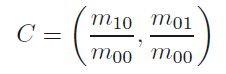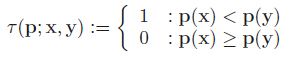【特征匹配】ORB原理与源码解析
相关 :
Fast原理与源码解析
Brief描述子原理与源码解析
Harris原理与源码解析
转载请注明出处: http://blog.csdn.net/luoshixian099/article/details/48523267
CSDN-勿在浮沙筑高台
为了满足实时性的要求,前面文章中介绍过快速提取特征点算法Fast,以及特征描述子Brief。本篇文章介绍的ORB算法结合了Fast和Brief的速度优势,并做了改进,且ORB是免费。
Ethan Rublee等人2011年在《ORB:An Efficient Alternative to SIFT or SURF》文章中提出了ORB算法。结合Fast与Brief算法,并给Fast特征点增加了方向性,使得特征点具有旋转不变性,并提出了构造金字塔方法,解决尺度不变性,但文章中没有具体详述。实验证明,ORB远优于之前的SIFT与SURF算法。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
论文核心内容概述:
1.构造金字塔,在每层金字塔上采用Fast算法提取特征点,采用Harris角点响应函数,按角点响应值排序,选取前N个特征点。
2. oFast:计算每个特征点的主方向,灰度质心法,计算特征点半径为r的圆形邻域范围内的灰度质心位置。从中心位置到质心位置的向量,定义为该特 征点的主方向。
定义矩的计算公式,x,y∈[-r,r]:
质心位置:
主方向:
3.rBrief:为了解决旋转不变性,把特征点的Patch旋转到主方向上(steered Brief)。通过实验得到,描述子在各个维度上的均值比较离散(偏离0.5),同时维度间相关性很强,说明特征点描述子区分性不好,影响匹配的效果。论文中提出采取学习的方法,采用300K个训练样本点。每一个特征点,选取Patch大小为wp=31,Patch内每对点都采用wt=5大小的子窗口灰度均值做比较,子窗口的个数即为N=(wp-wt)*(wp-wt),从N个窗口中随机选两个做比较即构成描述子的一个bit,论文中采用M=205590种可能的情况:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1.对所有样本点,做M种测试,构成M维的描述子,每个维度上非1即0;
2.按均值对M个维度排序(以0.5为中心),组成向量T;
3.贪婪搜索:把向量T中第一个元素移动到R中,然后继续取T的第二个元素,与R中的所有元素做相关性比较,如果相关性大于指定的阈值Threshold, 抛弃T的这个元素,否则加入到R中;
4.重复第3个步骤,直到R中有256个元素,若检测完毕,少于256个元素,则降低阈值,重复上述步骤;
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
rBrief:通过上面的步骤取到的256对点,构成的描述子各维度间相关性很低,区分性好;
训练前 训练后
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ORB算法步骤,参考opencv源码:
1.首先构造尺度金字塔;
金字塔共n层,与SIFT不同,每层仅有一副图像;
第s层的尺度为![]() ,Fator初始尺度(默认为1.2),原图在第0层;
,Fator初始尺度(默认为1.2),原图在第0层;
第s层图像大小:
2.在不同尺度上采用Fast检测特征点;在每一层上按公式计算需要提取的特征点数n,在本层上按Fast角点响应值排序,提取前2n个特征点,然后根据Harris 角点响应值排序, 取前n个特征点,作为本层的特征点;
3.计算每个特征点的主方向(质心法);
4.旋转每个特征点的Patch到主方向,采用上述步骤3的选取的最优的256对特征点做τ测试,构成256维描述子,占32个字节;
4.采用汉明距离做特征点匹配;
----------OpenCV源码解析-------------------------------------------------------
ORB类定义:位置..\features2d.hpp
nfeatures:需要的特征点总数;
scaleFactor:尺度因子;
nlevels:金字塔层数;
edgeThreshold:边界阈值;
firstLevel:起始层;
WTA_K:描述子形成方法,WTA_K=2表示,采用两两比较;
scoreType:角点响应函数,可以选择Harris或者Fast的方法;
patchSize:特征点邻域大小;
/*!
ORB implementation.
*/
class CV_EXPORTS_W ORB : public Feature2D
{
public:
// the size of the signature in bytes
enum { kBytes = 32, HARRIS_SCORE=0, FAST_SCORE=1 };
CV_WRAP explicit ORB(int nfeatures = 500, float scaleFactor = 1.2f, int nlevels = 8, int edgeThreshold = 31,//构造函数
int firstLevel = 0, int WTA_K=2, int scoreType=ORB::HARRIS_SCORE, int patchSize=31 );
// returns the descriptor size in bytes
int descriptorSize() const; //描述子占用的字节数,默认32字节
// returns the descriptor type
int descriptorType() const;//描述子类型,8位整形数
// Compute the ORB features and descriptors on an image
void operator()(InputArray image, InputArray mask, vector& keypoints) const;
// Compute the ORB features and descriptors on an image
void operator()( InputArray image, InputArray mask, vector& keypoints, //提取特征点与形成描述子
OutputArray descriptors, bool useProvidedKeypoints=false ) const;
AlgorithmInfo* info() const;
protected:
void computeImpl( const Mat& image, vector& keypoints, Mat& descriptors ) const;//计算描述子
void detectImpl( const Mat& image, vector& keypoints, const Mat& mask=Mat() ) const;//检测特征点
CV_PROP_RW int nfeatures;//特征点总数
CV_PROP_RW double scaleFactor;//尺度因子
CV_PROP_RW int nlevels;//金字塔内层数
CV_PROP_RW int edgeThreshold;//边界阈值
CV_PROP_RW int firstLevel;//开始层数
CV_PROP_RW int WTA_K;//描述子形成方法,默认WTA_K=2,两两比较
CV_PROP_RW int scoreType;//角点响应函数
CV_PROP_RW int patchSize;//邻域Patch大小
}; 特征提取及形成描述子:通过这个函数对图像提取Fast特征点或者计算特征描述子
_image:输入图像;
_mask:掩码图像;
_keypoints:输入角点;
_descriptors:如果为空,只寻找特征点,不计算特征描述子;
_useProvidedKeypoints:如果为true,函数只计算特征描述子;
/** Compute the ORB features and descriptors on an image
* @param img the image to compute the features and descriptors on
* @param mask the mask to apply
* @param keypoints the resulting keypoints
* @param descriptors the resulting descriptors
* @param do_keypoints if true, the keypoints are computed, otherwise used as an input
* @param do_descriptors if true, also computes the descriptors
*/
void ORB::operator()( InputArray _image, InputArray _mask, vector& _keypoints,
OutputArray _descriptors, bool useProvidedKeypoints) const
{
CV_Assert(patchSize >= 2);
bool do_keypoints = !useProvidedKeypoints;
bool do_descriptors = _descriptors.needed();
if( (!do_keypoints && !do_descriptors) || _image.empty() )
return;
//ROI handling
const int HARRIS_BLOCK_SIZE = 9;//Harris角点响应需要的边界大小
int halfPatchSize = patchSize / 2;.//邻域半径
int border = std::max(edgeThreshold, std::max(halfPatchSize, HARRIS_BLOCK_SIZE/2))+1;//采用最大的边界
Mat image = _image.getMat(), mask = _mask.getMat();
if( image.type() != CV_8UC1 )
cvtColor(_image, image, CV_BGR2GRAY);//转灰度图
int levelsNum = this->nlevels;//金字塔层数
if( !do_keypoints ) //不做特征点检测
{
// if we have pre-computed keypoints, they may use more levels than it is set in parameters
// !!!TODO!!! implement more correct method, independent from the used keypoint detector.
// Namely, the detector should provide correct size of each keypoint. Based on the keypoint size
// and the algorithm used (i.e. BRIEF, running on 31x31 patches) we should compute the approximate
// scale-factor that we need to apply. Then we should cluster all the computed scale-factors and
// for each cluster compute the corresponding image.
//
// In short, ultimately the descriptor should
// ignore octave parameter and deal only with the keypoint size.
levelsNum = 0;
for( size_t i = 0; i < _keypoints.size(); i++ )
levelsNum = std::max(levelsNum, std::max(_keypoints[i].octave, 0));//提取特征点的最大层数
levelsNum++;
}
// Pre-compute the scale pyramids
vector imagePyramid(levelsNum), maskPyramid(levelsNum);//创建尺度金字塔图像
for (int level = 0; level < levelsNum; ++level)
{
float scale = 1/getScale(level, firstLevel, scaleFactor); //每层对应的尺度
/*
static inline float getScale(int level, int firstLevel, double scaleFactor)
{
return (float)std::pow(scaleFactor, (double)(level - firstLevel));
}
*/
Size sz(cvRound(image.cols*scale), cvRound(image.rows*scale));//每层对应的图像大小
Size wholeSize(sz.width + border*2, sz.height + border*2);
Mat temp(wholeSize, image.type()), masktemp;
imagePyramid[level] = temp(Rect(border, border, sz.width, sz.height));
if( !mask.empty() )
{
masktemp = Mat(wholeSize, mask.type());
maskPyramid[level] = masktemp(Rect(border, border, sz.width, sz.height));
}
// Compute the resized image
if( level != firstLevel ) //得到金字塔每层的图像
{
if( level < firstLevel )
{
resize(image, imagePyramid[level], sz, 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR);
if (!mask.empty())
resize(mask, maskPyramid[level], sz, 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR);
}
else
{
resize(imagePyramid[level-1], imagePyramid[level], sz, 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR);
if (!mask.empty())
{
resize(maskPyramid[level-1], maskPyramid[level], sz, 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR);
threshold(maskPyramid[level], maskPyramid[level], 254, 0, THRESH_TOZERO);
}
}
copyMakeBorder(imagePyramid[level], temp, border, border, border, border,//扩大图像的边界
BORDER_REFLECT_101+BORDER_ISOLATED);
if (!mask.empty())
copyMakeBorder(maskPyramid[level], masktemp, border, border, border, border,
BORDER_CONSTANT+BORDER_ISOLATED);
}
else
{
copyMakeBorder(image, temp, border, border, border, border,//扩大图像的四个边界
BORDER_REFLECT_101);
if( !mask.empty() )
copyMakeBorder(mask, masktemp, border, border, border, border,
BORDER_CONSTANT+BORDER_ISOLATED);
}
}
// Pre-compute the keypoints (we keep the best over all scales, so this has to be done beforehand
vector < vector > allKeypoints;
if( do_keypoints )//提取角点
{
// Get keypoints, those will be far enough from the border that no check will be required for the descriptor
computeKeyPoints(imagePyramid, maskPyramid, allKeypoints, //对每一层图像提取角点,见下面(1)的分析
nfeatures, firstLevel, scaleFactor,
edgeThreshold, patchSize, scoreType);
// make sure we have the right number of keypoints keypoints
/*vector temp;
for (int level = 0; level < n_levels; ++level)
{
vector& keypoints = all_keypoints[level];
temp.insert(temp.end(), keypoints.begin(), keypoints.end());
keypoints.clear();
}
KeyPoint::retainBest(temp, n_features_);
for (vector::iterator keypoint = temp.begin(),
keypoint_end = temp.end(); keypoint != keypoint_end; ++keypoint)
all_keypoints[keypoint->octave].push_back(*keypoint);*/
}
else //不提取角点
{
// Remove keypoints very close to the border
KeyPointsFilter::runByImageBorder(_keypoints, image.size(), edgeThreshold);
// Cluster the input keypoints depending on the level they were computed at
allKeypoints.resize(levelsNum);
for (vector::iterator keypoint = _keypoints.begin(),
keypointEnd = _keypoints.end(); keypoint != keypointEnd; ++keypoint)
allKeypoints[keypoint->octave].push_back(*keypoint); //把角点信息存入allKeypoints内
// Make sure we rescale the coordinates
for (int level = 0; level < levelsNum; ++level) //把角点位置信息缩放到指定层位置上
{
if (level == firstLevel)
continue;
vector & keypoints = allKeypoints[level];
float scale = 1/getScale(level, firstLevel, scaleFactor);
for (vector::iterator keypoint = keypoints.begin(),
keypointEnd = keypoints.end(); keypoint != keypointEnd; ++keypoint)
keypoint->pt *= scale; //缩放
}
}
Mat descriptors;
vector pattern;
if( do_descriptors ) //计算特征描述子
{
int nkeypoints = 0;
for (int level = 0; level < levelsNum; ++level)
nkeypoints += (int)allKeypoints[level].size();//得到所有层的角点总数
if( nkeypoints == 0 )
_descriptors.release();
else
{
_descriptors.create(nkeypoints, descriptorSize(), CV_8U);//创建一个矩阵存放描述子,每一行表示一个角点信息
descriptors = _descriptors.getMat();
}
const int npoints = 512;//取512个点,共256对,产生256维描述子,32个字节
Point patternbuf[npoints];
const Point* pattern0 = (const Point*)bit_pattern_31_;//训练好的256对数据点位置
if( patchSize != 31 )
{
pattern0 = patternbuf;
makeRandomPattern(patchSize, patternbuf, npoints);
}
CV_Assert( WTA_K == 2 || WTA_K == 3 || WTA_K == 4 );
if( WTA_K == 2 ) //WTA_K=2使用两个点之间作比较
std::copy(pattern0, pattern0 + npoints, std::back_inserter(pattern));
else
{
int ntuples = descriptorSize()*4;
initializeOrbPattern(pattern0, pattern, ntuples, WTA_K, npoints);
}
}
_keypoints.clear();
int offset = 0;
for (int level = 0; level < levelsNum; ++level)//依次计算每一层的角点描述子
{
// Get the features and compute their orientation
vector& keypoints = allKeypoints[level];
int nkeypoints = (int)keypoints.size();//本层内角点个数
// Compute the descriptors
if (do_descriptors)
{
Mat desc;
if (!descriptors.empty())
{
desc = descriptors.rowRange(offset, offset + nkeypoints);
}
offset += nkeypoints; //偏移量
// preprocess the resized image
Mat& workingMat = imagePyramid[level];
//boxFilter(working_mat, working_mat, working_mat.depth(), Size(5,5), Point(-1,-1), true, BORDER_REFLECT_101);
GaussianBlur(workingMat, workingMat, Size(7, 7), 2, 2, BORDER_REFLECT_101);//高斯平滑图像
computeDescriptors(workingMat, keypoints, desc, pattern, descriptorSize(), WTA_K);//计算本层内角点的描述子,(3)
}
// Copy to the output data
if (level != firstLevel) //角点位置信息返回到原图上
{
float scale = getScale(level, firstLevel, scaleFactor);
for (vector::iterator keypoint = keypoints.begin(),
keypointEnd = keypoints.end(); keypoint != keypointEnd; ++keypoint)
keypoint->pt *= scale;
}
// And add the keypoints to the output
_keypoints.insert(_keypoints.end(), keypoints.begin(), keypoints.end());//存入描述子信息,返回
}
} (1)提取角点:computeKeyPoints
imagePyramid:即构造好的金字塔
/** Compute the ORB keypoints on an image
* @param image_pyramid the image pyramid to compute the features and descriptors on
* @param mask_pyramid the masks to apply at every level
* @param keypoints the resulting keypoints, clustered per level
*/
static void computeKeyPoints(const vector& imagePyramid,
const vector& maskPyramid,
vector >& allKeypoints,
int nfeatures, int firstLevel, double scaleFactor,
int edgeThreshold, int patchSize, int scoreType )
{
int nlevels = (int)imagePyramid.size(); //金字塔层数
vector nfeaturesPerLevel(nlevels);
// fill the extractors and descriptors for the corresponding scales
float factor = (float)(1.0 / scaleFactor);
float ndesiredFeaturesPerScale = nfeatures*(1 - factor)/(1 - (float)pow((double)factor, (double)nlevels));//
int sumFeatures = 0;
for( int level = 0; level < nlevels-1; level++ ) //对每层图像上分配相应角点数
{
nfeaturesPerLevel[level] = cvRound(ndesiredFeaturesPerScale);
sumFeatures += nfeaturesPerLevel[level];
ndesiredFeaturesPerScale *= factor;
}
nfeaturesPerLevel[nlevels-1] = std::max(nfeatures - sumFeatures, 0);//剩下角点数,由最上层图像提取
// Make sure we forget about what is too close to the boundary
//edge_threshold_ = std::max(edge_threshold_, patch_size_/2 + kKernelWidth / 2 + 2);
// pre-compute the end of a row in a circular patch
int halfPatchSize = patchSize / 2; //计算每个特征点圆邻域的位置信息
vector umax(halfPatchSize + 2);
int v, v0, vmax = cvFloor(halfPatchSize * sqrt(2.f) / 2 + 1);
int vmin = cvCeil(halfPatchSize * sqrt(2.f) / 2);
for (v = 0; v <= vmax; ++v) //
umax[v] = cvRound(sqrt((double)halfPatchSize * halfPatchSize - v * v));
// Make sure we are symmetric
for (v = halfPatchSize, v0 = 0; v >= vmin; --v)
{
while (umax[v0] == umax[v0 + 1])
++v0;
umax[v] = v0;
++v0;
}
allKeypoints.resize(nlevels);
for (int level = 0; level < nlevels; ++level)
{
int featuresNum = nfeaturesPerLevel[level];
allKeypoints[level].reserve(featuresNum*2);
vector & keypoints = allKeypoints[level];
// Detect FAST features, 20 is a good threshold
FastFeatureDetector fd(20, true);
fd.detect(imagePyramid[level], keypoints, maskPyramid[level]);//Fast角点检测
// Remove keypoints very close to the border
KeyPointsFilter::runByImageBorder(keypoints, imagePyramid[level].size(), edgeThreshold);//去除邻近边界的点
if( scoreType == ORB::HARRIS_SCORE )
{
// Keep more points than necessary as FAST does not give amazing corners
KeyPointsFilter::retainBest(keypoints, 2 * featuresNum);//按Fast强度排序,保留前2*featuresNum个特征点
// Compute the Harris cornerness (better scoring than FAST)
HarrisResponses(imagePyramid[level], keypoints, 7, HARRIS_K); //计算每个角点的Harris强度响应
}
//cull to the final desired level, using the new Harris scores or the original FAST scores.
KeyPointsFilter::retainBest(keypoints, featuresNum);//按Harris强度排序,保留前featuresNum个
float sf = getScale(level, firstLevel, scaleFactor);
// Set the level of the coordinates
for (vector::iterator keypoint = keypoints.begin(),
keypointEnd = keypoints.end(); keypoint != keypointEnd; ++keypoint)
{
keypoint->octave = level; //层信息
keypoint->size = patchSize*sf; //
}
computeOrientation(imagePyramid[level], keypoints, halfPatchSize, umax); //计算角点的方向,(2)分析
}
}
static void computeOrientation(const Mat& image, vector& keypoints,
int halfPatchSize, const vector& umax)
{
// Process each keypoint
for (vector::iterator keypoint = keypoints.begin(), //为每个角点计算主方向
keypointEnd = keypoints.end(); keypoint != keypointEnd; ++keypoint)
{
keypoint->angle = IC_Angle(image, halfPatchSize, keypoint->pt, umax);//计算质心方向
}
} static float IC_Angle(const Mat& image, const int half_k, Point2f pt,
const vector & u_max)
{
int m_01 = 0, m_10 = 0;
const uchar* center = &image.at (cvRound(pt.y), cvRound(pt.x));
// Treat the center line differently, v=0
for (int u = -half_k; u <= half_k; ++u)
m_10 += u * center[u];
// Go line by line in the circular patch
int step = (int)image.step1();
for (int v = 1; v <= half_k; ++v) //每次处理对称的两行v
{
// Proceed over the two lines
int v_sum = 0;
int d = u_max[v];
for (int u = -d; u <= d; ++u)
{
int val_plus = center[u + v*step], val_minus = center[u - v*step];
v_sum += (val_plus - val_minus); //计算m_01时,位置上差一个符号
m_10 += u * (val_plus + val_minus);
}
m_01 += v * v_sum;//计算上下两行的m_01
}
return fastAtan2((float)m_01, (float)m_10);//计算角度
} static void computeDescriptors(const Mat& image, vector& keypoints, Mat& descriptors,
const vector& pattern, int dsize, int WTA_K)
{
//convert to grayscale if more than one color
CV_Assert(image.type() == CV_8UC1);
//create the descriptor mat, keypoints.size() rows, BYTES cols
descriptors = Mat::zeros((int)keypoints.size(), dsize, CV_8UC1);
for (size_t i = 0; i < keypoints.size(); i++)
computeOrbDescriptor(keypoints[i], image, &pattern[0], descriptors.ptr((int)i), dsize, WTA_K);
} static void computeOrbDescriptor(const KeyPoint& kpt,
const Mat& img, const Point* pattern,
uchar* desc, int dsize, int WTA_K)
{
float angle = kpt.angle;
//angle = cvFloor(angle/12)*12.f;
angle *= (float)(CV_PI/180.f);
float a = (float)cos(angle), b = (float)sin(angle);
const uchar* center = &img.at(cvRound(kpt.pt.y), cvRound(kpt.pt.x));
int step = (int)img.step;
#if 1
#define GET_VALUE(idx) \ //取旋转后一个像素点的值
center[cvRound(pattern[idx].x*b + pattern[idx].y*a)*step + \
cvRound(pattern[idx].x*a - pattern[idx].y*b)]
#else
float x, y;
int ix, iy;
#define GET_VALUE(idx) \ //取旋转后一个像素点,插值法
(x = pattern[idx].x*a - pattern[idx].y*b, \
y = pattern[idx].x*b + pattern[idx].y*a, \
ix = cvFloor(x), iy = cvFloor(y), \
x -= ix, y -= iy, \
cvRound(center[iy*step + ix]*(1-x)*(1-y) + center[(iy+1)*step + ix]*(1-x)*y + \
center[iy*step + ix+1]*x*(1-y) + center[(iy+1)*step + ix+1]*x*y))
#endif
if( WTA_K == 2 )
{
for (int i = 0; i < dsize; ++i, pattern += 16)//每个特征描述子长度为32个字节
{
int t0, t1, val;
t0 = GET_VALUE(0); t1 = GET_VALUE(1);
val = t0 < t1;
t0 = GET_VALUE(2); t1 = GET_VALUE(3);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 1;
t0 = GET_VALUE(4); t1 = GET_VALUE(5);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 2;
t0 = GET_VALUE(6); t1 = GET_VALUE(7);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 3;
t0 = GET_VALUE(8); t1 = GET_VALUE(9);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 4;
t0 = GET_VALUE(10); t1 = GET_VALUE(11);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 5;
t0 = GET_VALUE(12); t1 = GET_VALUE(13);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 6;
t0 = GET_VALUE(14); t1 = GET_VALUE(15);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 7;
desc[i] = (uchar)val;
}
}
else if( WTA_K == 3 )
{
for (int i = 0; i < dsize; ++i, pattern += 12)
{
int t0, t1, t2, val;
t0 = GET_VALUE(0); t1 = GET_VALUE(1); t2 = GET_VALUE(2);
val = t2 > t1 ? (t2 > t0 ? 2 : 0) : (t1 > t0);
t0 = GET_VALUE(3); t1 = GET_VALUE(4); t2 = GET_VALUE(5);
val |= (t2 > t1 ? (t2 > t0 ? 2 : 0) : (t1 > t0)) << 2;
t0 = GET_VALUE(6); t1 = GET_VALUE(7); t2 = GET_VALUE(8);
val |= (t2 > t1 ? (t2 > t0 ? 2 : 0) : (t1 > t0)) << 4;
t0 = GET_VALUE(9); t1 = GET_VALUE(10); t2 = GET_VALUE(11);
val |= (t2 > t1 ? (t2 > t0 ? 2 : 0) : (t1 > t0)) << 6;
desc[i] = (uchar)val;
}
}
else if( WTA_K == 4 )
{
for (int i = 0; i < dsize; ++i, pattern += 16)
{
int t0, t1, t2, t3, u, v, k, val;
t0 = GET_VALUE(0); t1 = GET_VALUE(1);
t2 = GET_VALUE(2); t3 = GET_VALUE(3);
u = 0, v = 2;
if( t1 > t0 ) t0 = t1, u = 1;
if( t3 > t2 ) t2 = t3, v = 3;
k = t0 > t2 ? u : v;
val = k;
t0 = GET_VALUE(4); t1 = GET_VALUE(5);
t2 = GET_VALUE(6); t3 = GET_VALUE(7);
u = 0, v = 2;
if( t1 > t0 ) t0 = t1, u = 1;
if( t3 > t2 ) t2 = t3, v = 3;
k = t0 > t2 ? u : v;
val |= k << 2;
t0 = GET_VALUE(8); t1 = GET_VALUE(9);
t2 = GET_VALUE(10); t3 = GET_VALUE(11);
u = 0, v = 2;
if( t1 > t0 ) t0 = t1, u = 1;
if( t3 > t2 ) t2 = t3, v = 3;
k = t0 > t2 ? u : v;
val |= k << 4;
t0 = GET_VALUE(12); t1 = GET_VALUE(13);
t2 = GET_VALUE(14); t3 = GET_VALUE(15);
u = 0, v = 2;
if( t1 > t0 ) t0 = t1, u = 1;
if( t3 > t2 ) t2 = t3, v = 3;
k = t0 > t2 ? u : v;
val |= k << 6;
desc[i] = (uchar)val;
}
}
else
CV_Error( CV_StsBadSize, "Wrong WTA_K. It can be only 2, 3 or 4." );
#undef GET_VALUE
} 参考:
Ethan Rublee et. ORB:An Efficient Alternative to SIFT or SURF
http://www.cnblogs.com/ronny/p/4083537.html