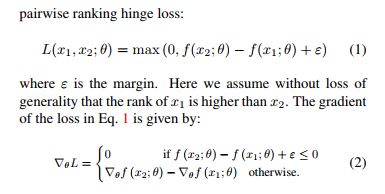- AI+Python赋能!长时序植被遥感动态分析全攻略:从物候提取到生态评估
梦想的初衷~
土壤植被遥感人工智能遥感植被土壤
在遥感技术与人工智能深度融合的2025年,AI大模型正重塑长时序植被遥感数据分析范式。从Landsat/Sentinel卫星数据的智能化去云处理,到MODIS植被产品的AI辅助质量控制,以ChatGPT、DeepSeeK为代表的大模型技术已成为提升遥感数据处理效率与精度的核心工具——尤其在长时序植被动态监测、物候期精准提取、时空变异归因分析及生态环境质量评估等领域,展现出传统方法难以企及的技术优势
- 天文图像处理:星系分类与天体定位
xcLeigh
计算机视觉CV图像处理分类人工智能AI计算机视觉
天文图像处理:星系分类与天体定位一、前言二、天文图像处理基础2.1天文图像的获取2.2天文图像的格式2.3天文图像处理的基本流程三、天文图像预处理3.1去噪处理3.2平场校正3.3偏置校正四、星系分类4.1星系的分类体系4.2基于特征提取的星系分类方法4.3基于深度学习的星系分类方法五、天体定位5.1天体坐标系统5.2基于星图匹配的天体定位方法5.3基于深度学习的天体定位方法六、总结与展望致读者一
- 深度学习——CNN(3)
飘涯
前言:前面介绍了最基本的Lenet,下面介绍几种其他的网络结构CNN-AlexNet网络结构如下图:从图中可以看出,采用双gpu训练增加LRN归一化层:本质上,这个层也是为了防止激活函数的饱和的。采用dropout防止过拟合基于AlexNet进行微调,诞生了ZF-netCNN-GoogleNetGoogLeNet借鉴了NIN的特性,在原先的卷积过程中附加了11的卷积核加上ReLU激活。这不仅仅提升
- #Datawhale组队学习#7月-强化学习Task1
fzyz123
Datawhale组队学习强化学习人工智能AI
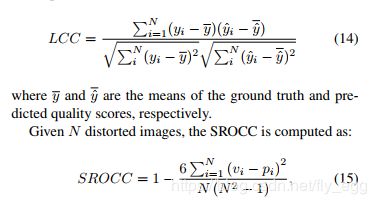
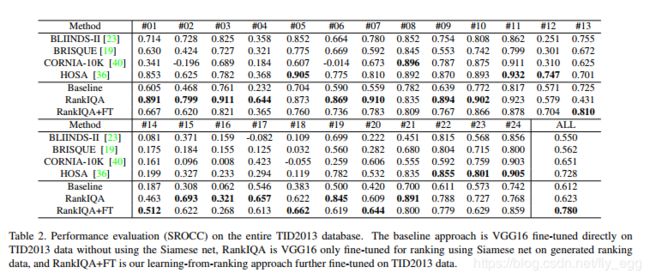
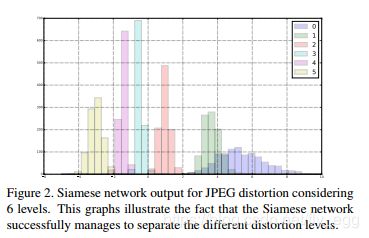
这里是Datawhale组织的组队学习《强化学习入门202507》,Datawhale是一个开源的社区。第一章绪论1.1为什么要学习强化学习?强化学习(ReinforcementLearning,RL)是机器学习中专注于智能体(Agent)如何通过与环境交互学习最优决策策略的分支。与监督学习依赖静态数据集、无监督学习聚焦数据内在结构不同,强化学习的核心在于序贯决策:智能体通过试错探索环境,根据行动
- 微算法科技技术突破:用于前馈神经网络的量子算法技术助力神经网络变革
MicroTech2025
量子计算算法神经网络
随着量子计算和机器学习的迅猛发展,企业界正逐步迈向融合这两大领域的新时代。在这一背景下,微算法科技(NASDAQ:MLGO)成功研发出一套用于前馈神经网络的量子算法,突破了传统神经网络在训练和评估中的性能瓶颈。这一创新性的量子算法以经典的前馈和反向传播算法为基础,借助量子计算的强大算力,极大提升了网络训练和评估效率,并带来了对过拟合的天然抗性。前馈神经网络是深度学习的核心架构,广泛应用于图像分类、
- 图机器学习(13)——图相似性检测
图机器学习(13)——图相似性检测0.前言1.基于图嵌入的方法2.基于图核的方法3.基于GNN的方法4.应用0.前言图机器学习(machinelearning,ML)方法能广泛应用于各类任务,其应用场景涵盖从药物设计到社交网络推荐系统等多个领域。值得注意的是,由于这类方法在设计上具有通用性,同一算法可用于解决不同问题。学习图之间相似性的定量度量是一个关键问题。事实上,这是网络分析的重要步骤,同时也
- 英伟达Triton 推理服务详解
leo0308
基础知识机器人Triton人工智能
1.TritonInferenceServer简介TritonInferenceServer(简称Triton,原名NVIDIATensorRTInferenceServer)是英伟达推出的一个开源、高性能的推理服务器,专为AI模型的部署和推理服务而设计。它支持多种深度学习框架和硬件平台,能够帮助开发者和企业高效地将AI模型部署到生产环境中。Triton主要用于模型推理服务化,即将训练好的模型通过
- Java NLP炼金术:从词袋到深度学习,构建AI时代的语言魔方
墨夶
Java学习资料人工智能java自然语言处理
一、JavaNLP的“三剑客”:框架与工具链1.1ApacheOpenNLP:传统NLP的“瑞士军刀”目标:用词袋模型实现文本分类与实体识别代码实战:文档分类器的“炼成术”//OpenNLP文档分类器(基于词袋模型)importopennlp.tools.doccat.*;importopennlp.tools.util.*;publicclassDocumentClassifier{//训练模型
- PyTorch & TensorFlow速成复习:从基础语法到模型部署实战(附FPGA移植衔接)
阿牛的药铺
算法移植部署pytorchtensorflowfpga开发
PyTorch&TensorFlow速成复习:从基础语法到模型部署实战(附FPGA移植衔接)引言:为什么算法移植工程师必须掌握框架基础?针对光学类产品算法FPGA移植岗位需求(如可见光/红外图像处理),深度学习框架是算法落地的"桥梁"——既要用PyTorch/TensorFlow验证算法可行性,又要将训练好的模型(如CNN、目标检测)转换为FPGA可部署的格式(ONNX、TFLite)。本文采用"
- 深度学习模型表征提取全解析
ZhangJiQun&MXP
教学2024大模型以及算力2021AIpython深度学习人工智能pythonembedding语言模型
模型内部进行表征提取的方法在自然语言处理(NLP)中,“表征(Representation)”指将文本(词、短语、句子、文档等)转化为计算机可理解的数值形式(如向量、矩阵),核心目标是捕捉语言的语义、语法、上下文依赖等信息。自然语言表征技术可按“静态/动态”“有无上下文”“是否融入知识”等维度划分一、传统静态表征(无上下文,词级为主)这类方法为每个词分配固定向量,不考虑其在具体语境中的含义(无法解
- 【Qualcomm】高通SNPE框架简介、下载与使用
Jackilina_Stone
人工智能QualcommSNPE
目录一高通SNPE框架1SNPE简介2QNN与SNPE3Capabilities4工作流程二SNPE的安装与使用1下载2Setup3SNPE的使用概述一高通SNPE框架1SNPE简介SNPE(SnapdragonNeuralProcessingEngine),是高通公司推出的面向移动端和物联网设备的深度学习推理框架。SNPE提供了一套完整的深度学习推理框架,能够支持多种深度学习模型,包括Pytor
- 不同行业的 AI 数据安全与合规实践:7 大核心要点全解析
观熵
人工智能DeepSeek私有化部署
不同行业的AI数据安全与合规实践:7大核心要点全解析关键词AI数据安全、行业合规、私有化部署、数据分类分级、国产大模型、隐私保护、DeepSeek部署摘要随着国产大模型在金融、医疗、政务、教育等关键领域的深入部署,AI系统对数据安全与行业合规提出了更高要求。本文结合DeepSeek私有化部署实战,系统梳理当前各行业主流的数据安全合规标准与落地策略,从数据分类分级、访问控制、审计追踪到敏感信息识别与
- 深度学习篇---昇腾NPU&CANN 工具包
Atticus-Orion
上位机知识篇图像处理篇深度学习篇深度学习人工智能NPU昇腾CANN
介绍昇腾NPU是华为推出的神经网络处理器,具有强大的AI计算能力,而CANN工具包则是面向AI场景的异构计算架构,用于发挥昇腾NPU的性能优势。以下是详细介绍:昇腾NPU架构设计:采用达芬奇架构,是一个片上系统,主要由特制的计算单元、大容量的存储单元和相应的控制单元组成。集成了多个CPU核心,包括控制CPU和AICPU,前者用于控制处理器整体运行,后者承担非矩阵类复杂计算。此外,还拥有AICore
- 深度学习图像分类数据集—桃子识别分类
AI街潜水的八角
深度学习图像数据集深度学习分类人工智能
该数据集为图像分类数据集,适用于ResNet、VGG等卷积神经网络,SENet、CBAM等注意力机制相关算法,VisionTransformer等Transformer相关算法。数据集信息介绍:桃子识别分类:['B1','M2','R0','S3']训练数据集总共有6637张图片,每个文件夹单独放一种数据各子文件夹图片统计:·B1:1601张图片·M2:1800张图片·R0:1601张图片·S3:
- AI MCP教程之 什么是 MCP?利用本地 LLM 、MCP、DeepSeek 集成构建您自己的 AI 驱动工具
知识大胖
NVIDIAGPU和大语言模型开发教程人工智能mcpdeepseek
介绍利用模型上下文协议(MCP)的工具吸引了我们的注意力—将AI变成触手可及的生产力引擎。它们巧妙、高效,让人难以抗拒。但如果您可以将这样的功能添加到自己的工具中,会怎么样呢?在本指南中,我将引导您构建一个具有本地运行的大型语言模型(LLM)和MCP集成的AI工具-让您以类似的方式自动执行利用MCP的工具您喜欢的任务。推荐文章《AnythingLLM教程系列之12AnythingLLM上的Olla
- 使用 Ollama 、 DeepSeek和QWEN的模型上下文协议 (MCP) ,使用本地 LLM 教程的 MCP 服务器
知识大胖
NVIDIAGPU和大语言模型开发教程服务器运维人工智能qwen2vldeepseek
简介模型上下文协议:MCP服务器据称是AI领域的下一个重大改变者,它将使AI代理变得比我们想象的更加先进。MCP或模型上下文协议由Anthropic去年发布,它可以帮助LLM连接软件并对其进行控制。但有一个问题大多数MCP服务器都与ClaudeAI兼容,尤其是ClaudeAI桌面应用程序,但它们有自己的限制。有没有办法我们可以使用本地LLM运行MCP服务器?是的,在这个特定的逐步详细教程中,我们将
- 12 个强大的 DeepSeek AI 提示将彻底改变您的日常生活
知识大胖
NVIDIAGPU和大语言模型开发教程人工智能deepseek
内容写作的最佳提示让我们从写作开始吧。无论您是博主、学生还是社交媒体创作者,这些提示都将帮助您创作出精彩的内容。提示1:“扮演专业文案撰稿人,为[产品/服务]撰写引人注目的广告文案。文案应引人入胜、具有说服力,且字数不得超过100个字。”这使得ChatGPT的响应结构就像真实的广告文案一样。提示2:“以更具吸引力和说服力的方式重写此段落,同时保持含义不变:[插入文本]。”推荐文章《Neo4j上使用
- 使用 Deepseek Zero Coding Experience 创建类似飞扬的小鸟游戏
知识大胖
NVIDIAGPU和大语言模型开发教程游戏deepseekollamajanuspro
简介Flappybird在苹果商店推出后,每天大约能赚5000美元,但后来被苹果故意下架。现在我正尝试使用Deepseek制作这样一款游戏。技术在不断变化,编码知识也在不断变化,只需修改代码即可获得结果。让我们在Deepseek上试试这款游戏:推荐文章《如何在本地电脑上安装和使用DeepSeekR-1》权重1,DeepSeek《Nvidia系列之使用NVIDIAIsaacSim和ROS2的命令行控
- 24GB GPU 中的 DeepSeek R1:Unsloth AI 针对 671B 参数模型进行动态量化
知识大胖
NVIDIAGPU和大语言模型开发教程人工智能deepseekollama
简介最初的DeepSeekR1是一个拥有6710亿个参数的语言模型,UnslothAI团队对其进行了动态量化,将模型大小减少了80%(从720GB减少到131GB),同时保持了强大的性能。当添加模型卸载功能时,该模型可以在24GBVRAM下以低令牌/秒的推理速度运行。推荐文章《本地构建AI智能分析助手之01快速安装,使用PandasAI和Ollama进行数据分析,用自然语言向你公司的数据提问为决策
- 在 Obsidian 中本地使用 DeepSeek — 无需互联网!
知识大胖
NVIDIAGPU和大语言模型开发教程人工智能deepseek
简介您是否想在Obsidian内免费使用类似于ChatGPT的本地LLM?如果是,那么本指南适合您!我将引导您完成在Obsidian中安装和使用DeepSeek-R1模型的确切步骤,这样您就可以在笔记中拥有一个由AI驱动的第二大脑。推荐文章《24GBGPU中的DeepSeekR1:UnslothAI针对671B参数模型进行动态量化》权重1,DeepSeek类《在RaspberryPi上运行语音识别
- 使用 DeepSeek R1 和 Ollama 开发 RAG 系统 使用 DeepSeek R1 和 Ollama 构建强大的 RAG 系统。了解开发智能 AI 解决方案的设置过程、最佳实践和技巧。
知识大胖
NVIDIAGPU和大语言模型开发教程人工智能deepseekollama
简介DeepSeekR1和Ollama提供了用于构建检索增强生成(RAG)系统的强大工具。本指南介绍了使用这些技术开发RAG应用程序的设置、实施和最佳实践。为什么RAG系统会改变游戏规则检索增强生成(RAG)系统结合了搜索和生成AI的优点,可实现精确且准确的情境感知响应。借助DeepSeekR1和Ollama等工具,创建RAG系统不再令人生畏。无论您是构建聊天机器人、知识助手还是AI驱动的搜索引擎
- 【实战AI】macbook M1 本地ollama运行deepseek
东方鲤鱼
chatAImacosaillamaAIGCchatgpt
由于deepseek官网或者Aapi调用会有网络延迟或不响应的情况,故在本地搭建部署;前提条件1.由于需要拉取开源镜像,受网络限制,部分资源在前提中会下载的更快!请自行;2.设备macbookM132G下载ollamaOllama是一款跨平台推理框架客户端(MacOS、Windows、Linux),专为无缝部署大型语言模型(LLM)(如Llama2、Mistral、Llava等)而设计。通过一键式
- NumPy-@运算符详解
GG不是gg
numpynumpy
NumPy-@运算符详解一、@运算符的起源与设计目标1.从数学到代码:符号的统一2.设计目标二、@运算符的核心语法与运算规则1.基础用法:二维矩阵乘法2.一维向量的矩阵语义3.高维数组:批次矩阵运算4.广播机制:灵活的形状匹配三、@运算符与其他乘法方式的核心区别1.对比`np.dot()`2.对比元素级乘法`*`3.对比`np.matrix`的`*`运算符四、典型应用场景:从基础到高阶1.深度学习
- NLP_知识图谱_大模型——个人学习记录
macken9999
自然语言处理知识图谱大模型自然语言处理知识图谱学习
1.自然语言处理、知识图谱、对话系统三大技术研究与应用https://github.com/lihanghang/NLP-Knowledge-Graph深度学习-自然语言处理(NLP)-知识图谱:知识图谱构建流程【本体构建、知识抽取(实体抽取、关系抽取、属性抽取)、知识表示、知识融合、知识存储】-元気森林-博客园https://www.cnblogs.com/-402/p/16529422.htm
- DeepSeek解读道德经 第五十九章
cal_
道德经道德经
一、原文与译文原文:治人事天,莫若啬。夫唯啬,是谓早服;早服谓之重积德;重积德则无不克;无不克则莫知其极;莫知其极,可以有国;有国之母,可以长久。是谓深根固柢,长生久视之道。译文:治理百姓侍奉天道,没有比珍爱能量更重要的。唯有珍惜能量,才叫早作准备;早作准备就是厚积德性;厚积德性则无往不胜;无往不胜则力量无穷;力量无穷便可守护国家;掌握治国根本,方能长久延续。这便是根深柢固、长生久存之道。二、核心
- 解决 Python 包安装失败问题:以 accelerate 为例
在使用Python开发项目时,我们经常会遇到依赖包安装失败的问题。今天,我们就以accelerate包为例,详细探讨一下可能的原因以及解决方法。通过这篇文章,你将了解到Python包安装失败的常见原因、如何切换镜像源、如何手动安装包,以及一些实用的注意事项。一、问题背景在开发一个深度学习项目时,我需要安装accelerate包来优化模型的训练过程。然而,当我运行以下命令时:bash复制pipins
- Golang面试题二(slice,map,chan)
os-lee
go高级golang开发语言后端
目录1.slice的底层实现1.结构体定义2.slice四种初始化方式3.底层函数2.Go语言当中数组和slice的区别是什么?1.长度不同2.函数传参不同3.计算长度方式不同3.slice的扩容机制,有什么注意点扩容机制总结4.扩容前后的Slice是否相同5.深拷贝和浅拷贝浅拷贝(ShallowCopy)深拷贝(DeepCopy)总结6.slice为什么不是线程安全的7.map底层实现8.map
- 在mac m1基于llama.cpp运行deepseek
lama.cpp是一个高效的机器学习推理库,目标是在各种硬件上实现LLM推断,保持最小设置和最先进性能。llama.cpp支持1.5位、2位、3位、4位、5位、6位和8位整数量化,通过ARMNEON、Accelerate和Metal支持Apple芯片,使得在MACM1处理器上运行Deepseek大模型成为可能。1下载llama.cppgitclonehttps://github.com/ggerg
- 从RNN循环神经网络到Transformer注意力机制:解析神经网络架构的华丽蜕变
熊猫钓鱼>_>
神经网络rnntransformer
1.引言在自然语言处理和序列建模领域,神经网络架构经历了显著的演变。从早期的循环神经网络(RNN)到现代的Transformer架构,这一演变代表了深度学习方法在处理序列数据方面的重大进步。本文将深入比较这两种架构,分析它们的工作原理、优缺点,并通过实验结果展示它们在实际应用中的性能差异。2.循环神经网络(RNN)2.1基本原理循环神经网络是专门为处理序列数据而设计的神经网络架构。RNN的核心思想
- Python桌面应用开发的未来——智能化工具与大模型赋能
IronwoodStag78
开发AI智能应用,就下载InsCodeAIIDE,一键接入DeepSeek-R1满血版大模型!标题:Python桌面应用开发的未来——智能化工具与大模型赋能随着人工智能技术的飞速发展,传统软件开发模式正在被重新定义。Python作为一门功能强大且灵活的语言,在桌面应用开发领域一直占据重要地位。然而,面对日益复杂的用户需求和快速变化的技术环境,如何提升开发效率、降低开发门槛,成为开发者亟需解决的问题
- PHP,安卓,UI,java,linux视频教程合集
cocos2d-x小菜
javaUIPHPandroidlinux
╔-----------------------------------╗┆
- 各表中的列名必须唯一。在表 'dbo.XXX' 中多次指定了列名 'XXX'。
bozch
.net.net mvc
在.net mvc5中,在执行某一操作的时候,出现了如下错误:
各表中的列名必须唯一。在表 'dbo.XXX' 中多次指定了列名 'XXX'。
经查询当前的操作与错误内容无关,经过对错误信息的排查发现,事故出现在数据库迁移上。
回想过去: 在迁移之前已经对数据库进行了添加字段操作,再次进行迁移插入XXX字段的时候,就会提示如上错误。
&
- Java 对象大小的计算
e200702084
java
Java对象的大小
如何计算一个对象的大小呢?
- Mybatis Spring
171815164
mybatis
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
CustomerService userService = (CustomerService) ac.getBean("customerService");
Customer cust
- JVM 不稳定参数
g21121
jvm
-XX 参数被称为不稳定参数,之所以这么叫是因为此类参数的设置很容易引起JVM 性能上的差异,使JVM 存在极大的不稳定性。当然这是在非合理设置的前提下,如果此类参数设置合理讲大大提高JVM 的性能及稳定性。 可以说“不稳定参数”
- 用户自动登录网站
永夜-极光
用户
1.目标:实现用户登录后,再次登录就自动登录,无需用户名和密码
2.思路:将用户的信息保存为cookie
每次用户访问网站,通过filter拦截所有请求,在filter中读取所有的cookie,如果找到了保存登录信息的cookie,那么在cookie中读取登录信息,然后直接
- centos7 安装后失去win7的引导记录
程序员是怎么炼成的
操作系统
1.使用root身份(必须)打开 /boot/grub2/grub.cfg 2.找到 ### BEGIN /etc/grub.d/30_os-prober ### 在后面添加 menuentry "Windows 7 (loader) (on /dev/sda1)" {
- Oracle 10g 官方中文安装帮助文档以及Oracle官方中文教程文档下载
aijuans
oracle
Oracle 10g 官方中文安装帮助文档下载:http://download.csdn.net/tag/Oracle%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87API%EF%BC%8COracle%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87%E6%96%87%E6%A1%A3%EF%BC%8Coracle%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0%E6%96%87%E6%A1%A3 Oracle 10g 官方中文教程
- JavaEE开源快速开发平台G4Studio_V3.2发布了
無為子
AOPoraclemysqljavaeeG4Studio
我非常高兴地宣布,今天我们最新的JavaEE开源快速开发平台G4Studio_V3.2版本已经正式发布。大家可以通过如下地址下载。
访问G4Studio网站
http://www.g4it.org
G4Studio_V3.2版本变更日志
功能新增
(1).新增了系统右下角滑出提示窗口功能。
(2).新增了文件资源的Zip压缩和解压缩
- Oracle常用的单行函数应用技巧总结
百合不是茶
日期函数转换函数(核心)数字函数通用函数(核心)字符函数
单行函数; 字符函数,数字函数,日期函数,转换函数(核心),通用函数(核心)
一:字符函数:
.UPPER(字符串) 将字符串转为大写
.LOWER (字符串) 将字符串转为小写
.INITCAP(字符串) 将首字母大写
.LENGTH (字符串) 字符串的长度
.REPLACE(字符串,'A','_') 将字符串字符A转换成_
- Mockito异常测试实例
bijian1013
java单元测试mockito
Mockito异常测试实例:
package com.bijian.study;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.mock;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.mockito.
- GA与量子恒道统计
Bill_chen
JavaScript浏览器百度Google防火墙
前一阵子,统计**网址时,Google Analytics(GA) 和量子恒道统计(也称量子统计),数据有较大的偏差,仔细找相关资料研究了下,总结如下:
为何GA和量子网站统计(量子统计前身为雅虎统计)结果不同?
首先:没有一种网站统计工具能保证百分之百的准确出现该问题可能有以下几个原因:(1)不同的统计分析系统的算法机制不同;(2)统计代码放置的位置和前后
- 【Linux命令三】Top命令
bit1129
linux命令
Linux的Top命令类似于Windows的任务管理器,可以查看当前系统的运行情况,包括CPU、内存的使用情况等。如下是一个Top命令的执行结果:
top - 21:22:04 up 1 day, 23:49, 1 user, load average: 1.10, 1.66, 1.99
Tasks: 202 total, 4 running, 198 sl
- spring四种依赖注入方式
白糖_
spring
平常的java开发中,程序员在某个类中需要依赖其它类的方法,则通常是new一个依赖类再调用类实例的方法,这种开发存在的问题是new的类实例不好统一管理,spring提出了依赖注入的思想,即依赖类不由程序员实例化,而是通过spring容器帮我们new指定实例并且将实例注入到需要该对象的类中。依赖注入的另一种说法是“控制反转”,通俗的理解是:平常我们new一个实例,这个实例的控制权是我
- angular.injector
boyitech
AngularJSAngularJS API
angular.injector
描述: 创建一个injector对象, 调用injector对象的方法可以获得angular的service, 或者用来做依赖注入. 使用方法: angular.injector(modules, [strictDi]) 参数详解: Param Type Details mod
- java-同步访问一个数组Integer[10],生产者不断地往数组放入整数1000,数组满时等待;消费者不断地将数组里面的数置零,数组空时等待
bylijinnan
Integer
public class PC {
/**
* 题目:生产者-消费者。
* 同步访问一个数组Integer[10],生产者不断地往数组放入整数1000,数组满时等待;消费者不断地将数组里面的数置零,数组空时等待。
*/
private static final Integer[] val=new Integer[10];
private static
- 使用Struts2.2.1配置
Chen.H
apachespringWebxmlstruts
Struts2.2.1 需要如下 jar包: commons-fileupload-1.2.1.jar commons-io-1.3.2.jar commons-logging-1.0.4.jar freemarker-2.3.16.jar javassist-3.7.ga.jar ognl-3.0.jar spring.jar
struts2-core-2.2.1.jar struts2-sp
- [职业与教育]青春之歌
comsci
教育
每个人都有自己的青春之歌............但是我要说的却不是青春...
大家如果在自己的职业生涯没有给自己以后创业留一点点机会,仅仅凭学历和人脉关系,是难以在竞争激烈的市场中生存下去的....
&nbs
- oracle连接(join)中使用using关键字
daizj
JOINoraclesqlusing
在oracle连接(join)中使用using关键字
34. View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the ORDERS and ORDER_ITEMS tables.
Evaluate the following SQL statement:
SELECT oi.order_id, product_id, order_date
FRO
- NIO示例
daysinsun
nio
NIO服务端代码:
public class NIOServer {
private Selector selector;
public void startServer(int port) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(
- C语言学习homework1
dcj3sjt126com
chomework
0、 课堂练习做完
1、使用sizeof计算出你所知道的所有的类型占用的空间。
int x;
sizeof(x);
sizeof(int);
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int x1;
char x2;
double x3;
float x4;
printf(&quo
- select in order by , mysql排序
dcj3sjt126com
mysql
If i select like this:
SELECT id FROM users WHERE id IN(3,4,8,1);
This by default will select users in this order
1,3,4,8,
I would like to select them in the same order that i put IN() values so:
- 页面校验-新建项目
fanxiaolong
页面校验
$(document).ready(
function() {
var flag = true;
$('#changeform').submit(function() {
var projectScValNull = true;
var s ="";
var parent_id = $("#parent_id").v
- Ehcache(02)——ehcache.xml简介
234390216
ehcacheehcache.xml简介
ehcache.xml简介
ehcache.xml文件是用来定义Ehcache的配置信息的,更准确的来说它是定义CacheManager的配置信息的。根据之前我们在《Ehcache简介》一文中对CacheManager的介绍我们知道一切Ehcache的应用都是从CacheManager开始的。在不指定配置信
- junit 4.11中三个新功能
jackyrong
java
junit 4.11中两个新增的功能,首先是注解中可以参数化,比如
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runn
- 国外程序员爱用苹果Mac电脑的10大理由
php教程分享
windowsPHPunixMicrosoftperl
Mac 在国外很受欢迎,尤其是在 设计/web开发/IT 人员圈子里。普通用户喜欢 Mac 可以理解,毕竟 Mac 设计美观,简单好用,没有病毒。那么为什么专业人士也对 Mac 情有独钟呢?从个人使用经验来看我想有下面几个原因:
1、Mac OS X 是基于 Unix 的
这一点太重要了,尤其是对开发人员,至少对于我来说很重要,这意味着Unix 下一堆好用的工具都可以随手捡到。如果你是个 wi
- 位运算、异或的实际应用
wenjinglian
位运算
一. 位操作基础,用一张表描述位操作符的应用规则并详细解释。
二. 常用位操作小技巧,有判断奇偶、交换两数、变换符号、求绝对值。
三. 位操作与空间压缩,针对筛素数进行空间压缩。
&n
- weblogic部署项目出现的一些问题(持续补充中……)
Everyday都不同
weblogic部署失败
好吧,weblogic的问题确实……
问题一:
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException: Failed to read candidate component class: URL [zip:E:/weblogic/user_projects/domains/base_domain/serve
- tomcat7性能调优(01)
toknowme
tomcat7
Tomcat优化: 1、最大连接数最大线程等设置
<Connector port="8082" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
useBodyEncodingForURI="t
- PO VO DAO DTO BO TO概念与区别
xp9802
javaDAO设计模式bean领域模型
O/R Mapping 是 Object Relational Mapping(对象关系映射)的缩写。通俗点讲,就是将对象与关系数据库绑定,用对象来表示关系数据。在O/R Mapping的世界里,有两个基本的也是重要的东东需要了解,即VO,PO。
它们的关系应该是相互独立的,一个VO可以只是PO的部分,也可以是多个PO构成,同样也可以等同于一个PO(指的是他们的属性)。这样,PO独立出来,数据持