1-bin-hadoop2.7/jars/slf4j-log4j12-1.7.16.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#multiple_bindings for an explanation.
SLF4J: Actual binding is of type [org.slf4j.impl.Log4jLoggerFactory]
18/04/12 16:57:46 WARN spark.SparkConf:
SPARK_WORKER_INSTANCES was detected (set to '2').
This is deprecated in Spark 1.0+.
Please instead use:
- ./spark-submit with --num-executors to specify the number of executors
- Or set SPARK_EXECUTOR_INSTANCES
- spark.executor.instances to configure the number of instances in the spark config.
Spark context Web UI available at http://192.168.10.83:4040
Spark context available as 'sc' (master = local[*], app id = local-1523523467622).
Spark session available as 'spark'.
Welcome to
____ __
/ __/__ ___ _____/ /__
_\ \/ _ \/ _ `/ __/ '_/
/___/ .__/\_,_/_/ /_/\_\ version 2.1.0
/_/
Using Scala version 2.11.8 (Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM, Java 1.8.0_77)
Type in expressions to have them evaluated.
Type :help for more information.
scala> 本地打开jvisualvm.exe
这里的端口要和配置的一样
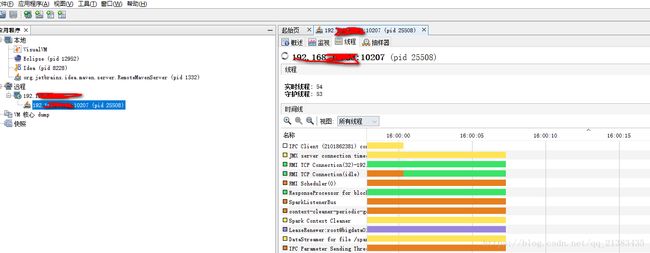
查看效果
3.查看调用结构
查看线程,然后找到main
可以找到main的信息
"main" - Thread t@1
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
at java.io.FileInputStream.read0(Native Method)
at java.io.FileInputStream.read(FileInputStream.java:207)
at jline.internal.NonBlockingInputStream.read(NonBlockingInputStream.java:169)
- locked <63f65caa> (a jline.internal.NonBlockingInputStream)
at jline.internal.NonBlockingInputStream.read(NonBlockingInputStream.java:137)
at jline.internal.NonBlockingInputStream.read(NonBlockingInputStream.java:246)
at jline.internal.InputStreamReader.read(InputStreamReader.java:261)
- locked <63f65caa> (a jline.internal.NonBlockingInputStream)
at jline.internal.InputStreamReader.read(InputStreamReader.java:198)
- locked <63f65caa> (a jline.internal.NonBlockingInputStream)
at jline.console.ConsoleReader.readCharacter(ConsoleReader.java:2145)
at jline.console.ConsoleReader.readLine(ConsoleReader.java:2349)
at jline.console.ConsoleReader.readLine(ConsoleReader.java:2269)
at scala.tools.nsc.interpreter.jline.InteractiveReader.readOneLine(JLineReader.scala:57)
at scala.tools.nsc.interpreter.InteractiveReader$class.readLine(InteractiveReader.scala:38)
at scala.tools.nsc.interpreter.jline.InteractiveReader.readLine(JLineReader.scala:28)
at scala.tools.nsc.interpreter.ILoop.readOneLine(ILoop.scala:404)
at scala.tools.nsc.interpreter.ILoop.loop(ILoop.scala:413)
at scala.tools.nsc.interpreter.ILoop$$anonfun$process$1.apply$mcZ$sp(ILoop.scala:923)
at scala.tools.nsc.interpreter.ILoop$$anonfun$process$1.apply(ILoop.scala:909)
at scala.tools.nsc.interpreter.ILoop$$anonfun$process$1.apply(ILoop.scala:909)
at scala.reflect.internal.util.ScalaClassLoader$.savingContextLoader(ScalaClassLoader.scala:97)
at scala.tools.nsc.interpreter.ILoop.process(ILoop.scala:909)
at org.apache.spark.repl.Main$.doMain(Main.scala:68)
at org.apache.spark.repl.Main$.main(Main.scala:51)
at org.apache.spark.repl.Main.main(Main.scala)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)
at org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit$.org$apache$spark$deploy$SparkSubmit$$runMain(SparkSubmit.scala:738)
at org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit$.doRunMain$1(SparkSubmit.scala:187)
at org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit$.submit(SparkSubmit.scala:212)
at org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit$.main(SparkSubmit.scala:126)
at org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit.main(SparkSubmit.scala)
Locked ownable synchronizers:
- None
然后从这里可以看到,main线程的栈信息中可以看到程序的调用顺序:sparkSubmit.main ---> repl.main --> lLoop.process
3.1 源码分析
根据这句话
"${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-submit --class org.apache.spark.repl.Main --name "Spark shell" "$@"我们看到使用bin/spark-submit去先运行了org.apache.spark.repl.Main的main方法
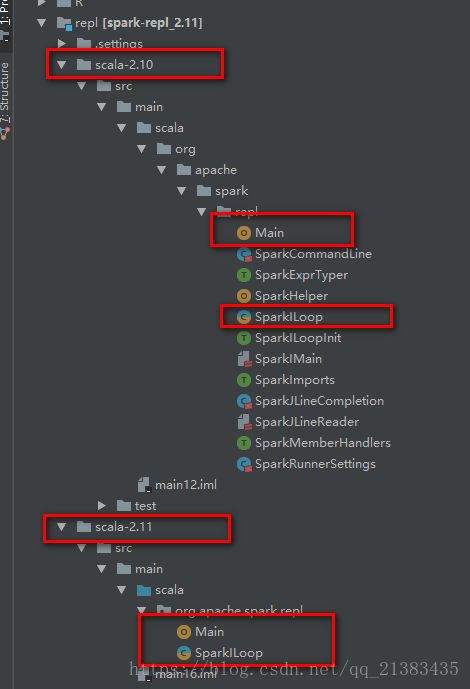
可以看到有俩,但是暂且不看2.10的因为毕竟老了一辈,而且还那么多文件,表示不爽,直接看新的
先看main对象方法
前几行
日志
// 初始化日志
initializeLogIfNecessary(true) protected def initializeLogIfNecessary(isInterpreter: Boolean): Unit = {
// initialized默认为false,这里为true
if (!Logging.initialized) {
Logging.initLock.synchronized {
// initialized默认为false,这里为true
if (!Logging.initialized) {
// 默认isInterpreter为true
initializeLogging(isInterpreter)
}
}
}
}/**
* 初始化日志
* @param isInterpreter
*/
private def initializeLogging(isInterpreter: Boolean): Unit = {
// Don't use a logger in here, as this is itself occurring during initialization of a logger
// If Log4j 1.2 is being used, but is not initialized, load a default properties file
// 在这里不要使用logger,因为如果Log4j 1.2被使用,但是没有初始化,加载一个默认属性文件,就会发生这种情况。
val binderClass = StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton.getLoggerFactoryClassStr
// This distinguishes the log4j 1.2 binding, currently
// org.slf4j.impl.Log4jLoggerFactory, from the log4j 2.0 binding, currently
// org.apache.logging.slf4j.Log4jLoggerFactory
// 这区分了log4j 1.2绑定,目前是org.slf4j.impl。log4j 2.0绑定的Log4jLoggerFactory,
// 当前org.apache.logging.slf4j.Log4jLoggerFactory。
val usingLog4j12 = "org.slf4j.impl.Log4jLoggerFactory".equals(binderClass)
if (usingLog4j12) {
val log4j12Initialized = LogManager.getRootLogger.getAllAppenders.hasMoreElements
// scalastyle:off println
if (!log4j12Initialized) {
val defaultLogProps = "org/apache/spark/log4j-defaults.properties"
Option(Utils.getSparkClassLoader.getResource(defaultLogProps)) match {
case Some(url) =>
PropertyConfigurator.configure(url)
// Using Spark's default log4j profile: org/apache/spark/log4j-defaults.properties 第一句话
System.err.println(s"Using Spark's default log4j profile: $defaultLogProps")
case None =>
System.err.println(s"Spark was unable to load $defaultLogProps")
}
}
if (isInterpreter) {
// Use the repl's main class to define the default log level when running the shell,
// overriding the root logger's config if they're different.
// 使用repl的主类来定义运行shell时的默认日志级别,如果它们不同,则重写根日志记录器的配置。
val rootLogger = LogManager.getRootLogger()
val replLogger = LogManager.getLogger(logName)
// 日志级别默认为warn
val replLevel = Option(replLogger.getLevel()).getOrElse(Level.WARN)
if (replLevel != rootLogger.getEffectiveLevel()) {
System.err.printf("Setting default log level to \"%s\".\n", replLevel)
System.err.println("To adjust logging level use sc.setLogLevel(newLevel). " +
"For SparkR, use setLogLevel(newLevel).")
rootLogger.setLevel(replLevel)
}
}
// scalastyle:on println
}
Logging.initialized = true
// Force a call into slf4j to initialize it. Avoids this happening from multiple threads
// and triggering this: http://mailman.qos.ch/pipermail/slf4j-dev/2010-April/002956.html
log
}原来ctrl+c能终止程序的原因在这里
main对象
// z注册一个信号事件:当我们按下ctrl+c键的时候,会调用对应的信号处理程序,先获取活动的SparkContext,然后取消全部的job
Signaling.cancelOnInterrupt()注册一个ctrl+c监听事件
/**
* Register a SIGINT handler, that terminates all active spark jobs or terminates
* when no jobs are currently running.
* This makes it possible to interrupt a running shell job by pressing Ctrl+C.
*
* 注册一个SIGINT处理程序,在当前没有作业时终止所有活跃的spark作业或终止。
* 这使得通过按Ctrl+C来中断运行的shell任务成为可能。
*
* 当我们按下ctrl+c键的时候,会调用对应的信号处理程序,先获取活动的SparkContext,然后取消全部的job
*/
def cancelOnInterrupt(): Unit = SignalUtils.register("INT") {
// 获取活动的SparkContext,并且遍历
SparkContext.getActive.map { ctx =>
if (!ctx.statusTracker.getActiveJobIds().isEmpty) {
logWarning("Cancelling all active jobs, this can take a while. " +
"Press Ctrl+C again to exit now.")
ctx.cancelAllJobs()
true
} else {
false
}
}.getOrElse(false)
}
然后调用了SparkContext的方法
/** Cancel all jobs that have been scheduled or are running.
* 取消所有的jobs已被预定或运行。
* */
def cancelAllJobs() {
assertNotStopped()
dagScheduler.cancelAllJobs()
}然后调用了DAG的方法
/**
* Cancel all jobs that are running or waiting in the queue.
* 取消正在运行或在队列中等待的所有作业。
*/
def cancelAllJobs(): Unit = {
eventProcessLoop.post(AllJobsCancelled)
}
正式看我们的main函数
/**
* main方法
* @param args
*/
def main(args: Array[String]) {
// 这里先new SparkILoop,然后才是调用doMain()
doMain(args, new SparkILoop)
}
然后看new SparkILoop,但是里面都是方法,所以先不管,然后看看你doMain()
// Visible for testing 可见测试
private[repl] def doMain(args: Array[String], _interp: SparkILoop): Unit = {
interp = _interp
val jars = Utils.getUserJars(conf, isShell = true).mkString(File.pathSeparator)
val interpArguments = List(
"-Yrepl-class-based",
"-Yrepl-outdir", s"${outputDir.getAbsolutePath}",
"-classpath", jars
) ++ args.toList
val settings = new GenericRunnerSettings(scalaOptionError)
// 一个可变对象设置。
settings.processArguments(interpArguments, true)
// 默认为false,这里为true
if (!hasErrors) {
/** 这里调用lLoop的process() --> SparkILoop.loadFiles --> SparkILoop.initializeSpark() */
interp.process(settings) // Repl starts and goes in loop of R.E.P.L
Option(sparkContext).foreach(_.stop)
}
}先看这一句 interp.process(settings),这句话调用了scala.tools.nsc.interpreter.ILoop的process方法。
// start an interpreter with the given settings
def process(settings: Settings): Boolean = savingContextLoader {
this.settings = settings
createInterpreter()
// sets in to some kind of reader depending on environmental cues
in = in0.fold(chooseReader(settings))(r => SimpleReader(r, out, interactive = true))
globalFuture = future {
intp.initializeSynchronous()
loopPostInit()
!intp.reporter.hasErrors
}
loadFiles(settings)
printWelcome()
try loop() match {
case LineResults.EOF => out print Properties.shellInterruptedString
case _ =>
}
catch AbstractOrMissingHandler()
finally closeInterpreter()
true
}这里面主要调用了下面两个方法
loadFiles(settings)
printWelcome()而SparkILoop继承了scala.tools.nsc.interpreter.ILoop,并且重写了上面两个方法,先看重写的loadFiles方法
/**
* We override `loadFiles` because we need to initialize Spark *before* the REPL
* sees any files, so that the Spark context is visible in those files. This is a bit of a
* hack, but there isn't another hook available to us at this point.
*
*
*
*
* lLoop的process滴啊用了loadFiles方法,而,SparkLoop继承了lloop并且重写了loadFiles()方法
*/
override def loadFiles(settings: Settings): Unit = {
/**
* 这里调用了SparkLoop的初始化方法
*/
initializeSpark()
super.loadFiles(settings)
}这里调用了初始化方法initializeSpark()
def initializeSpark() {
intp.beQuietDuring {
// initializeSpark向交互式shell发送一大串代码,Scala的交互shell将调用org.apache.spark.repl.Main的
// createSparkSession方法创建Spark-Session。我们看到常量spark将持有SparkSession的引用,并且sc持有
// SparkSession内部初始化好的SparkContext.所以我们才能在spark-shell的交互式shell中使用sc和spark.
/**
* val spark = if (org.apache.spark.repl.Main.sparkSession != null) {
* org.apache.spark.repl.Main.sparkSession
* } else {
* org.apache.spark.repl.Main.createSparkSession()
* }
*
* 这里开始org.apache.spark.repl.Main.sparkSession为null,所以调用org.apache.spark.repl.Main.createSparkSession()
* 否则重用这个org.apache.spark.repl.Main.sparkSession
*/
processLine("""
@transient val spark = if (org.apache.spark.repl.Main.sparkSession != null) {
org.apache.spark.repl.Main.sparkSession
} else {
org.apache.spark.repl.Main.createSparkSession()
}
@transient val sc = {
val _sc = spark.sparkContext
if (_sc.getConf.getBoolean("spark.ui.reverseProxy", false)) {
val proxyUrl = _sc.getConf.get("spark.ui.reverseProxyUrl", null)
if (proxyUrl != null) {
println(s"Spark Context Web UI is available at ${proxyUrl}/proxy/${_sc.applicationId}")
} else {
println(s"Spark Context Web UI is available at Spark Master Public URL")
}
} else {
_sc.uiWebUrl.foreach {
webUrl => println(s"Spark context Web UI available at ${webUrl}")
}
}
println("Spark context available as 'sc' " +
s"(master = ${_sc.master}, app id = ${_sc.applicationId}).")
println("Spark session available as 'spark'.")
_sc
}
""")
processLine("import org.apache.spark.SparkContext._")
processLine("import spark.implicits._")
processLine("import spark.sql")
processLine("import org.apache.spark.sql.functions._")
replayCommandStack = Nil // remove above commands from session history.
}
}
这里创建了名字为spark和sc的SparkSession对象。
然后看printWelcome() 看子类SparkILoop的
/** Print a welcome message */
override def printWelcome() {
import org.apache.spark.SPARK_VERSION
echo("""Welcome to
____ __
/ __/__ ___ _____/ /__
_\ \/ _ \/ _ `/ __/ '_/
/___/ .__/\_,_/_/ /_/\_\ version %s
/_/
""".format(SPARK_VERSION))
val welcomeMsg = "Using Scala %s (%s, Java %s)".format(
versionString, javaVmName, javaVersion)
echo(welcomeMsg)
echo("Type in expressions to have them evaluated.")
echo("Type :help for more information.")
}看到这里我们知道了,原来每次执行Spark-shell打印的welcom信息了